TTU Held BIOL 1402 Exam 2
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
Karyotpying
- a display if micrographs of the metaphase chromosomes of a cell arranged by size and centometer position; to determine of there's an abnormal number of chromosomes (due to non- disjunction)
a. if we brake open human cells in metaphase of mitosis, stain the chromosomes with dyes, take a picture with a microscope and arrange then in matching pairs
Pedigree Analysis
- To determine whether a gene is dominant/recessive and uses Mendel's concept of dominant and recessive alleles and his law of segregation. ; the X chromosomes vs. autosomal
Down Syndrome
Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 ("Trisomy 21"); characterized by heart and respiratory defects and varrining degrees of mental retardation.
Turner Syndrome
females lacking an X chromosome ; XO, O refers to the absence of the other X chromosome. They are short in stature and have webbing around the neck and shoulders but have normal intelligence. Have only 45 chromosomes but is NOT fatal. They are sterile
Klinefelter Syndrome
a male with an extra X chromosome (XXY or XXXY) that is sterile and has abnormally small teestes. Often has more feminine body characteristics. The abnormal sets with more than three chromosome( sex) are a result of disjunction.
Nondisjunction
an accident of meiosis or mitosis in which a pair of homologous chromosomes or pair of sister chromatids fails to separate at anaphase; causes down syndrome.
disjunction
the normal separation of chromosomes in meiosis or mitosis
Carrier
- Parents are heterozygotes for a recessively inherited disorder and who therefore does not show any symptoms of that disorder
Amniocentesis
- Genetic testing in the fetus
- Requires collection of fetal cells by inserting a needle through the abdomen into the uterus
- Cells are cultured to allow karyotyping to look for abnormalities
-Inform mother whether the child will have birth defect
Cystic Fibrosis
a genetic disease that occurs in people with two copies of a certain recessive allele characterized by an excessive secreation of mucus and concequent venerability; fatal if untreated
Achondroplasis
a form of human dwarfism caused by a single dominant allele
Huntingtions Disease
A human genetic disorder caused by a dominant allele, charaterized by uncontrollable body movements and degeneration of nervous system; usually fatal 10 to 20 years after the on set of symptoms
Alzheimers
a from of mental deteroration or dementia; characterized by confusion or memory loss
Chorionic Villi Sampling
- Doctor extracts sample of chorionic villus tissue from placenta
- Karyotyping results take only 24 hours and can be done earlier than amniocentesis
Aminocentesis
a genetic testing of the fetus to detect the presence of disease causing alleles in an individual genome. The test is done by extracting from the fetus with a needle
Heredity
Transmission of traits/features from one generation to the next.
In{her}itance of traits
Ultrasound
Uses waves to produce a picture of the fetus
Genetics
- Study of heredity
Parts of chromosomes and make of DNA
BLENDING THEORY
- Ancient theory of heredity
- Hereditary materials contributed by the male and female parents mix in forming the offspring (horse and donkey)
-irreversible and original colors are gone
Particulate Theory
- Traits are inherited like particles = genes
- Mendel's theory
-reversible and colors stay
Self-fertilization
In plants, sperm-carrying pollen lands on the egg-containing carpel of the same flower.
Cross-fertilization
- Fertilization of one plant by another plant.
- Mendel used this with pea plants to observe traits.
Pure-breeding strain
- Crosses between identical homozygotes
-same alleles
(ex. both parents are SS or ss)
Hybrid
The offspring of two different varieties.
HERETOZYGOUS- diff alleles (ex. Ss)
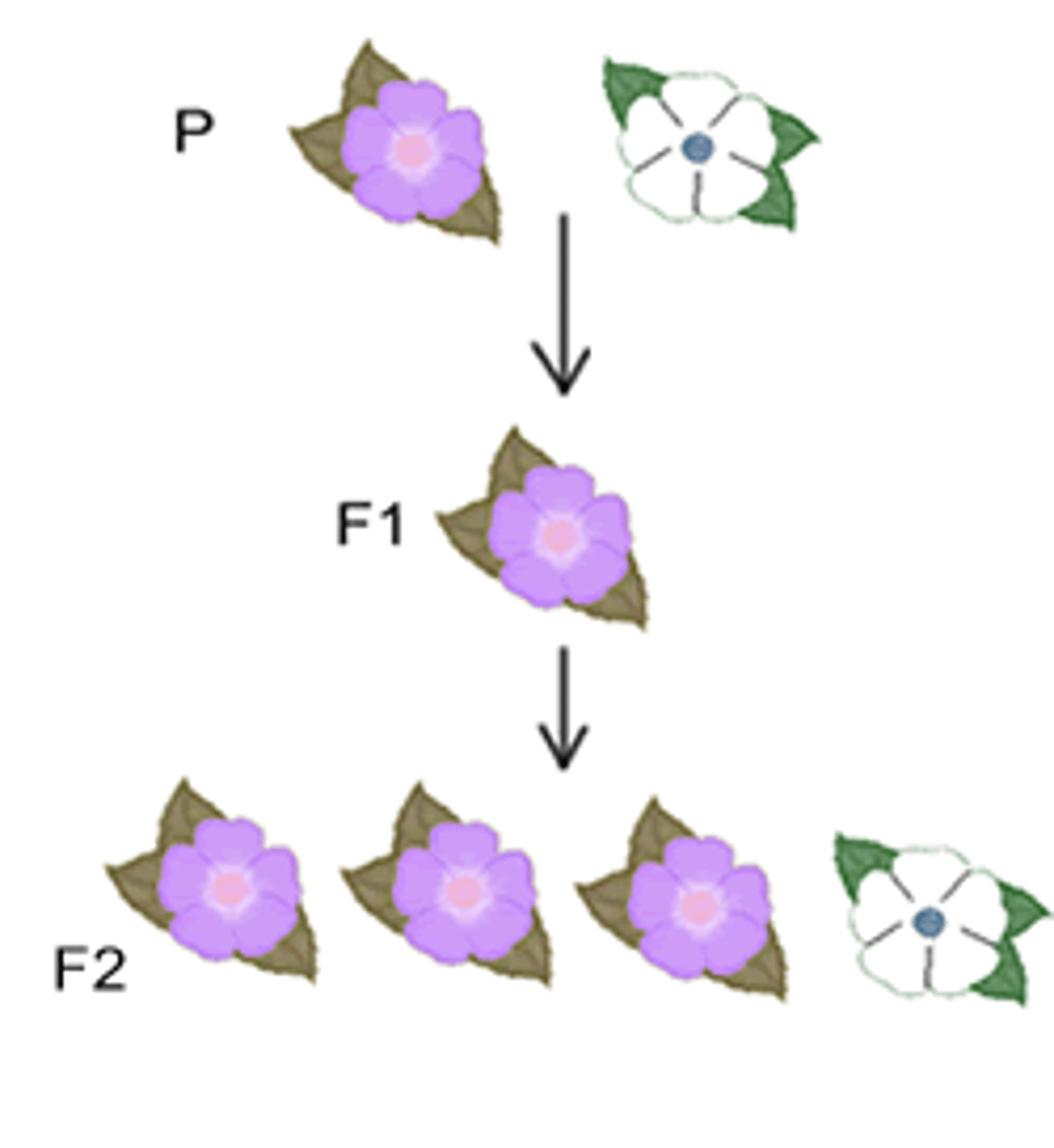
"P"
the parent individuals from which offspring are derived in studies of inheritance.
-parental generation
F1
The offspring of two (P) parental individuals F1 stands for the first filial. hybrid.
-Child generation
F2
F1 plants self-fertilize or fertilize each other giving an offspring F2 = second filial
-Grandchild generation
Allele
Diff/ alternate forms of gene (ex. long vs short S=dominant s=recessive)
Gene
Unit of inheritance, contains DNA. Consisting of a nucleotide sequence of a polypeptide
Dominant
Allele that determine's the appearance (represented by a capital letter)
Recessive
Allele that has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance
- Only shows up if there are two (bb)
- Represented by lowercase letters
Locus
the particular site where a gene is found on a chromosome
Homozygous
Organism that has two identical alleles (ex. BB or bb)
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for one gene. (Bb)
Punnett Square
A diagram that shows the possible combinations of alleles that could occur when gametes combine (can show proportions of combinations). Studies the inheritance of random fertilization.
