Unit 2A Homework and Quiz questions
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is acceptable when drawing resonance structures?
Move electrons to sp or sp2 hybridized atoms, lone-pair electrons, pi electrons, and use double-headed arrows between resonance hybrid structures (Not correct: Positive charges are moved toward electrons, use equilibrium arrows)
What criteria must be met for a molecule to be aromatic?
Must be cyclic, planar, every atom must have a p orbital (i.e., a continuous system/contiguous pi-complex), meet Huckel's Rule (and thus contain an odd number of pairs of π electrons.)
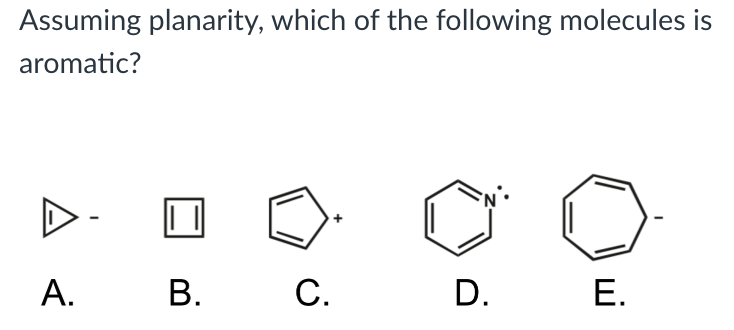
Assuming planarity, which of the following molecules is aromatic?
D ((This compound meets Huckel’s Rule and has an odd number of π electrons. The lone-pair electrons on the nitrogen are perpendicular to the π electrons and are not part of the π cloud.)

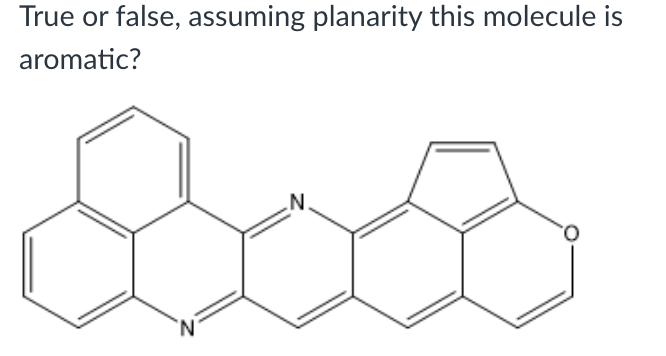
True or false, assuming planarity this molecule is aromatic?
True
True or false, assuming planarity this molecule is aromatic?
False
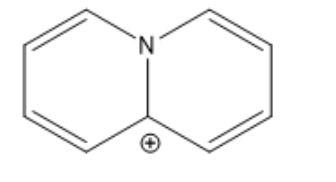
What is the value of n in Hückel’s rule for the following compound?
2
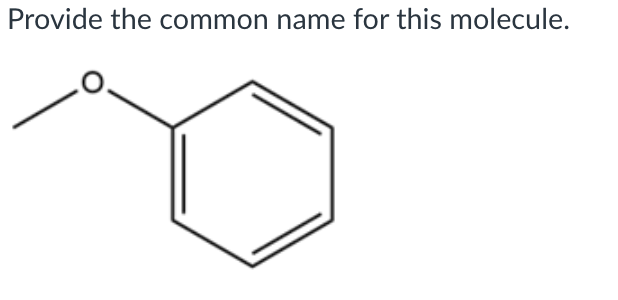
Provide the common name for this molecule
Anisole
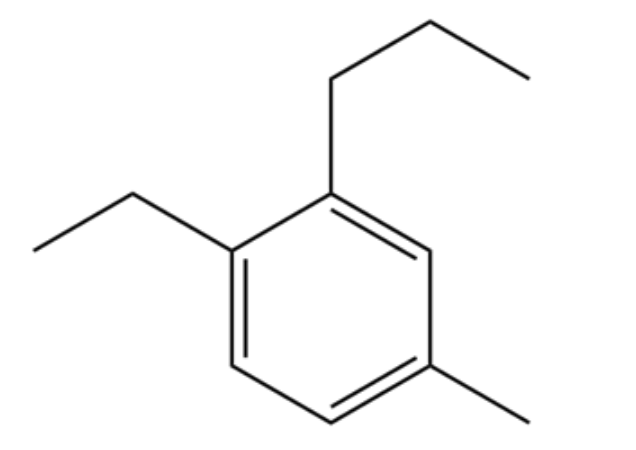
Provide the proper IUPAC name for this molecule
1-ethyl-4-methyl-2-propylbenzene
Anti-aromaticity has what effect on a molecule?
