Normal Anatomy and Physiology of the Female Pelvis
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
Mons pubis
The rounded mass of fatty tissue lying over the pubic bone.
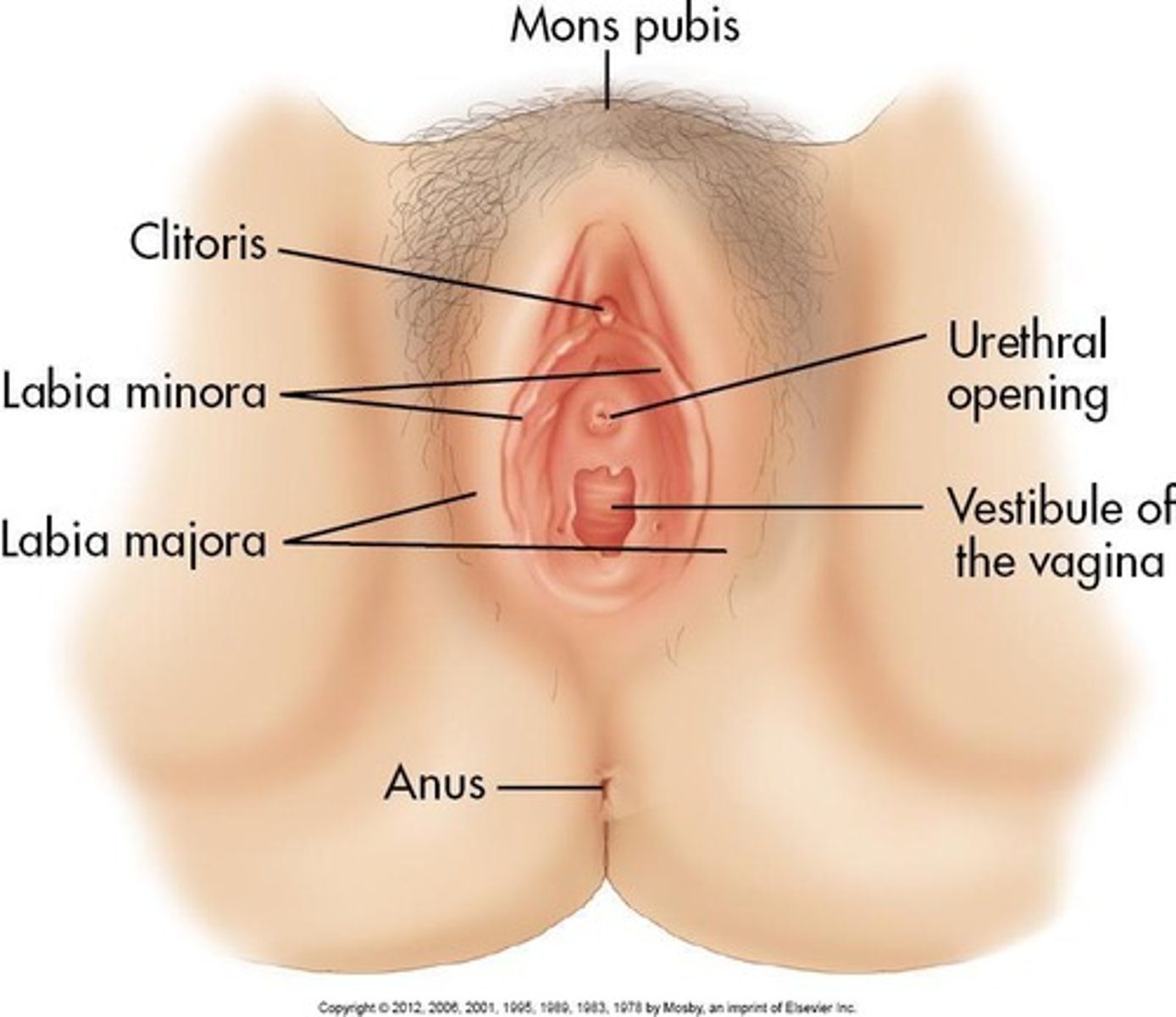
Labia majora
The larger outer folds of skin that protect the external genitalia.
Labia minora
The smaller inner folds of skin that protect the vaginal opening.
Clitoris
A small, sensitive organ located at the top of the vulva.
Urethral opening
The external opening through which urine is expelled from the body.
Vestibule of vagina
The area surrounding the vaginal opening.
Bony pelvis
Consists of four bones: two innominate (coxal) bones, sacrum, and coccyx.
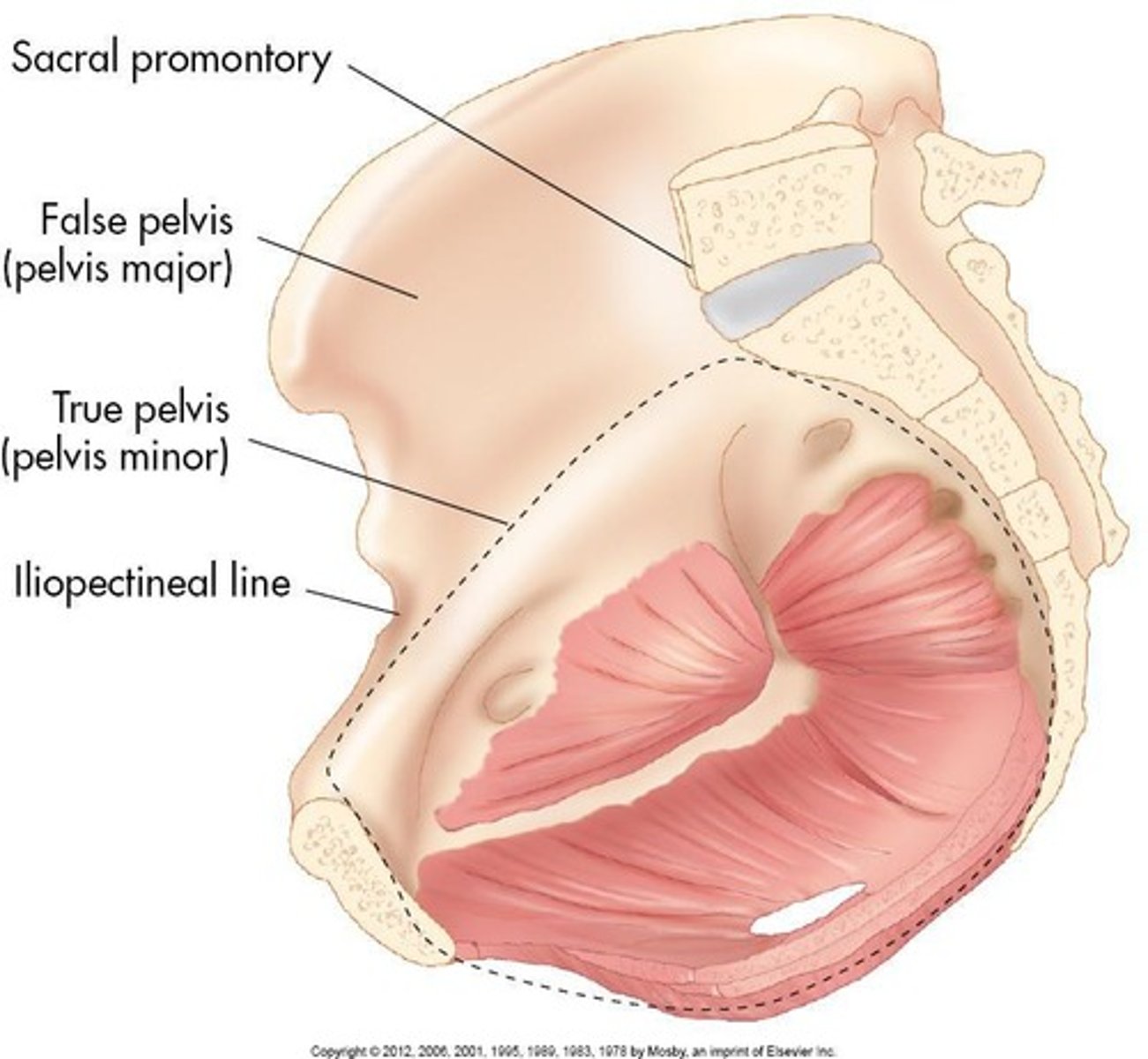
True pelvis
The compartment situated inferior to the caudal portion of the parietal peritoneum.