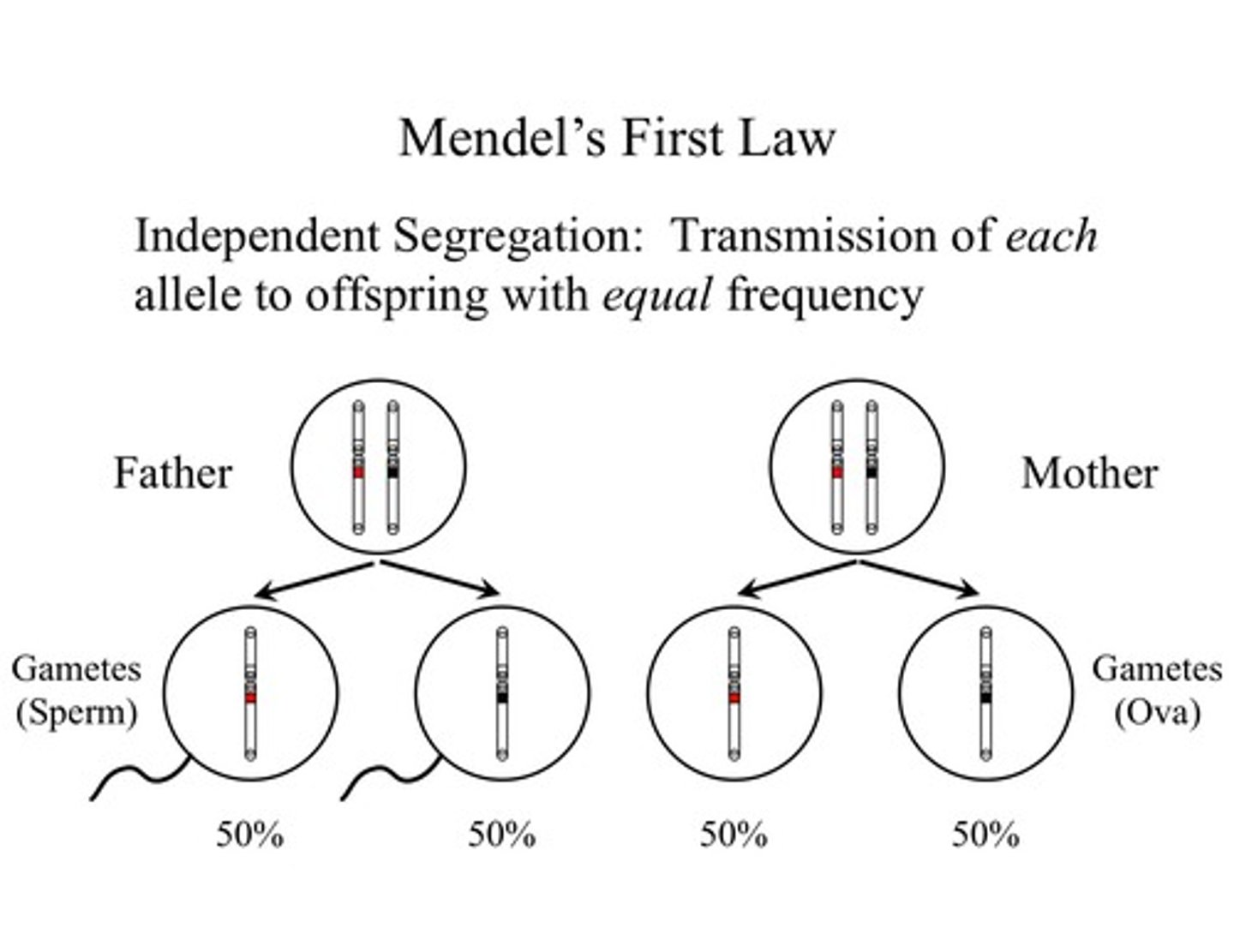
Allele Segregation
Law 1
A sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inherited characteristic because they combine at fertilization.
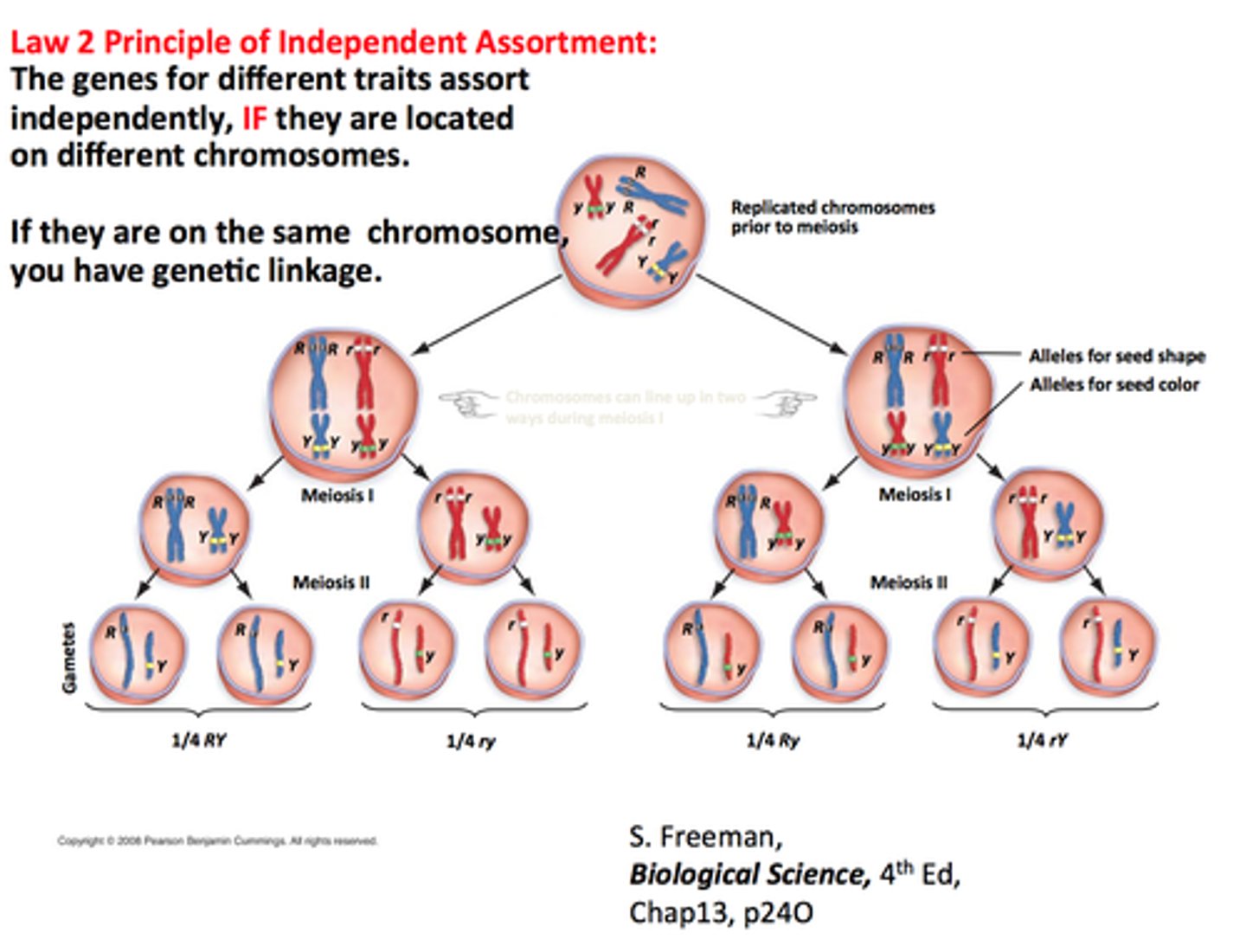
Independent Assortment
Law 2 Dihybrid
The inheritance of one characteristic has no impact of the inheritance of another (ex. you can have brown hair, but you don't have to have brown eyes)
-In meiosis the homologs pair but in mitosis they do not (shuffling of the deck)
Monohybrid Cross
Cross between two different homozygous organisms (ex. crossing PP purple plant with pp white plant)
3:1 (f2) of phenotypes of F2
3=dominant 1-recessive
Dihybrid Cross
Mating of parental varieties differing in two characters
(ex. RRYY with rryy) would produce all RrYy.
