Earth's Structure: Earth's Interior, Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes, & Volcanoes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Earth's Interior
Inner to Outer: (1) inner core, (2) outer core, (3) mantle, (4) asthenosphere (upper mantle), (5) lithosphere (part of lower crust & uppermost mantle), (6) crust
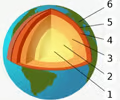
crust
Earth's rigid outermost layer of rock made up of both dry land and ocean floor
mantle
dense layer made of hot, semisolid rock is located directly below the crust
outer core
the only liquid layer of the earth - a sea of mostly iron and nickel
inner core
extremely hot, solid sphere of mostly iron and nickel at the center of the earthlithosphere
lithosphere
made up of the crust and a tiny bit of the upper mantle, this layer is divided into several constantly (very slowly) moving plates of solid rock that hold the continents and oceans
asthenosphere
hot, malleable semiliquid zone in the upper mantle, directly underneath the lithosphere, on which the plates of the lithosphere move (or float)tectonics
tectonics
large-scale processes affecting the structure of Earth's crust
evidence for Plate Tectonics
puzzle fit of continents across the Atlantic Ocean supported by matching rocks, fossils, and glacial deposits on continents on opposite sides of Atlantic; corresponding rock ages and magnetic alignment of iron-rich minerals on opposite sides of the Atlantic's mid-oceanic ridge where seafloor spreading occurs
scientific hypothesis
a possible and testable answer to a scientific question or explanation of what scientists observe in nature
scientific theory
a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations
endogenic processes
forces within Earth that affect its surface, such as plate tectonics, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes
exogenic processes
processes driven by the solar energy; includes weathering and erosion--the hydrologic cycle interacts with the rock cycle
orogenesis
the process of mountain building
convergent boundary
plate boundary where two plates move toward each other
divergent boundary
plate boundary where two plates move away from each other
transform boundary
plate boundary where two plates that are sliding past each other horizontally
San Andreas Fault
major geological fault in California formed by a sliding transform boundary
subduction zone
the region where an oceanic plate sinks down into the asthenosphere at a convergent boundary, usually between continental and oceanic plates
Juan de Fuca Plate
lies between the Pacific & North American plates in northwestern U.S./southwestern Canada
ocean trench
deep valley in the ocean floor that forms along a subduction zone
Marianas Trench
deepest spot in the oceans, over 35,000 feet deep, near the Philippines.
magma
molten rock beneath the Earth's surface
lava
magma that reaches Earth's surface and flows from volcanoes
volcano
vent or fissure in the Earth's surface through which magma and gases are expelled
shield volcano
large with gentle slopes of basaltic (iron-rich) lavas; common at divergent plate boundaries and oceanic hot spots; less viscous; Kilauea on the big island of Hawaii
composite volcanoes
large, steep-sided volcanoes that result from explosive eruptions of andesitic and rhyolitic (silica-rich) lava and ash along convergent boundaries; more viscous, so more explosive; also called a stratovolcano; e.g. Mt. Rainier and Mt. Fuji
cinder cones
small steep-sided volcanoes that erupt gas-rich, basaltic lavas
volcanic ash
tiny particles of pulverized volcanic rock and glass
pyroclastic flow
fast-moving avalanches of hot gas, ash, and rock
viscosity
a liquid's resistance to flowing
volcanic arc
curving chain of active volcanoes formed adjacent to a convergent plate boundaryisland arc
island arc
string of volcanoes that form as the result of subduction of one more dense oceanic plate beneath a second less dense oceanic plate.hot spot
hot spot
a volcanically active area of Earth's surface far from a tectonic plate boundary
tsunami
long high sea wave caused by an earthquake, submarine landslide, or other disturbance
Fukushima Daiichi Disaster
nuclear power plant disaster caused by a tsunami in 2011 triggered by an earthquake at the subduction zone off the east coast of Japan
sea floor spreading
process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies
mid-ocean ridge
undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary
East African Rift Valley
valley that begins in the north with the Red Sea, extending 6,000 miles through Ethiopia to the Lake Victoria region, where it divides into eastern and western segments and continues southward
fault
a break in Earth's lithosphere where one block to rock moves toward, away from, or past another
earthquake
the vibrations in the ground that result from movement along breaks in Earth's lithosphere
strike-slip fault
a type of fault where rocks on either side move past each other sideways with little up or down motion
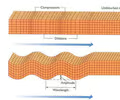
seismic waves
waves that originate where rocks first move along the fault
focus
the location where seismic waves originateprimary (P) waves
primary (P) waves
a type of seismic wave that involves alternating compression and expansion of the material through which it passes; these waves arrive first
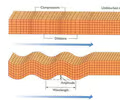
epicenter
the location on the surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
secondary (S) waves
a type of seismic wave that involves moving at right angles to primary waves causing rocks to move up and down and side to side
seismograph
device that records ground movements caused by seismic waves as they move through Earth
Richter scale
scale that rates an earthquake's magnitude based on the size of its seismic waves
Mercalli scale
scale that rates earthquake's intensity based on the damage that results