PAS 313 Lecture 12 Peripheral Nervous System
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
PNS
the network of nerves (sensory and motor) that extends from the CNS to the rest of the body, relaying sensory information and controlling bodily functions
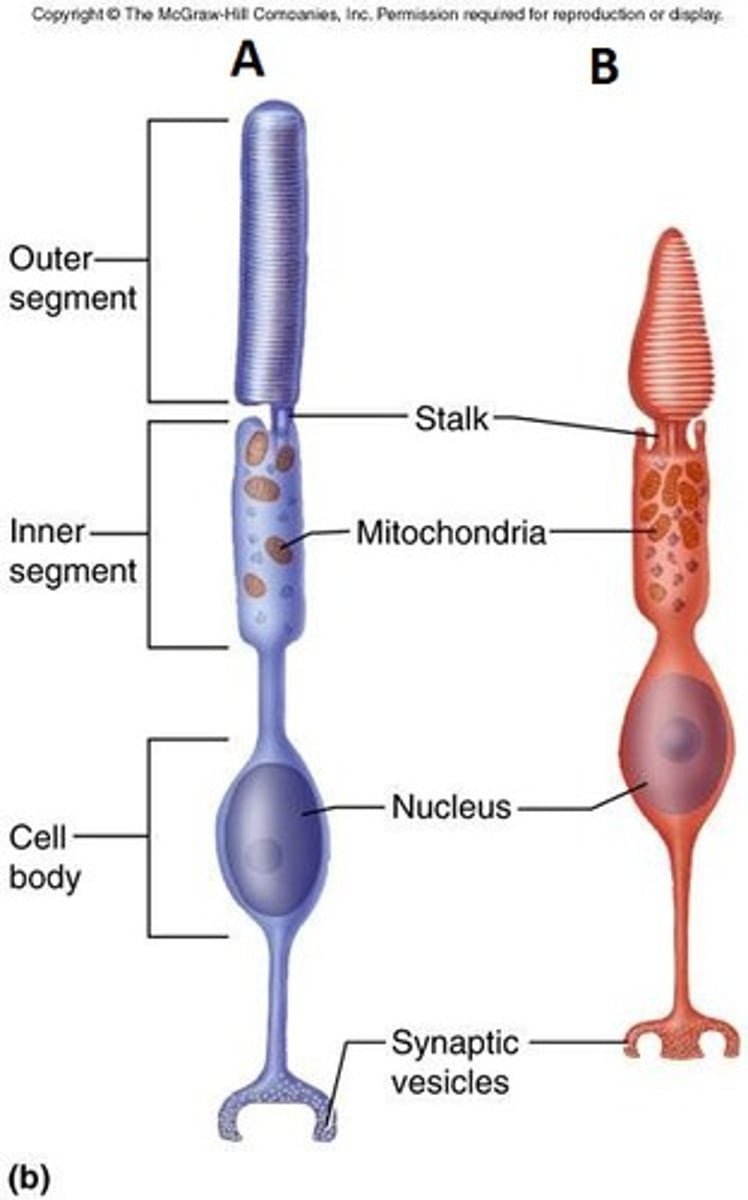
Photoreceptors
Sensory receptor that detects light
Ex: Rods and cones in retina
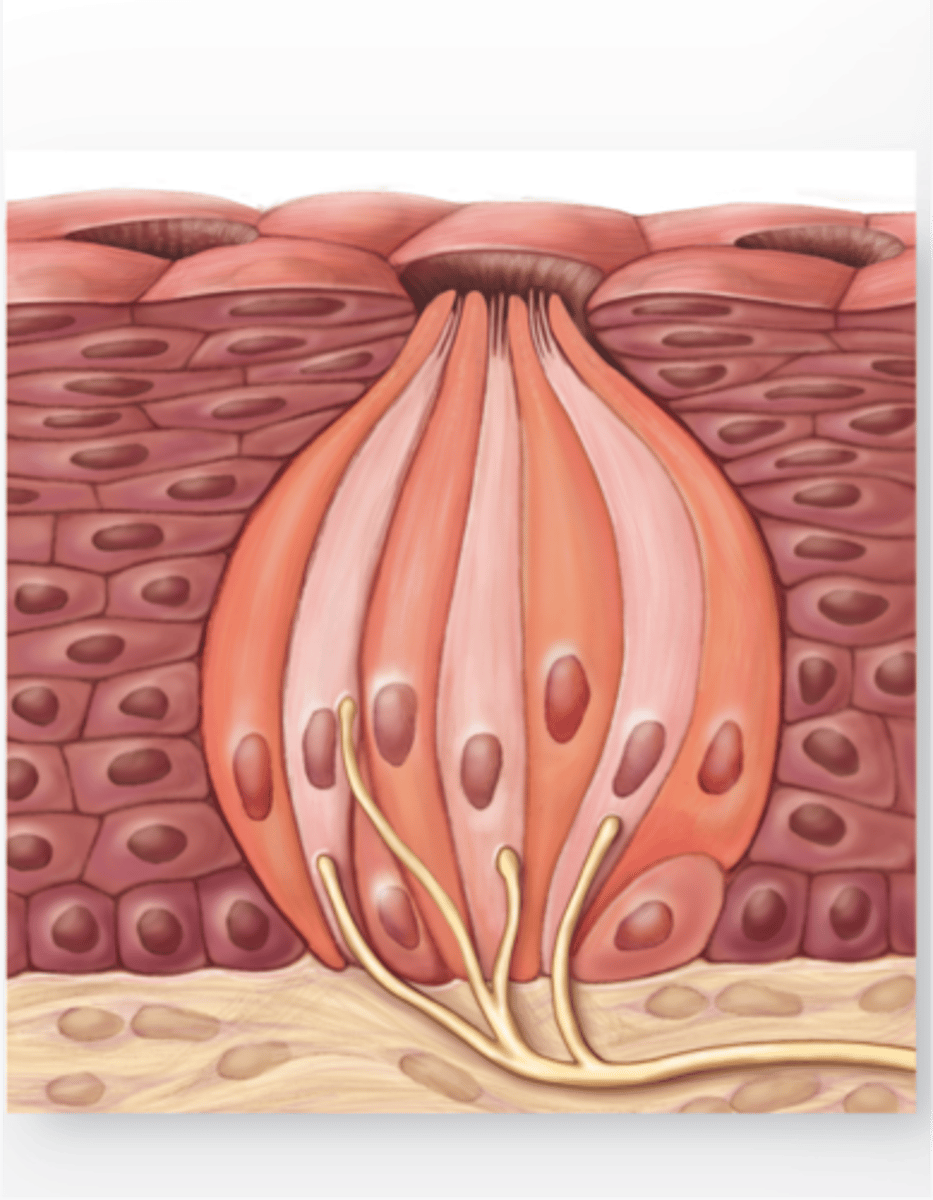
chemoreceptors
Sensory Receptor that responds to chemicals
Examples of chemoreceptors (respond to chemicals)
Olfactory nerve - smell
Taste buds - flavor
Carotid body & sinus - blood CO2 and pressure
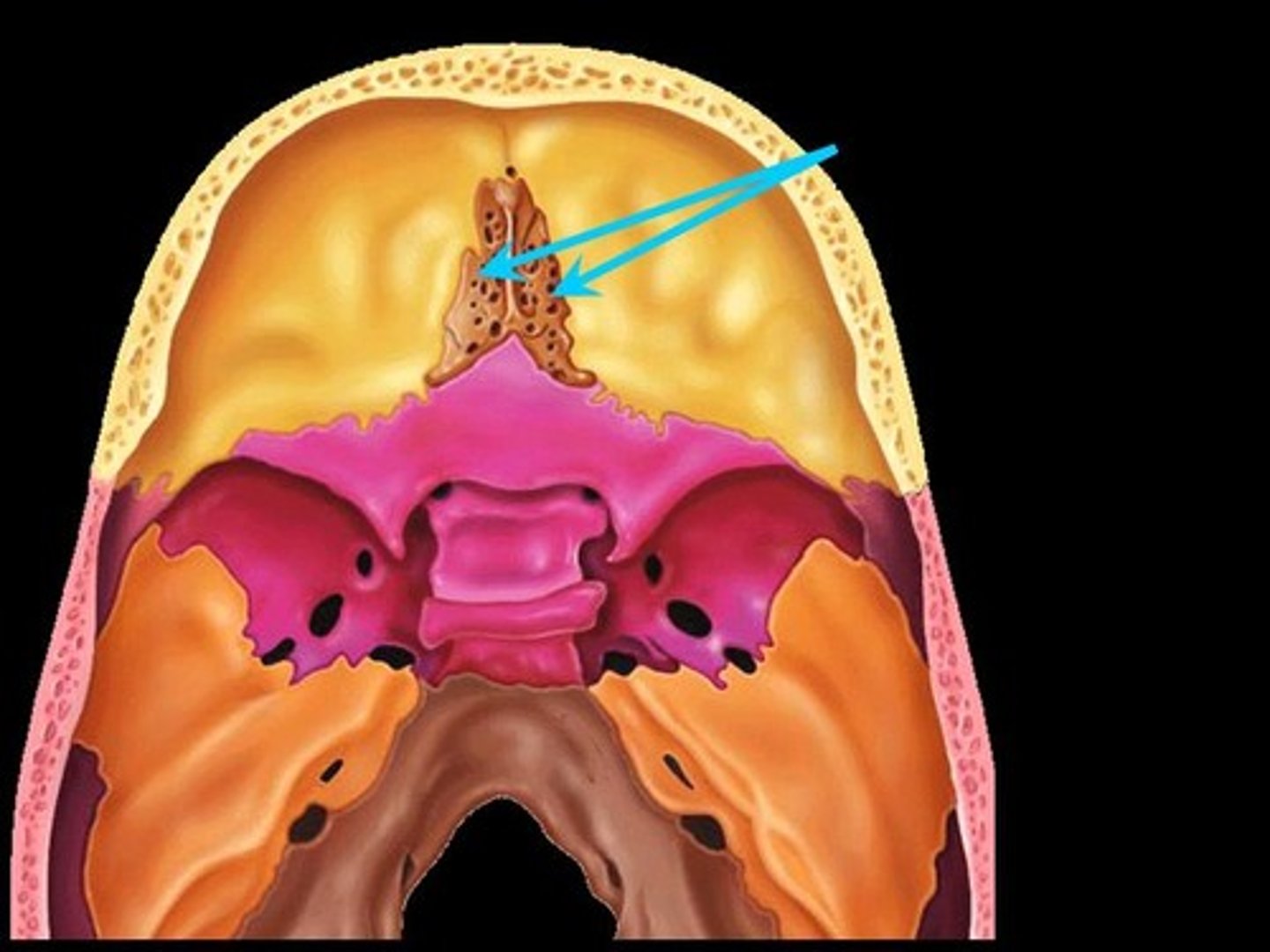
Olfactory nerves
Chemoreceptor that reacts to smell.