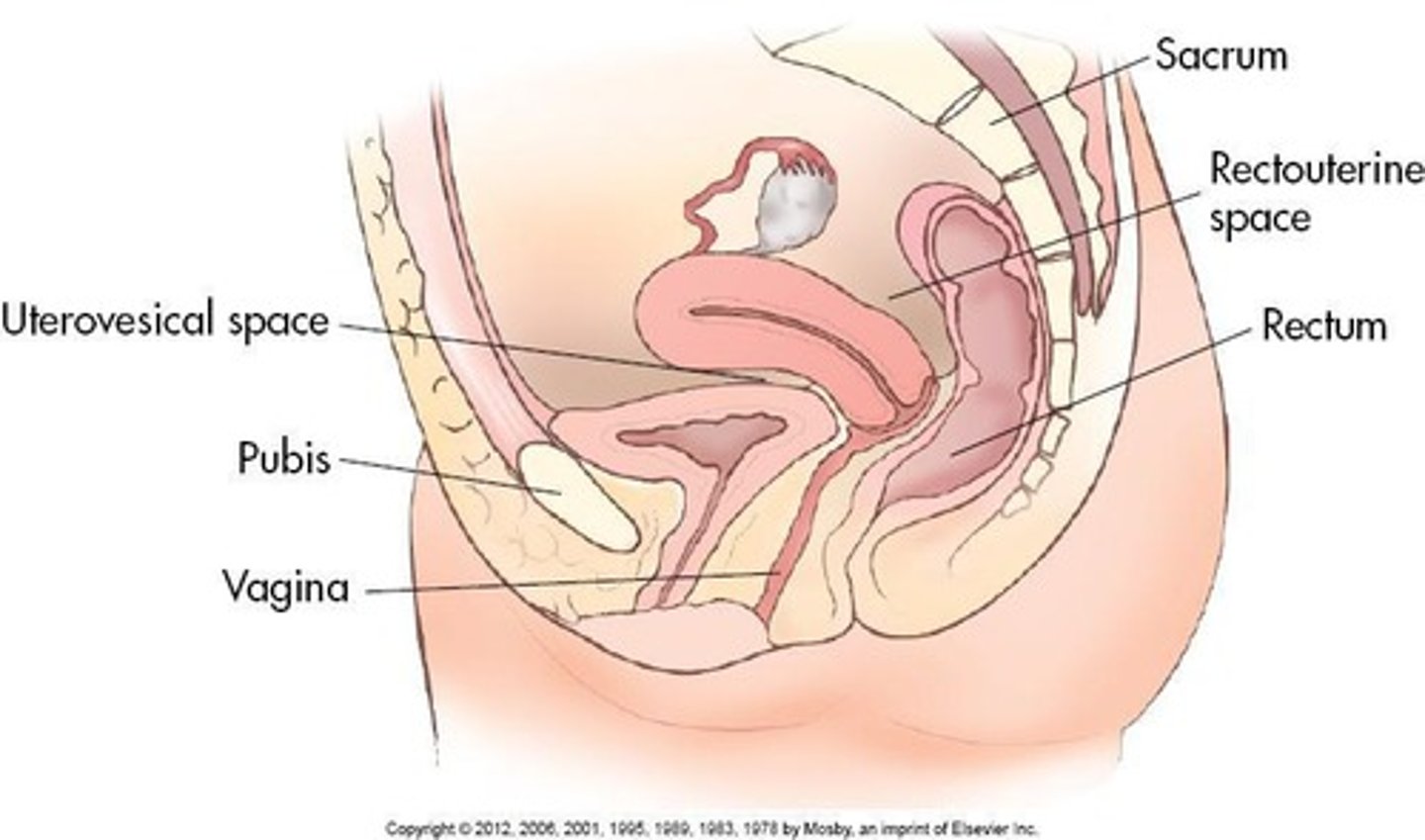
Pelvic cavity
The space within the true pelvis, occupied by various organs.
Perineum
The area below the pelvic floor.
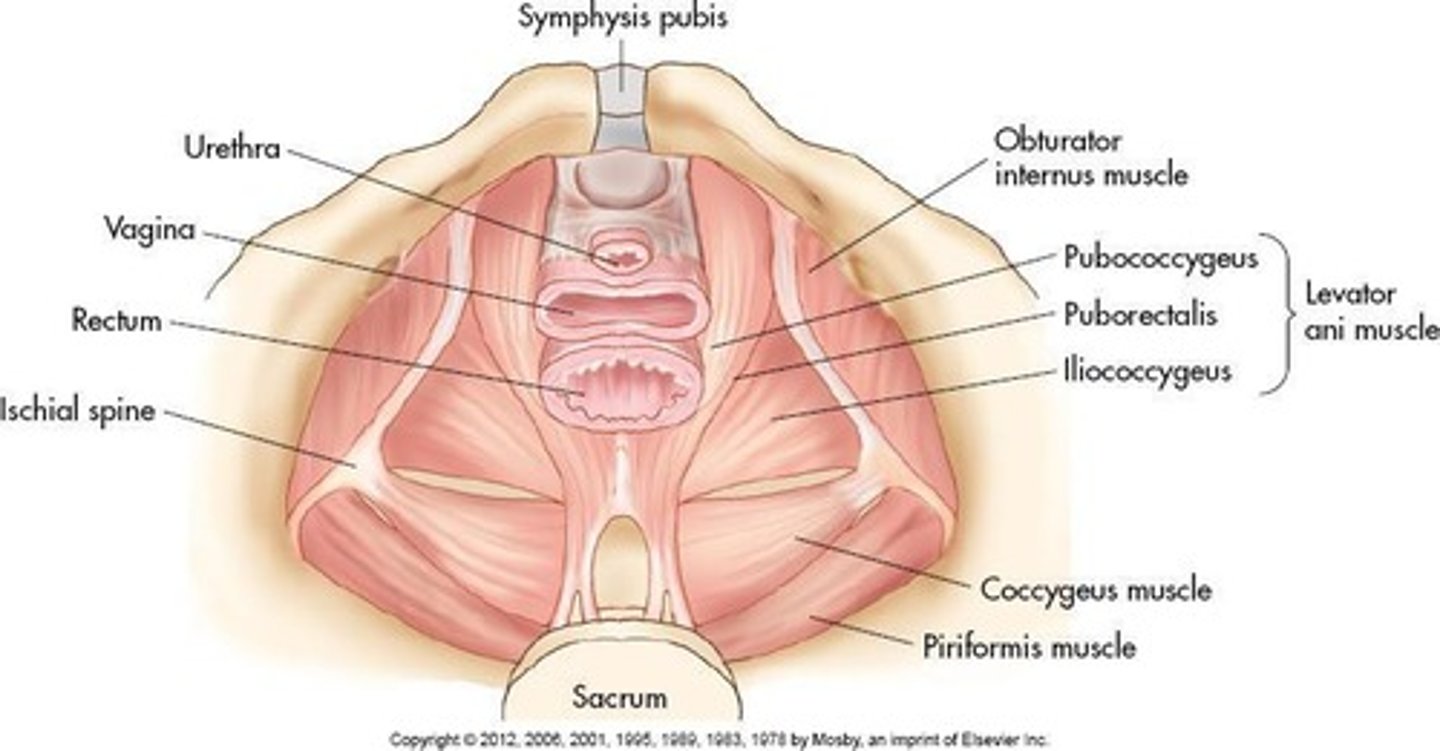
Pelvic diaphragm
The lower margin of the pelvic cavity formed by levator ani and coccygeus muscles.