Destabilizing effect
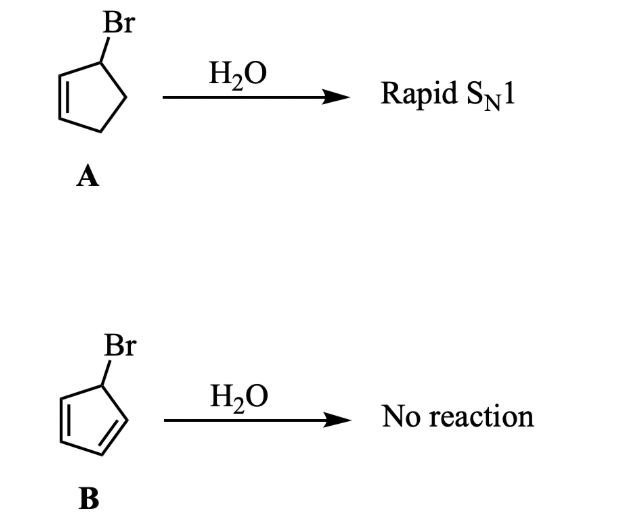
Molecule A, shown below, undergoes a rapid SN1 reaction with water. However, molecule B does not undergo any reaction with water. Using your knowledge about SN1 reactions and mechanisms, along with other topics from this chapter, explain the surprising lack of reactivity of molecule B.
The carbocation intermediate would be anti-aromatic for molecule B.
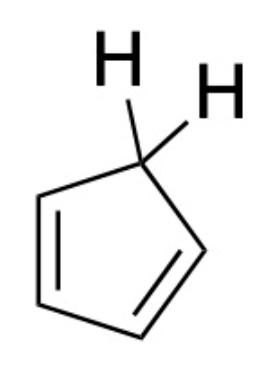
1,3-cyclopentadiene, shown below, is a very interesting molecule from a physical organic standpoint.
The geminal sp3 hydrogens on 1,3-cyclopentadiene, drawn explicitly above, are unusually acidic for alkane (C—H) hydrogens: as opposed to typical alkane hydrogens, which have a pKa of ~50, the geminal sp3 hydrogens on 1,3-cyclopentadiene boast a pKa of ~16, on the order of non-phenolic alcohols. Please choose the best explanation for the unusually high acidity of these hydrogens.
The conjugate base that results from removal of one of these hydrogens is aromatic and therefore very stable
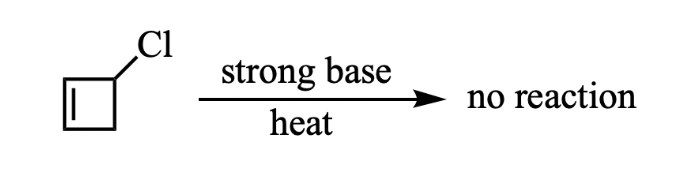
A student in the undergraduate organic chemistry lab attempted to perform the following elimination reaction. However, the student was unable to recover any of the desired product, why is that?
The desired product is anti-aromatic and therefore too unstable to form
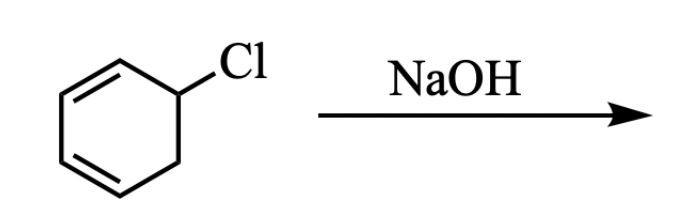
In CH 331 you learned that there are many circumstances where substitution and elimination reactions can occur under the same conditions. However, in the reaction below, only one reaction predominates.
