Bovine MEDICINE and RESTRAINT
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Angus
Developed from cattle native
to Aberdeenshire and Angus
in Scotland.Very hardy.
Most common breed of beef
cattle in US.Horn status: Polled
Colors can be solid black or red.
Bulls can weigh 1850+ lbs. Cows can weigh 1200+ lbs.
Can also be used in crossbreeding to reduce the chance of dystocia and to create polled calves.
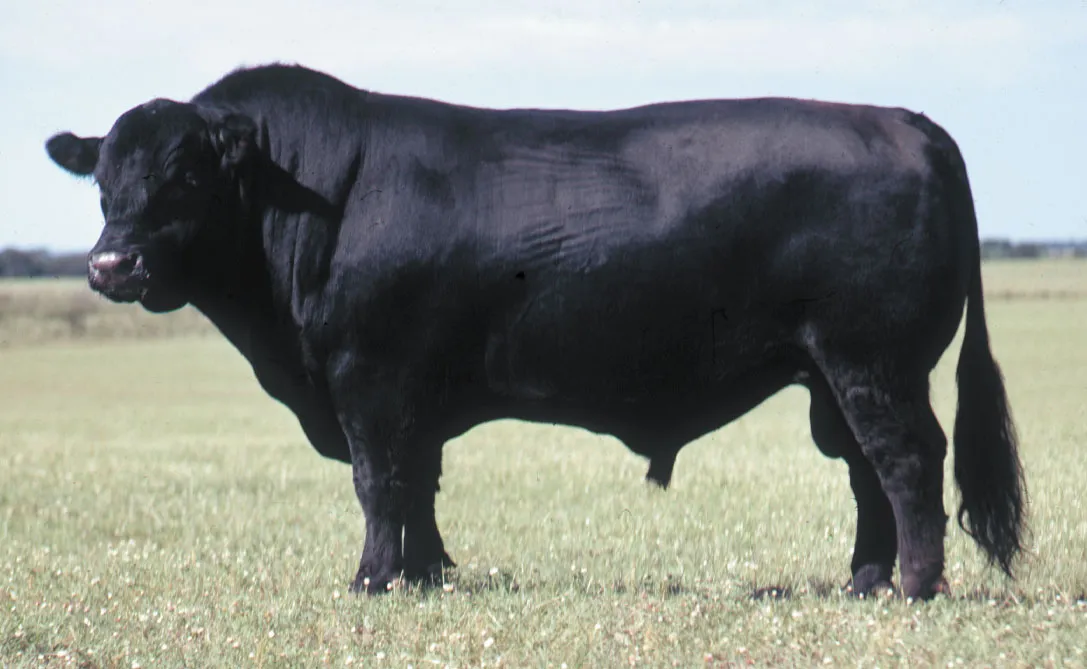

Brahman
First bred in US from cattle imported from India. These are the sacred cattle of India.
Characterized by a large hump over the top of the shoulder and neck; ears are large and pendulous.
Mainly used for breeding and meat industry.
Extensively cross-bred with other beef breeds to develop new breeds.
Known for extreme tolerance to heat and resistance to insects due to thick hide.
Horn Status: Horned.
Colors: red, very light gray to almost black.
Bulls: 1600 – 2200 lbs. Cows: 1000 – 1400 lbs.

Hereford
Originally from Herefordshire, England.
Herefords in 1700’s & 1800’s were much larger than modern breed.
Hardy and thrifty breed.
Prone to eye cancer.
Horn Status: Polled and Horned
Color: (deep cherry red to a light buckskin-orange color),white on face, withers, chest, bottom line, tail switch and feet.
Bulls: 2000 to 2600 lbs. Cows: 1300 to 1700 lbs.

Limousin cattle
Originated from Limousin and
Marche regions of France.Initially used as draft animals.
Popular due to low birth weights
(ease of calving).Heavily muscled; high yielding
production of lean beef.Horn Status: Horned, but now
selectively bred to be Polled.Color: Light wheat to dark
golden-red, although black
Limousins are now being bred.Bulls: 2200 – 2500 lbs. Cows: 1400 – 1550 lbs

Short horn
Originated in North East
England.Developed as dual-purpose
dairy and beef, now are two
separate breeds.Slang term for Shorthorns:
ShortiesHorn Status: Polled, but
some bloodlines have horns.Color; red, white or roan.
Bulls: 2000 – 2200 lbs. Cows: 1500 – 1700 lbs