2 genes at a time (dom and rec)
9:3:3:1 (F2)
Testcross
Allows you to determine the genotype of an unknown parent
(Helps you tell if the unknown is heterozygous or homozygous)
3:1
The ratio of phenotypes in the F2 of a monohybrid cross (see p. 156)
9:3:3:1
The ratio of phenotypes in the F2 of a dihybrid cross.
Incomplete Dominance
- Heterozygote shows intermediate phenotype
- If the protein is a structure, the traits mix
- If it's an enzyme, the dominant trait shows, but it takes longer (pink rose)
Codominance
Heterozygote expresses both traits (alleles)
(ex. Blood type: A and B are dominant, creates AB)
Pleiotropy
One gene causes many traits
- "Go to many"
- Gene for albino causes white hair, pink iris, crossed eyes
-syndrome
Polygenic Trait
One trait is caused by many genes
- Quantitative traits (height, weight, etc.) are often this (ex. human skin color)
Epistasis
One gene masks or "dominates" a different gene, rather than an allele. (ex. the hair color of laborador retrievers)
Mosaicism
A trait of female mammals due to inactivation of one X chromosome in every cell.
- Solution of double proteins in XX is X-inactivation.
(calico cats - splotchy/patches of color)
Dosage Compensation
A trick for equalizing the "dose" of X genes in XX vs. YY individuals
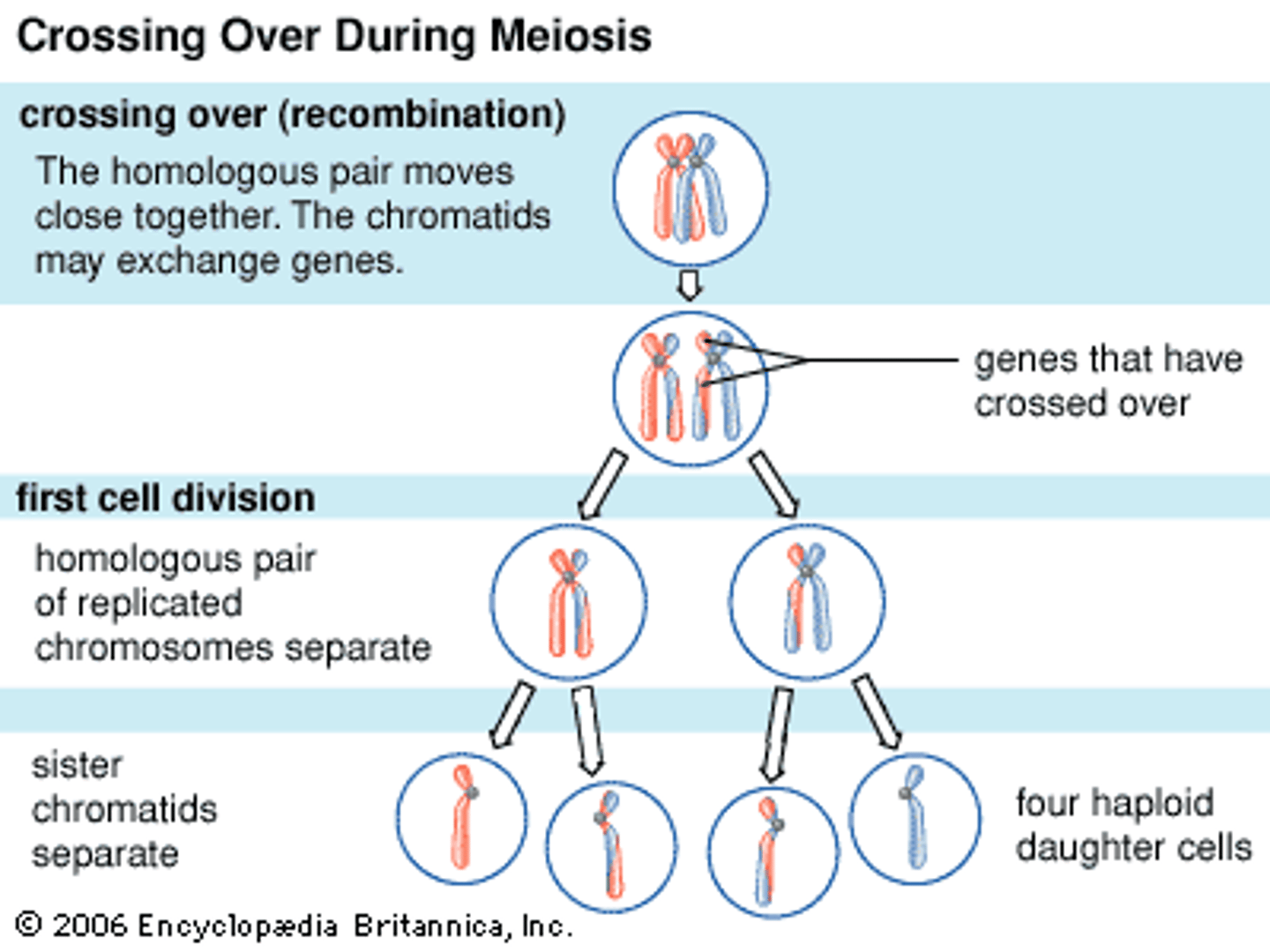
Crossing Over=Genetic Recombination
Shuffling of genes on each chromosome (creates variety by shuffling genes)
Sex Chromosomes
The nonidentical pair of chromosomes
- Determine an individual's sex, and other functions (males have one X and one Y, females have two X)
Autosomes
The 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes.
Criss-Cross Inheritance
How sex-linked (X-chromosome) genes are passed from Mom to son.
-Sons inherit their X from their mother
Mutant Allele
The less-occurring trait, not necessarily recessive. (weird traits)
Wild-Type Allele
Traits prevailing in nature (the more common traits)
- Not necessarily the dominant trait
Parental Phenotypes
Offspring looks like the parents
Recombinant Phenotypes
Offspring doesn't look like the parents (got recessive alleles).
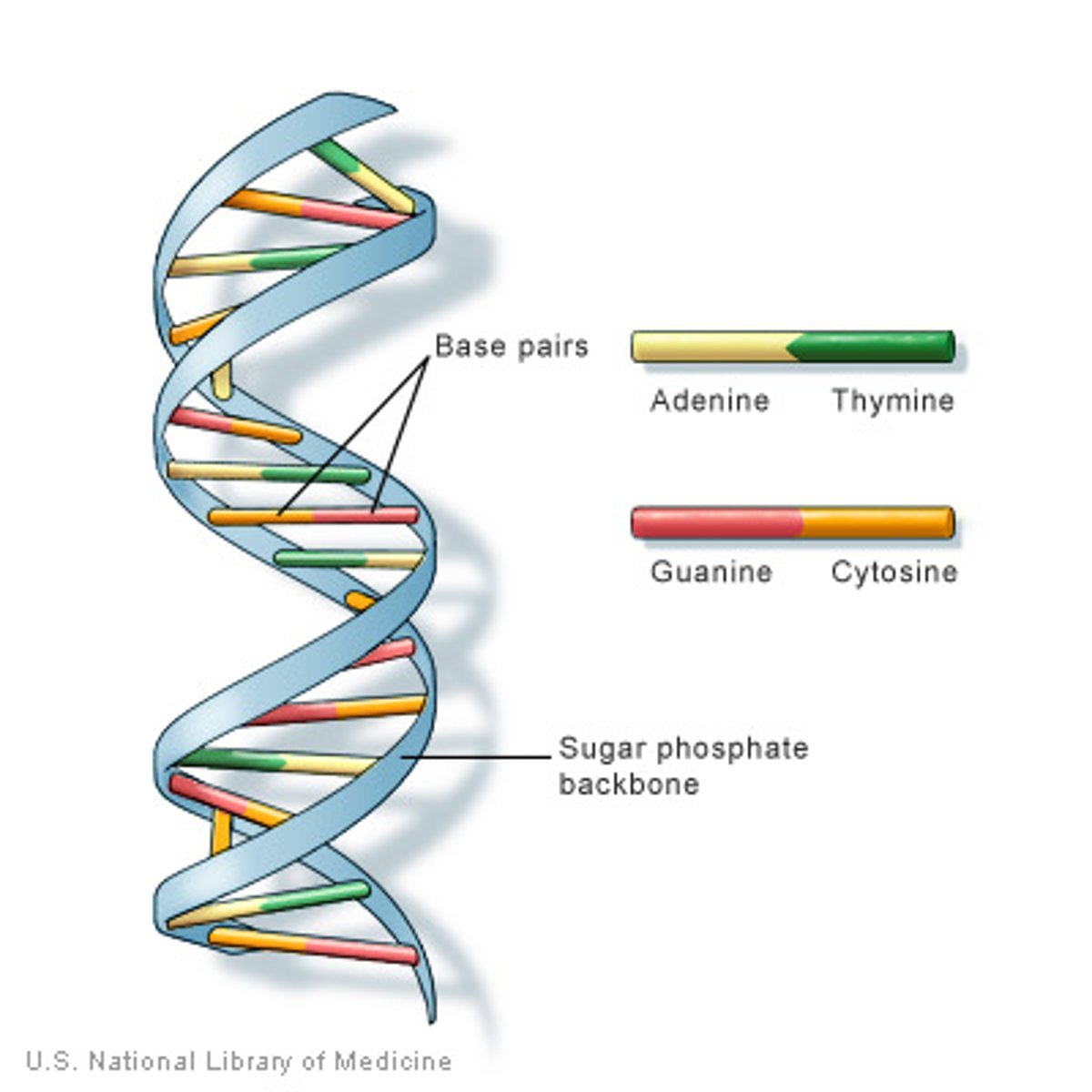
DNA
- Double helix, bases are A,T,C,G, no oxygen (deoxyribose sugar), long, storage of genetic information.
