anatomy unit 3: skeletal system
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
connective tissue
most tissues in the skeletal system are _______
osseous tissue
bone tissue
dense and mineralized matrix (what surrounds the cells)
concentric rings make it able to hold a lot of weight
tendons
connect muscle to bones
ligaments
connect bone to bone
fibroblasts
cells in the tendons and ligaments
elastic cartilage
has the most elastic fibers
found in the outer ear & epiglottis
hyaline cartilage
found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi
fibrocartilage
has the least amount of elastic fibers
found in the vertebrae
holds pelvis together
chondrocytes
cells in cartilage
bone tissue
what type of tissue is this?
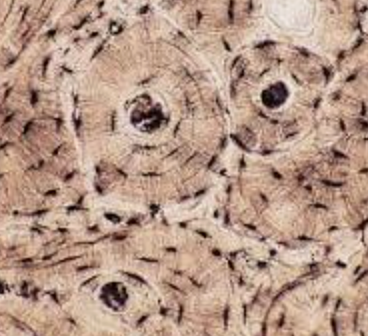
dense regular tissue
what type of tissue is this?
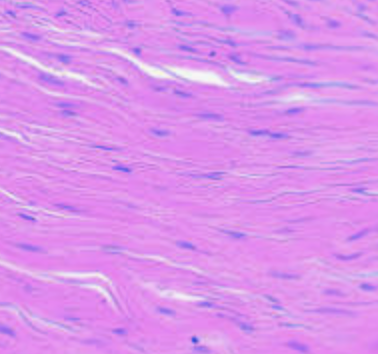
elastic tissue
what type of tissue is this?
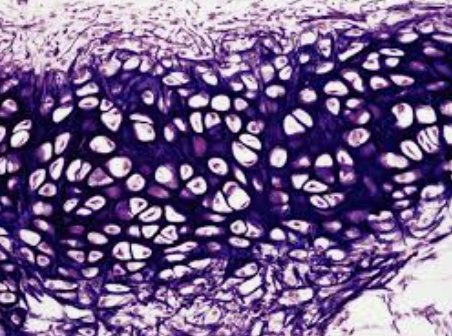
hyaline tissue
what type of tissue is this?
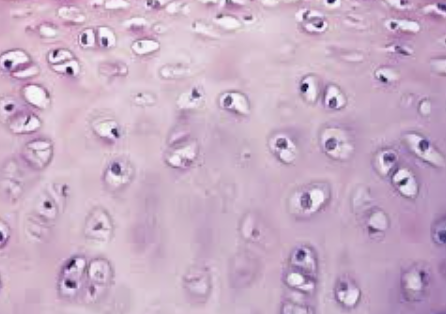
fibrocartilage
what type of tissue is this?
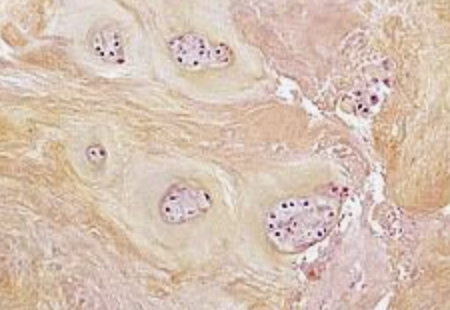
axial skeleton
includes the skull, vertebral column, and bony thorax (ribs)
protects the brain, spinal cord, and thoracic organs
divided into 3 regions: skull, vertebral column, bony thorax (ribs)
appendicular skeleton
includes the shoulders, upper limbs, hands, lower limbs, hips, legs, and feet
parietal & temporal
paired bones of the cranium
frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid
unpaired bones of the cranium
sutures
interlocking joints that unite bones of the skull
coronal suture
frontal bone and parietal bones
sagittal suture
two parietal bones
squamous suture
parietal bone and temporal bone
lambdoid suture
parietal bone and occipital bone
vomer & mandible
only unpaired bones of the face
palatine bone
bone that is affected by cleft lip disease
vomer bone
makes up the nasal septum
five skull bones with sinus cavities
frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillary 1, maxillary 2
functions of sinuses
lightens skull
voice resonance
warms and humidifies air
mucus accumulation
hyoid bone
only bone that does not articulate (touch or conjoin) with any other bone
miniature version of the mandible
moveable bas of tongue
scoliosis
lateral curvature of the thoracic region
kyphosis
hunchback; dorsally exaggerated thoracic curvature
lordosis
sway back; lumbar curvature; can happen in overweight or pregnant people
true ribs
attach to the sternum at their own attachment
false ribs
all grouped together at one attachment point to the sternum
floating ribs
aren’t attached to the sternum at all, just the vertebrae
femur
largest bone in the body
functions of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage
support, protection, movement, mineral and adipose storage, and hematopoiesis (blood cell formation)
long bones
all bones of limbs except patella and bones of wrist and ankle
short bones
cube-shaped, wrist and ankle
flat bones
thin & flattened; shoulder blades, ribs, skull
irregular bones
vertebrae and hip bones
bone marrow
soft tissue occupying the medullary cavity of a long bone
red bone marow
forms blood cells in the spongy bone
yellow bone marrow
makes fat cells in the medullary cavity
phosphorus & calcium
two minerals stored in bones
osteoblasts
bone-building cells
osteocytes
mature bone cells
osteoclasts
bone-destroying cells
bone remodelling
occurs every day due to microfractures in the bone
bone matrix
organic compounds (collagen) secreted by osteoblasts provide bone with resiliency
inorganic compounds (calcium, phosphate, calcium hydroxide) help with hardness and resistance of compression
osteons
cylindrical structural units that make up bone; weight-bearing pillars
haversian canal
a passage of blood vessels down the length of the bone
lamellae
tiny, small, concentric circles that make up an osteon
volkman’s canal
perpendicular to osteons and connects osteons together
lacune
spider-shaped osteocytes that reside in tiny gaps in the lamellae
canaliculi
canals that connect lacunae together
compact bone
dense, solid outer layer of bone