Simmental
Originated in Western Switzerland.
Oldest and most widely distributed of
all cattle breeds in the world.Arrived in US late 1800’s.
Simmental have been used as dairy,
beef and draft animals.Beef yield is high, well-marbled.
Renowned for rapid growth of young.
Provides more combined weaning
growth and milk yield than any other
breed.Colors: black, red, red/white, white
face, ears same color as body, lot of
white on belly and legs.Horn Status: Polled and Horned,
depending on genetics.Bulls: 2200 – 2800 lbs. Cows: 1100 – 1500+ lbs

Texas Longhorn
Descendants of the first cattle
brought to the New World.Have a natural resistance to many
diseases and parasites that infect
herds of other breeds.Known for its characteristic horns
which can extend to over 7 ft.Hardy animals – heat and drought
tolerant – low maintenance.Produce exceptionally lean meat.
Commercial ranchers cross breed
longhorns with other breeds for
increasing vigor and ease of calving.Color: diverse, can be any color or
mix of colors; dark red and white are
the most dominant.

Ayrshire
Originated in the County of Ayr in
Scotland.Ayrshires do better under pasture
conditions than other major dairy breeds.Calves are strong and easy to raise.
Milk has moderate butterfat.
Color: red and white (red varies in shade
from very light to very dark).Color markings vary from nearly all red to
nearly all whiteThe spots are usually very jagged at the
edges and often small and scattered over
the entire body; spots are distinct with a
break between the red and white hair.Horn Status: Horned
Bulls: 1500 – 2000 lbs Cows: 950 – 1300 lbs.

Brown swiss
Long lifespan, sturdy and strong.
Large bodied with large fuzzy ears.
Quiet temperament.
Known for large quantity of milk
(second highest annual milk yield per
year); ability to stay in lactation longer
than other breeds.Due to ration of protein to fat in the
milk, makes it ideal for cheese-making.Color: Light brown or gray/silver;
hooves, nose and switch are black,
white ring around muzzle.Horn Status: Horned
Bulls: 1900 – 2600 lbs. Cows: 1300 – 1400 lbs.
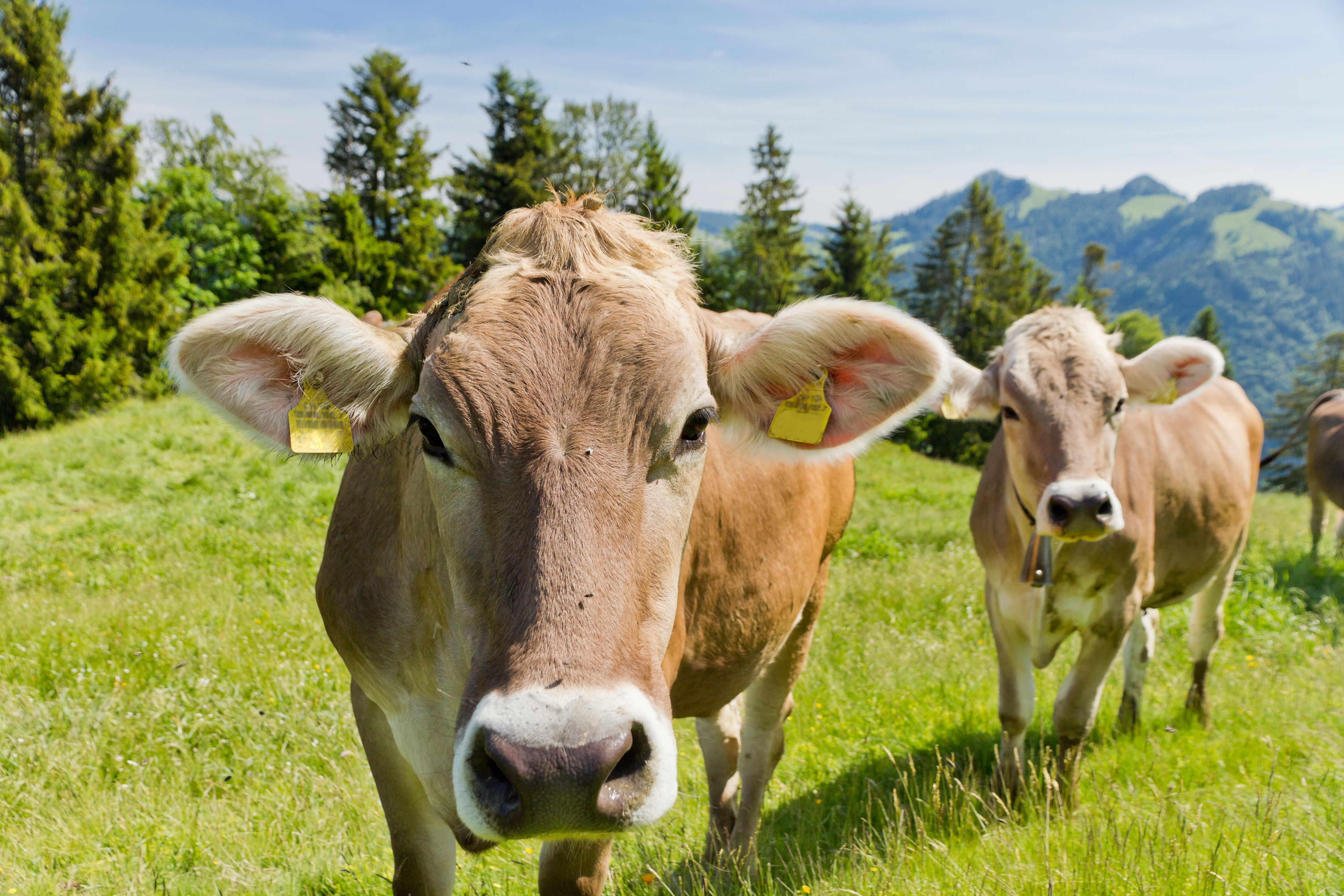