Rectum
The posterior part of the pelvic cavity occupied by the rectum.
Bladder
An organ that stores urine, located anterior to the vagina and superior to the uterus.
Ureters
Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
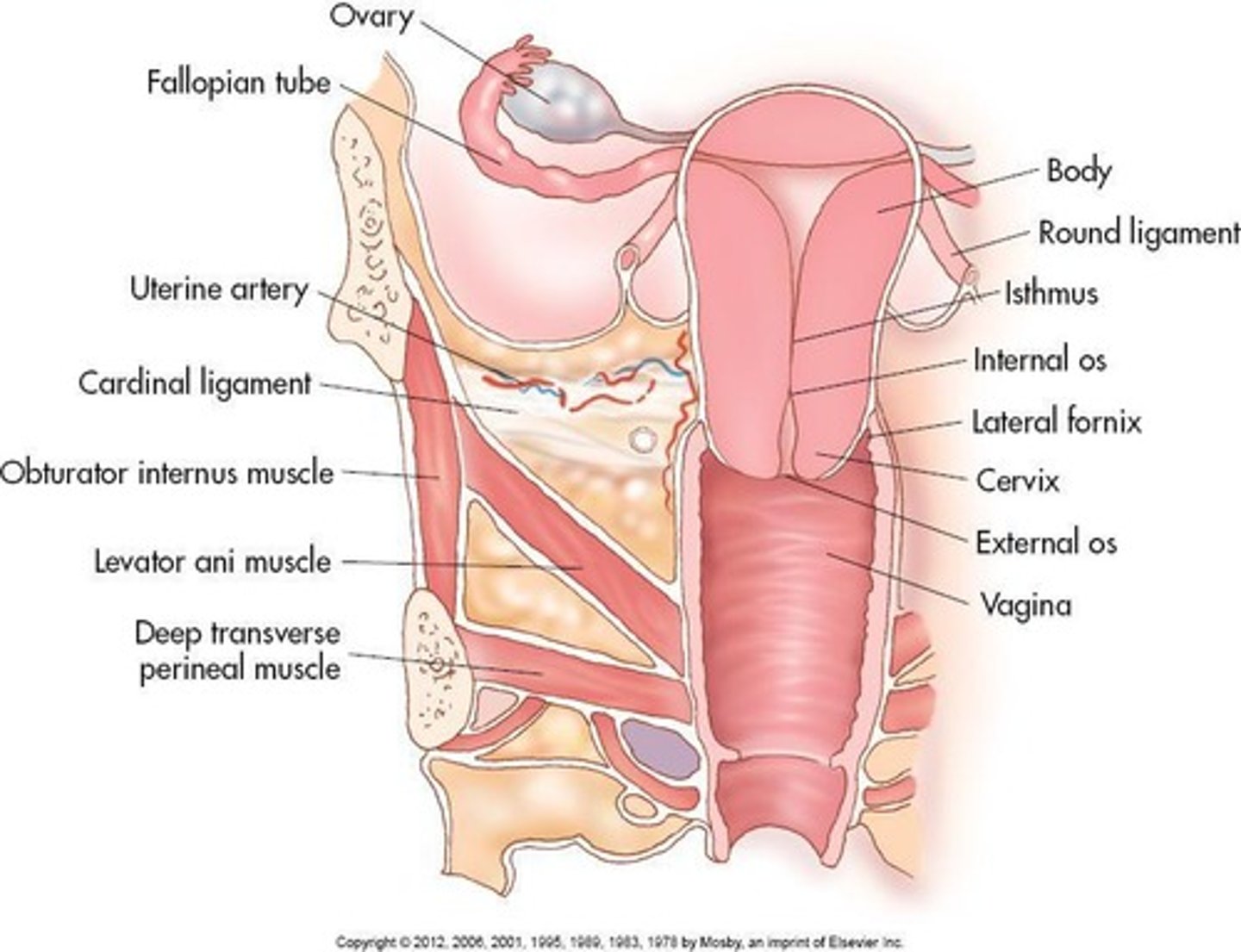
Vagina
A collapsed muscular tube that extends from external genitalia to the cervix of the uterus.
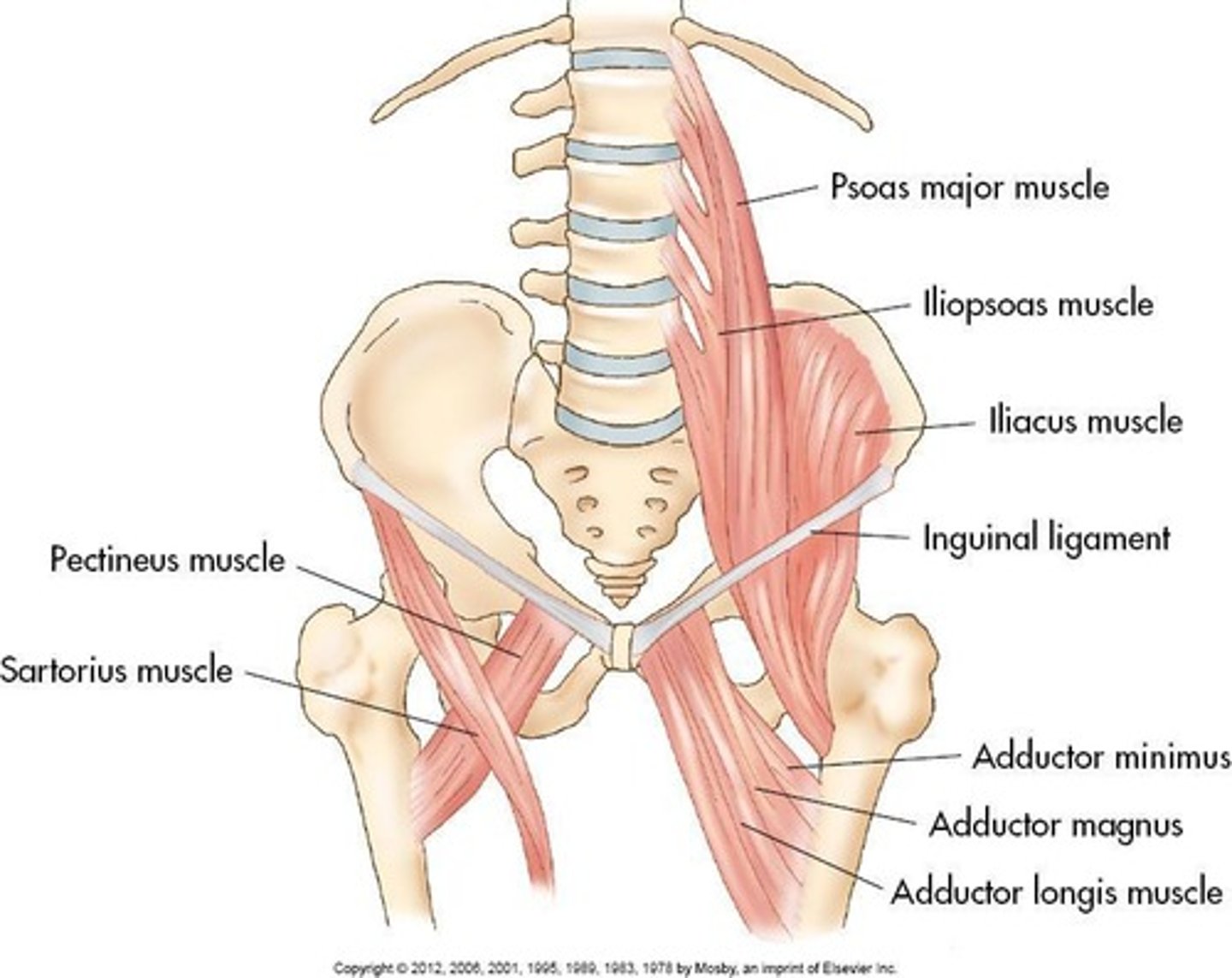
Psoas major
A muscle located in the pelvic sidewall.
