Unit 3 - Audition, Reflexes & Adaptation
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Sound Waves are
Longitudinal waves with compressions and rarefactions
Universal Equation
v = xf and v = x/T
Speed of Sound
344m/s
Smaller Length Materials have
A higher natural frequency because they’re stiffer and oscillates faster
Spiral Cochlea
Cell bodies of cochlea nerve axons
8th Cranial Nerve
Sensory nerve that transmits sound and balance from inner ear to brain
Auditory Pathway
Auditory nerve heads to rostral medulla
Synapses in cochlear nuclei in the dorsolateral part of the rostral medulla
Axons sent to part of the pons with superior olivary complex
Inputs enters thalamus to medial geniculate nucleus
Travels to primary auditory cortex, layer 4
Superior Olivary Complex
Has lateral and medial superior olive in mid pons from both ears to compare sound
Tonotopic Mapping of Primary Auditory Cortex
Low frequencies (rostral) to High frequencies (c)audal
Humans Hearing Range
20 - 20000 Hz
Lateral Superior Olive
Monitors interaural level intensity different for high frequency sounds when head is greater than wavelength, ~ 2Khz or more to create sound shadow
Medial Nucleus of the Trapezoid Body
Interneurons connected to other side’s LSO and inhibits LSO from decussating axons from other ear sending signals
Interaural Level Intensity Pathway
Noise from each ear excites cochlear nucleus which excites ipsilateral LSO and contralateral MNTB
Difference between the signals determines which ears gets more sound (If L ear > R ear, left LSO fires more)
Medial Superior Olive
Monitors interaural time differences for decreased frequency when wavelength is greater than the head (2000Hz)
Jeffress Model
MSO contains many coincidence detectors that each connect to the left and right, when sound enters an ear earlier, it’ll get a head start and hit a coincidence detector farther down than the other ear at the same time
Coincidence Detection
Only 1 neuron get input from both and the brain calculates delay
External Ear
Pinna > concha > external auditory meatus
Middle Ear
Tympanic membrane > malleus > incus > stapes
Inner Ear
Oval window > cochlear > round window
Eustachian Tube
Connects middle ear and throat to maintain pressure or else it’ll bulge out
Tensor Tympani Muscle
Connects maleus with bone in middle ear
Stapedius Muscle
Connects stapes and bone in middle ear
Auditory Attenuation Reflex
Middle ear muscle hamper ossicles to decrease volume when it’s loud for awhile
Ossicles use mechanical advantage by
Turning large movements to result in smaller but larger force
Mechanical Advantage of Ossicles Pathway
Force is funneled from a large eardrum to small oval window, increasing pressure
Stapes displaces about 1/10 of eardrum but with increased force
Scala Vestibuli
Upper area of cochlea, near oval window
Scala Tympani
Lower area of cochlea, near round window
Basilar Membrane Lengths
Narrows at base (150um), wide at apex (500um)
Perilymph
Fluid in cochlea
Scala Media
3rd chamber with endolymph fluid and higher K ions
Tectorial Membrane
Simulates hair cells
Organ of Corti
Structure in inner ear making nerve impulses from sound
Stereocilia
Hair protruding from hair cells
Inner Hair Cells
Main receptor for sound, close to inner axis spiral (around 3500)
Outer Hair Cells
More prevalent (15000), but increases amplitude of sound by contracting itself by prestin when depolarized
Audition to Nerve Impulses Pathway
Basilar membrane moves, hair cells move against tectorial membrane that rotates on a hinge
When Hair cell is pushed to longer side
Springs stretch, opening channels to allow K and Ca in to transmit signal to afferent nerve
When Hair cell is pushed to shorter side
Springs compress, closing channel and stopping K and Ca, hyperpolarizing
Prestin
Motor protein in OHC membrane
Conductive Hearing Loss
Vibrations can’t reach inner ear
Causes for Conductive Hearing Loss
Wax
Ottis media
Otosclerosis
Ottis Media
Ear infection of middle ear, common in kids because their tube is shorter and more horizontal making it harder to drain, causing pus to build and push on the eardrum
Otosclerosis
Stapes gets fused with bone onto cochlea
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Neural processing damaged
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Occupational deafness
Presbycusis
Antibiotic Ototoxicity
Vestibular Schwannoma
Presbycusis
Death of base hair cells from old age
Antibiotic Ototoxicity
Certain antibiotics can damage hair cells
Vestibular Schwannoma
Benign tumor compresses auditory nerves, preventing APs and weird facial sensation
Immunostaining
Using antibiotics to stain neurons
Immunohistochemistry
Using antibodies to do tissue chemistry
Antigens
Proteins recognized by immune system by antibodies where it binds to antibodies areas
Immunofluorescence Direct Method