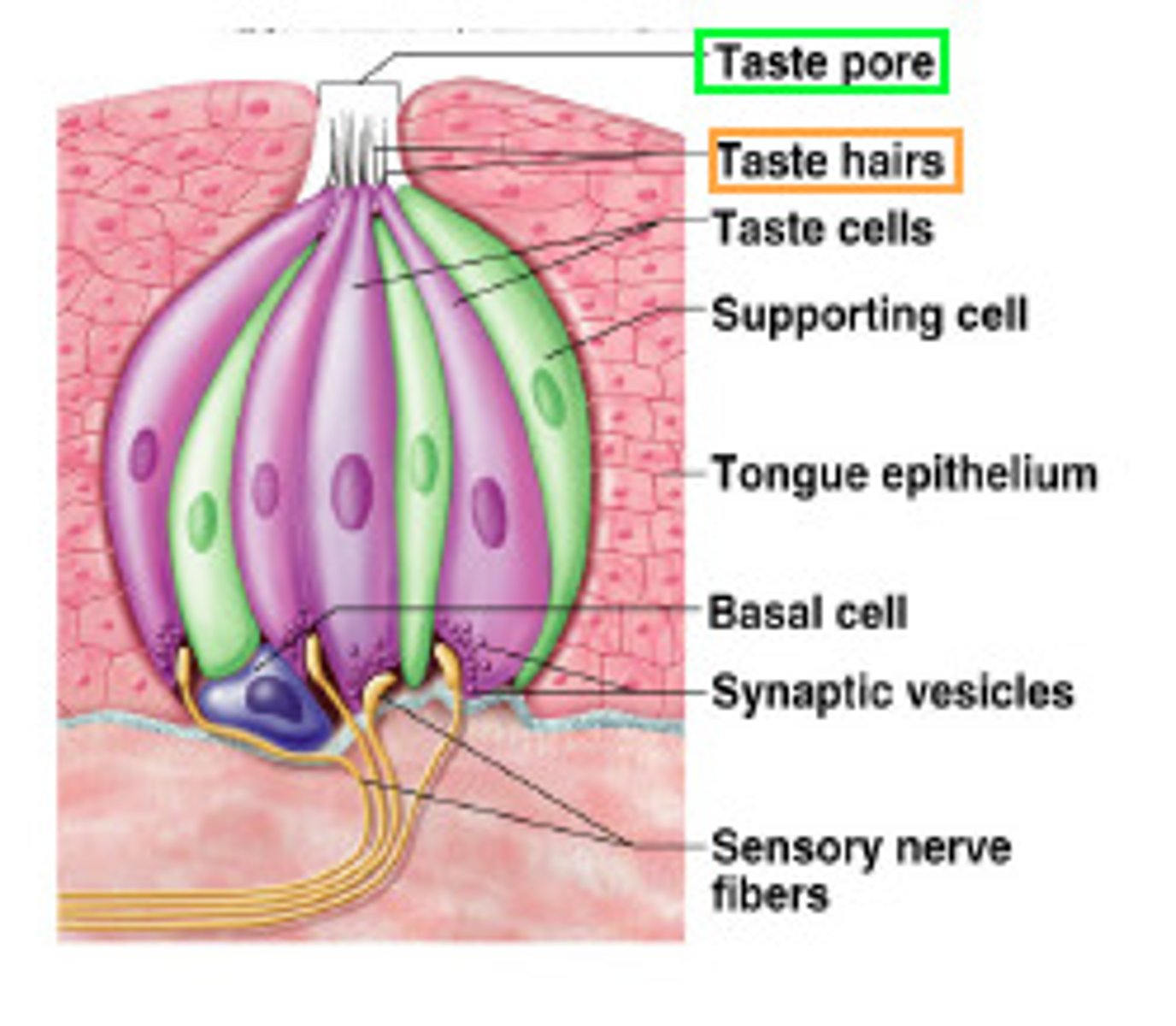
Taste Buds
Chemoreceptor that reacts to tastes
carotid body and sinus
Chemorecptor that reacts to changes in blood carbon dioxide (CO2) levels and blood pressure.
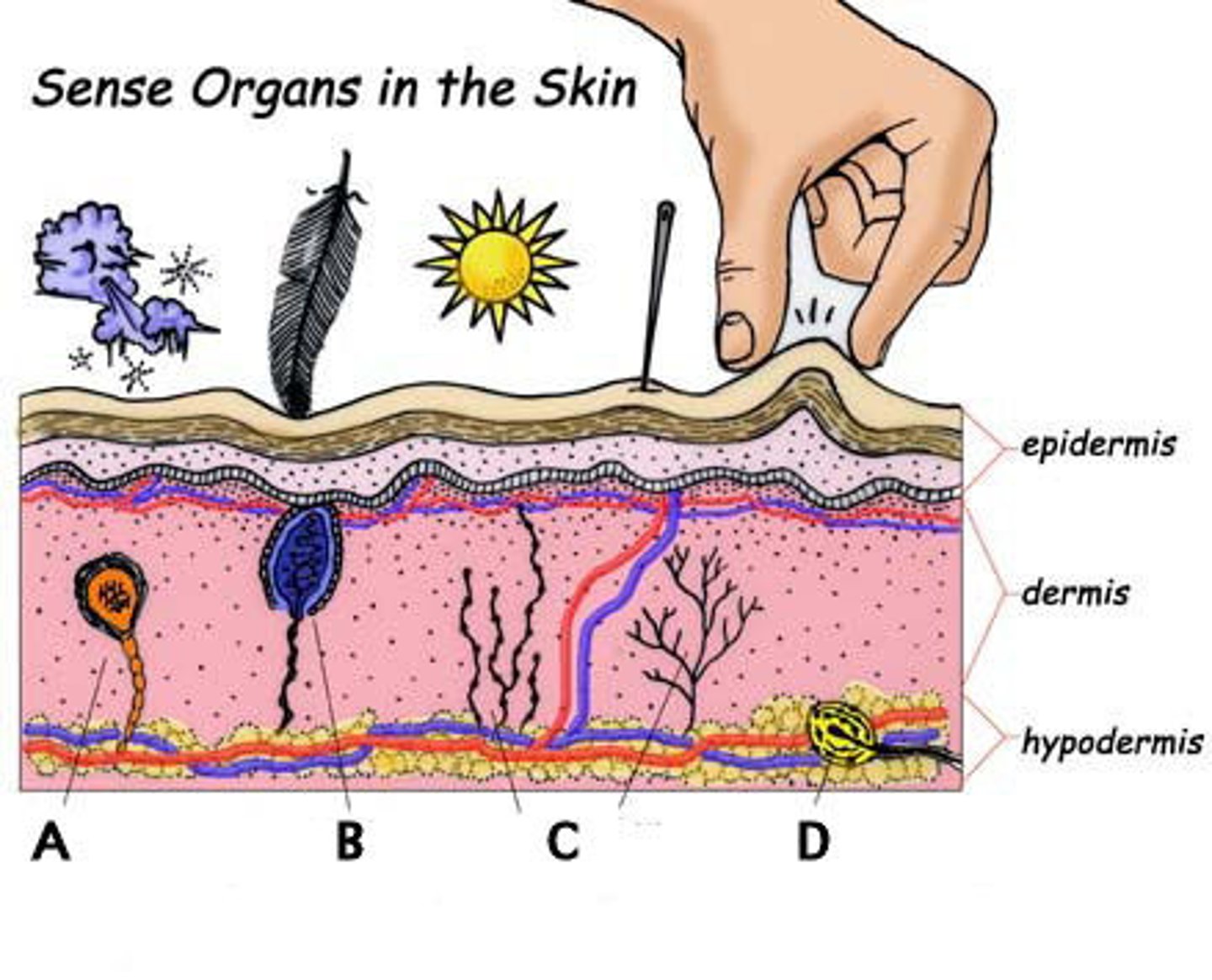
Mechanoreceptor
Sensory Nerve that reacts to touching/pressure
Meissner’s corpuscle and Pacinian corpuscle
Meissner’s corpuscle
Light pressure aka tactile corpuscle
Pacinian corpuscle
Deep pressure aka lamellar corpuscle
Thermoreceptor
Sensory Nerve that reacts to Temperatures, free nerve endings
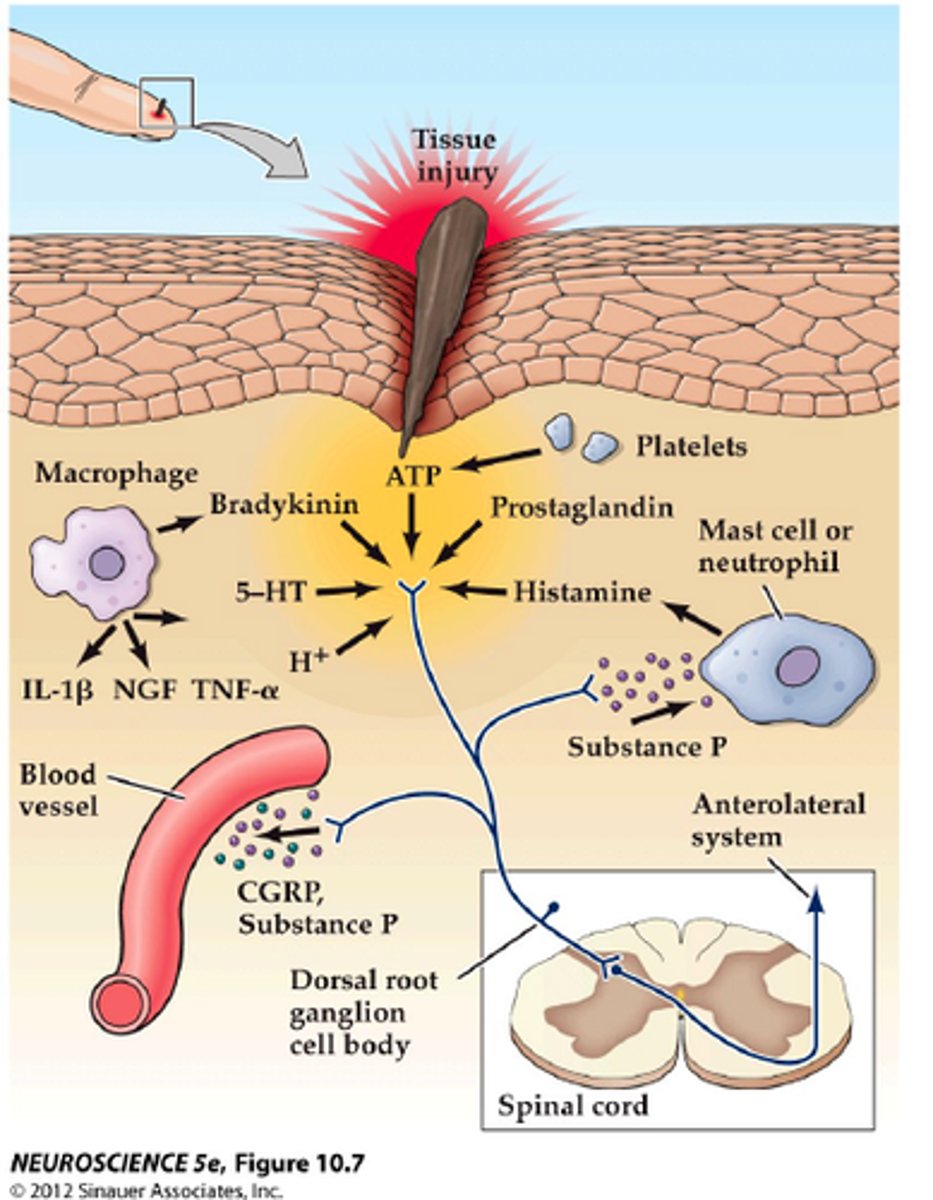
Nociceptors
Sensory Nerve that reacts to pain, free nerve endings
Proprioceptor
Sense of position in space where receptors detects changes is length, tension, and position
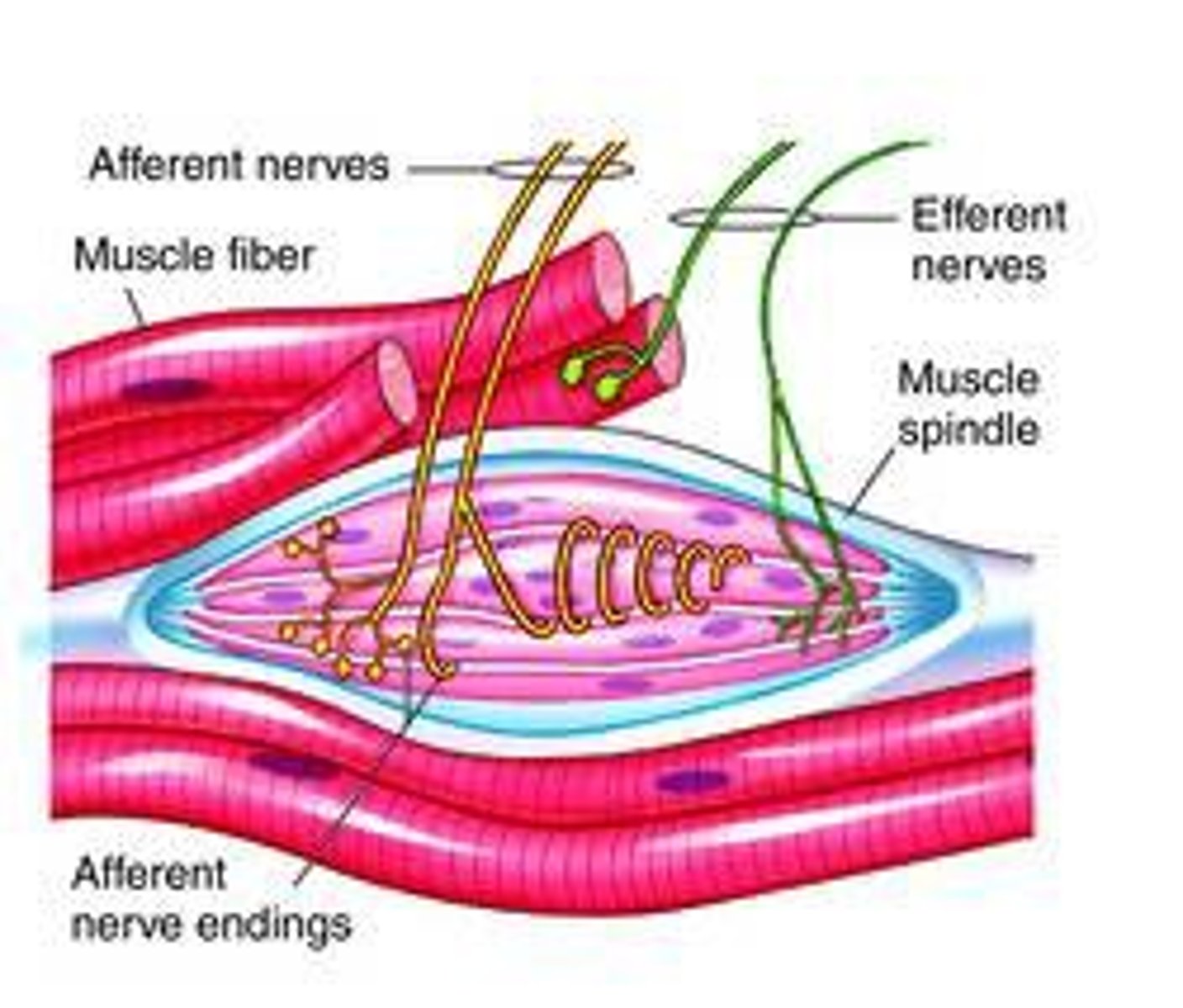
Neuromuscular Spindles
Proprioceptor that reacts to stretching
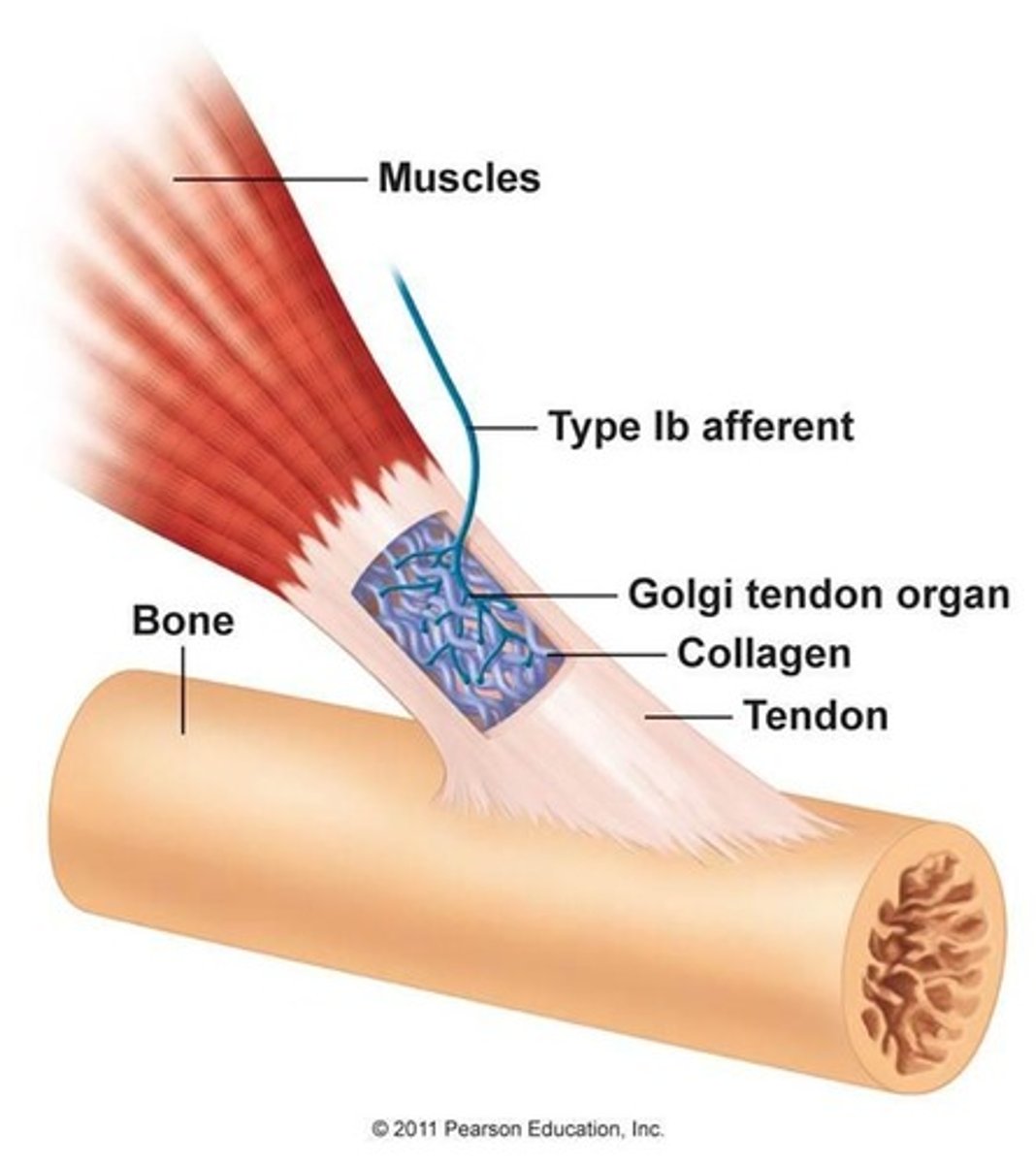
Golgi Tendon
Proprioceptor that reacts to muscle force
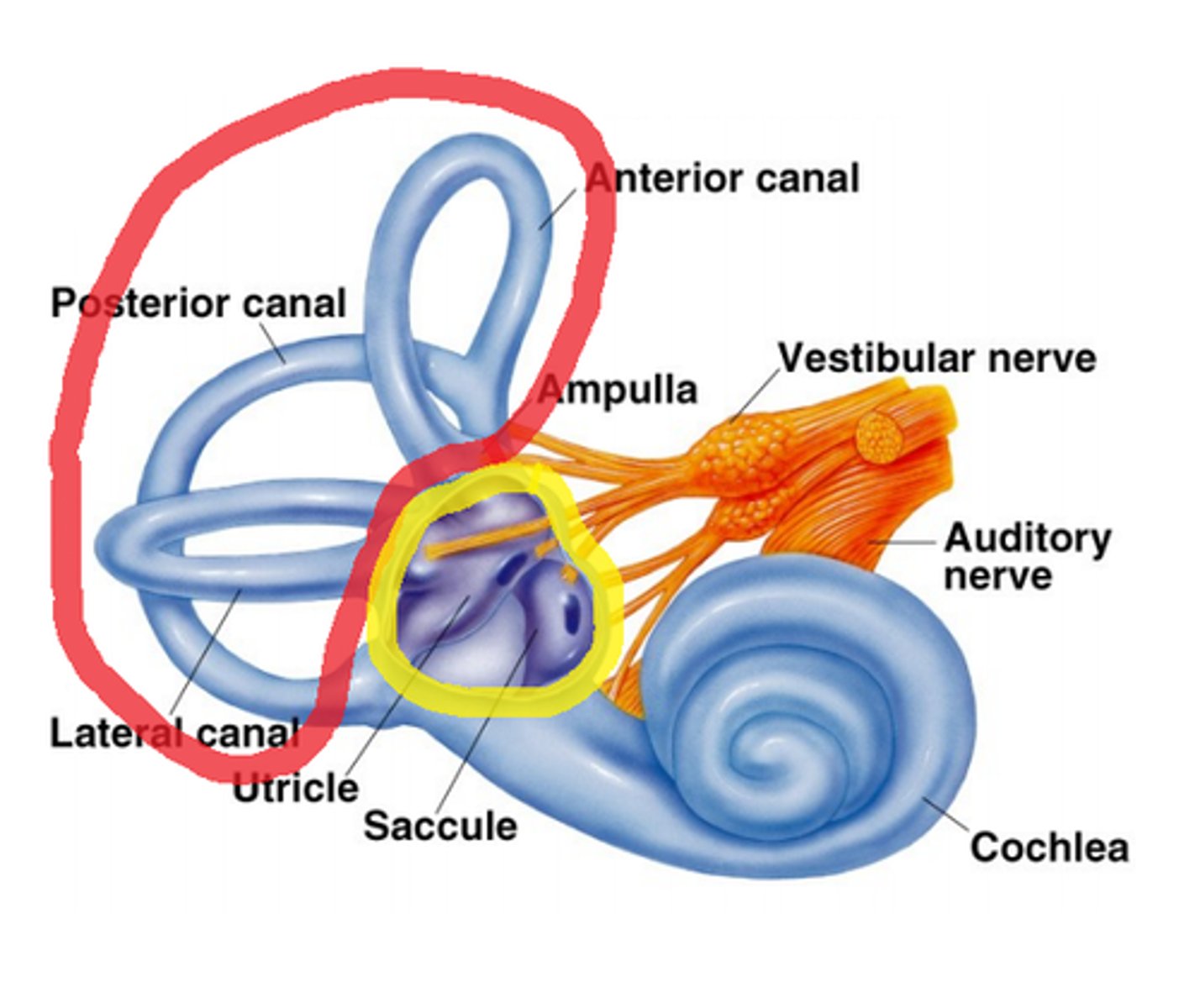
Vestibular System
Proprioceptor that controls Balance
>Inner ear
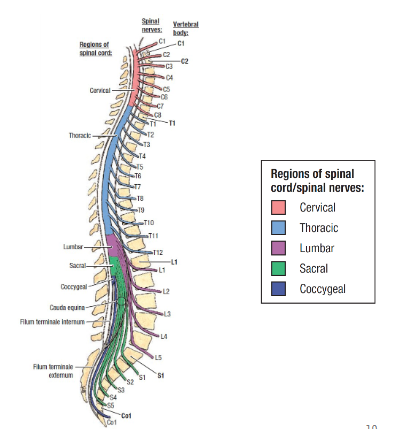
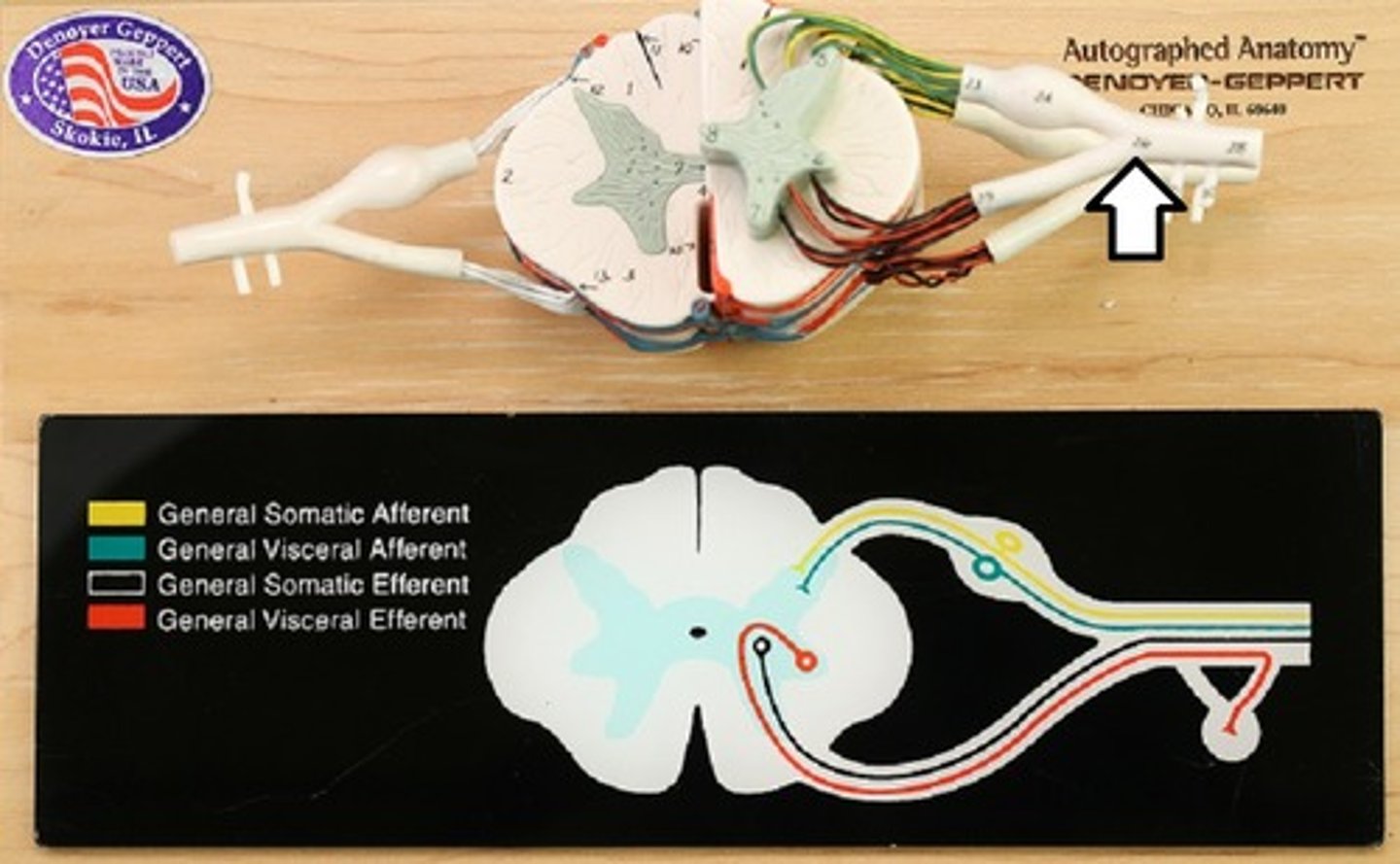
