Exam 2 APK2100C Nyugen
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Three organs of the skeletal system
Bones cartilage and joints
Three types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
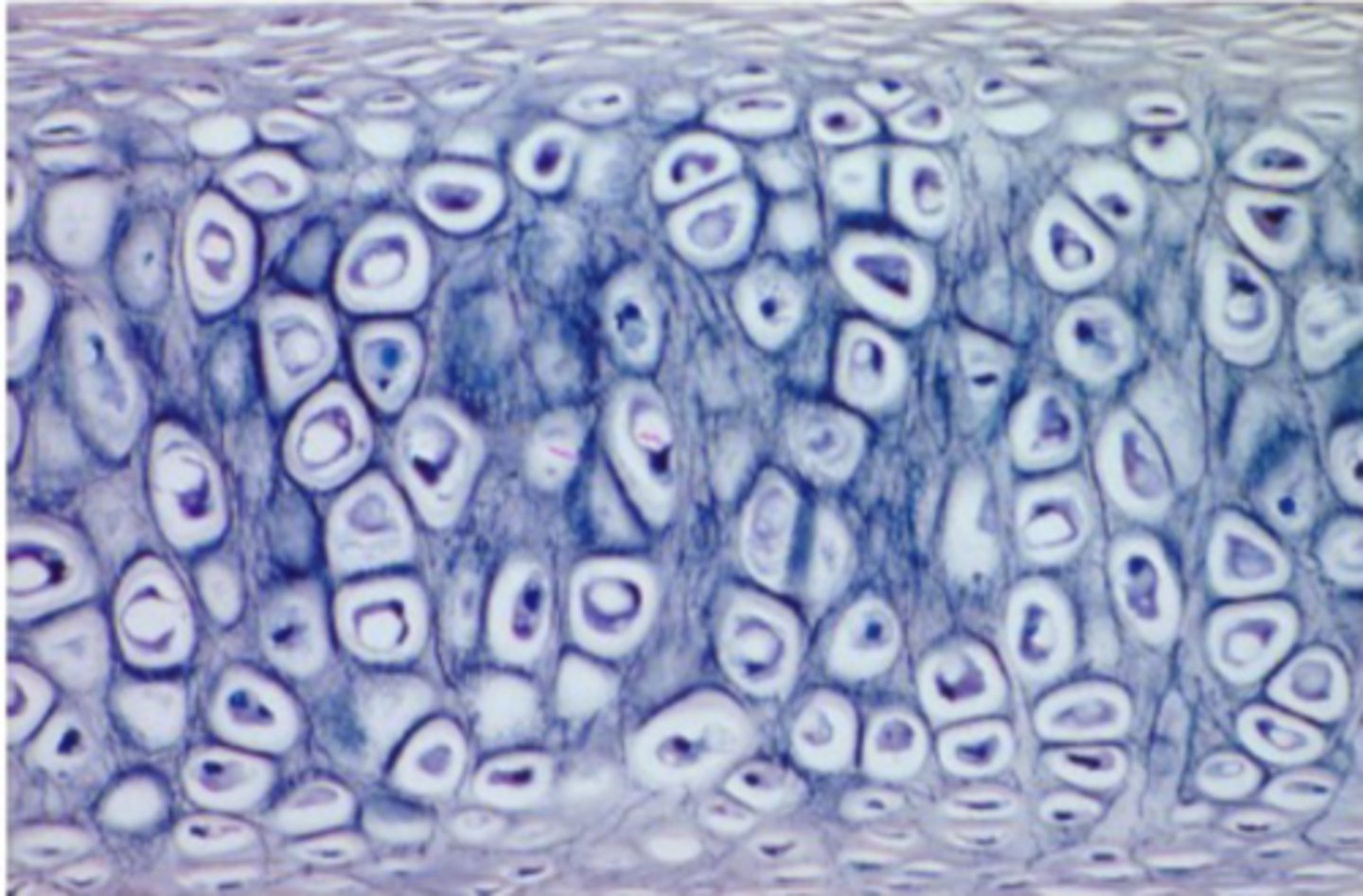
hyaline cartilage
Found at end of bones, meant to reduce friction between bones
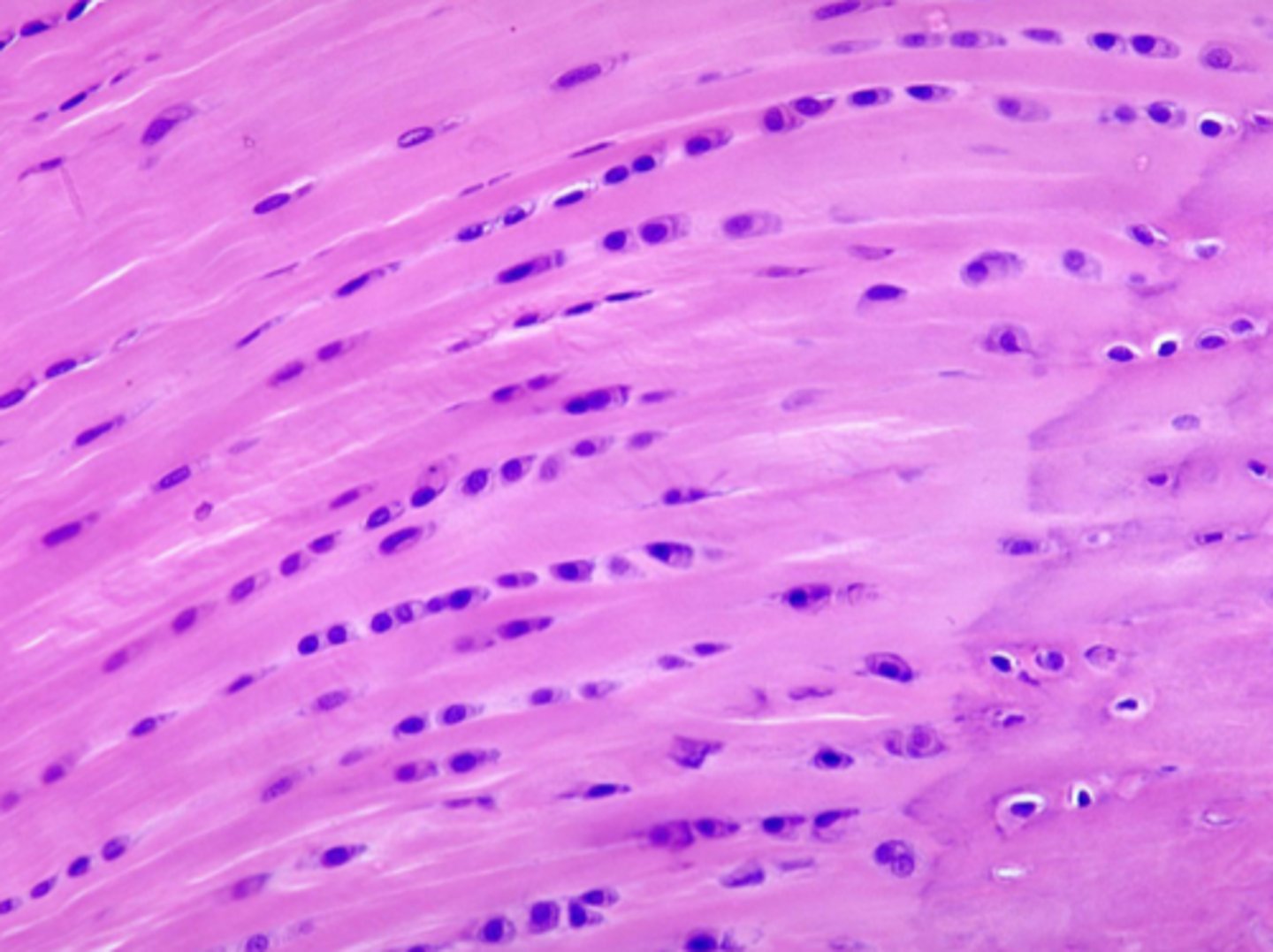