Iliacus
A muscle located in the pelvic sidewall.
Piriformis
A muscle forming the posterolateral wall of the pelvis.
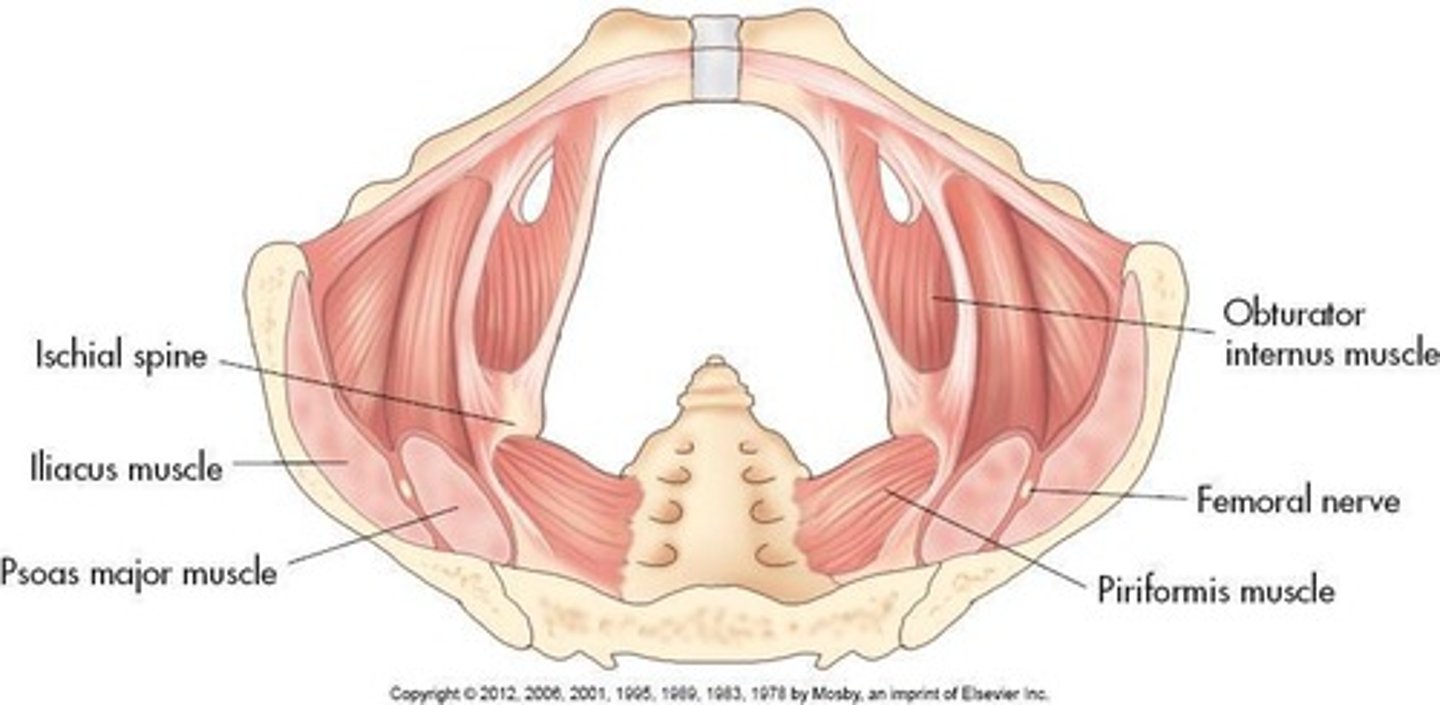
Obturator internus
A muscle forming the anterolateral pelvic sidewall.
Levator ani
A muscle forming the pelvic floor (diaphragm).
Coccygeus
A muscle forming the posterior pelvic floor (diaphragm).
Iliopsoas
A muscle formed by the joining of psoas major and iliacus muscles in the false pelvis.
Pubococcygeus
A muscle that is part of the levator ani.
Iliococcygeus
A muscle that is part of the levator ani.
Puborectalis
A muscle that is part of the levator ani.
Vagina
Normally directed upward and backward, forming 90-degree angle with uterine cervix.
Vagina Length
Measures approximately 9 cm in length; is longest along posterior wall.
Vagina Structure
Extends upward and backward from vulva; upper half lies above pelvic floor, lower half lies within perineum.
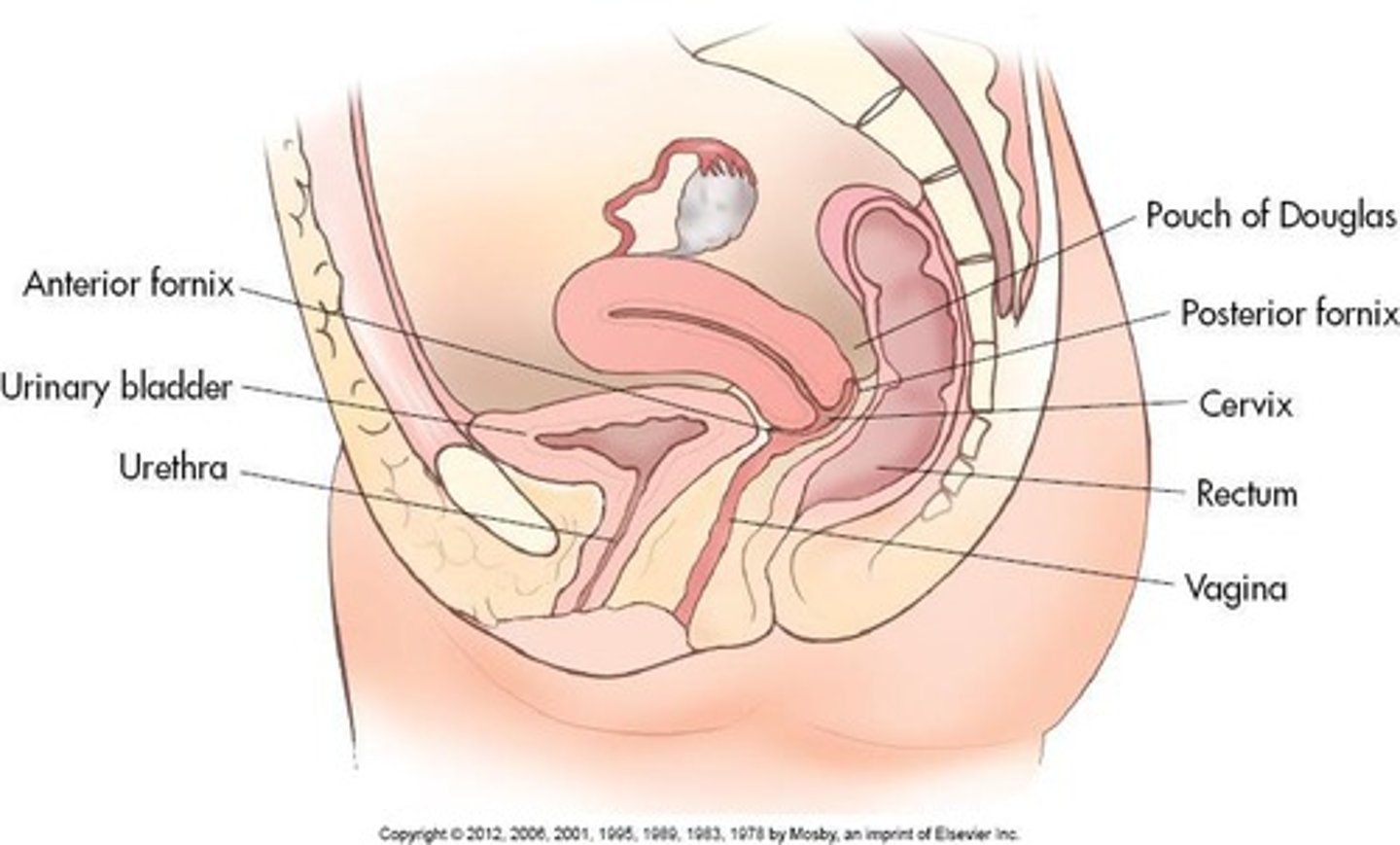
Vaginal Fornices
Area of vaginal lumen surrounding cervix divided into four fornices.