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs
C8, T12, L5, S5, C1
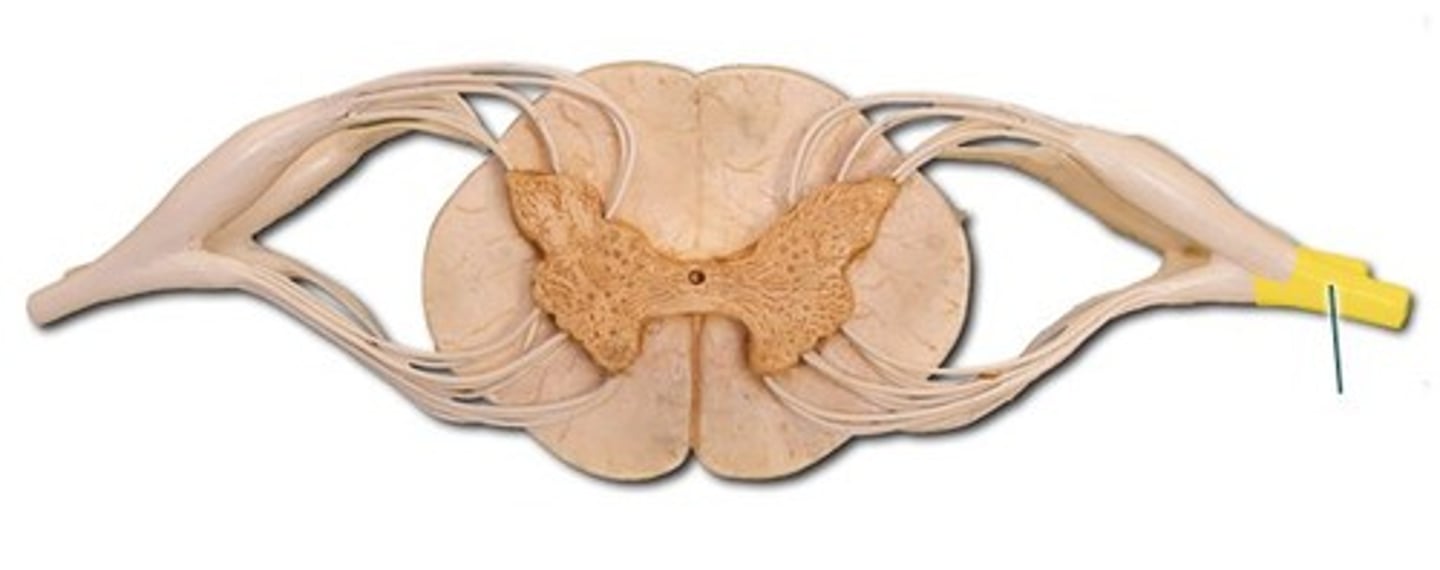
Rami
Sensory and Motor nerves that send impulses to different parts of the body
Dorsal Ramus
spinal nerve that carries both motor and sensory signals to the deep muscles and skin of the back
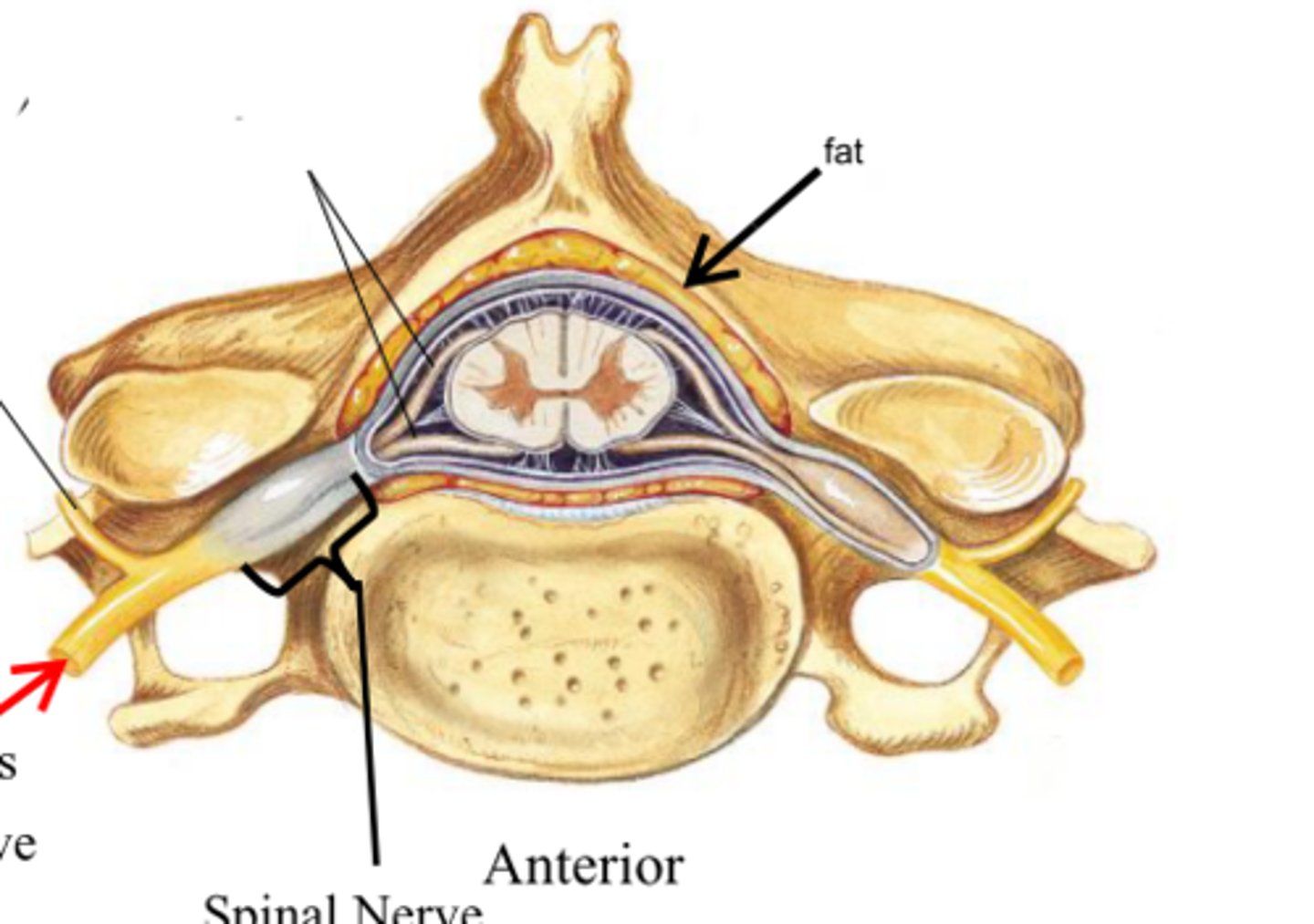
Ventral Ramus
spinal nerve that carries both sensory and motor information to the anterior (front) part of the body
Dermatones
"Map" of sensory innervation of skin
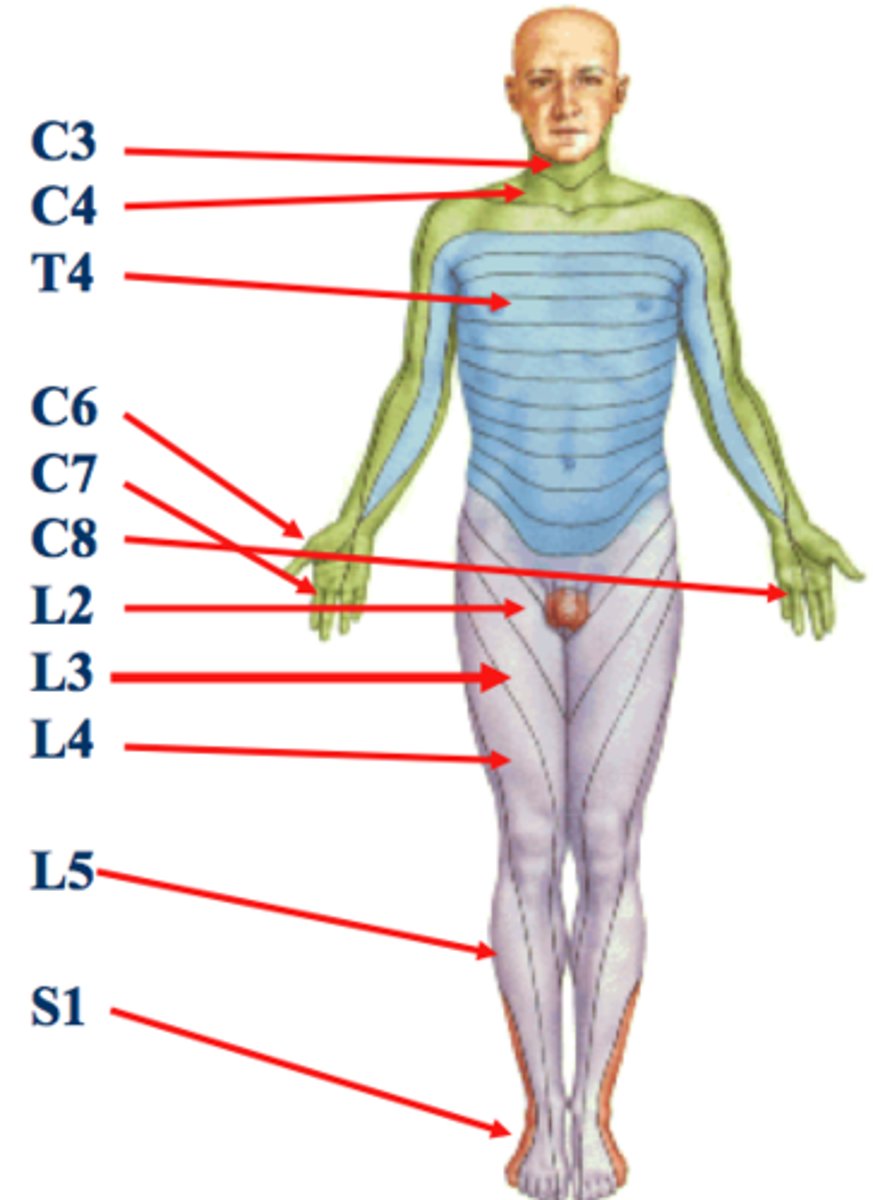
T4 Dermatome
Nipple
T 10 Dermatome
Belly Button
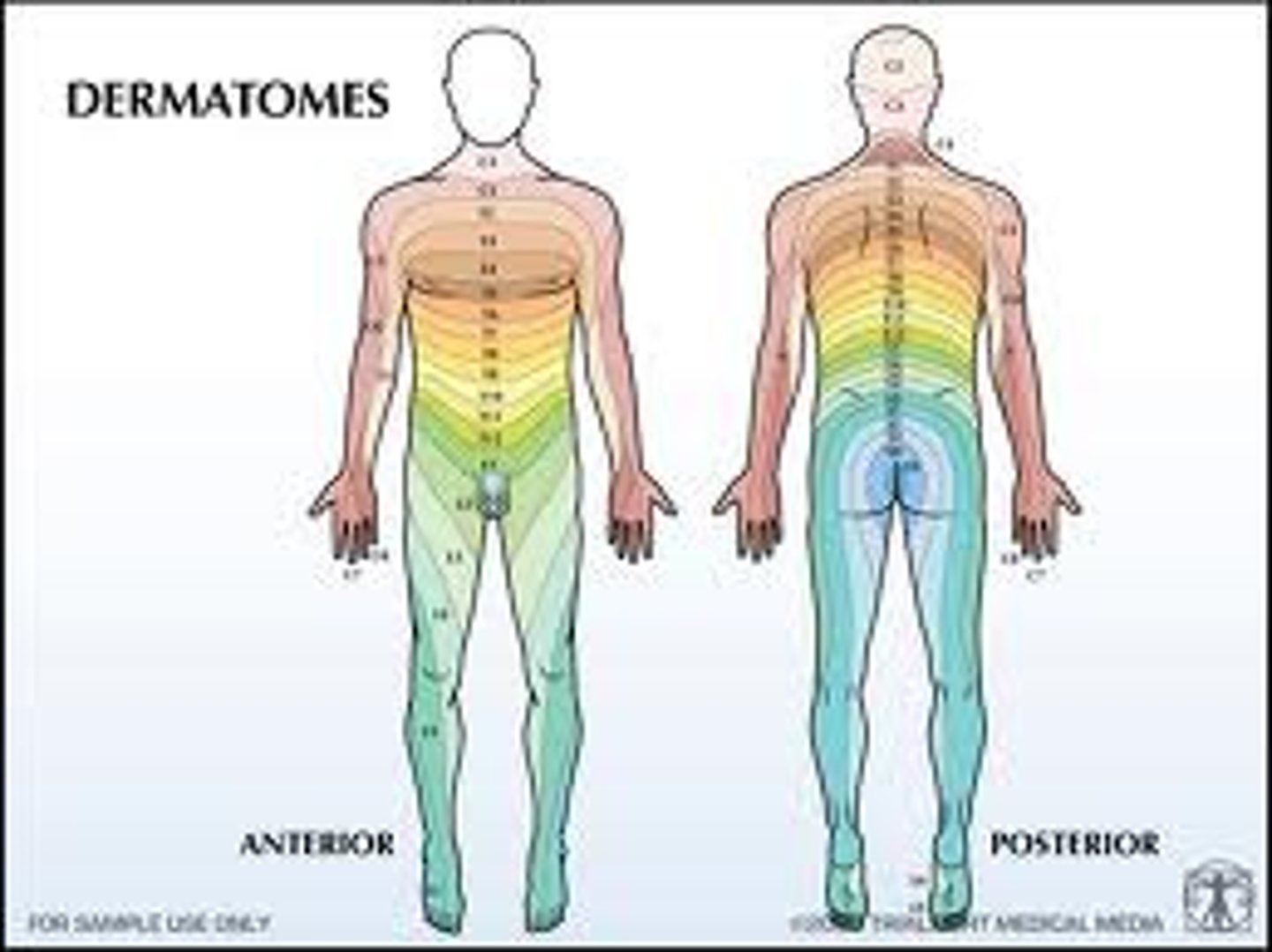
Key factor regarding Dermatomes
Dermatomes overlap above and below
>Ie: if Navel(T10) is affected T9 to T11 are affected

Referred Pain
Pain in organs results in perceived pain somewhere else, generalization of where the pain is not the actual location
Involves visceral (organs) and somatic (skin) sensory
Referred pain examples : Myocardial Ischemia
Poor or no blood supply to cardiac, pain in upper left limb, and pain can radiate to right limb,jaw, and neck
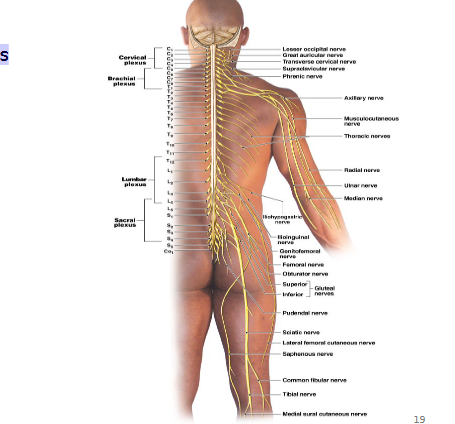