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage
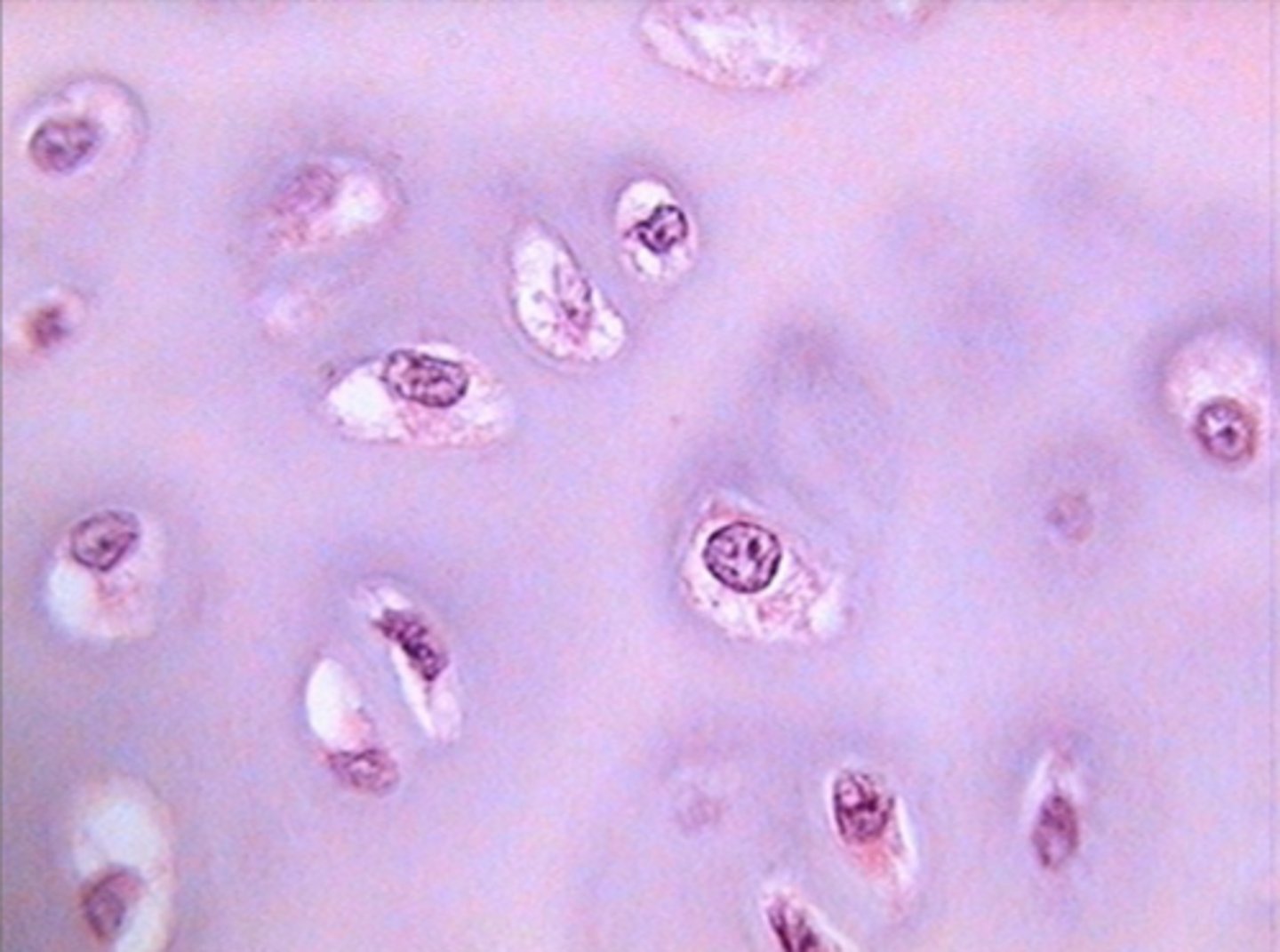
Fibrocartilage
cartilage that contains fibrous bundles of collagen, absorbs force
A connective tissue with an abundant extracelullar matrix that is gel and fiber like
Cartilage
Gel like and opaque ecm
Hyaline
More elastic fibers within the ecm
Elastic
More strand like ecm
Fibrocartilage