Vaginal Blood Supply
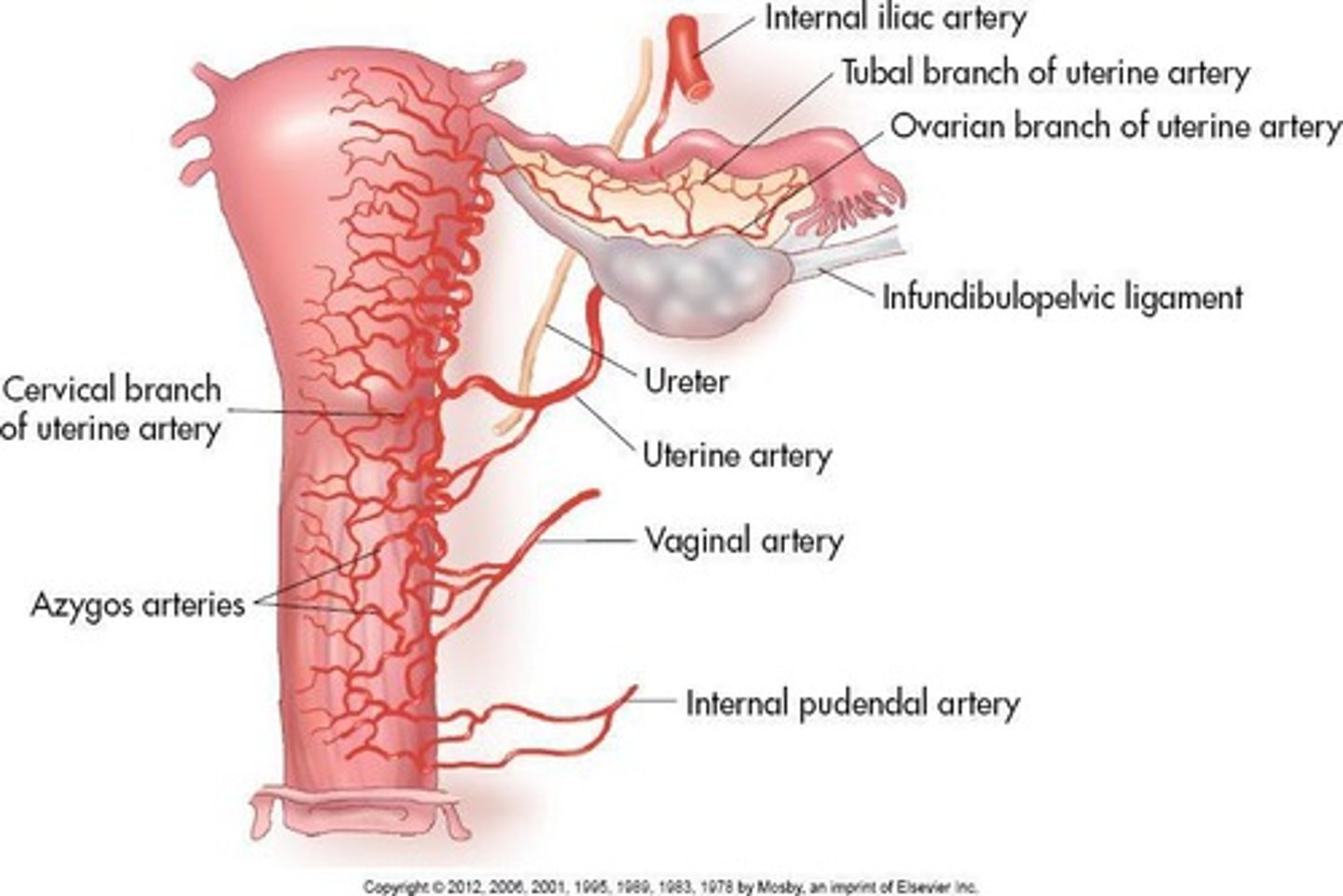
Arterial supply from vaginal and uterine arteries; drains into internal iliac vein.
Cervix
Projects into vaginal canal.
Endocervix
Cervical canal; communicates with uterine cavity by internal os; vagina by external os.
Exocervix
Continuous with vagina.
Cervical Fornices
Protrudes into upper portion of vaginal canal forming four archlike recesses called fornices.
Cervical Anatomy
Posterior vaginal wall attaches higher on cervix, and fornices are blind pockets formed by inner surface of vaginal walls and outer surface of cervix.
Cervical Space
Is a continuous ring-shaped space with posterior fornix running deeper than its anterior counterpart.
Uterus
Hollow, pear-shaped organ divided into fundus, body, cervix.