Nervous Plexuses
Both motor and sensory derived from ventral rami that are Intertwined network of nerves
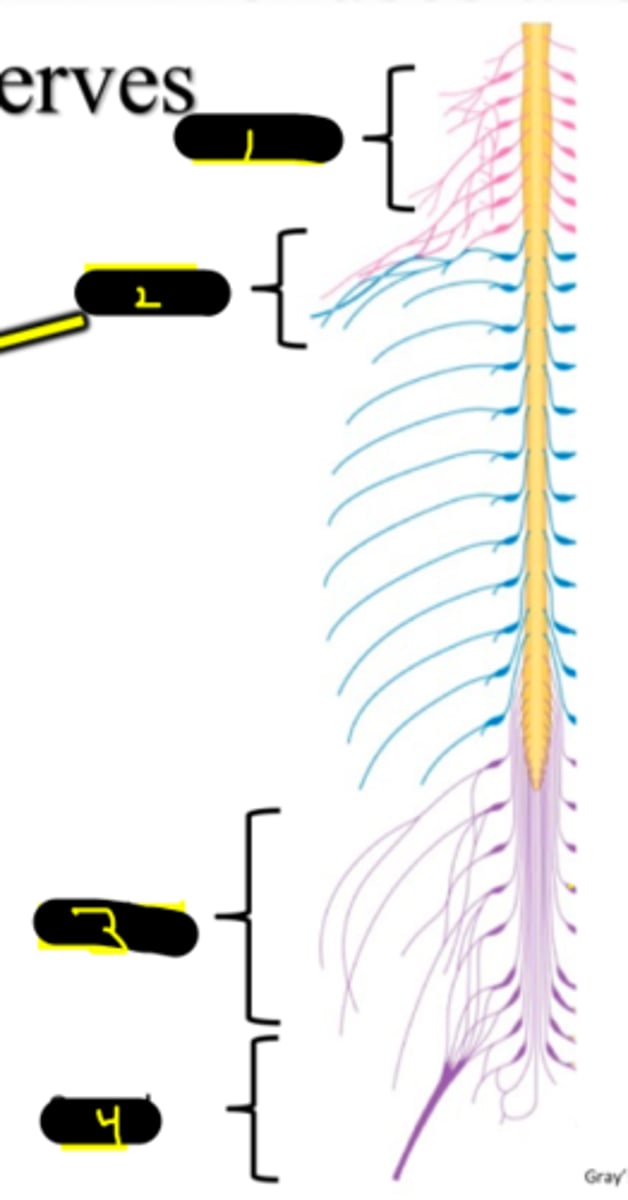
What are the 4 major Plexuses
Cervical, Lumbar, Sacral, Brachial
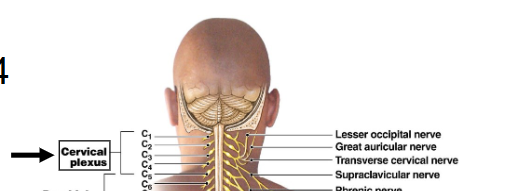
Cervical Plexus
C1 to C4, arises from cervical enlargement, muscles and skin of neck (Ventral Remember)
Cervical Plexus Nerves
Phrenic Nerve C3 to C5
phrenic nerve
Cervical Plexus Nerve that controls the diaphragm from C3, C4, C5
Brachial Plexus
C5-T1
Motor: muscles of shoulder and upper limbs
Sensory: skin of shoulder and upper limb
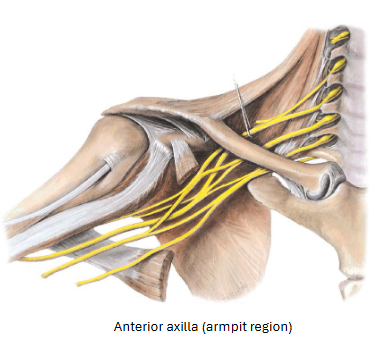
Nerves found in the Brachial Plexus
C5-T1 AMMUR
Axillary
Musculocutaneous
Median
Ulnar
Radial
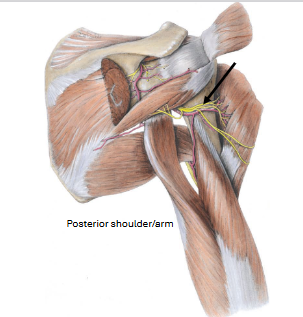
Axillary nerve
Brachial plexus C5-T1
Motor: deltoid muscle
Sensory: skin of shoulder
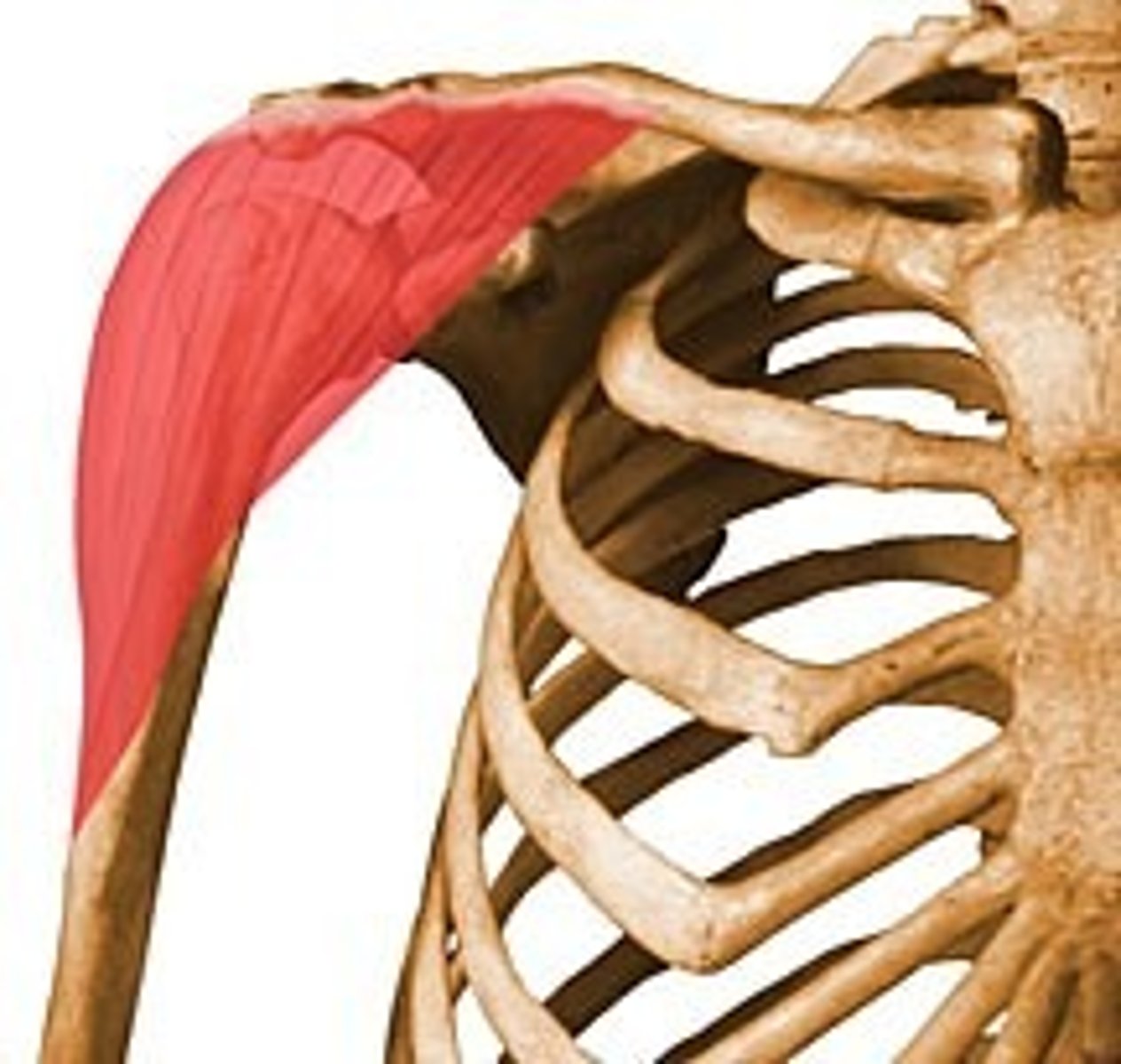
Damage to the Axillary Nerve
Limited arm abduction and loss of shoulder (Brachial Plexus)
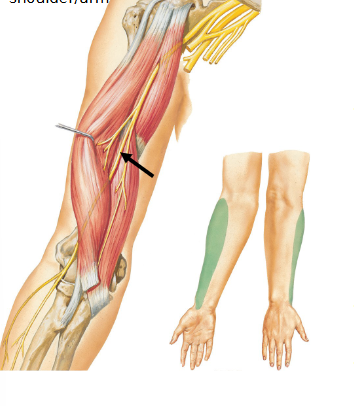
Musculocutaneous Nerve
Brachial plexus
Motor: muscles of anterior arm (biceps brachii and brachialis)