Connective dense irregular tissues that surrounds elastic cartilage
Perichondrium
functions of bones:
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation
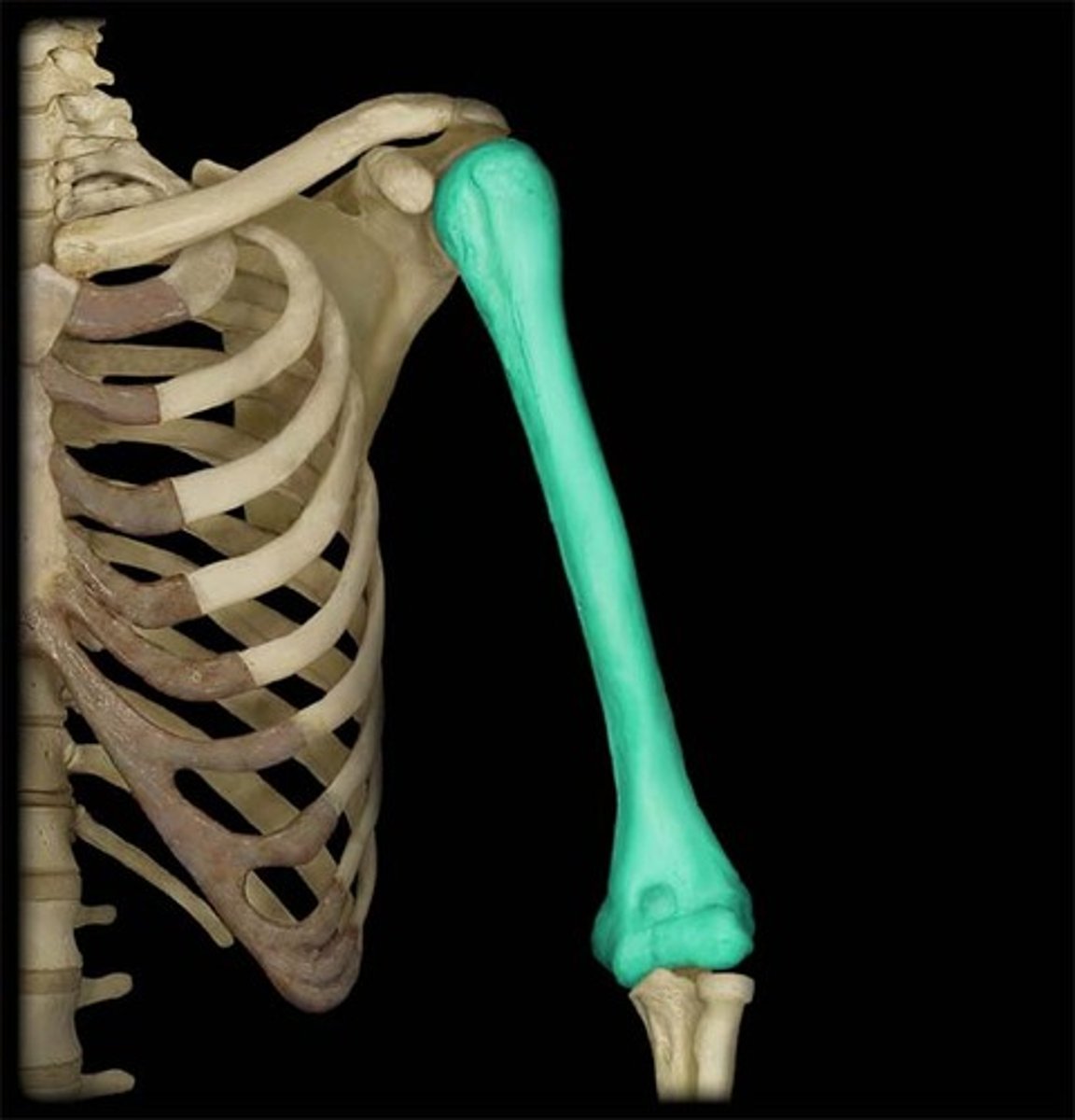
Long bone
Elongated shape with 2 distinct ends
Short bone
Cube shaped bone with no distinct ends,
sesamoid bones
round bones found near joints (e.g., the patella)
Flat bones
These bones are thin, flat, and curved.