Place foreign receptor into an organism where it makes antibodies, then fluorescently tagging the made antibodies
Immunofluorescence Indirect Method
Using the 1st antibody sample, to get another organism to create an antibody for the first one, and fluorescently tagging it so different primary antibodies have the same tail and can be used to amplify
Otolith Organs
Utricle and saccule detects head tilt and linear acceleration
Semicircular Canals
Superior, posterior, horizontal detect head rotation
Vestibular nerve joins auditory nerve into the
8th cranial nerve that enters the brainstem
Striola
Midline of otolith organs
Saccular Hair Cells point
Away from striola
Utricle Hair Cells point
To striola
Otolithic Membrane
Gelatinous layer on top of hair cells
Otoconia
CaCO3 crystal on top help deflection by adding mass and increasing shear force
The baseline for hair cells
-40mV
As calcium concentration in the hair cell increase
Motor protein controlling tension in the gated springs slips down actin filament
Horizontal canal is tilted
30 degrees
Ampulla
Bulge in bony canal
Crista
Supporting, epithelial cell which the hair cell bodies are embedded
Cupula
Gelatinous substance hair cell bundles are embedded
Adaptation in from Angular Acceleration
Hair cell and endolymph initially deflected by inertia of fluid catches up with rotation
Scarpa’s Ganglion
Cluster of cell bodies in internal auditory canal transmitting balance and motion information
Lateral Rectus
Muscles on the outside of the eye helping movement
Medial Rectus
Muscles on the inner eye helping with movement
Vestibulo-ocular Reflex
Eyes stabilized from body movement
Vestibulo-ocular Reflex Pathway
Horizontal circular canal sends through scarpa ganglion into the medulla medial vestibular nucleus
Synapse in the abducens nucleus
Lateral rectus axons exit the pons and insert ipsilaterally
Medial rectus axons decussate again at the medial longitudinal fasciculus then synapse at the oculomotor nucleus before going to medial rectus
When looking to the left
Left horizontal canal hair cells depolarizes, the right side axons receive excitatory signals and the left side axons get inhibitory signals to relax
Oculomotor Nerve
Eye movement, reflexes
Abducens Nerve
Abduction/lateral eye movements
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Sense of balance and hearing
Oscillopsia
Apparently motion of object and blurring of vision from bilateral loss of vestibulo-ocular reflex sometimes from hair cell damage by ototoxic medication
Positional Alcohol Nystagmus
Alcohol enters cupula causing it to become buoyant and rises to the top of the endolymph whenever it makes perceiving spinning and eyes stabilize where it slowly moves to the side then snaps back in place
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Otoconia breaks off from utricle and enters the posterior semicircular canal which can hit the cupula to cause dizziness in certain positions
Epley Maneuver
Series of positions to move otoconia back for BPPV
Pre Motor Cortex
Plans fine coordinated movements and six times larger in humans, but motor cortex is wrt body
Apraxia
Loss of ability to plan and execute complex voluntary motor tasks form lesion in the premotor cortex
Layer 5 of Primary Motor Cortex
Project to brain stem/spinal cord which connect to lower motor neurons
Corticobulbar Tract
Neurons in layer 5 of the proximal region from the cerebral cortex to brain stem
Internal Capsula
Stretch of white matter axons descend
Corticospinal Tract
Layer 5 neurons go to the spinal cord from the caudal medulla, either decussating or continue ipsilaterally
Pyramidal Decussation
Motor nerve fibers crossing to descend in the corticospinal tract in the medulla
Lateral Corticospinal
Motor nerves decussate in medulla synapse in the lateral ventral horn for limb movement
Ventral Corticospinal Tract
Descends ipsilaterally to the spinal cord medial ventral horn branching both sides from proximal muscle movement
Lateral Corticospinanl Tract Topography goes as
Lateral, like the STT (C,T,L,S)
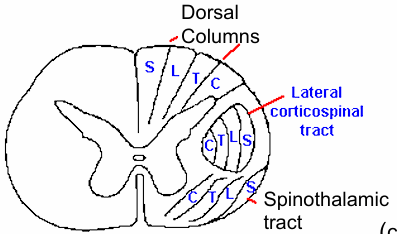
Ventral Horn Neurons near
Midline controls proximal muscles
Lateral Ventral Neurons controls
Distal muscles
Motor Neurons are
Direction tuned, firing more when movement a certain angle
Georgopoulos
Figured out turning curve and M1 population vector
Motor Neuron Pools
Many neurons project to same muscles but pools don’t come from a spinal segment to muscles
Motor Unit
Single alpha motor neuron branch to many muscle fibres
Bigger Motor Units gets more
Branching from units, smaller ones get less synapses to help make smooth contractions
Excitation Contraction Coupling
Physiological process that links AP (electrical) in muscles to the release of Ca ions
Acetylcholinerase
Enzyme in junction breaking down Ach to stop continual muscle contraction