Elimination
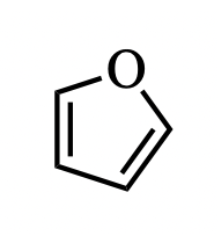
Like any oxygen with two bonds, the oxygen in the molecule below has two lone pairs. In which type of orbital(s) do these lone pairs reside?
one lone pair is in a p orbital, and the other lone pair is in an sp2 orbital
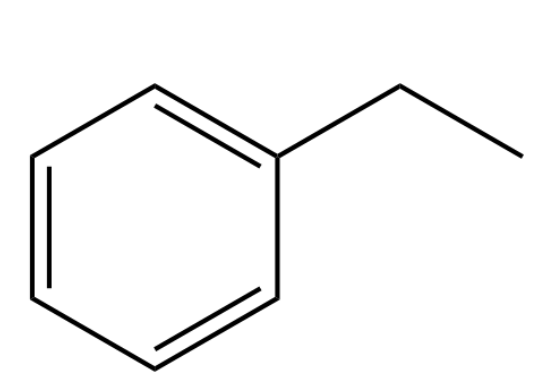
Provide the name of the following compound.
ethylbenzene
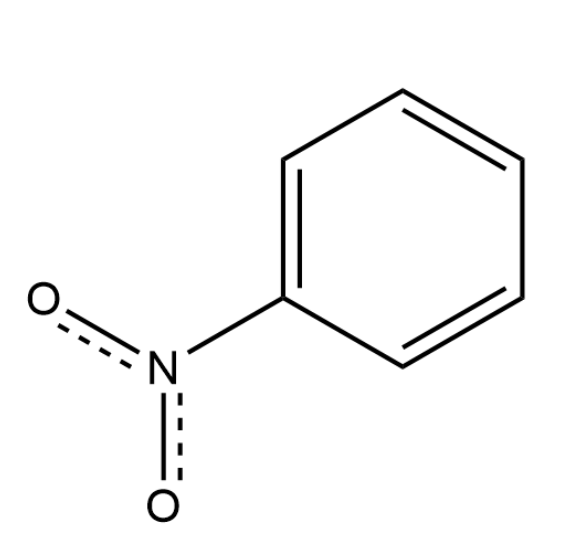
Provide the name of the following compound.
nitrobenzene
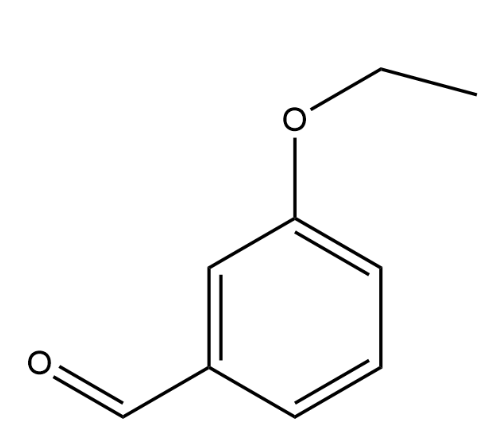
Using ortho, meta, or para nomenclature, provide the name of the following compound (do not italicize any letters). Please triple check your spelling and spaces!
m-ethoxybenzaldehyde
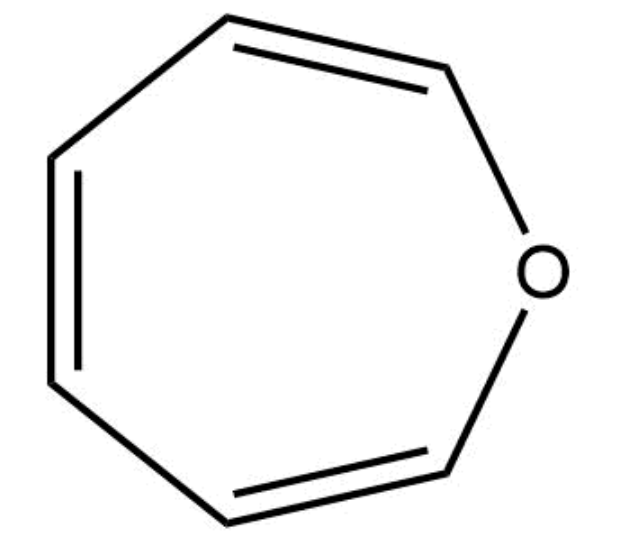
This compound is aromatic.
False
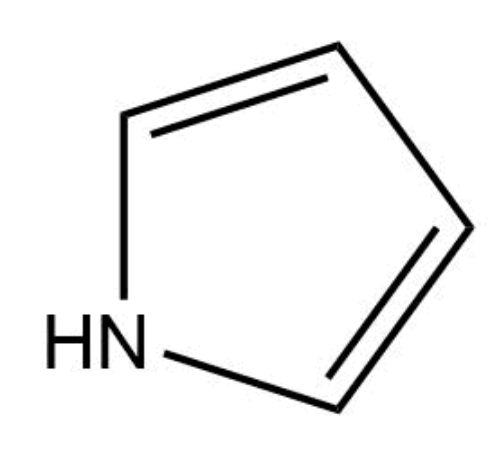
This compound is aromatic.