-Information storage (eye color, hair color, nose shape)
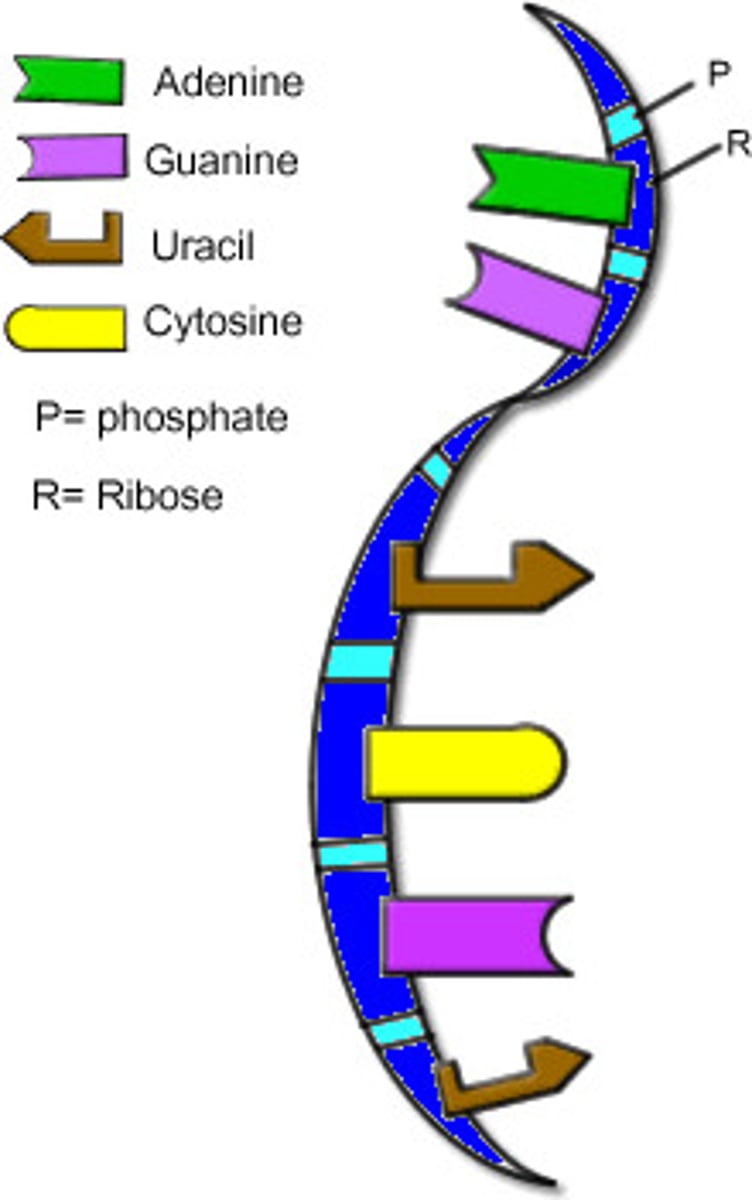
RNA
Ribose sugar, bases are A,U,C,G, single stranded, short, messenger of genetic information.
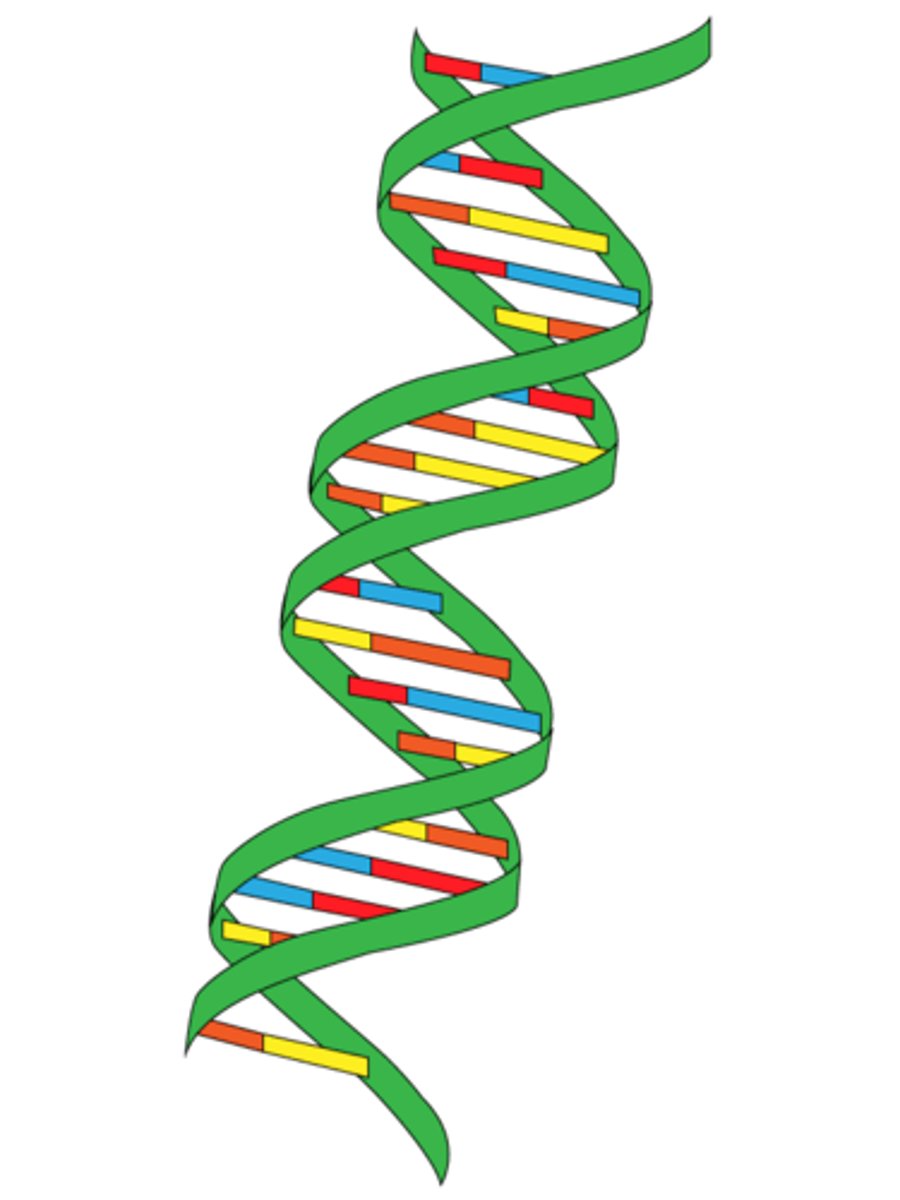
Double Helix
- Bases point in and correspond to a base on the other strand
- Shape of DNA
A bind with T
G bind with C
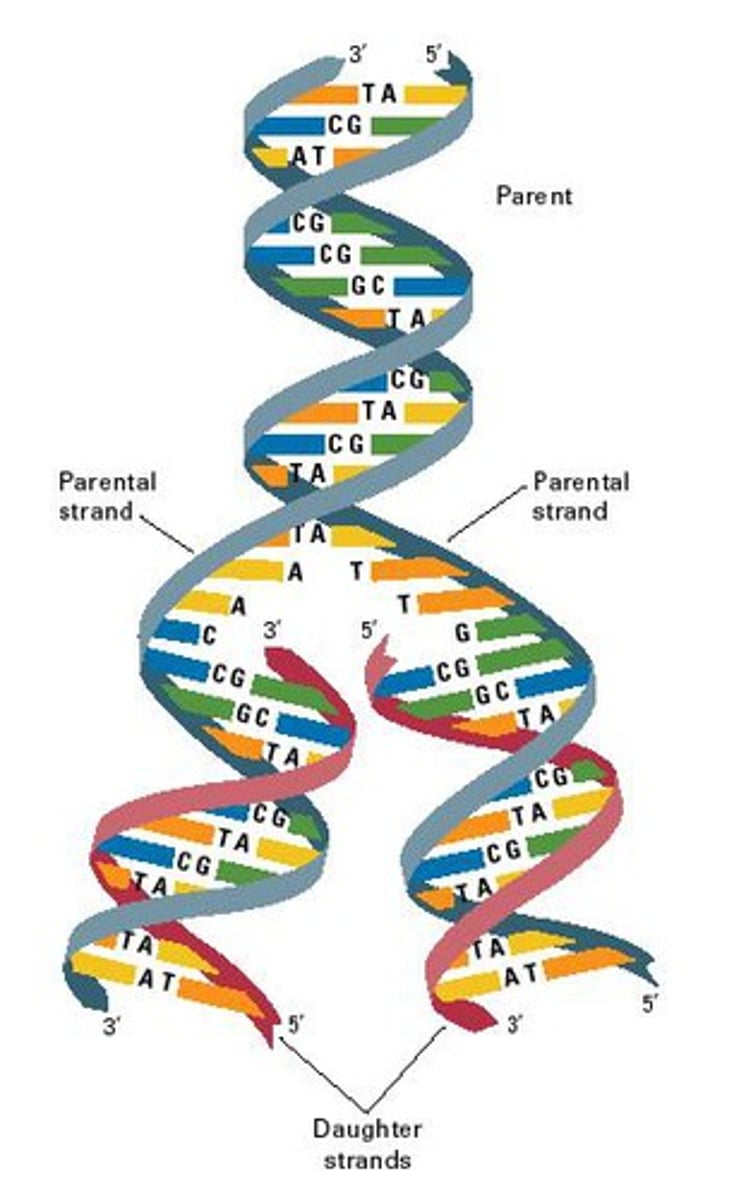
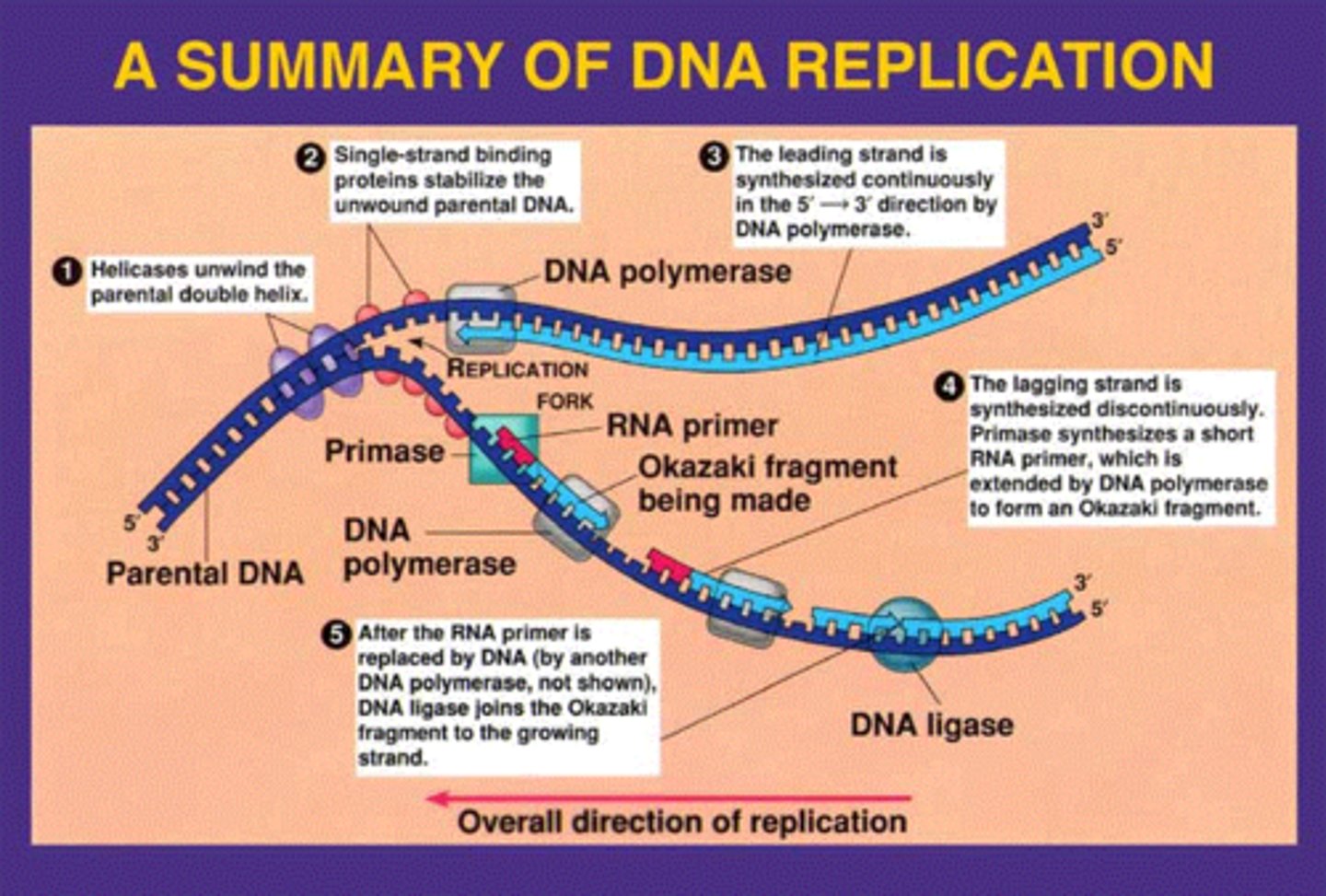
Replication