Guernsey
Genetics have been improved upon with the advent of AI
Known for producing milk
containing high butterfat, high
protein and a high concentration
of beta carotene, which gives the
milk a golden color.Excellent for use in pasture based
milk production.Horn Status: Horned
Color: orange/red and white.
Bulls: 1300 - 1600 lbs. Cows: 950 – 1100 lbs.

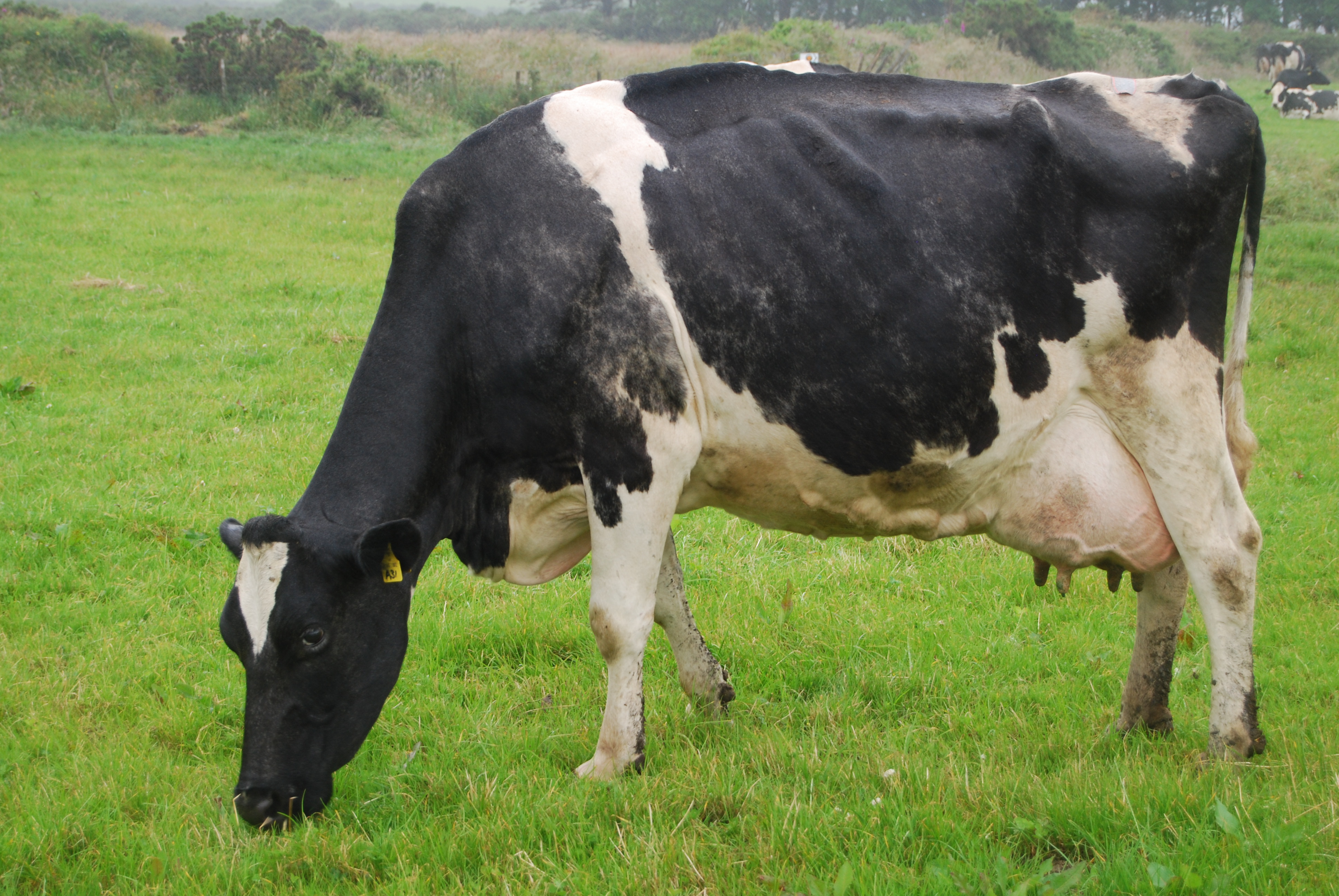
Holstein
Most common dairy breed in the US
Worlds highest producing dairy animal, but has less butterfat and protein in the milk compared to other breeds
Horned or polled
Bull = 2000-2400 Cows = 1100 - 1300

