Amines
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What amines?
derivatives of ammonia, in which one or more of the hydrogens is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group
What is the basis of classifying amines?
the number of substituted hydrogens
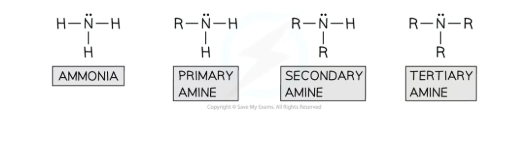
What is an aliphatic amine?
when the R group is an alkyl group
What is an aromatic amine?
when the R group is an aryl group
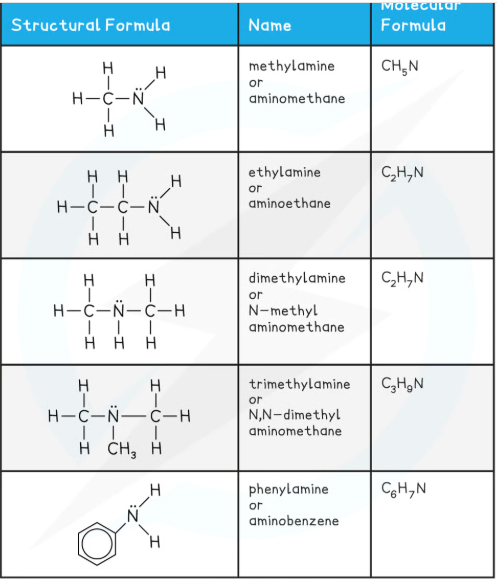
What is the common way to name amines?
to use alkyl (or aryl) prefix followed by -amine
the prefix amino- followed by the alkane or aromatic stem
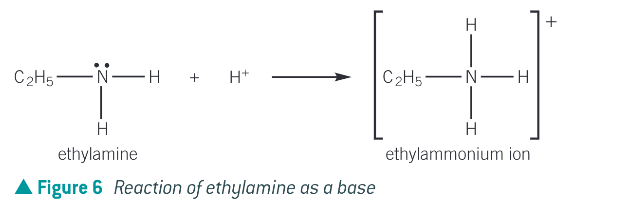
what are the basic properties of amines (hehe double meaning there)
the nitrogen atom in ammonia and amine molecules can accept a proton (H+), therefore they can act as bases in aq solutions by donating their lone pair of electrons to a proton and form a dative bond
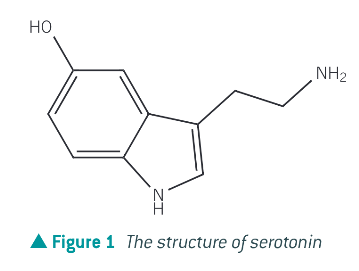
What is an amine that occurs in nature?
serotonin acts as a neurotransmitter, responsible for the control of appetite, sleep, memory and learning, temperature regulation, muscle contraction and depression
What is pseudoephedrine?
an active ingredient in decongestion medications such as in nose drops and in cold remedies. Works by shrinking nasal membranes and inhibiting nasal secretions
How do you name a primary amine which contains an amine group on any other carbon but carbon-1?
where a primary amine contains an amine group, on any other carbon but carbon-1, the amine is named using the prefix amino- and a number is added to indicate the position of the amine group along that chain
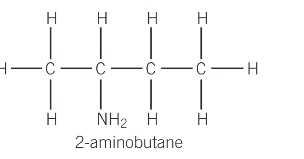
What happens when two or more different groups are attached to a nitrogen atom?
The compound is named as a N-substituted derivative of the larger group
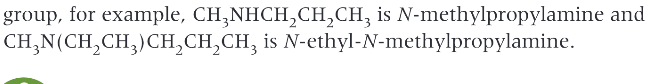
What do amines produce when they neutralise acids?
salts
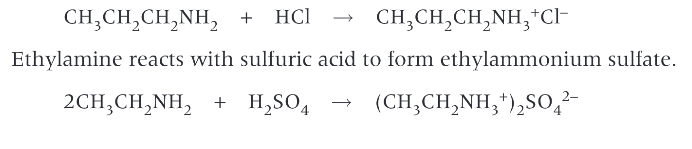
can amines undergo substitution reactions?
yes
How do you prepare primary amines?
ammonia has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom which allows ammonia to act as a nucleophile in a substitution reaction with a haloalkane. The product of this reaction is an ammonium salt, aq alkali is then added to generate the amine from the salt.