- Conversion/copying of DNA into DNA (DNA acts as it own template)
- Steps are 1)Unwinding 2)Pairing 3)Joining
Transcription
- Conversion of information in one gene (DNA) into a messenger RNA (mRNA), (like burning a song onto a CD)
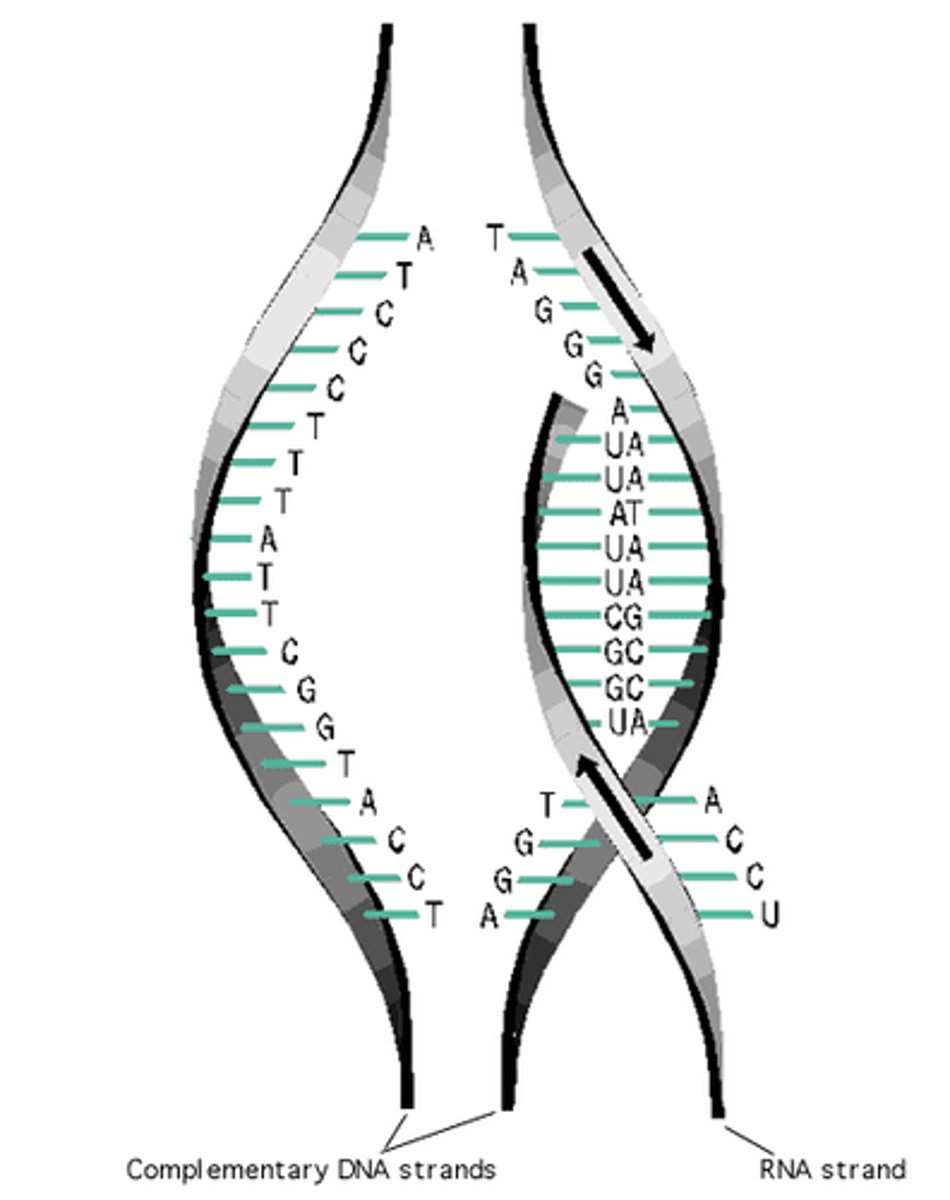
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
Unwinding
The two strands of DNA separate
Pairing
Free nucleotides in the DNA polymerase match up with the bases on the separated strands.
Joining