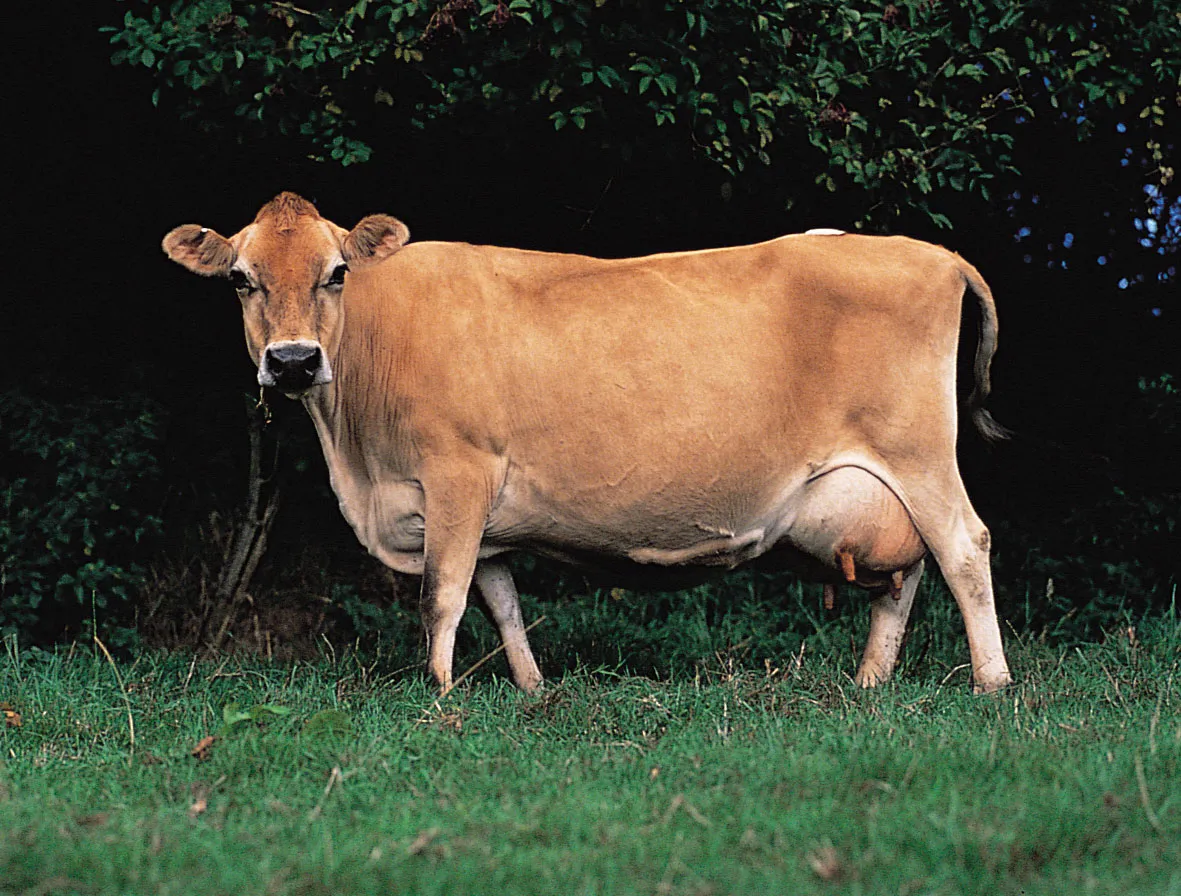
Jersey
Originated on the island of “ “, off the coast of France
Small in stature compared to other dairy breeds
Produce more pounds of milk per body weight than any other breed
Popular for high butterfat content of milk
Horned and Polled
color varies from light grey to very dark fawn or almost black
Bulls = 1200-1800 Cows = 800-1100