True
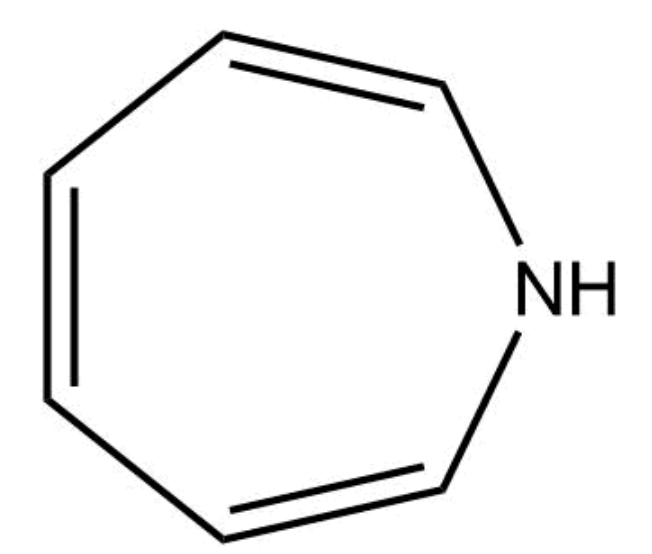
This compound is aromatic.
False
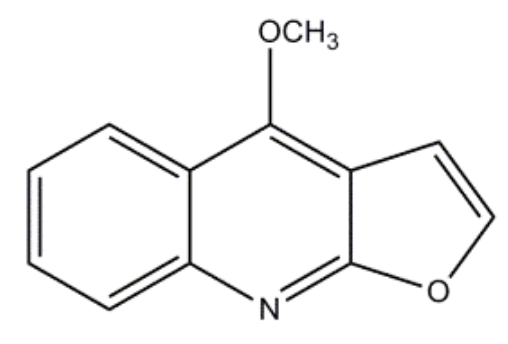
What is the value of n in Hückel’s rule for the following compound?
3
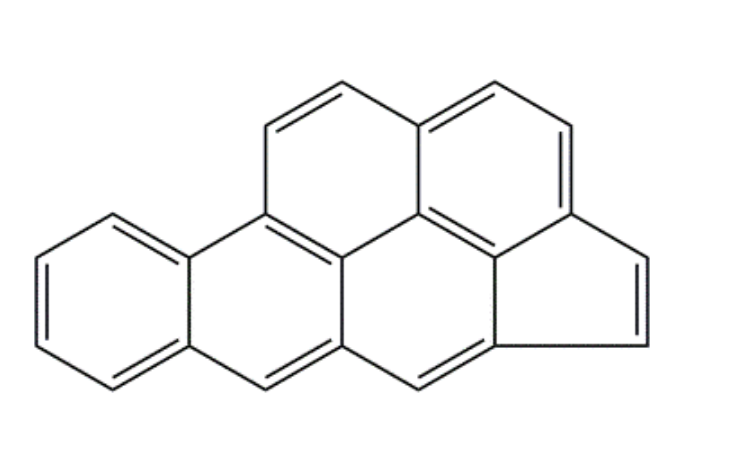
What is the value of n in Hückel’s rule for the following compound?
5
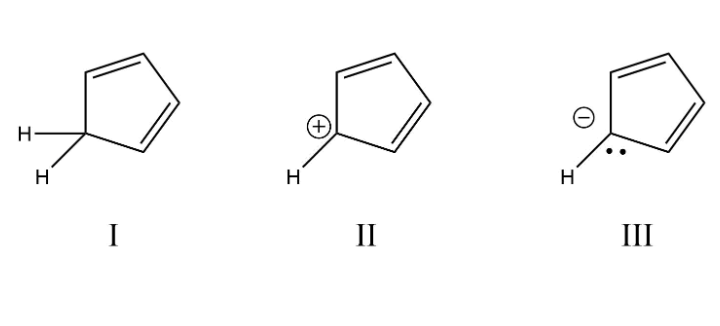
Which properly describes the order of decreasing stability (i.e., aromatic > non-aromatic > anti-aromatic) for the following molecules?