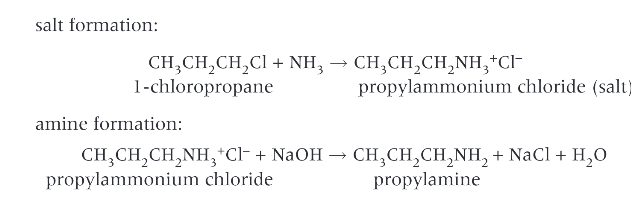
What are the conditions for the formation of primary amines?
ethanol is used as the solvent. This prevents any substitution of the haloalkane by water to produce alcohols
excess ammonia is used. This reduces further substitution of the amine group to form secondary and tertiary amines
Does nucleophilic substitution of amines make a pure primary amine?
no the product still contains a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom that can react further with a haloalkane to form a secondary amine. The product is an ammonium salt.

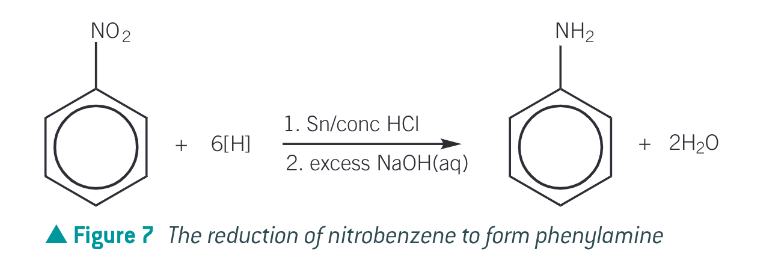
How do you prepare aromatic amines?
Phenylamine is made by the reduction of nitrobenzene. nitrobenzene is heated under reflux with tin and hydrochloric acid to form the ammonium salt, phenylammonium chloride chloride, which is then reaction with excess sodium hydroxide to produce the aromatic amine, phenylamine. Tin and hydrochloric acid act as a reducing agent
What is an amino acid?
an organic compound containing both amine, NH2 and carboxylic acid (COOH) functional groups
How many common amino acids are there in the body?
20
How do amino acids differ?
the R group
What is the general formula of α - amino acids?
RCH(NH2)COOH
What is a 𝛽-carbon and Y-carbon (gamma carbon) amino acid?
in 𝛽-carbon the amine group is connected to the third carbon and in Y - carbon the amine group is connected to the fourth carbon
What do amino acids react similarly to and why?
carboxylic acids and amines because they have similar reactions to them both
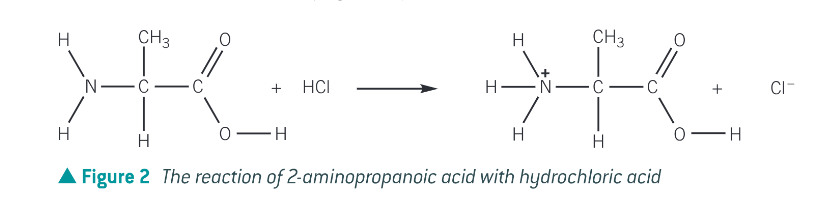
Reactions of the amine group of amino acids?
the amine group is basic and reacts with acids to make salts. As such amino acids will also react with acids to form salts.
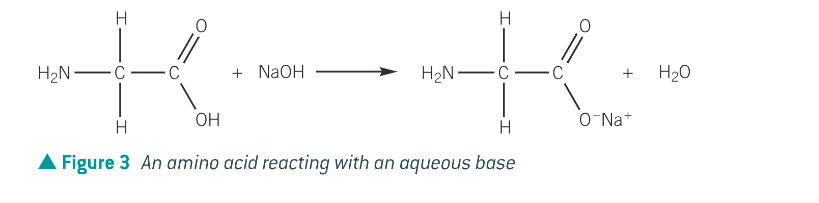
What happens when an amino acids reacts with aq alkali such as sodium or potassium hydroxide?