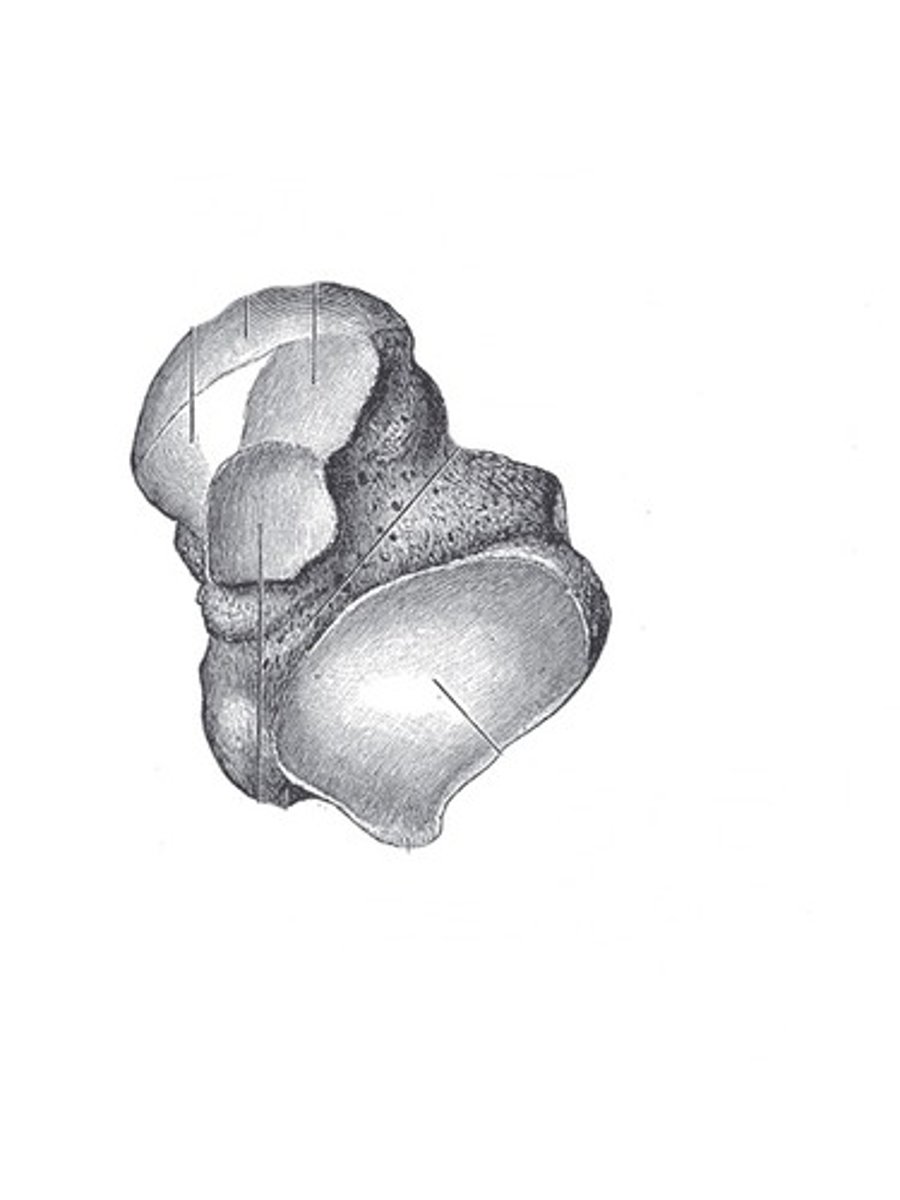
Irregular bones
bones of the vertebrae and face, don't fall into categories of others
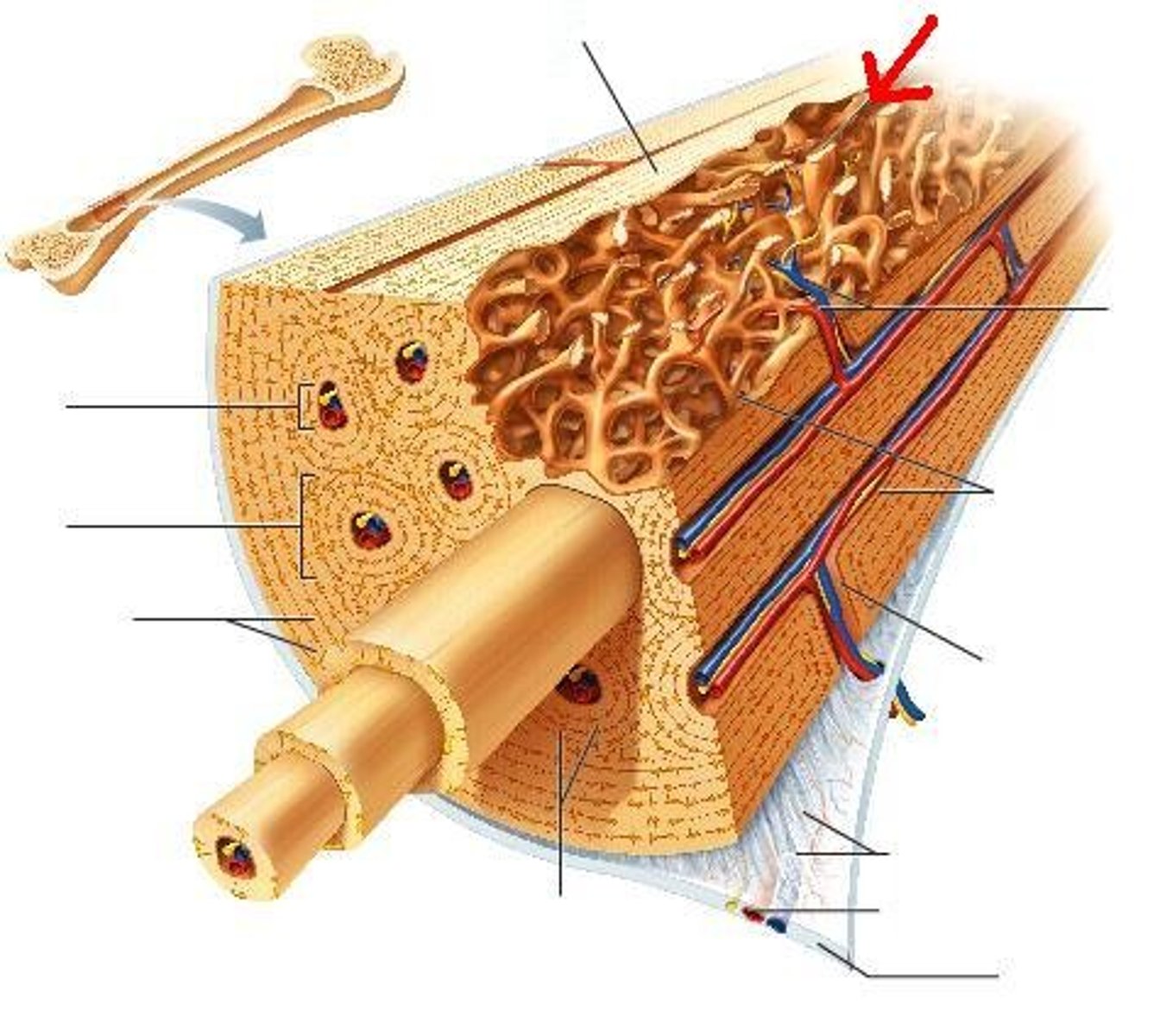
compact bone
Dense outer layer that has no air pockets
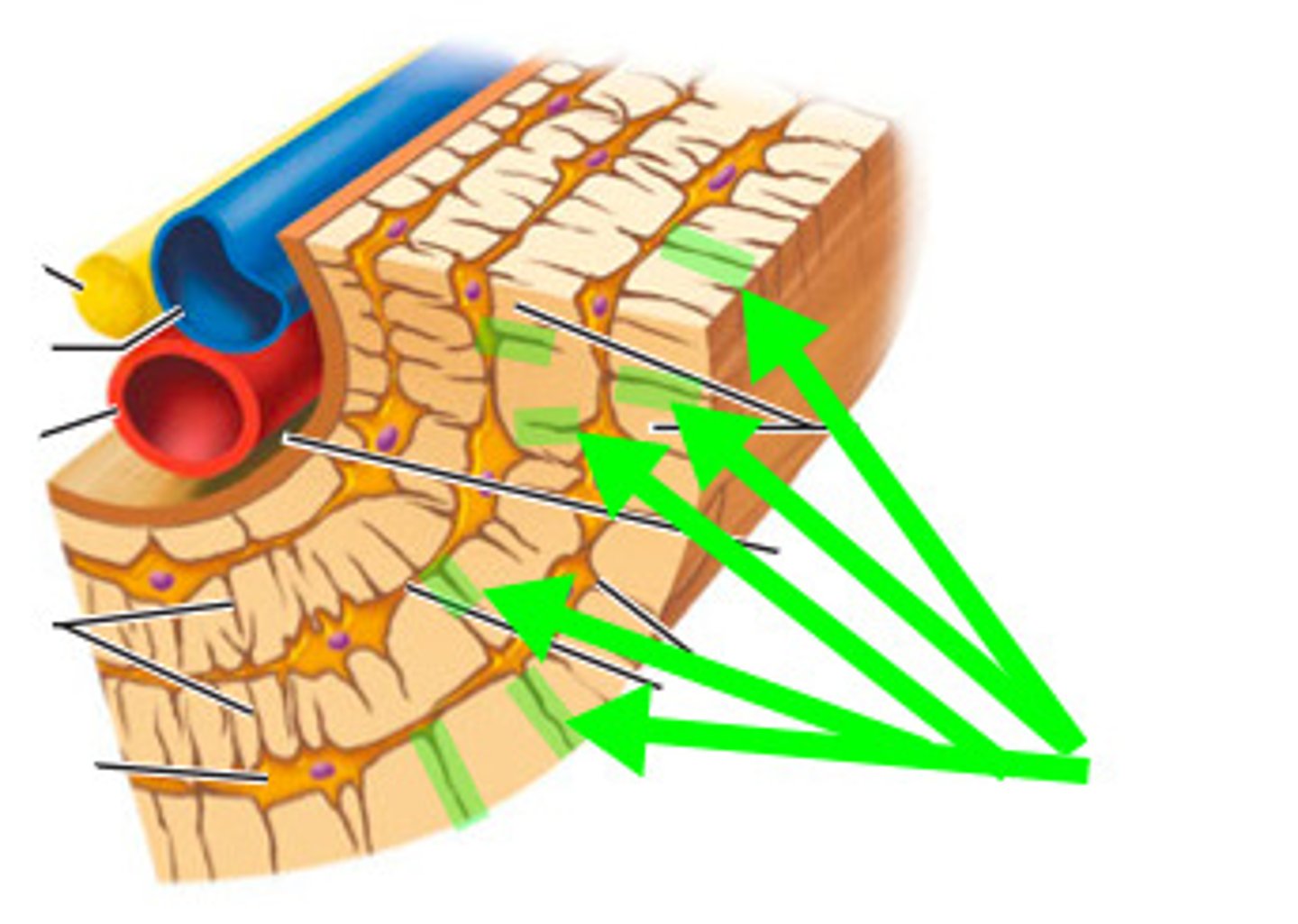
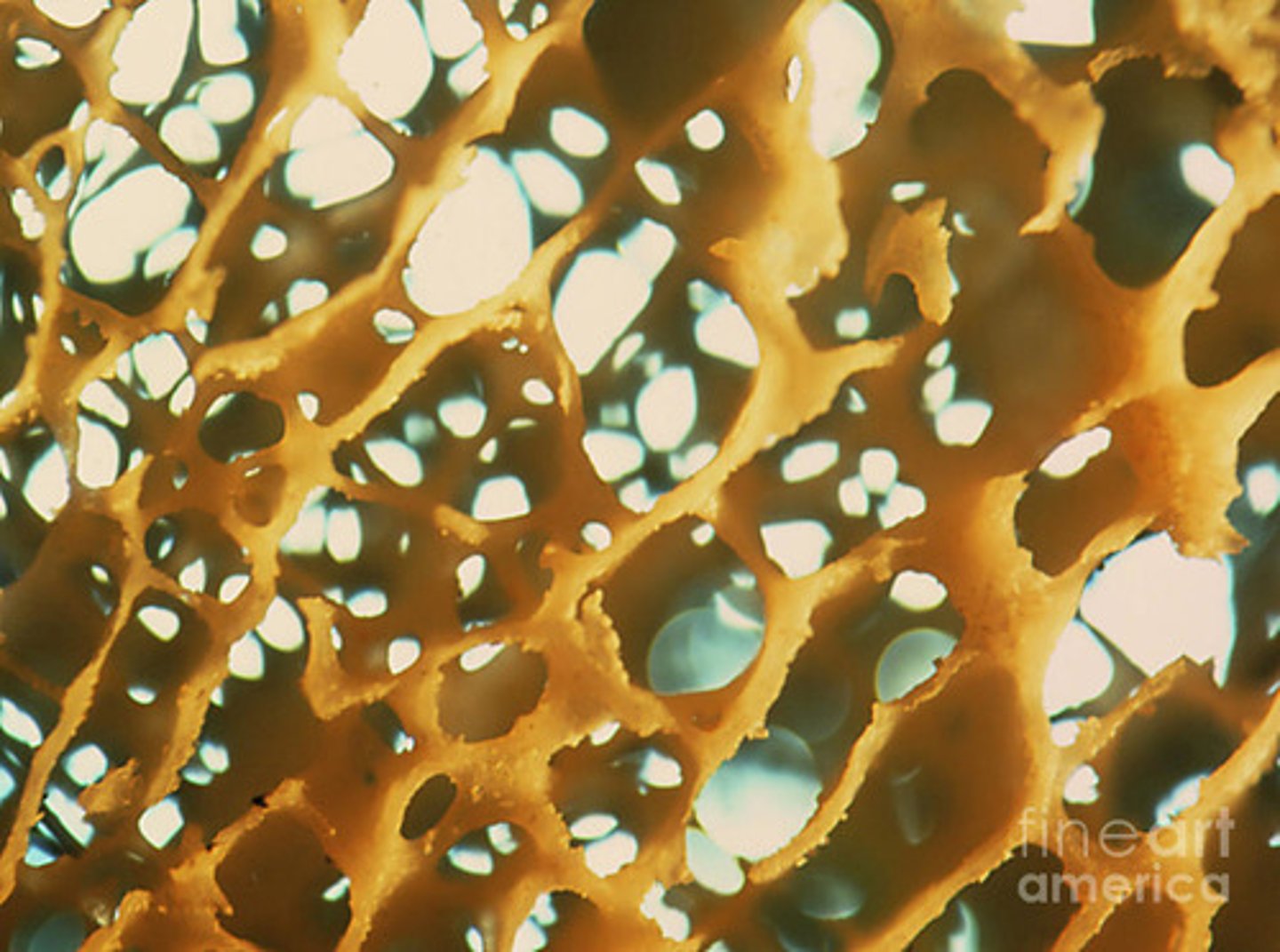
Spongy bones
Airy porricle bone (trabecular bone)