III > I > II
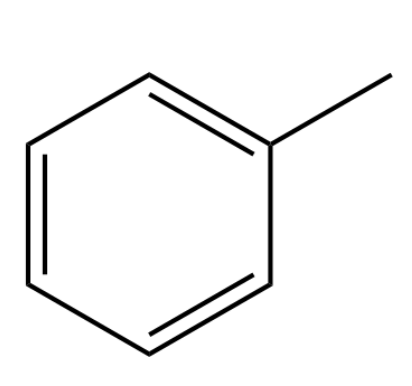
What are correct name(s) of the following compound
methylbenzene, toulene
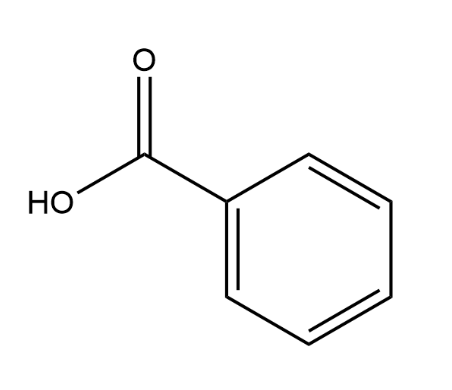
name this compound
benzoic acid
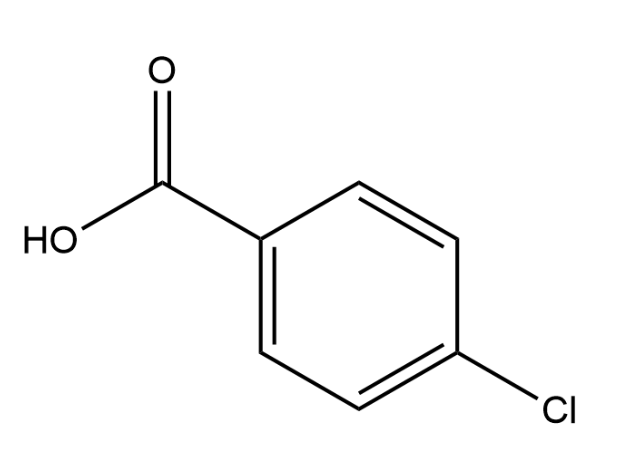
Using ortho, meta, or para nomenclature, provide the name of the following compound (do not italicize any letters). Please triple check your spelling and spaces!
p-chlorobenzoic acid
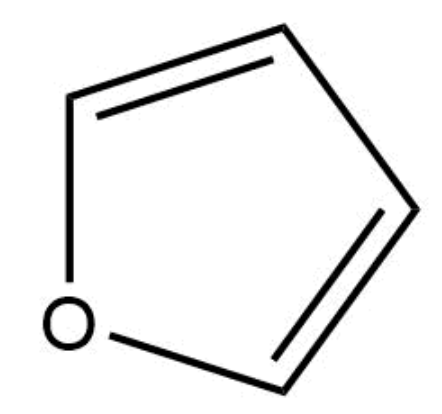
This compound is aromatic.
True
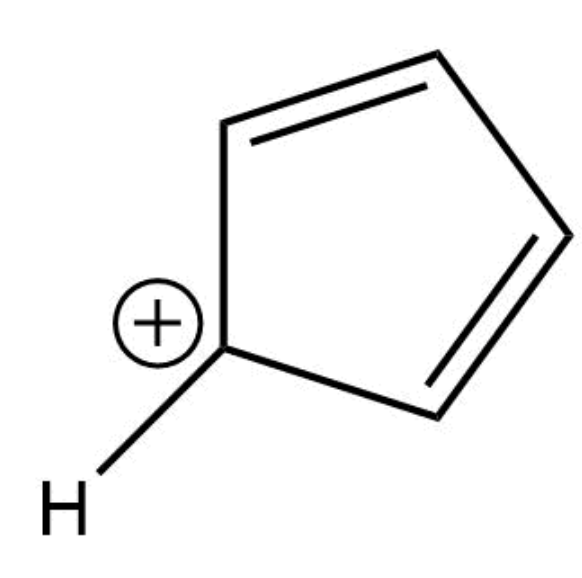
This compound is aromatic
False
Define anti-aromatic
A compound that is cyclic, planar and has an uninterrupted system of pi-bonds/p-orbitals, but violates Huckle’s rule
Define aromatic
A compound that is cyclic, planar, and has an uninterrupted system of pi-bonds/p-orbitals, and meets Huckle’s rule.