it forms a salt and water
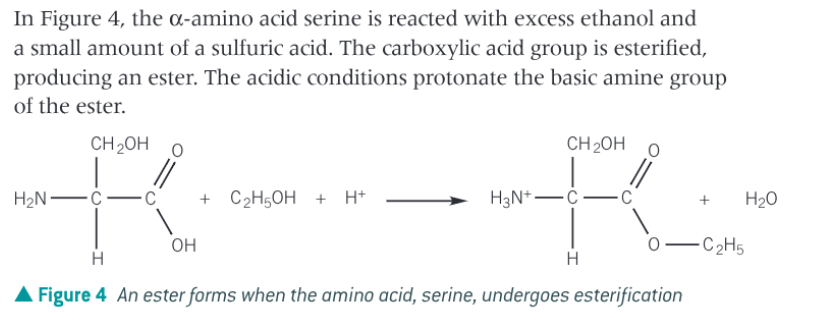
What is the esterification reaction of amino acids?
amino acids are heated with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid
What are amides?
the products of reactions of acyl chlorides with ammonia
What are primary amides?
one carbon atom bonded to N
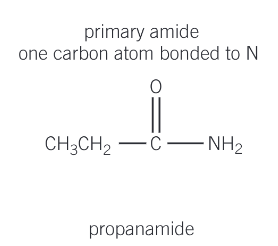
What are secondary amides?
Two carbon atoms bonded to N
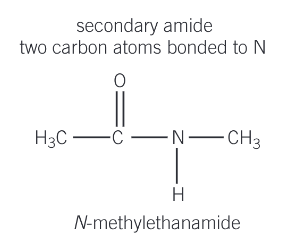
What are tertiary amides?
three carbon atoms bonded to N
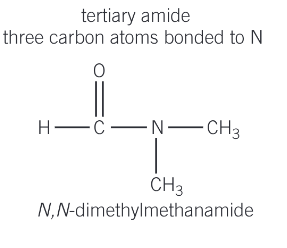
What is steroisomerism?
compounds with the same structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space
Where is optical isomerism found?
in molecules that contain a chiral centre
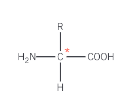
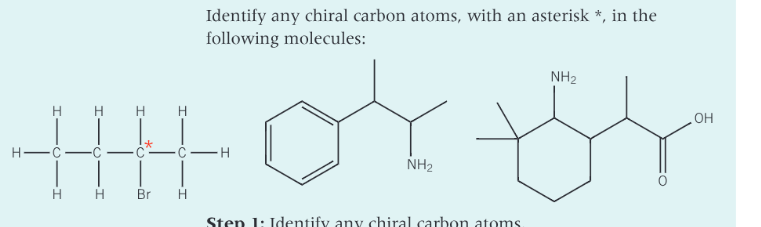
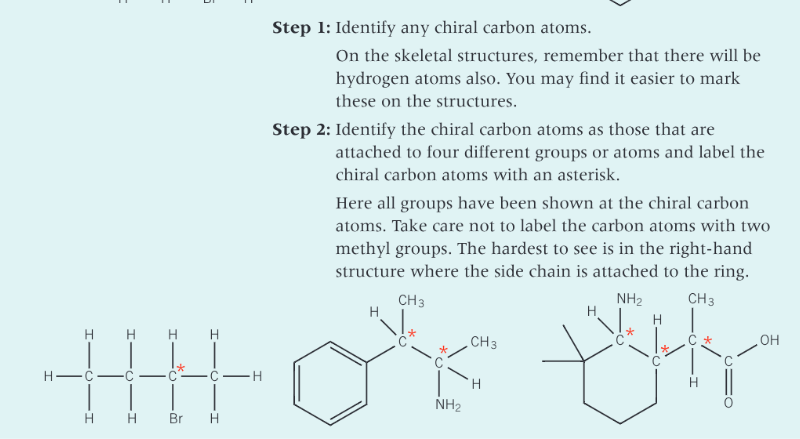
What is a chiral centre?
a carbon atom that is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms
What does the presence of a chiral carbon atom in a molecule lead to?