Sensory: lateral skin of forearm
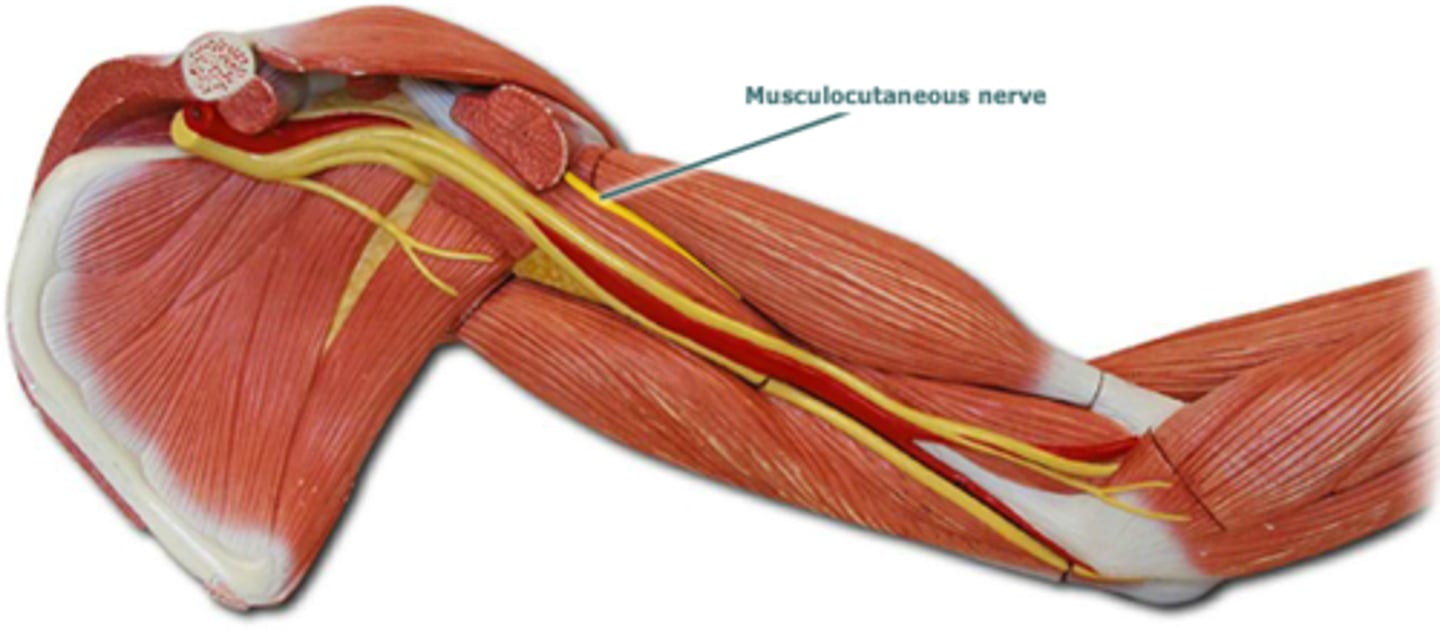
Damage to the Musculocutaneous Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
Reduced arm flexion, forearm supination, and numbness/pain in lateral forearm (Brachial Plexus)
Radial nerve
Brachial plexus C5-T1
Motor: extension of arm, forearm, wrist, and digits (Triceps, extensor carpi muscles, extensor digitorum)
Sensory: portions of posterior, lateral arm, and forearm
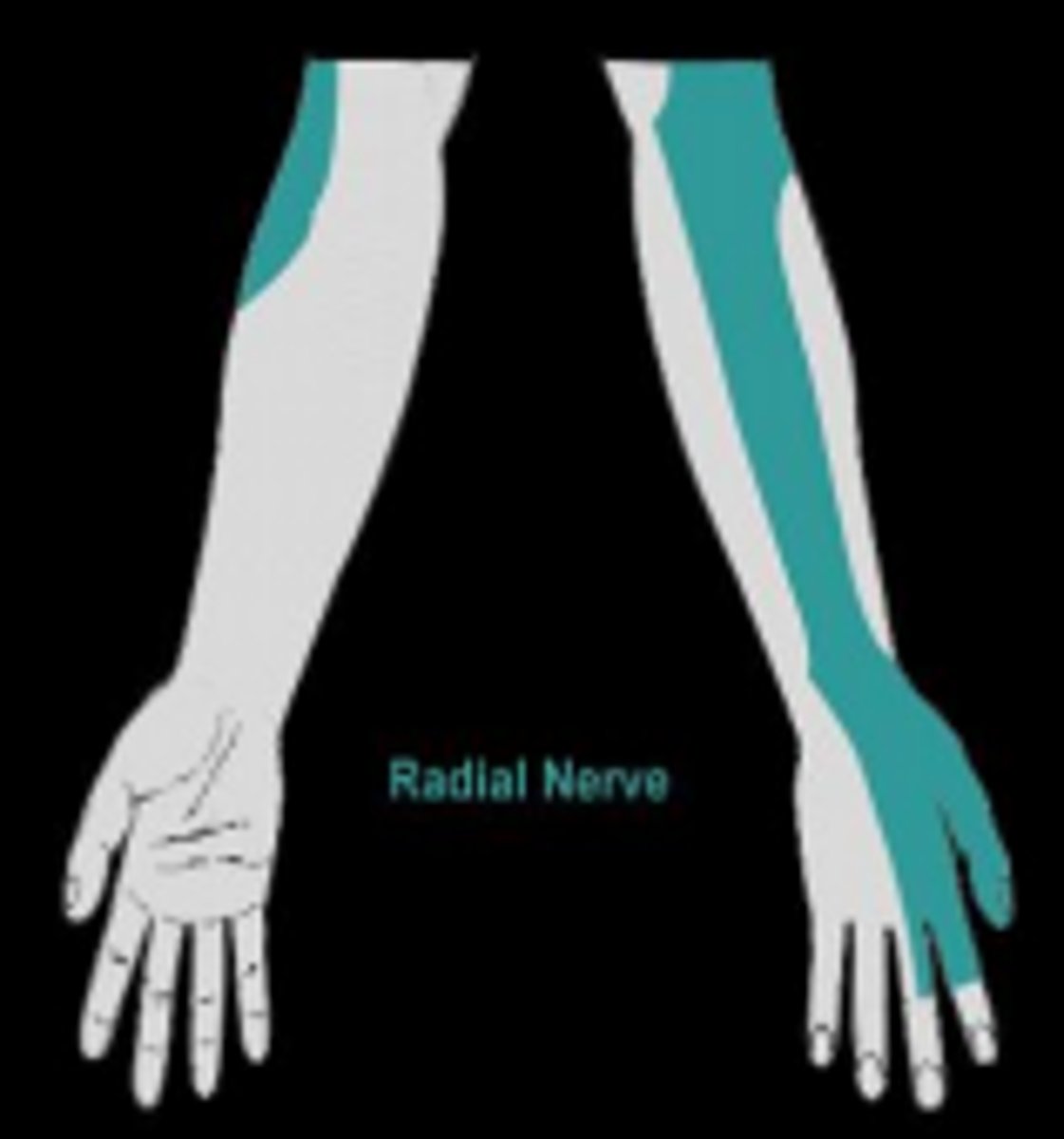
Damage to the Radial Nerve
Inability to do arm, wrist, digit extension, and numbess/pain in posterior arm/forearm (Brachial Plexus)
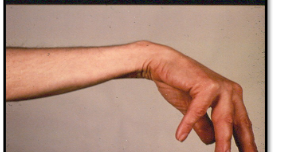
Wrist drop
Radial nerve is damaged so inability to extend wrist
If wrist involuntary drops into flexion = nerve damaged
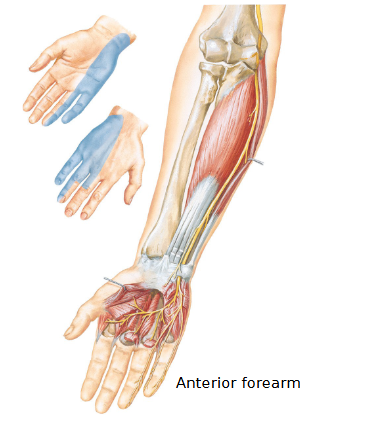
Ulnar nerve
Brachial plexus C5-T1
Motor: Intrinsic hand muscles (flexor carpi ulnaris, part of flexor digitorum profundus, hypothenar muscles, lumbricals III and IV)
Sensory: numbness/pain - medial skin of hand and half of digit IV
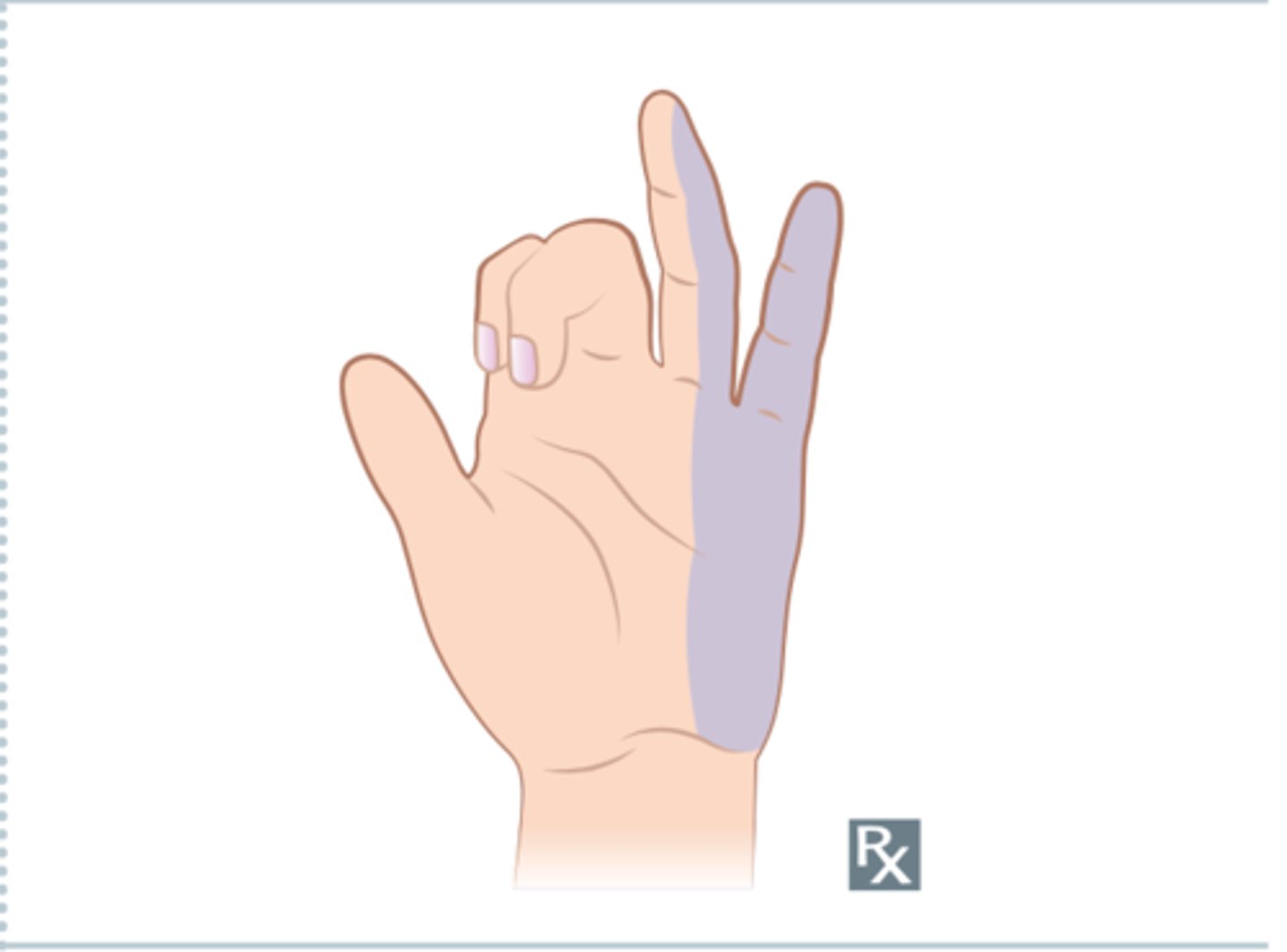
Claw Hand