Define non-aromatic
A compound that is not cyclic, planar, and/or has an uninterrupted system of pi-bonds/p-orbitals (it does not get to qualify for Huckle’s rule and is not classified as aromatic or anti-aromatic)
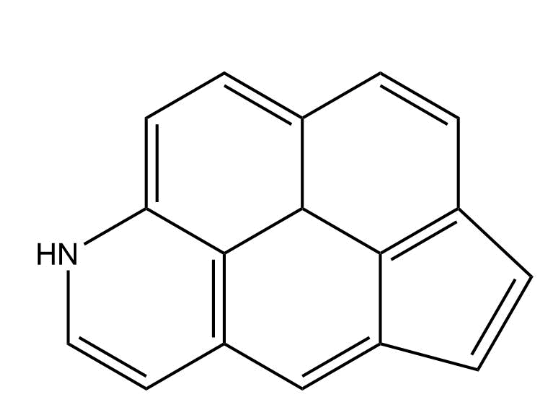
What is the value of n in Hückel’s rule for the following compound?
4
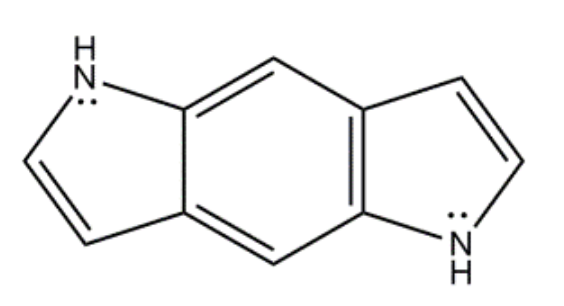
What is the value of n in Hückel’s rule for the following compound?
3
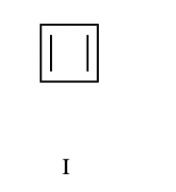
What is this compound (aromatic, non-aromatic, anti-aromatic)
anti-aromatic (because it violates Huckle’s rule)
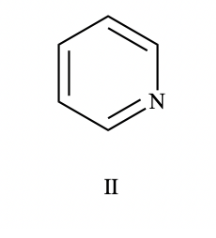
What is this compound (aromatic, non-aromatic, anti-aromatic)
aromatic (because it is cyclic, planar, has a contiguous system, and follows Huckle’s rule)
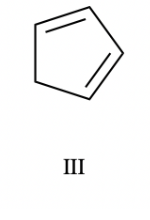
What is this compound (aromatic, non-aromatic, anti-aromatic)
non-aromatic (because it breaks the rules of aromaticity)
How do you tell is something is planar?
Are all atoms sp2 or sp? A sp3 carbon breaks planarity (aromatic , alkene , carbonyl carbons, usually pyrrole and pyridine)
How do you tell if the pi systm is contiguous?
(Can you trace a circle around the ring where every atom has a p orbital pointing up/down?) (What counts as a p-orbital?) double bond, carbocation, lone pair in a p-orbital (like N)
What breaks contiguity?
Sp3 carbon, lone pair in an sp2 orbital (pyridine-like N), atom with four sigma bonds (single)
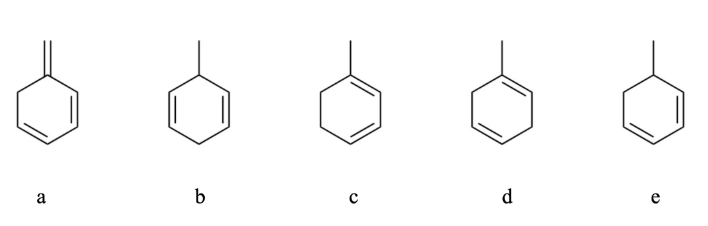
Choose the correct order for ranking the molecules below in terms of stability; e.g., most stable > lease stable
a > c > e > d > b
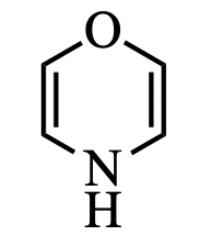
This molecule is expected to be _____________ with number of electrons = ?