the existence of 2 non-superimposable mirror image structures, known as optical isomers or enantiomers
For each chiral carbon atom how many optical isomers are there?
one paur
What is another word for optical isomers?
enantiomers
True or false chiral carbon atoms exist widely in naturally occurring organic molecules?
true e.g. all sugars, proteins and nucleic acids contain chiral carbon atoms
Do all aloha amino acids contain a chiral carbon atom?
yes they all have the alpha-carbon atom bonded to 4 different atom or groups. except from glycine which has an H as its R group
In the structure how is the chiral carbon atom labelled?
with an asterisk
Why can optical isomers be in real life and what is a real life example of chirality?
any centre that holds attachments that can be arranges as 2 non-superimposable mirror image forms, like a pair of hands. Optical isomers can be considered as right and left handed forms and one optical isomer cannot be superimposed upon the other
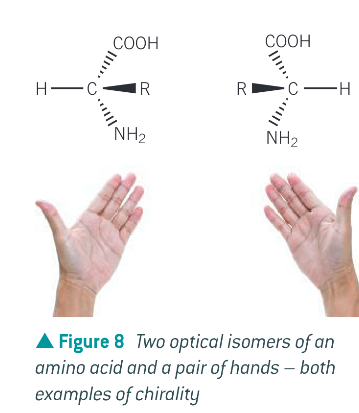
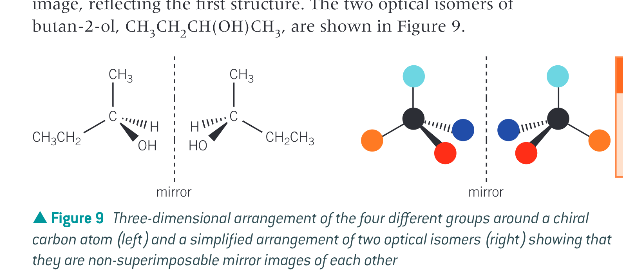
How are optical isomers drawn?
to show the 3D tetrahedral arrangement of the 4 different groups around the central chiral carbon atom, once one isomer has been drawn the other isomer is drawn as a mirror image reflecting the first structure.
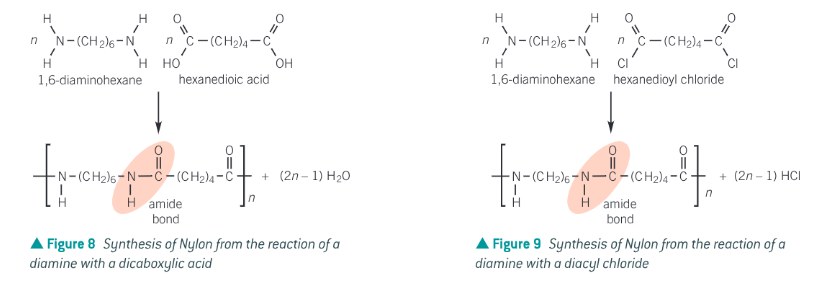
How are condensation polymers formed?
joining monomers with loss of a small molecule, usually water or hydrogen chloride
What is the terms for condensation polymers?
2 different functional groups are needed
How are polyesters formed?
monomers are joined together by ester linkages in a long chain to form the polymer.
they can be made from one monomer containing both a carboxylic acid and an alcohol group or from two monomers, one containing two carboxylic acid groups and the other containing two alcohol groups
What is the simplest polyester made from one monomer containing 2 different functional groups? And how does the polymer form?
poly(glycolic acid) (PGA) monomer: HOCH2COOH it contains both a hydroxyl and carboxyl group.