Severe damage to ulnar nerve where the lumbricals are affected and the extensor digitorum extends the metacarpophalangeal joint
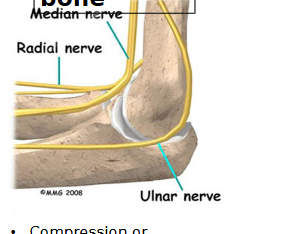
Funny Bone
Compression or damage to ulnar nerve at elbow
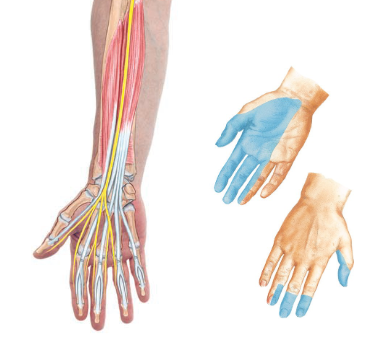
Median Nerve
Brachial plexus C5-T1
Motor: flexors of wrist, thenar muscles, lumbricals 1 and 2
Sensory: numbness/pain, skin of palm and digits, half of digit 4
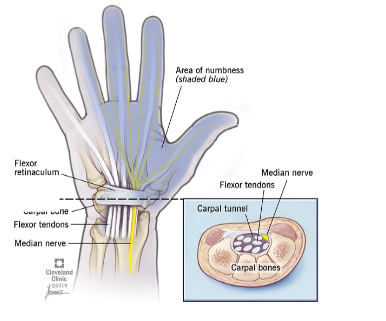
Damage to the Median Nerve
Carpal Tunnel and Ape Hand
> Opposition can't occur (Brachial Plexus)
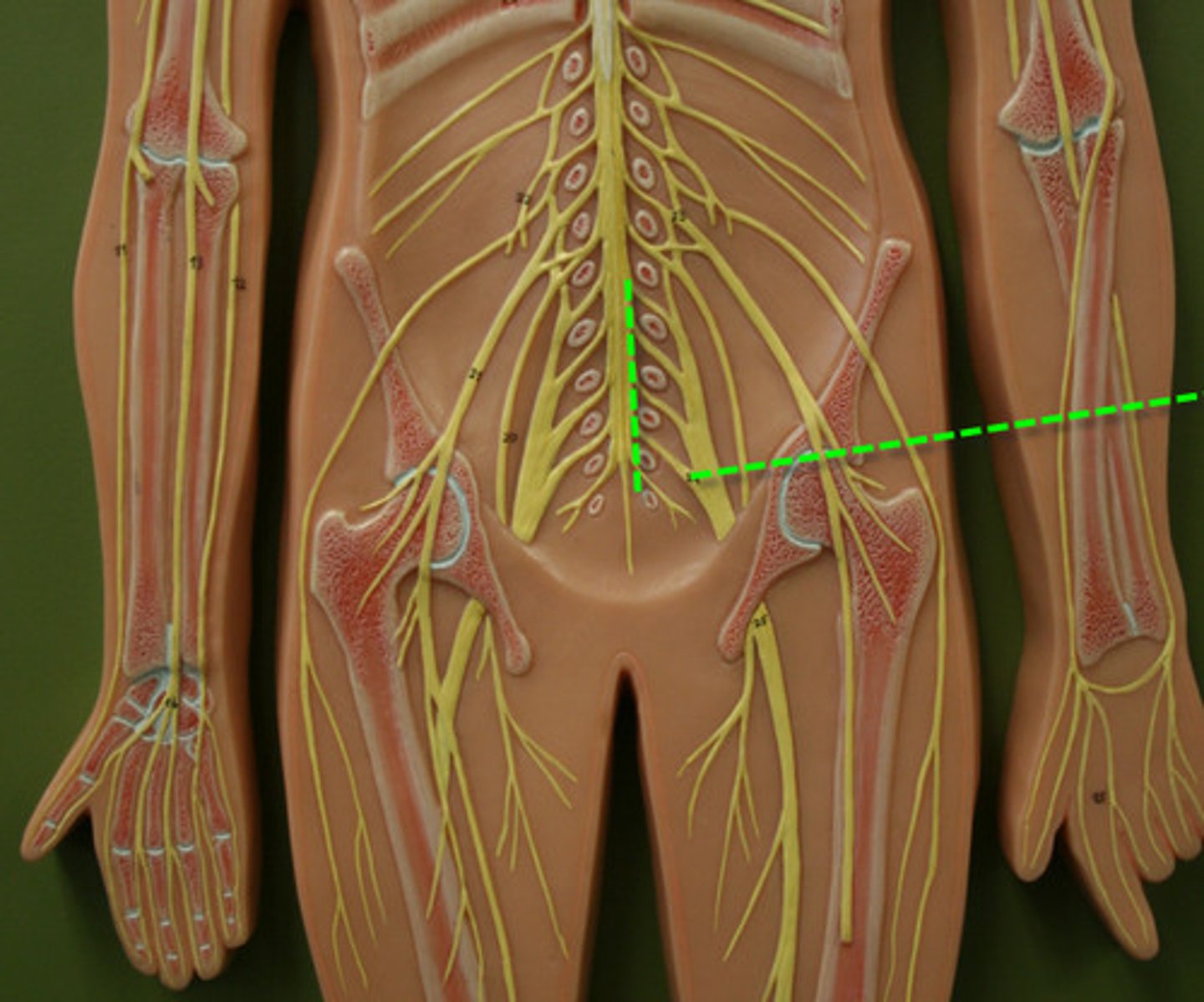
Lumbo-sacral Plexus
L1 to S4, ventral Rami that provides motor and sensory innervation to the lower limbs

Nerves found in Lumbo-sacral Plexus
Femoral Nerve
Obturator nerve
Sciatic nerve
Tibial Nerve
Common Fibular Nerve
Pudendal Nerve
(Find Our Silly Tiny Cat Paws)
Lumbo-sacral Plexus Mnemonic
Find Our Silly Tiny Cat Paws

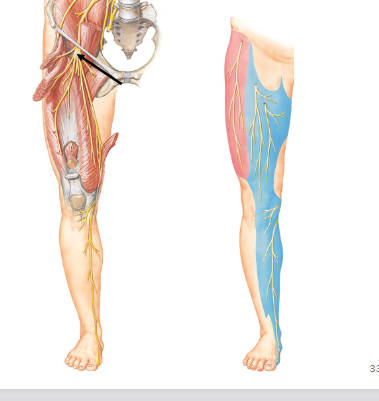
Femoral nerve
Lumbosacral plexus L1-S4
Motor: quadriceps
Sensory: skin of anterior thigh and leg
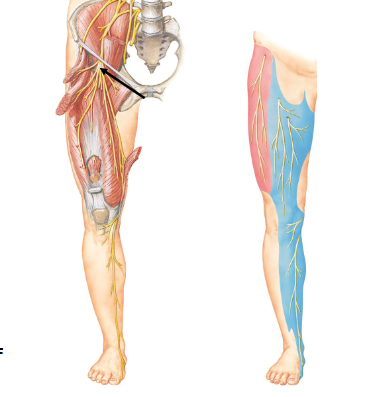
Damage to the Femoral Nerve