Normal bovine TPR
temp = 100.0 - 102.5
Pulse = 55-80 beats/min
RR = 10-30
Ruminations = 1-2 every 3 min
Calf
male/female less than 1 year
Heifer
female that had not had a calf
Cow
mature female, shows evidence of having produced one or more calves
Bull
intact male; generally of breeding age
Polled
lacking horns, either naturally or surgically removed
Bovine Gestation length
283 days
Age at first calf
24 months
Age at first breeding
13-15 months
Characteristics
cloven hoofed
Dairy or beef
Second largest type of livestock in the world by number
herbivores
Normal Behavior
Herd animals
will follow the leader
anxious when isolated, can be more dangerous
Means of Defense
Flight animals (prey)
Quick and agile
They will run over you, head for daylight (doors and windows), jump over walls or gates, run through fence
Head butting
charging
herd members help protect calves
cattle do not strike with front feet
reading body language
reasons to restrain
Castrate a calf
dehorning
administration of treatment and medication
treating sick calf
putting a ring in a bulls nose
Methods of restraint
Squeeze chute
Milking parlor
Stanchion
Halter
Nose tongs
bull ring
chemical sedation
Hobbles
What side is the rumen on
THE LEFT!!
Stressed Bovine
Inc. RR
Inc. HR
Feel hot, may sweat
open-month breathing
Breathing with head and neck extended
Flank Restraint