The carboxylic acid group in one molecule reacts with the alcohol group of another molecule to form the ester linkage and water
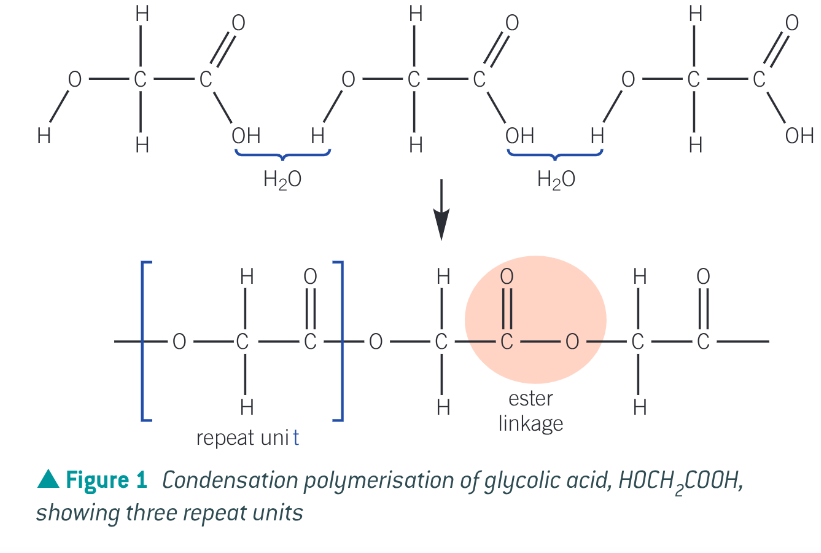
What is a natural acid that undergoes condensation polymerisation?
lactic acid HOCH(CH3)COOH to form poly(lactic acid) (PLA)
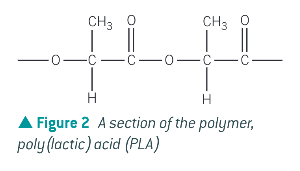
What are the benefits of PLA and PGA?
they are biodegradable polymers. Lactic acid is derives from maize, so its production is much more sustainable than polymers derived from fossil fuels.
e.g. a suture is made from PLA or PGA
How is a polyester formed from two monomers each containing 2 functional groups?
During the condensation reaction a hydroxyl group on the diol reacts with a carboxyl group on the dicarboxylic acid forming an ester linkage and water.
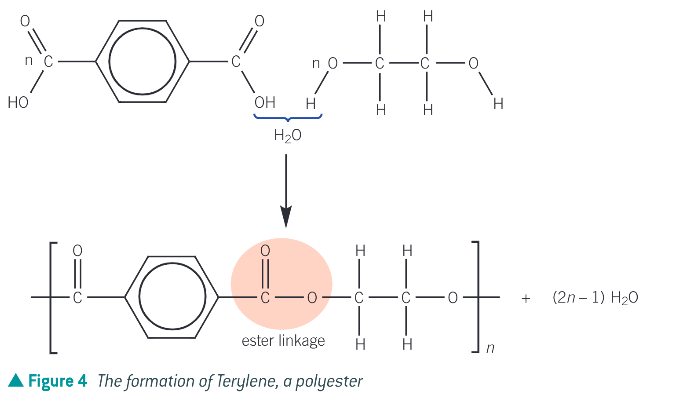
What is the uses of Terylene (polyethylene terephthalate) (PET) - a polyester made from two monomers each containing two functional groups?
many diverse uses ranging from clothing to plastic PET bottles
what can polyesters be used for?
electrical insulation
What are polyamides?
condensation polymers formed when monomers are joined together by amide linkages in a long chain to form the polymer.
they can be made from one monomer with a carboxylic acid (or acyl chloride) and an amine group or from 2 monomers, one containing two carboxylic acid groups (or acyl chloride) and the other containing two amine groups
How are polyamides from one monomer with two functional groups formed?
amino acids contain both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group. Amino acids undergo condensation polymerisation to form polypeptides or proteins. A polypeptide contains many amino acids linked together by amide bonds. When an amide bond is formed water is lost
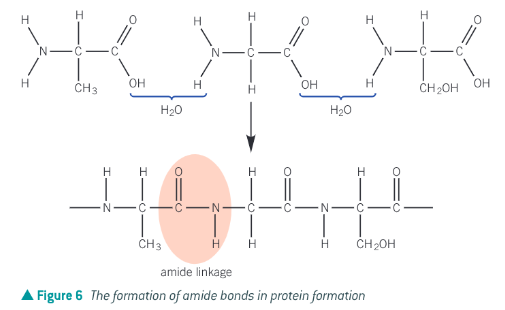
How are polyamides from two monomers each with two functional groups formed?
polyamides can be made by the reaction of a dicarboxylic acid (or acyl chloride) with a diamine. During the condensation reaction an amide bond formed between the amine on one monomer and the carboxyl (or acyl chloride) group on the other monomer.