Inability to extend knee and numbness/pain in skin of anterior lower leg Lumbo-Sacral)
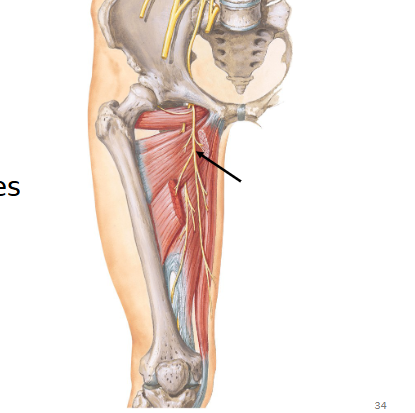
Obturator nerve
Lumbosacral plexus
Motor: adductor muscles
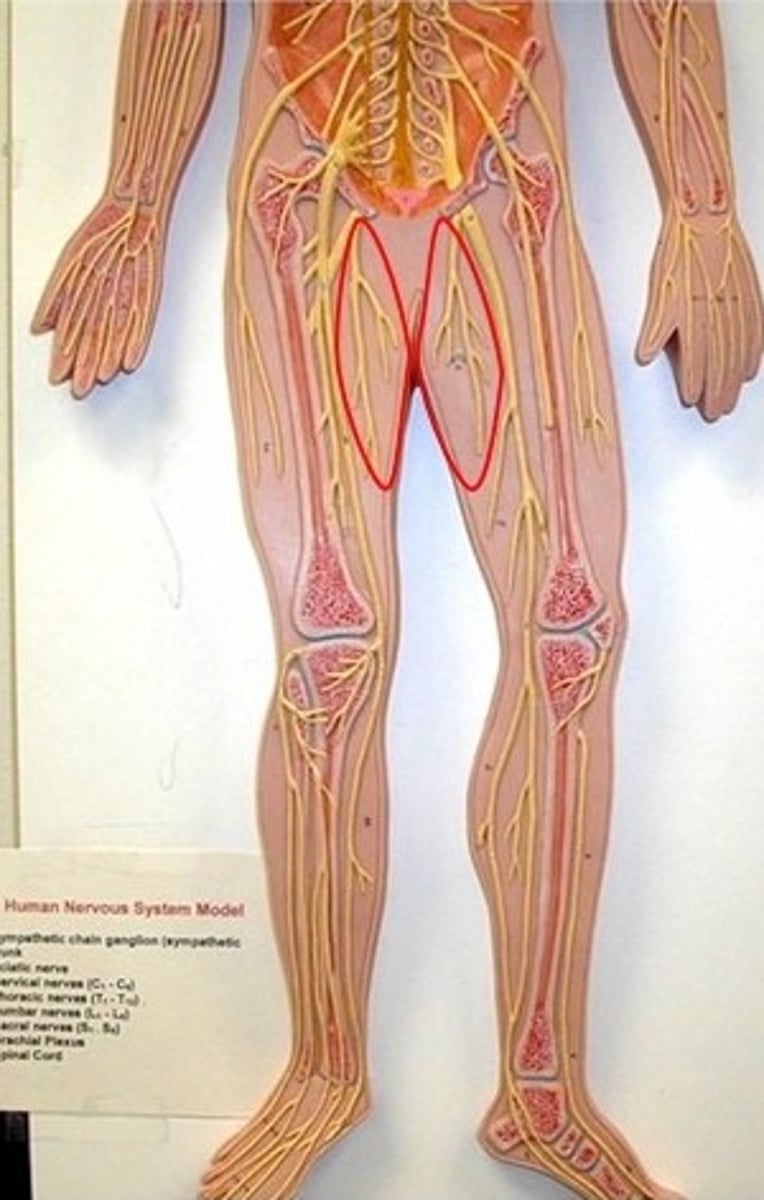
Damage to the Obturator Nerve
Inability to adduct thigh (Lumbo-Sacral)
Sciatic nerve
Lumbosacral plexus
Motor: hamstring
Sensory: posterior thigh
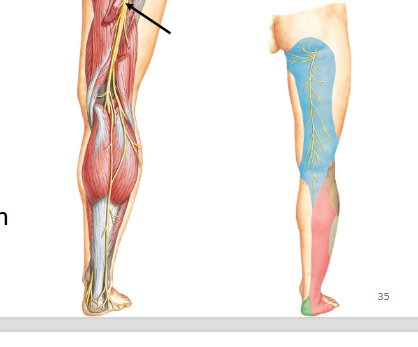
Damage to the Sciatic Nerve
Weakened thigh extension and inability to flex leg (Lumbo-Sacral)
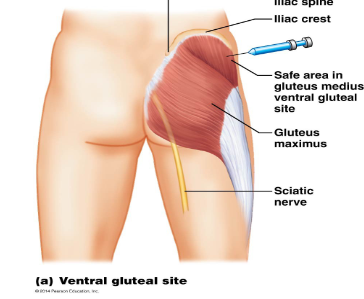
Gluteal injection
Able to inject in b/c not many nerves to damage and avoids sciatic nerve
Sciatica
Pain resulting from a pinched or compressed sciatic nerve
Results in: Posterior lower limb pain/numbness and possible weakness of posterior lower limb muscles
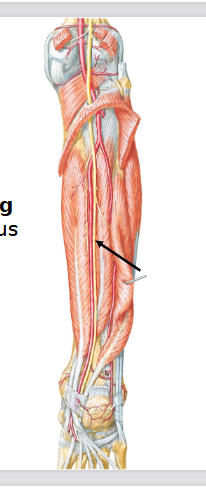
Tibial Nerve
Lumbosacral plexus L1-S4
Motor: all posterior leg muscles (gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis, flexor hallucis longus)
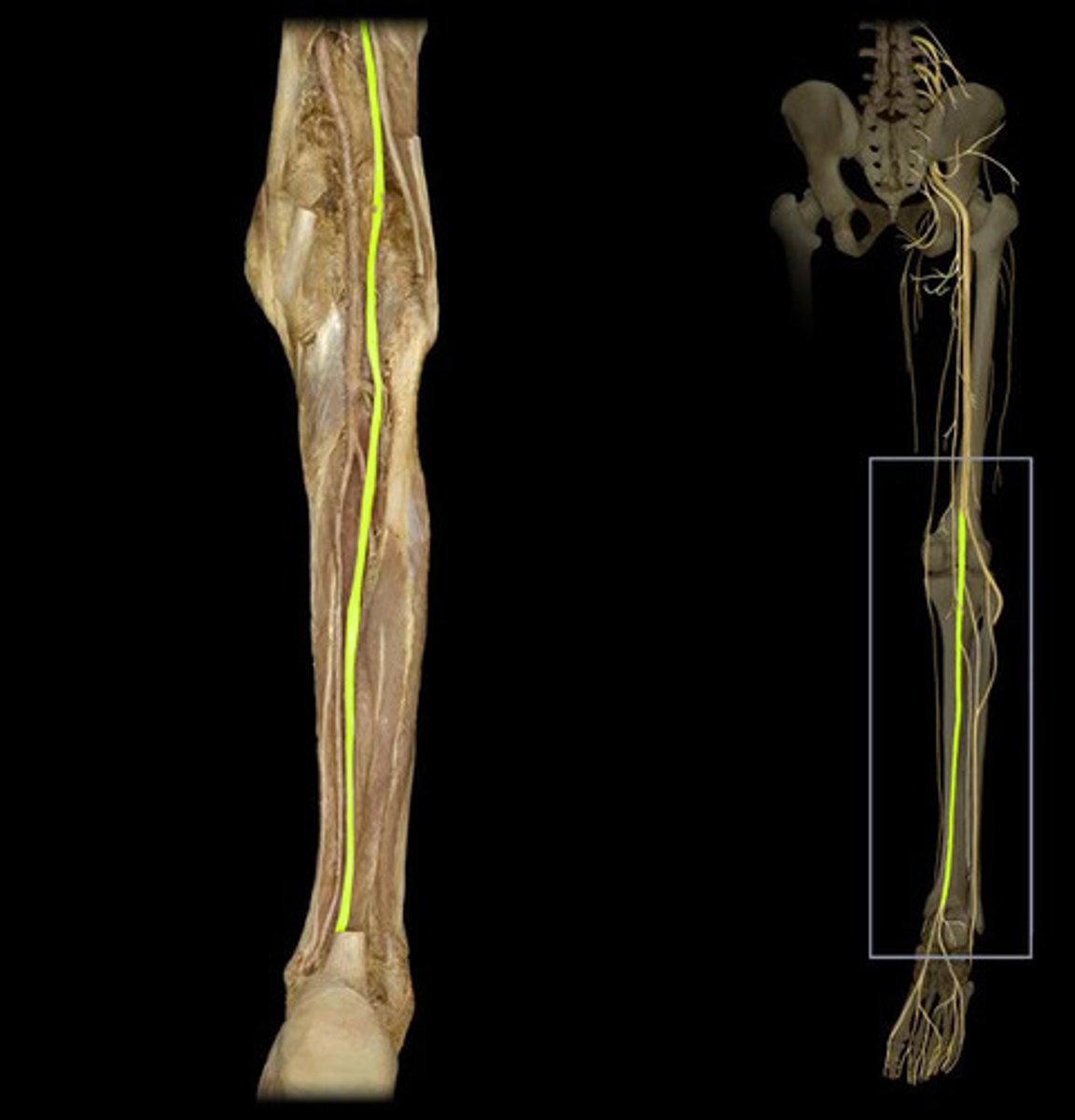
Damage to the Tibial Nerve
Reduced ability to plantarflex, flex digits, or inverts (Lumbo-Sacral)