End closest to the point of attachment in a long bone
Proximal Ephiphysis
End furthest from point of attachment of attachment on long bone
Distal Ephiphysis
Shaft (stick) of bone between both ends
Diaphysis
Region between Ephiphysis and diaphysis
Metaphysis
Calcified area of bone where growth plate used to be
Epiphyseal Line
Hyaline cartilage found on ends of epiphysis to prevent friction between bones
Articular Cartilage
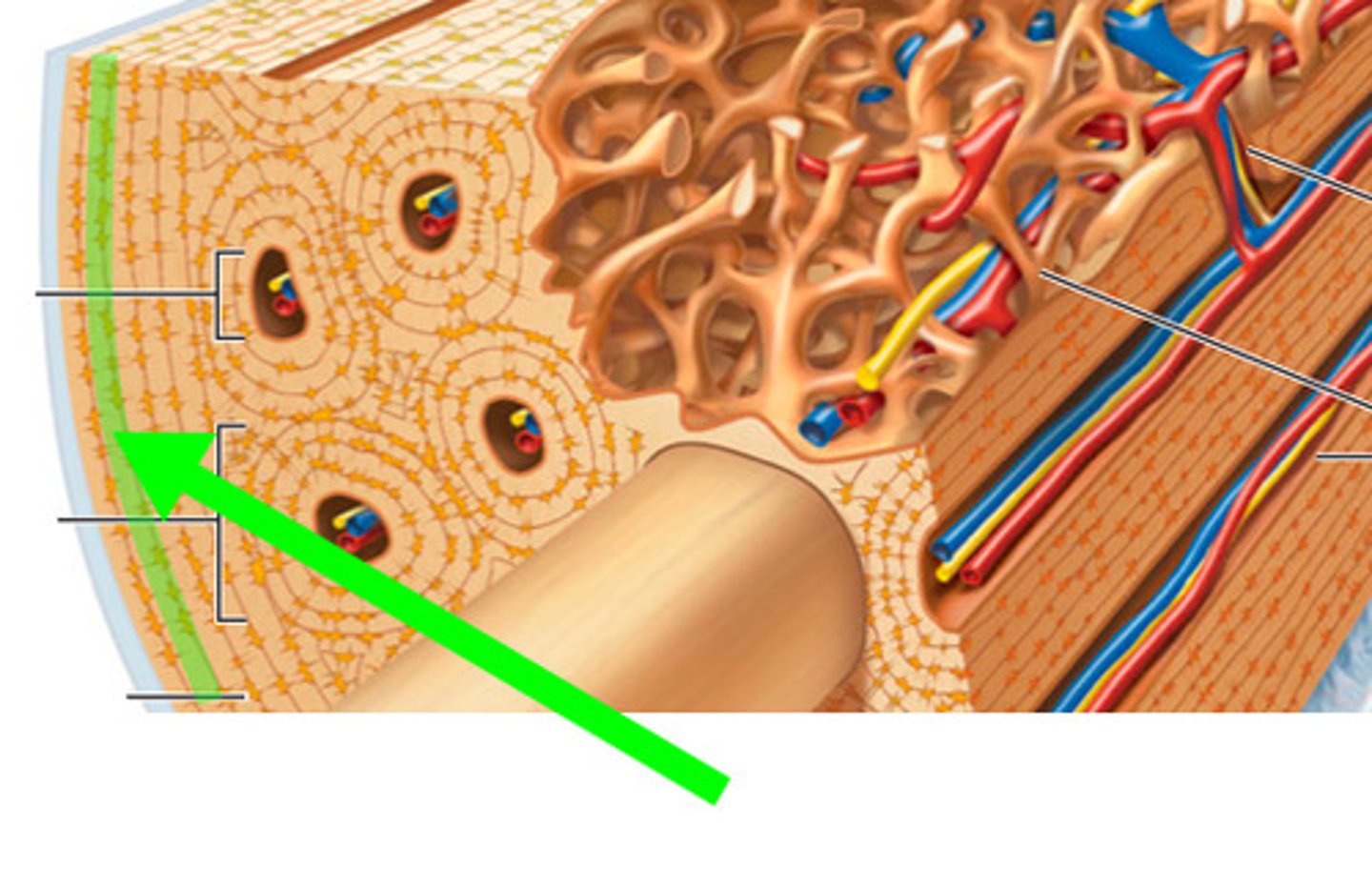
Membrane around bone
periosteum
Where yellow blood marrow is found, cavity in diaphysis
Medullary Cavity
Membrane lining medullary cavity and cavities in spongy bone
Endosteum
Only have inner spongey bone lined by continuous compact bone
All other bones then long bones
Membrane on outer surface that isn't present where articular cartilage is