The picture shows the synthesis of nylon. Different types of nylon can be made by varying the chain length.
How can polyesters and polyamides be hydrolysed?
using hot aq alkali such as sodium hydroxide or by hot aq acids such as hydrochloric acid
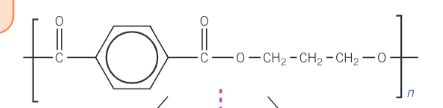
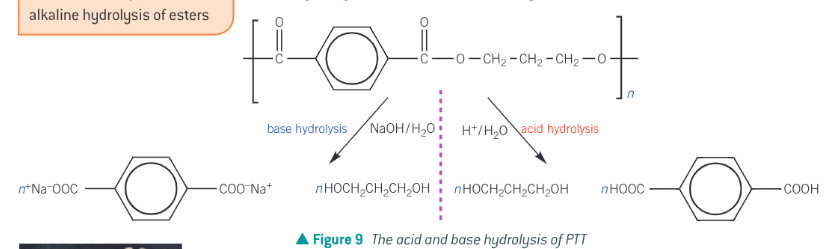
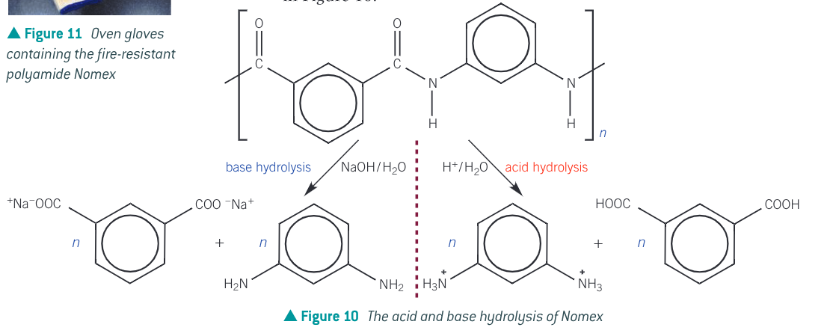
What is PTT and what is it used in and what does the hydrolysis of it look like
poly(Trimethylene Terephthalate) (PTT) is a polyester used in the manufacture of carpoets and clothing fabrics. The acid and base hydrolysis PTT is in pic
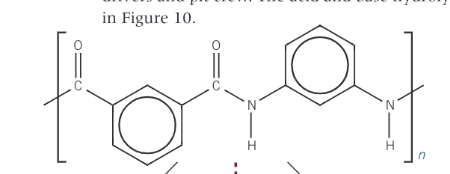
What is nomex? - what does the acid-base hydrolysis look like?
a synthetic heat and fire-retardant polyamide, used in oven gloves and in the fire-protective suits worn by formula 2 racing drivers and pit crew.
What should you look for when identifying monomers of addition polymers?
they contain a C=C bond and the backbone of the polymer is a continuous chain of carbon atoms
What should you look for when Identifying the monomers of a condensation polymer?
two monomers each with two functional groups e.g. HOOCCH2COOH and HOCH2CH2OH
one monomer with two different functional groups e.g. H2NNCH2COOH
polymers contain ester or amide linkages
What is the nitrile group?
the organic functional group -CN
How can nitriles be formed?
by reacting haloalkanes with sodium cyanide, NaCN or potassium cyanide, KCN, in ethanol. In this reaction the length of the carbon chain is increased
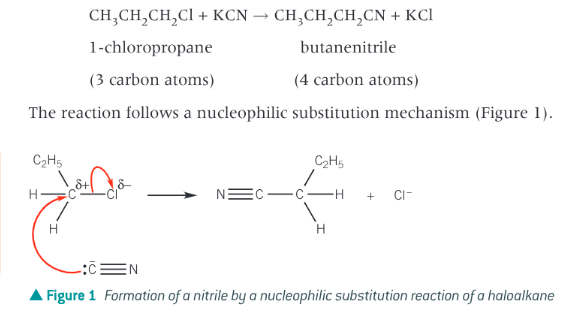
How do nitriles react?