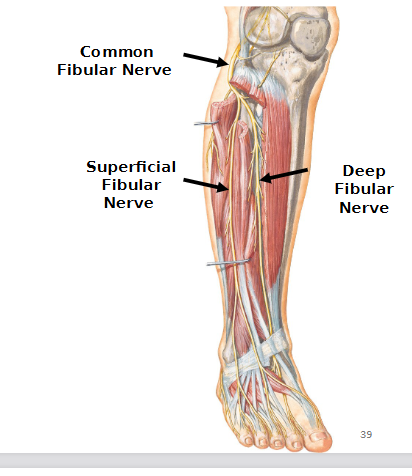
Common fibular nerve
Lumbosacral trunk and two branches: deep fibular nerve and superficial fibular nerve
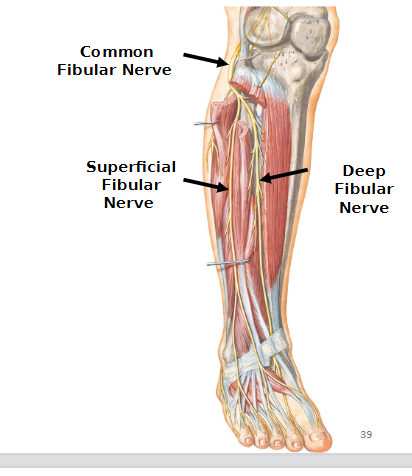
Deep Fibular nerve
Lumbosacral trunk
Motor: muscles of anterior leg
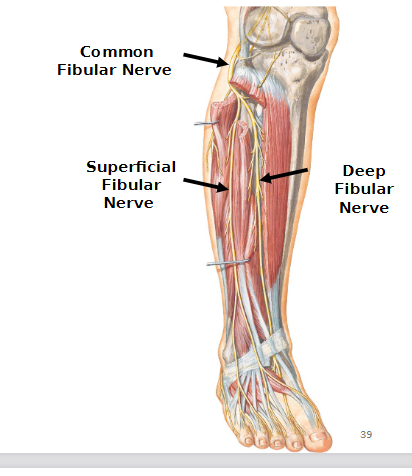
Superficial fibular nerve
Lumbosacral trunk
Motor: muscles of lateral leg
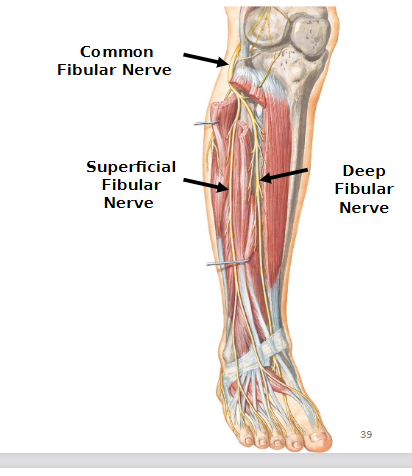
Damage to the Deep Common-Fibular nerve
Reduced or absent dorsiflexion, digit flexion, inversion (Lumbo-Sacral)
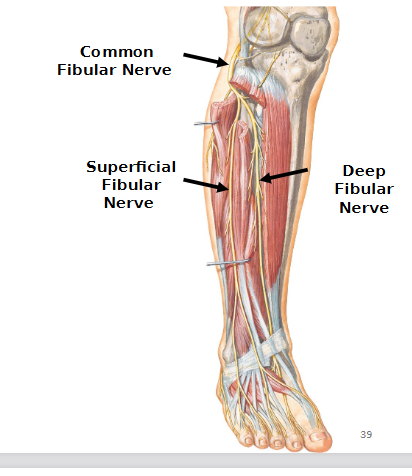
Damage to the Superficial Common-Fibular nerve
Eversion (Lumbo-Sacral)
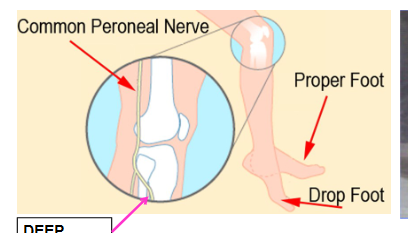
Foot drop
Damage to the Deep common fibular nerve causes an inability to dorsiflex, the foot automatically falls into plantarflexion
Pudendal Nerve
Lumbosacral plexus L1-S4
Motor and Sensory: pelvic floor/diaphragm
Damage to the Pudendal nerve
Incontinence and prolapse (Lumbo-Sacral)
Pudendal Nerve Block
a medical procedure that involves injecting a local anesthetic near the pudendal nerve to temporarily relieve pain in the genital, rectal, and pelvic areas