Tail twist
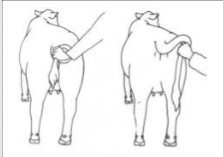
Tail jack
Restraint of Animals in general
Observe the animal first
Alert animals to your presence
Fewest number of people around is best
Avoid loud noise and fast movement
Approach at animal’s shoulder, not head (flight zone)
Use adequate but minimum restraint - less is more
When Herding Cattle
remember they are rarely halter broken
Make yourself bigger
Move cattle through chutes and panels
“Follow the Leader” (rattle grain bucket)
Use their flight zone to your advantage
What chemical sedations are ruminants very sensitive to?
Xylazine
Down cow
a bovine that is unable to get up due to a variety of causes, usually illness
Drench
a method of giving liquid medication, usually with a drenching gun
Dry cow
a cow that is not lactating
Drying off
the process of ending a cow’s period of lactation; i.e., quit milking her in preparation for parturition
Dystocia
difficulty in giving birth
Freshen
to give birth to a calf and to begin a period of lactation
Grade
a non-purebred or non registered
Heat
another name for estrus or that period of time in which the female is receptive to the male
Lactate
to produce milk
Mastitis
inflammation of one or more quarters of the mammary gland (udder)
Open
not pregnant
Scours
diarrhea in young animals
Scur
horn tissue attached to the head by skin only; usually the result of poor dehorning technique.
Steer
a male bovine castrated before sexual maturity
TMR
total mixed ration – feed for cattle (generally dairy) in which all the ingredients are mixed together so
Beef Cattle
Angus
Braham
Texas Longhorn
Hereford
limousin cattle
Shorthorn
Simmental
Dairy Cattle
Holstein
Jersey
Ayrshire
Guernsey
Brown Swiss
Common Beef breeds
Angus
Hereford
Simmental
Shorthorn
Carolais
Mixed
6 major Dairy breeds
Holstein
jersey
Brown Swiss
Ayrshire
Guernsey
Milking Shorthorn
Vaccination against
Respiratory - viruses and Bacteria
Diarrheal
Reproductive
Internal and External Parasite
“worms”
Lice, mites, and grubs (warbles)
Flies
Segments of the Beef industry
Cow-calf
Backgrounder or stocker
Feedlot
Keys to profit for Cow-Calf
decrease feed cost
increase weaning %
Increase or maintain pregnancy rate
Decrease unit cost of production
Common diseases - Cow-Calf
pinkeye, foot rot, neonatal calf scours, BRD, “agroceriosis”, coccidiosis, grass tetany
Calves: Diarrhea
Bacterial
Nutritional
Parasitic
Viral
Calves: Respiratory
Bacterial
Viral
Calves disease
Septicemia
TPR
100.0-102.5
55-80 beats/min
10-30 breaths/min
Ruminations: 1-2 every 3 min
Beef disease
Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex(BRDC)
shipping fever
Bacterial
Viral
Other Beef Diseases
Hypomagnesemia
Grass tetany
Ruminal acidosis
Bloat
Dairy Disease - Metabolic
hypocalcemia (milk fever)
Hepatic lipidosis (fatty liver)
ketosis
displaced abomasum
Dairy Disease - Mastitis
Clinical
Subclinical
Cow-Calf
Animals produced primarily for meat
Segment results in a 5-10 month old animal
will have spring and/or fall calving
Dairy diseases
Metabolic
Mastitis
Lameness
Neonatal Care
Oxygen/pulse assessment
Temperature regulation
Care of the umbilical cord and umbilicus
Nutrition (nursing)
Bonding of cow and calf
Passage of meconium (first defecation)
Adequacy of passive transfer of antibodies (colostrum)
Physical examination of the calf
Beef
Calving
Low maintenance
Sell beef
Wean at about 6-7 months
Calving season about 65 days
Save $$ = profit
Dairy
Freshening
High Maintenance
Sell milk
remove from dam at <1 day
Increased production = profit
Stocker
Grow frame (no interested in marbling) on animal prior to finishing at a feedlot
Animals usually 6-9 months of age while here
Feedlot
Finishing cattle for slaughter; interested in marbling/grades/and weight
Animals fed heavier concentrates to increase marbling
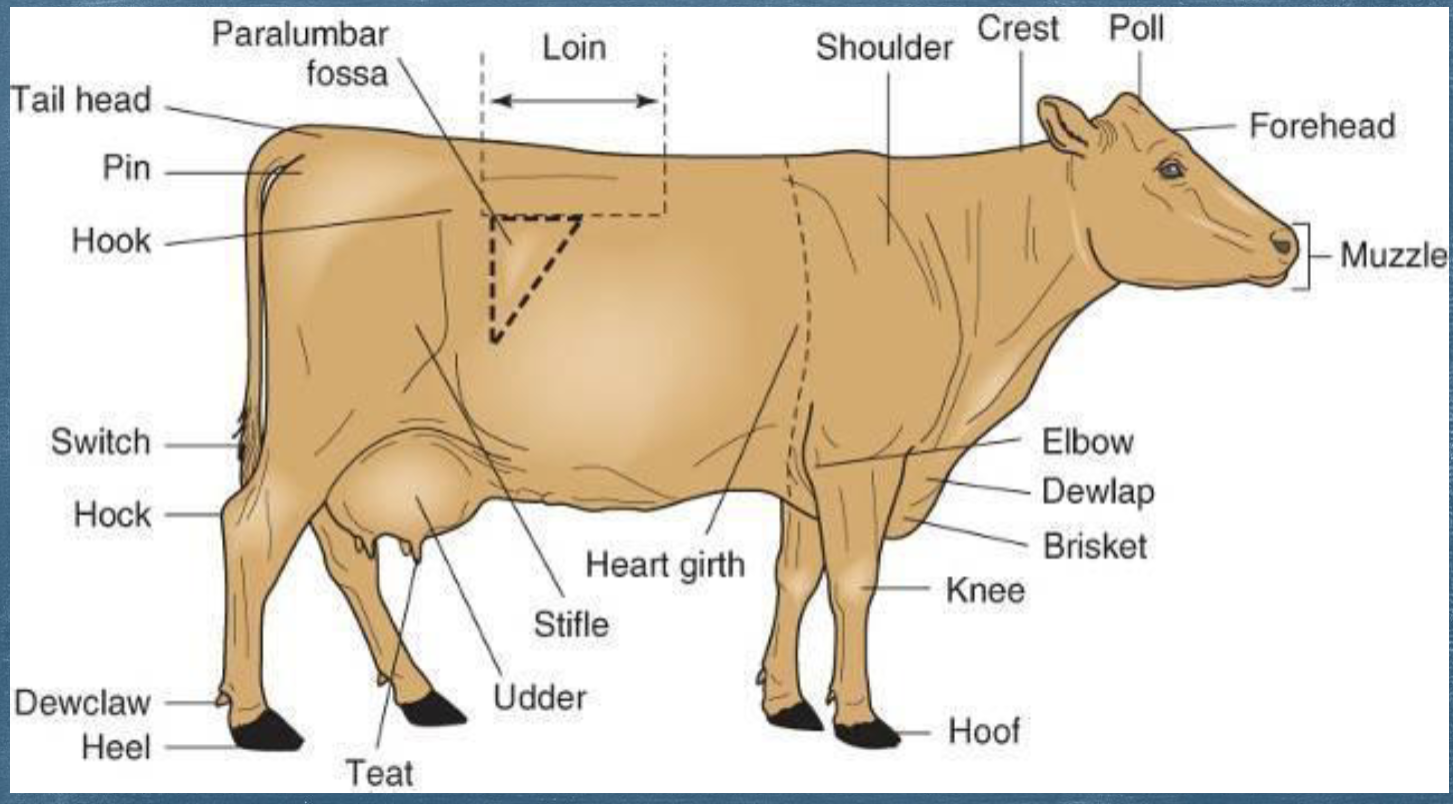
Bovine Anatomy
Squeeze chute
By removing pressure points and ensuring a clear line of sight, a good one of these will ensure that cattle do not feel pressured and will walk through the chute, limiting injury to live stock and handler