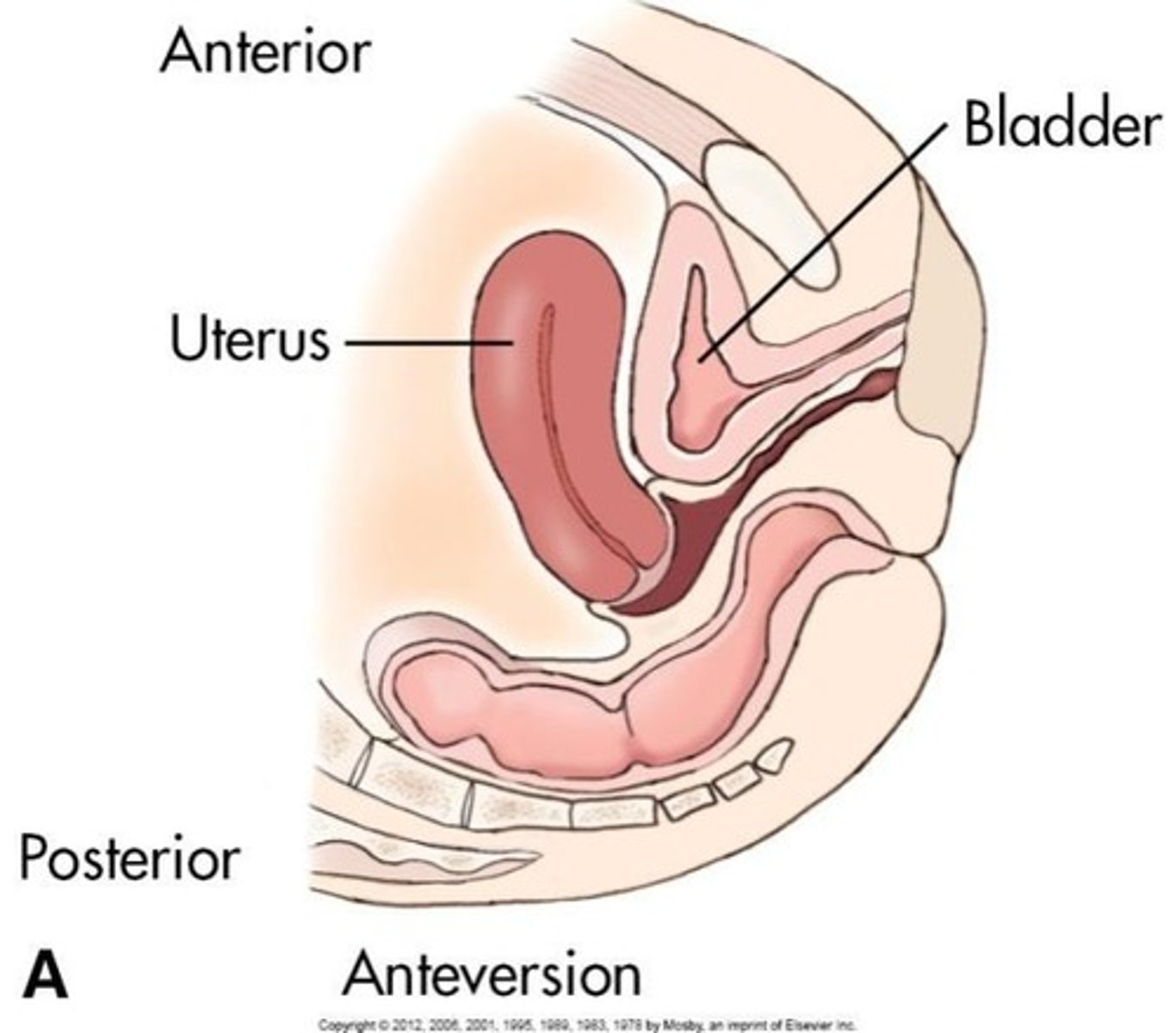
Uterine Position
Usually anteflexed and anteverted.
Uterine Support
Supported by levator ani muscles, cardinal ligaments, uterosacral ligaments.
Round Ligaments
Hold uterus in anteverted position.
Uterine Size Premenarchal
1.0 to 3.0 cm long by 0.5 to 1.0 cm wide.
Uterine Size Menarchal
6.0 to 8.0 cm long by 3.0 to 5.0 cm wide.
Uterine Size Multiparity
Increases size by 1.0 to 2.0 cm.
Uterine Size Postmenopausal
3.5 to 5.5 cm long by 2.0 to 3.0 cm wide.
Body of the Uterus
Posterior to vesicouterine pouch and superior surface of bladder; anterior to rectouterine pouch (of Douglas), ilium, colon.
Uterine Cavity Shape
Uterine cavity is funnel-shaped in coronal plane; 'slitlike' in sagittal plane.
Perimetrium
Serous outer layer of uterus; serosa.
Myometrium
Muscular middle layer of uterus composed of thick, smooth muscle supported by connective tissue.
Endometrium
Inner mucous membrane, glandular portion of uterine body.
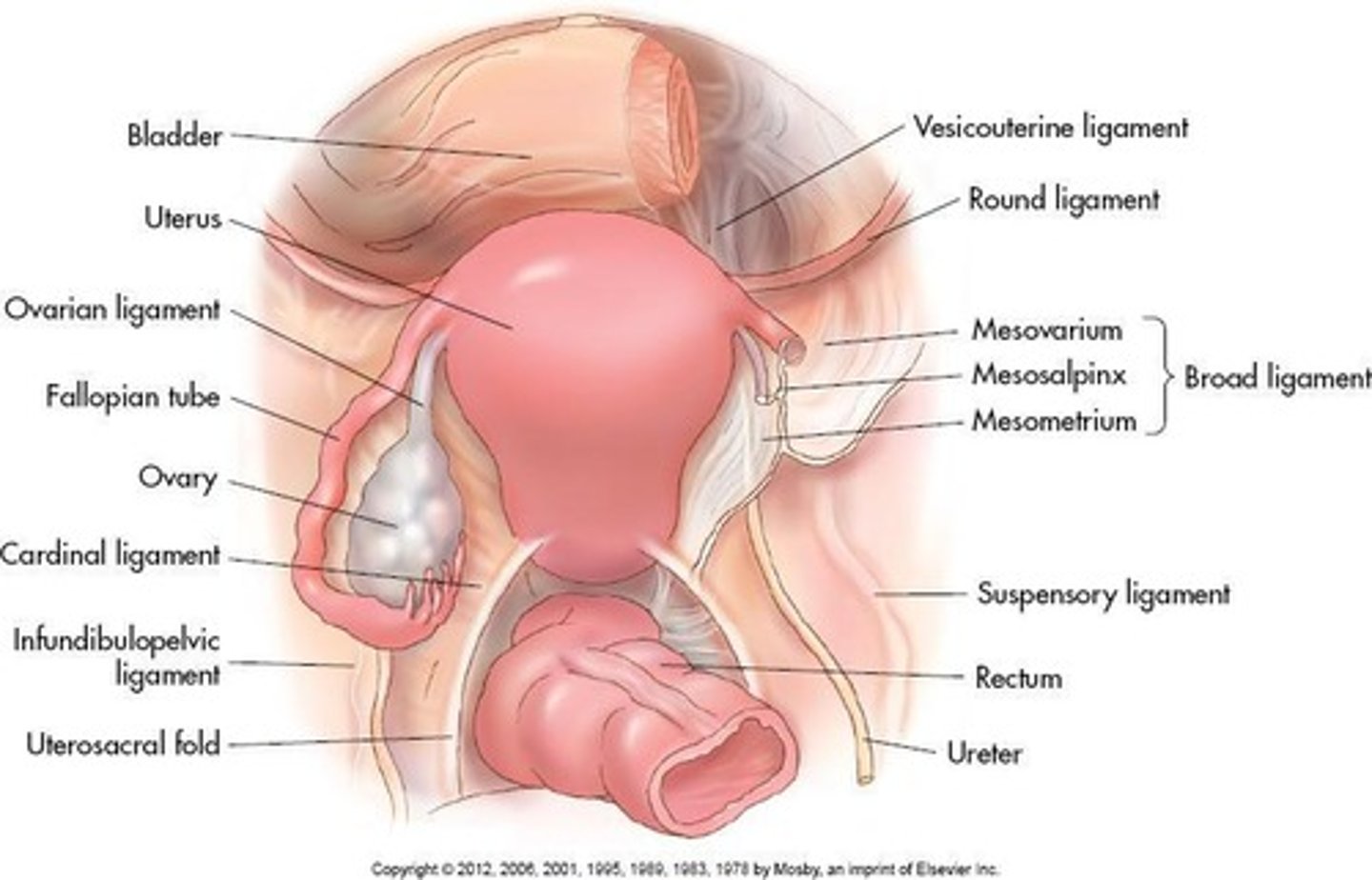
Broad Ligament
Lateral aspect of uterus to pelvic sidewall.
Mesovarium
Posterior fold of broad ligament; encloses ovary.
Mesosalpinx
Upper fold of broad ligament; encloses fallopian tube.