DNA ligase links the added bases together into a strand
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
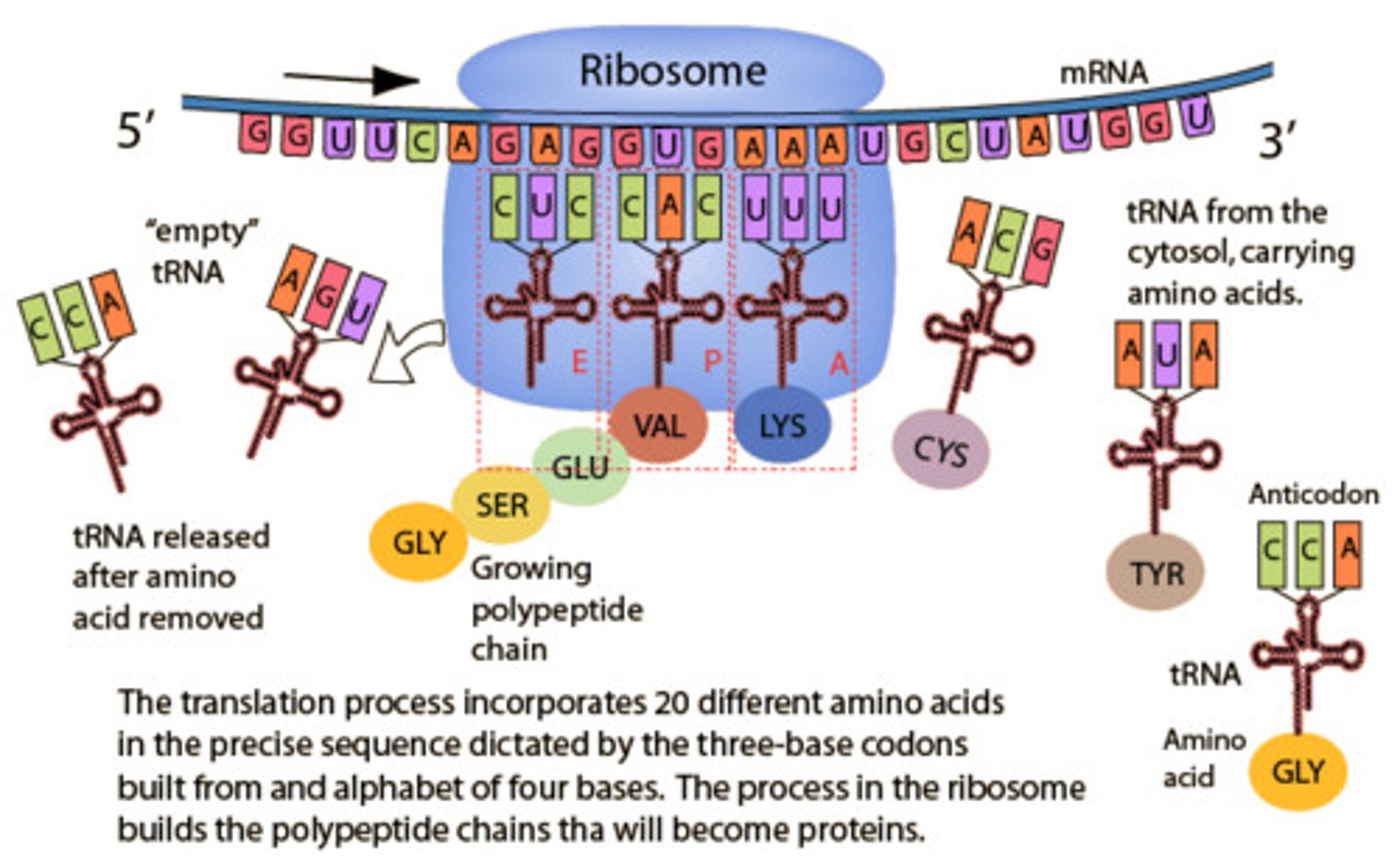
Ribosome
Structure in the cell that has RNA and protein
Triplet Code
Three bases correspond with one amino acid
Codon
Combination of three "letters", nucleotides. ("word" of genetic code)
Anticodon
Three bases that would match up with a codon.
Genetic Code
The chart that matches codons with amino acids.