Milking parlor
the place where milking happens. They are designed for optimal cow and form worker comfort
Parallel
Rotary
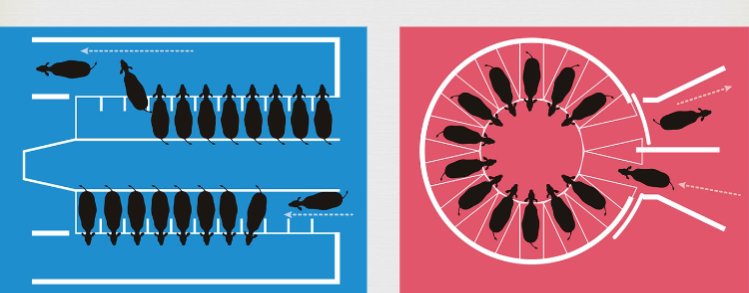
Stanchion

Nose tongs

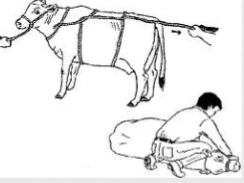
Rope casting methods
Double Half-hitch Method
Burley or Criss-Cross method
Double Half Hitch
Advantages:
Fewer people needed
better able to predict on which side animal will fall
Disadvantage:
May injure genitals
Goes down hard and fast
Loop around neck may cause respiratory distress
Need to know BOWLINE knot to start
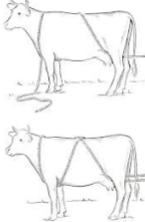
Burley or Criss-Cross method
Advantage:
No loop around neck or chest
Animal does not fall hard
Less chance of genital injury
No knots to tie
Disadvantages:
takes more people
less control over on which side animal falls
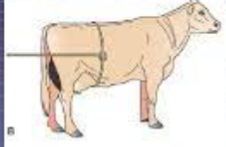
Where do you take the pulse at
The underside of the tail, femoral, or mandibular
Rope Flank Restraint
to keep from kicking
Where can you check CRT
the vulva
Where do you listen at for the rumen
the left paralumbar fossa
Ping of a left displaced abomasum
variable pitch ping, will also “slosh”
Ping sound for gas in the rumen
dull ping, no change in pitch.
Ping - location
Ping from hooks to elbow
Lymph node locations
Submandibular, Parotid, Retropharyngeal, Prescapular, Precrural, Supramammary
What gauge and length needle for IM/SQ
14-18 gauge and 1.5 inch
What gauge and length needle for IV
18-20 gauge and 1-1.5 inch