Round Ligament
Fundus to anterior pelvic sidewalls; holds uterus forward.
Cardinal Ligament
Extend across pelvic floor laterally; firmly supports cervix.
Uterosacral Ligament
Extend from uterine isthmus downward, along side rectum to sacrum; firmly supports cervix.
Suspensory Ligament
Extends from lateral aspect of ovary to pelvic sidewall.
Ovarian Ligament
Extends medially from ovary to uterine cornua.
Anteversion
Most common position; fundus and body bent forward toward cervix.
Dextroversion or Levoversion
Normal variant in absence of pelvic masses.
Retroversion
Entire uterus tilted posteriorly.
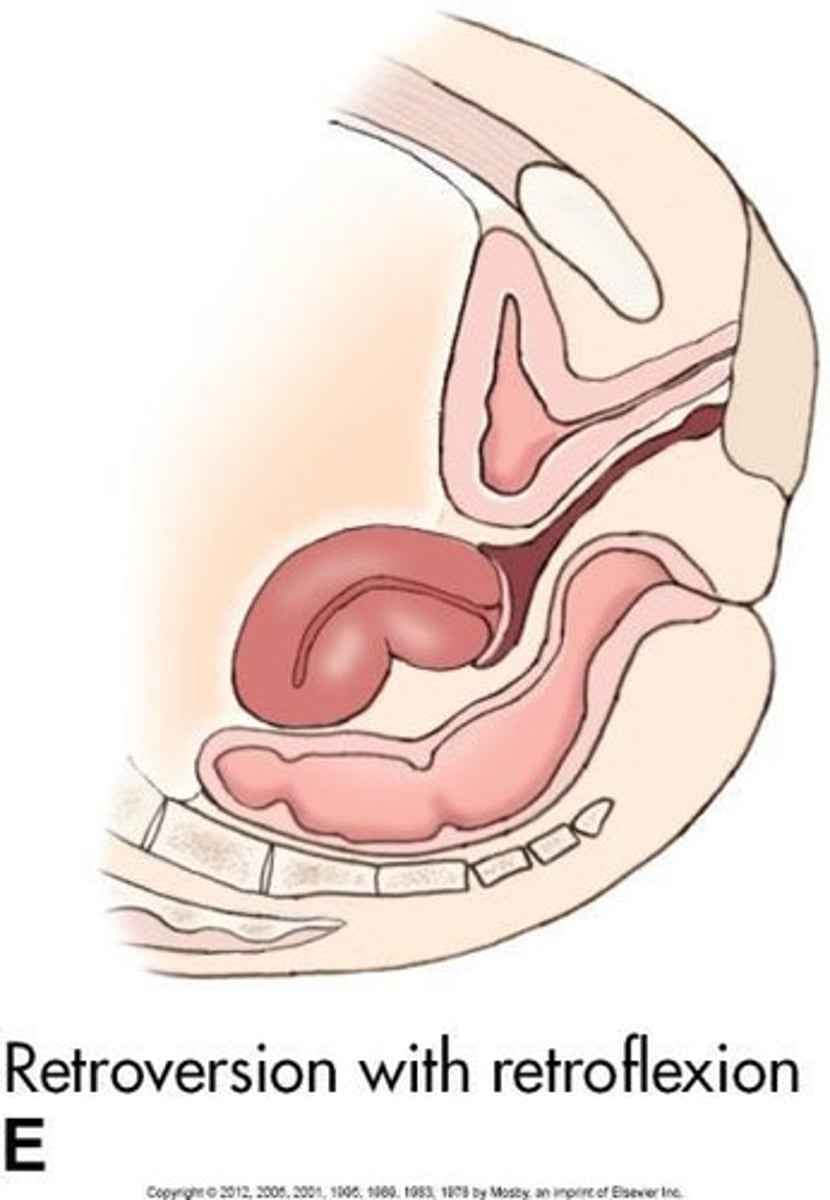
Retroflexion
Fundus and body bent backward towards cervix.
Fallopian Tubes
Infundibulum: Funnel-shaped lateral tube projects beyond broad ligament to overlie ovaries; 'free edge' of the funnel has fimbriae.
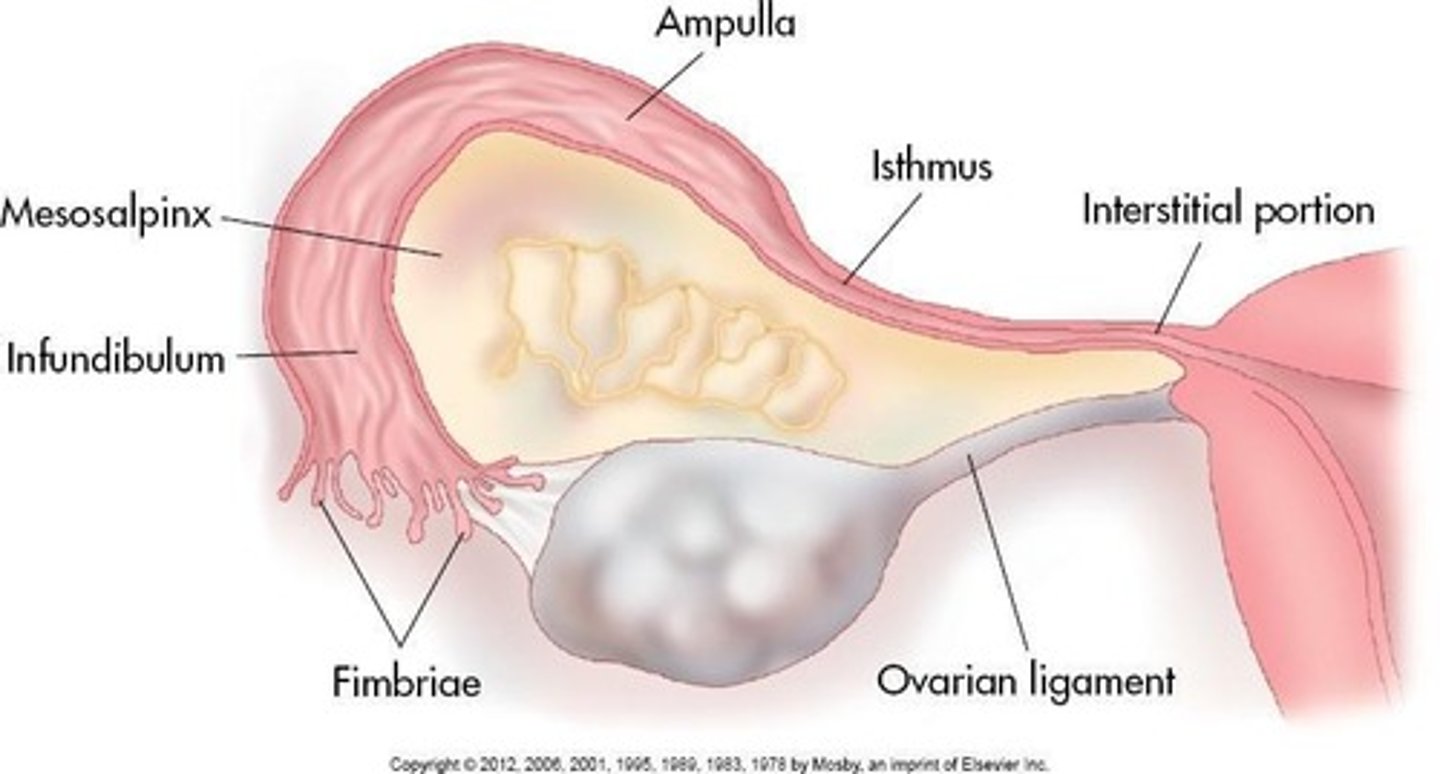
Ampulla
Widest part of tube where fertilization occurs.