Redundancy of the Code
There are more possible combinations of codons than amino acids, so some repeat
mRNA
Encodes amino acid sequences and carries information into the cytoplasm
tRNA
Interprets codons into proteins
rRNA
This and proteins make ribosomes (most abundant kind of RNA)
Mutation
Change in sequence of nucleotides in DNA (creates heritable changes)
Mutagen
Causes mutations (source)
Sickle Cell Anemia
Caused by mutation
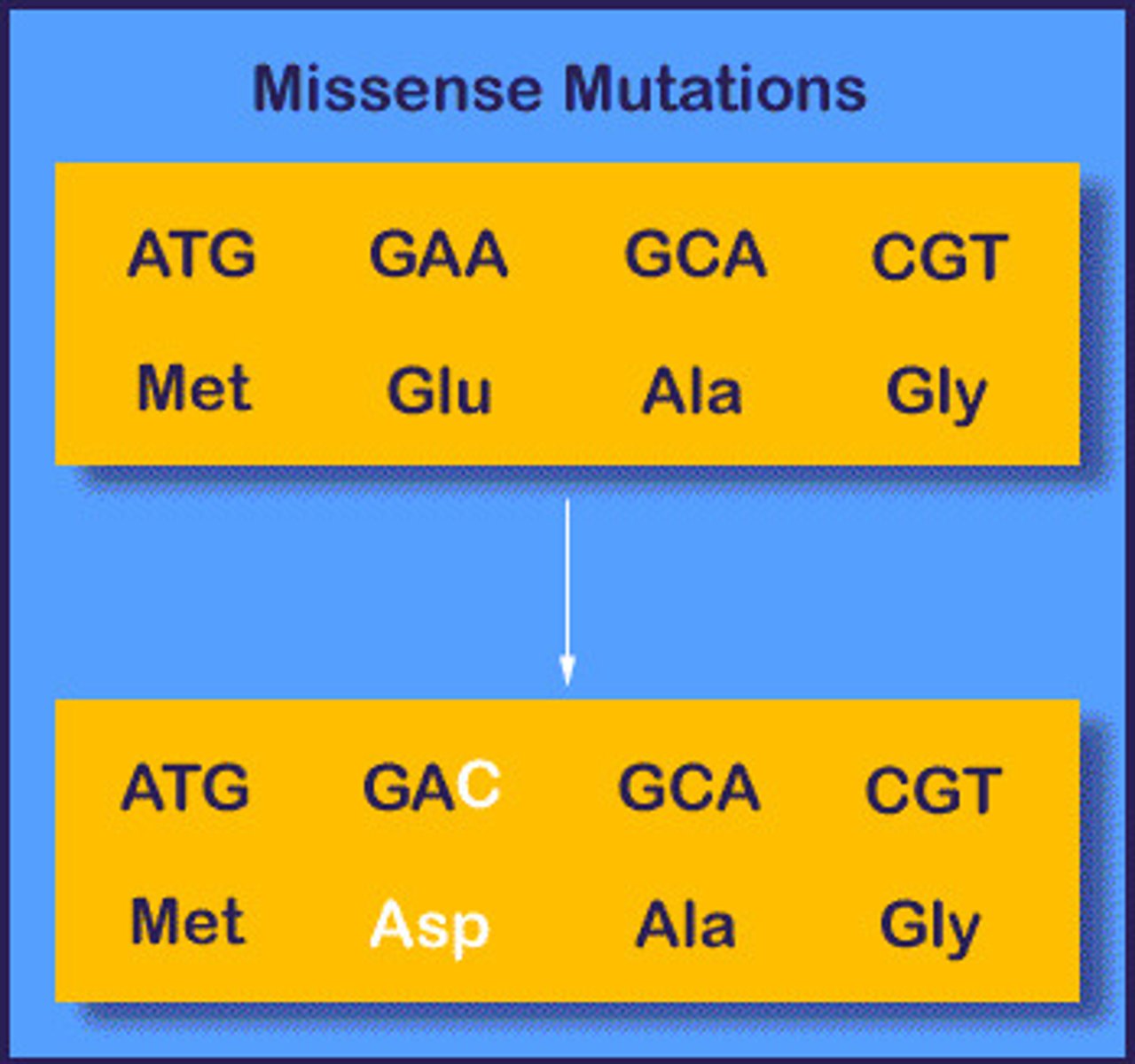
Missense Mutation
Base substitution which converts one amino acid into another
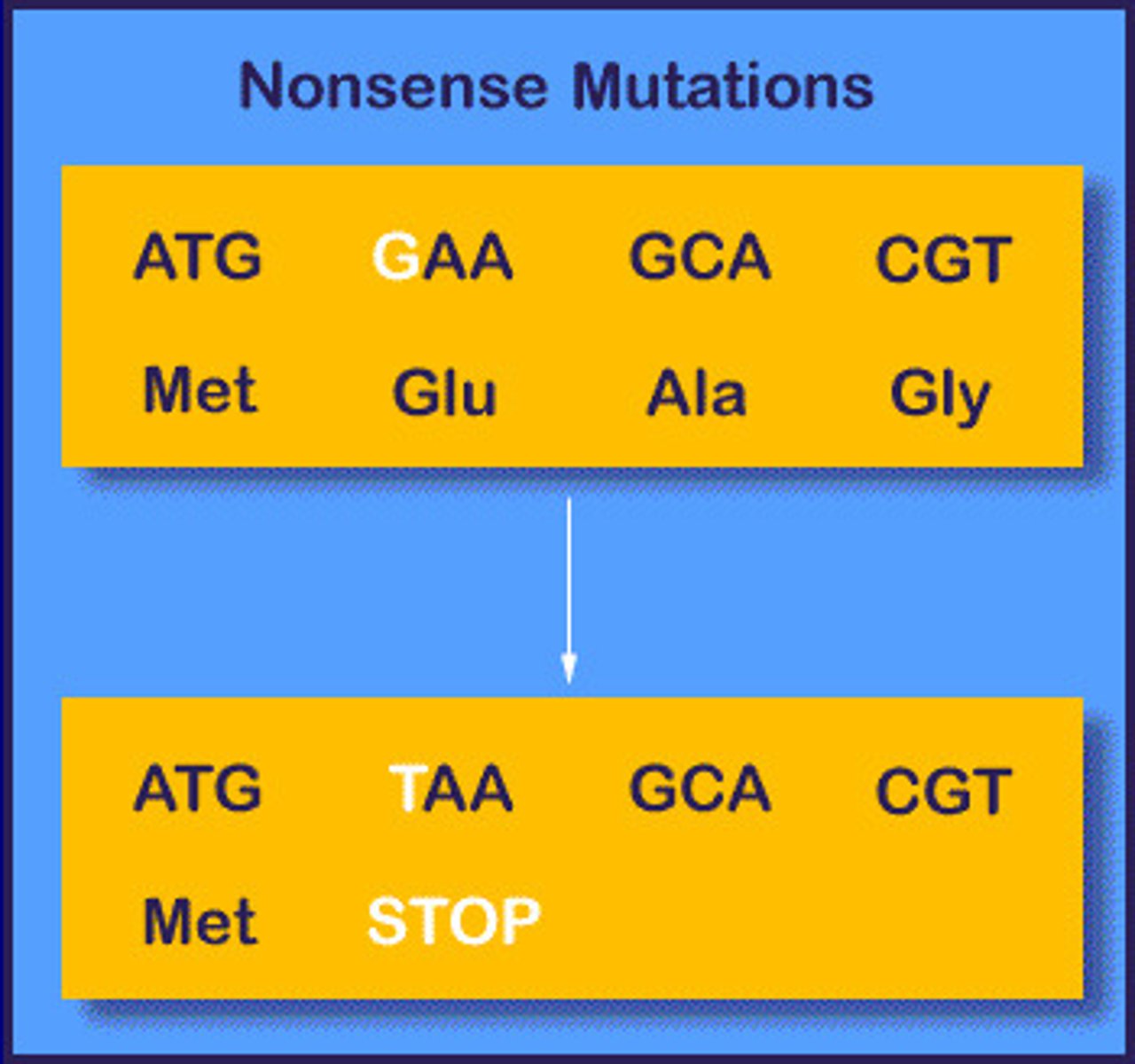
Nonsense Mutation
Converts an a.a. into a stop codon, causing a truncated protein.