non-aromatic, 6
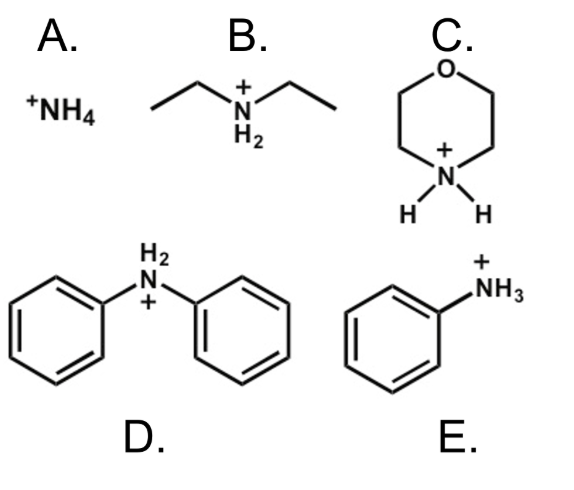
Which of the following is the strongest acid?
D The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in the conjugate base of D is more highly delocalized (stabilized), making it a weak base and thus it's conjugate acid quite strong. Inductive effects of the two sp2 substituents also lower the pKa.)
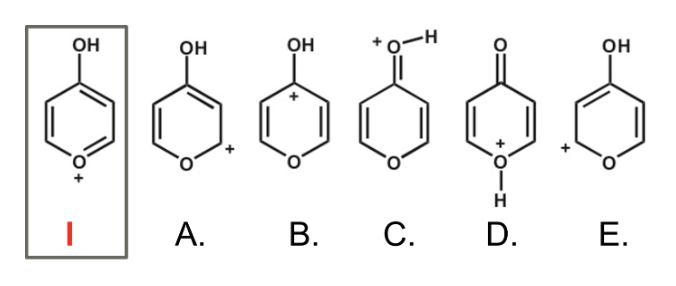
Which of the following is not an acceptable resonance structure of I?
D
What are some ways that a molecule will "avoid" being anti-aromatic?
The molecule will bend or kink to become non-planar, A heteroatom such as N or O will hybridize as sp3 to avoid conjugation, The molecule will dissociate one of its pi bonds to form a di-radical
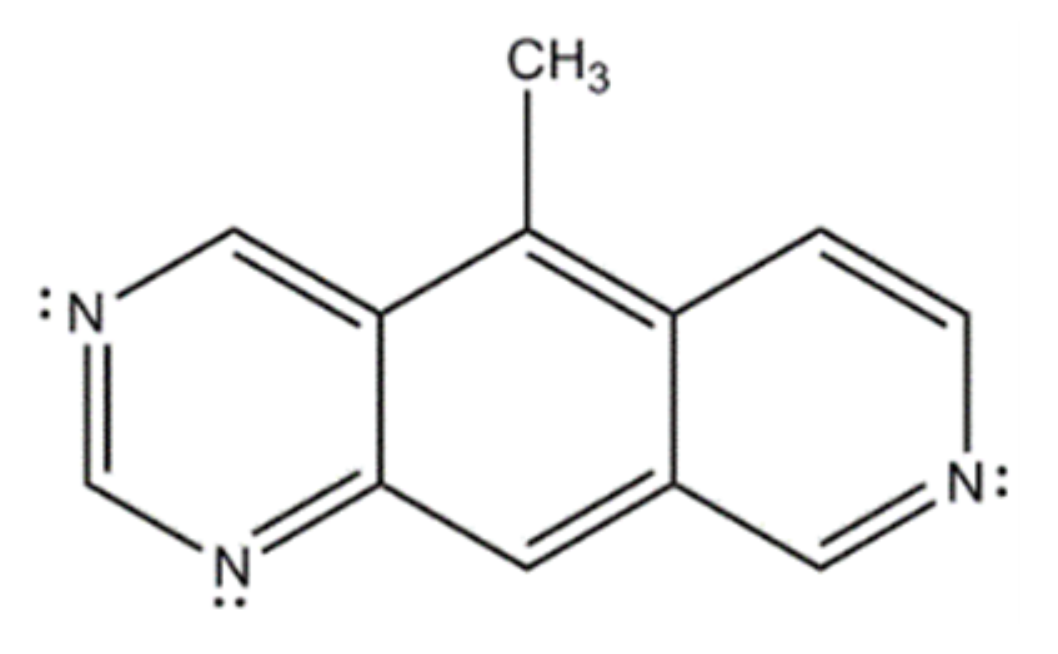
What is the value of n in Hückel’s rule for the following compound?
3