Isthmus
Hardest part; lies lateral to uterus.
Interstitial Portion
Pierces uterine wall at cornua.
Length of Fallopian Tubes
12 cm; blood is supplied by ovarian arteries and veins.
Infundibulum
Funnel-shaped lateral tube that projects beyond broad ligament to overlie ovaries; the 'free edge' of the funnel has fimbriae.
Ampulla
Widest part of the fallopian tube where fertilization occurs.
Isthmus
Hardest part of the fallopian tube; lies lateral to the uterus.
Interstitial portion
Part of the fallopian tube that pierces the uterine wall at cornua.
Ovaries
Almond-shaped structures attached at the posterior aspect of the broad ligament by mesovarium.
Ovarian fossa
The location where the ovaries lie, bounded by external iliac vessels, ureter, and obturator nerve.
Dual blood supply of Ovaries
Receives blood from ovarian artery and uterine artery.
Ovarian vein drainage
Blood drained by ovarian vein into IVC on the right and into renal vein on the left.
Variable Positions of the Ovaries
Ovaries are anterior to internal iliac artery and vein, medial to external iliac artery and vein, and their location is highly variable as ligaments loosen, especially after pregnancy.
Normal Anatomy of Ovaries
Consist of outer layer, or cortex, which surrounds central medulla.
Cortex of Ovaries
Consists primarily of follicles in varying stages of development and is covered by a layer of dense connective tissue, tunica albuginea.
Tunica albuginea
Surrounded by a single, thin layer of cells known as germinal epithelium.
Central medulla of Ovaries
Composed of connective tissue containing blood, nerves, lymphatic vessels, and some smooth muscle at the region of hilum.
Ovarian Hormones
Produce reproductive cell—ovum, and two known hormones: estrogen, secreted by follicles, and progesterone, secreted by corpus luteum.
Functions of Ovarian Hormones
Responsible for producing and maintaining secondary gender characteristics, preparing uterus for implantation of fertilized ovum, and development of mammary glands in females.
Ovarian Ligaments
Ovaries supported medially by ovarian ligaments, originating bilaterally at cornua of uterus.
Suspensory Ligament
Extends from infundibulum of fallopian tube and ovary to sidewall of pelvis.
Pelvic Vasculature
Includes external iliac arteries, external iliac veins, internal iliac arteries, internal iliac veins, uterine arteries, and veins.
Arcuate arteries
Arclike arteries that encircle the uterus in the outer third of myometrium.
Radial arteries
Branches of arcuate arteries that extend from myometrium to the base of endometrium.
Straight and spiral arteries
Branches of radial arteries that supply the zona basalis of endometrium.
Ovarian arteries
Branch laterally off aorta, run within suspensory ligaments and anastomose with uterine arteries.
Ovarian veins drainage
Right vein drains into IVC directly; left drains into left renal vein.
Menstrual Cycle
Female reproductive years begin around 11 to 13 years of age at onset of menses (menstruation) and end around age 50, when menses ceases.
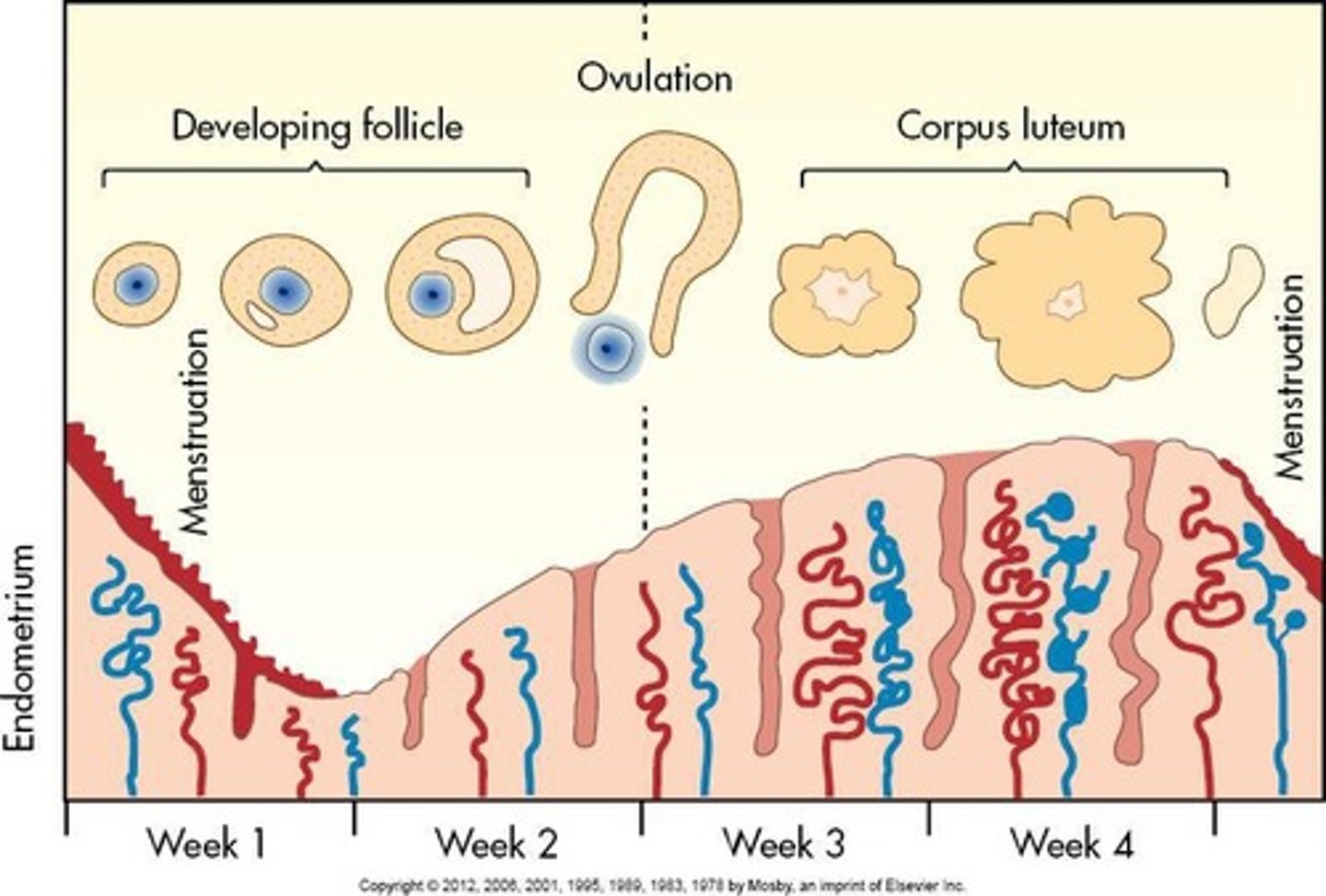
Length of Menstrual Cycle
Approximately 28 days in length, beginning with the first day of menstrual bleeding.
Polymenorrheic Cycle
When the menstrual cycle occurs at intervals of less than 21 days.
Oligomenorrheic Cycle
When the menstrual cycle is prolonged to more than 35 days.
Premenarche
prepuberty
Menarche
menstruating approximately every 28 days
Menopause
cessation of menses
Ovulation
during menarchal years, ovum released once a month by one of two ovaries
Ovulation timing
normally occurs midcycle on about day 14 of 28-day cycle
Ovum release alternation
speculated that ovum release alternates between the two ovaries; one month from right, next month from left
Oocyte development
all ova begin development during embryonic life