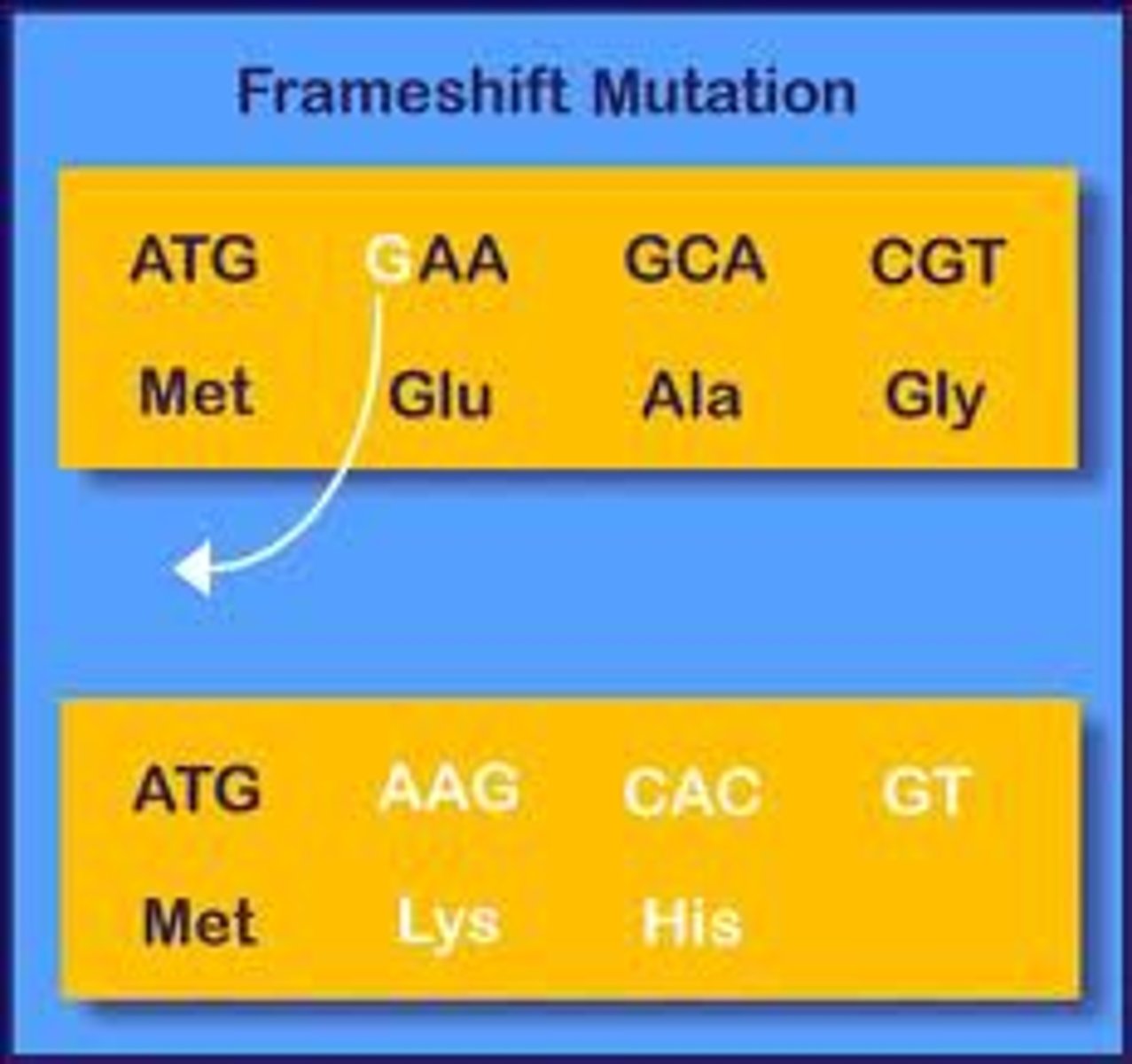
Frameshift Mutation
Base insertion or deletion, which shifts the reading frame.
Complementary
For every rung, big and little bases will fit like jigsaw pieces
- A with T, C with G
Template
When DNA replicates and unwinds, it acts as its own __________
Operon
One unit of operation in regulation.
Operator
Section of DNA where the repressor binds
-non coding
("cow on DNA railroad tracks")
Promoter
- Made of DNA and non coding
- RNA Polymerase binds here
Repressor
Protein that binds operator and lactose
Structural Gene
DNA which codes for a protein
Inducer
Sugar molecule (lactose) which binds repressor protein
-binds repressor and changes its shape so it can't bind operator
Exon
Parts of a gene in RNA that are expressed, coding regions
Intron
Non coding regions of RNA
inserted of pieces of DNA (viruses like herpes)
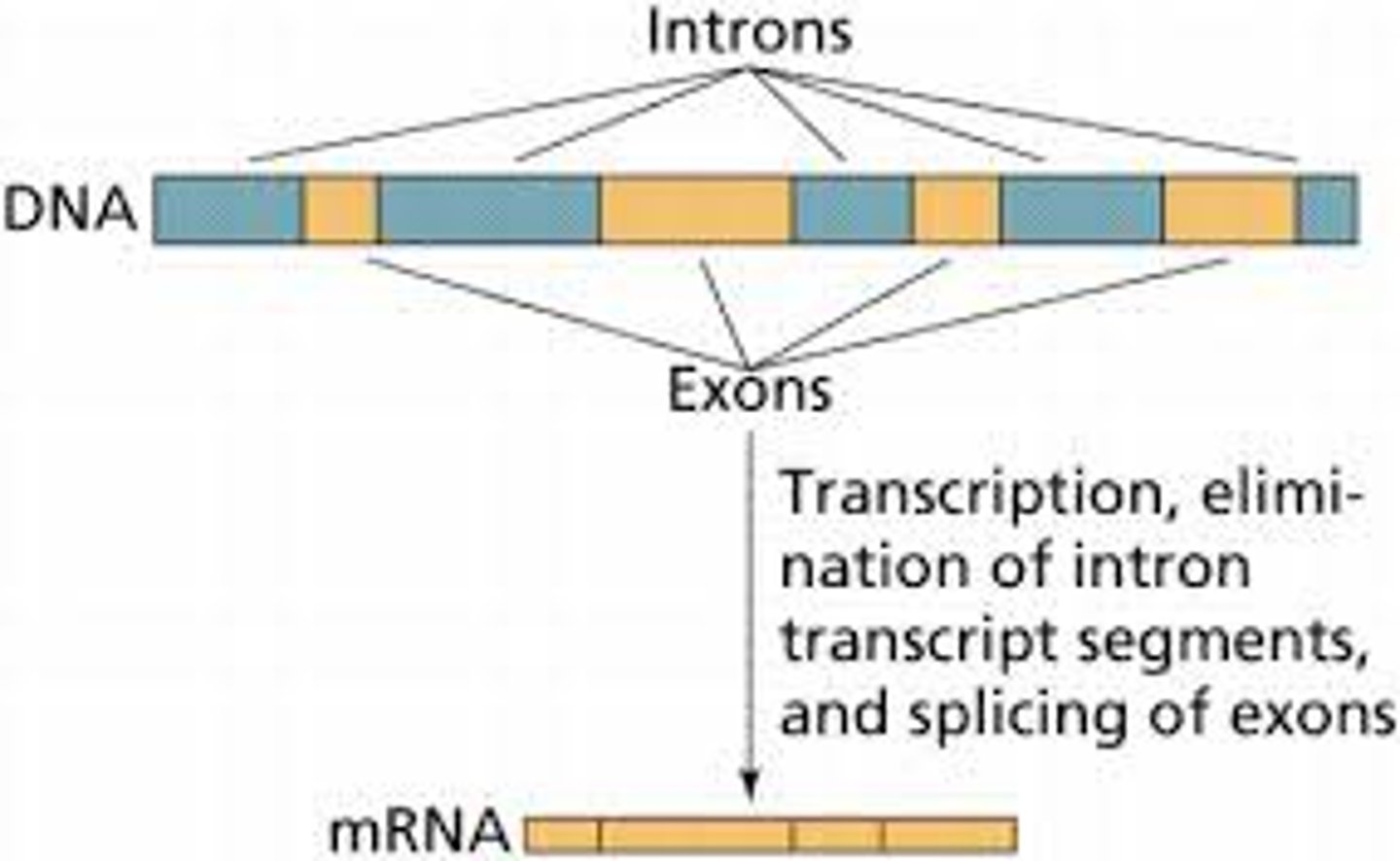
Splicing
When introns are removed from RNA and exons are joined together
convert RNA into an mRNA
RFLP's
Technique of DNA fingerprinting
PCR
-before RFLP
- Amplify DNA (replication)
DNA Fingerprinting
uses RFLP's; the anylsis of DNA from samples of body tissue or fluilds, esspecialy when conducted in order to identify individuals
Homologies
Shared developmental origins (clitoris = penis)
(labia = scrotum)
Ovary
Where eggs are made.
Oviduct
The pipe the egg travels through.
Ovulation
The release of a mature ovum (egg) into oviduct.