spongy bone
inner honeycomb-like structure made of trabeculae
diaphysis
aka the shaft; thick collar of compact bone with central marrow cavity
epiphysis
at the ends of the bones
thin layer above compact bone
covered in articular cartilage (helps cushion the bone and reduce friction)
periosteum
external double layer membrane of the bone
outer fibrous layer is dense irregular CT
inner cellular layer contains osteoblasts
rich in nerves, lymphatics, and blood vessels
Sharpey’s fibers - periostium connects to the bone vis these strong fibers
endosteum
inner bone surface covered with delicate connective tissue; covers the trabeculae of spongy bone
osetogenesis
process of ossifiication and bone formation
leads to the formation of bony skeleton in an embryo
children & adults
fibrous membrane and hyaline cartilage
makes up an embryo before week 8
intramembranous ossification
happens in face, cranial, and clavicles
development of bone from fibrous membrane
occurs in an embryo after week 8
endochondral ossification
replaces hyaline cartilage completely
happens in long bones
occurs in embryos after week 8
factors affecting bone growth
vitamins D, A, and C
growth hormone
thyroid hormone
parathyroid hormone
sex hormones
physical stress
osteomalacia
disease making bones soft due insufficient calcium and vitamin D & nutrient deficiency
rickets
children’s osteomalacia, more detrimental since bones aren’t done growing
osteomyelitis
inflammation of the bone marrow through an open wound
osteoporosis
when bone reabsorption happens too quickly
osteogenesis imperfecta
genetic brittle bone disease
bone cancers
can happen in the bone or cells within the bone
bone tumors = sarcomas
paget’s disease
elderly disease
excessive and haphazard bone deposits and resorption
spotty bone weakening
steps to a bone fracture
hematoma forms
granulation tissue forms
fibroblasts → collagen
osteoblasts → spongy bone
both = fibrocartilaginous callus
bony callus forms
continuous modification
open (compound) bone fracture
bone penetrates skin
closed (simple) bone fracture
bone does not penetrate skin
comminuted bone fracture
bone fragments in three or more pieces, usually due to brittle bones
greenstick bone fracture
bone breaks incompletely, common in children due to softer bones
spiral bone fracture
ragged break, usually in sports
impacted bone fracture
one bone fragment is driven into the medullary space of another
fibrous/syntharoses joints
generally immoveable
dense regular CT
sutures (skull), syndesmoses (distal end of tibia & fibula), gomphoses (root of tooth and mandible)
cartilaginous/amphiathroses joints
slightly moveable
connected by plate or pad of cartilage
synchondrosis (hyaline cartilage, first rib & sternum), symphysis (fibrocartilage, intervertebral joints, pubic symphysis)
synovial/diarthroses joints
freely moveable
fluid-filled joint cavity
plane, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, ball & socket
articular cartilage (covers the ends of bones), fibrous articular capsule (two layers of connective tissue), joint cavity
nonaxial
slipping motion, no axis
uniaxial
movement in one plane; hinge and pivot joints
biaxial
movement in two planes
multilateral
movement in all three planes
plane synovial joints
short movements
nonaxial
ex. femorpatellar
hinge synovial joints
like a door
uniaxial
ex. elbow
pivot synovial joints
shaking head no
uniaxial
ex. atlas and axis
condyloid synovial joints
side to side, back and forth
biaxial
ex. occipital and atlas
saddle synovial joints
side to side, back and forth
biaxial
ex. thumb joint
ball & socket synovial joints
most freely moving
multiaxial
ex. glenohumeral joint
sprains
happen when a ligament it stretched or torn
heal slow due to a lack of blood supply
dislocation
happens when a bone is out of its normal place
arthritis
inflammatory or degenerative disease of the joints
acute - bacterial infection
chronic - no cure
osteoarthritis
most common; due to aging and degrading of articular cartilage
rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disease; joint is attacked by immune cells
gout
buildup of uric acid in the joint cavity