Periosteum
Made of dense irregular CT
Periosteum Superficial Layer
Made of osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Periosteum Deep Layer
Attach periosteum to the bone
Sharpey's fibers (perforating collagen fibers)
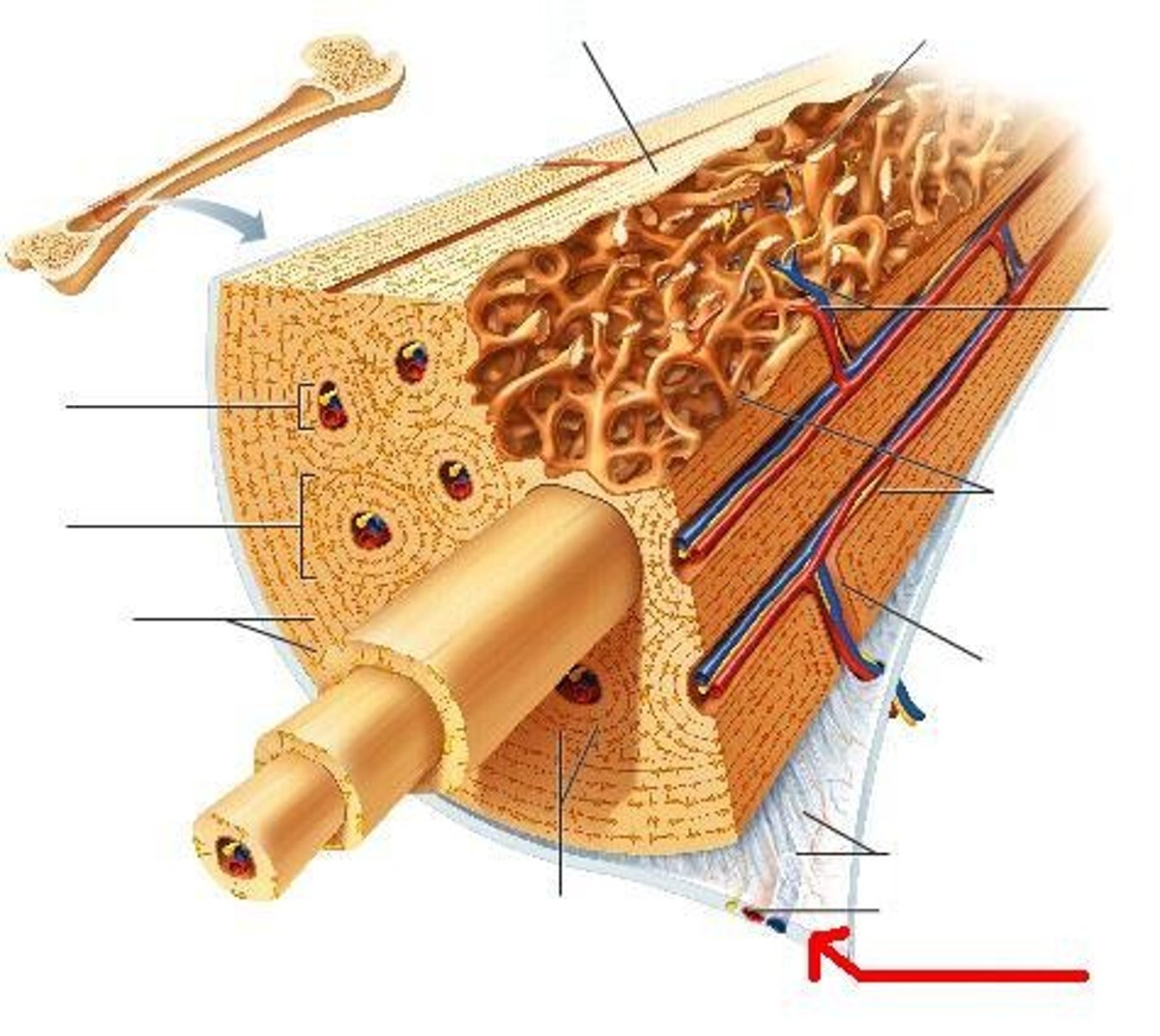
Thin osteogenic membrane that lines inner surfaces of bone
Endosteum
Bone generating
Osteogenic
Bone creating cells
osteoblasts
Bone deteriorating cells
Osteoclasts
Reflects stresses applied to specific locations
Bone markings
Bump on bone
Projection
Smooth and flat surface
Joint surface
Foramens (openings) to allow blood vessels in
Depressions and Openings
Made up of central canal surrounded by concentric lamellae
Osteon or Haversian System
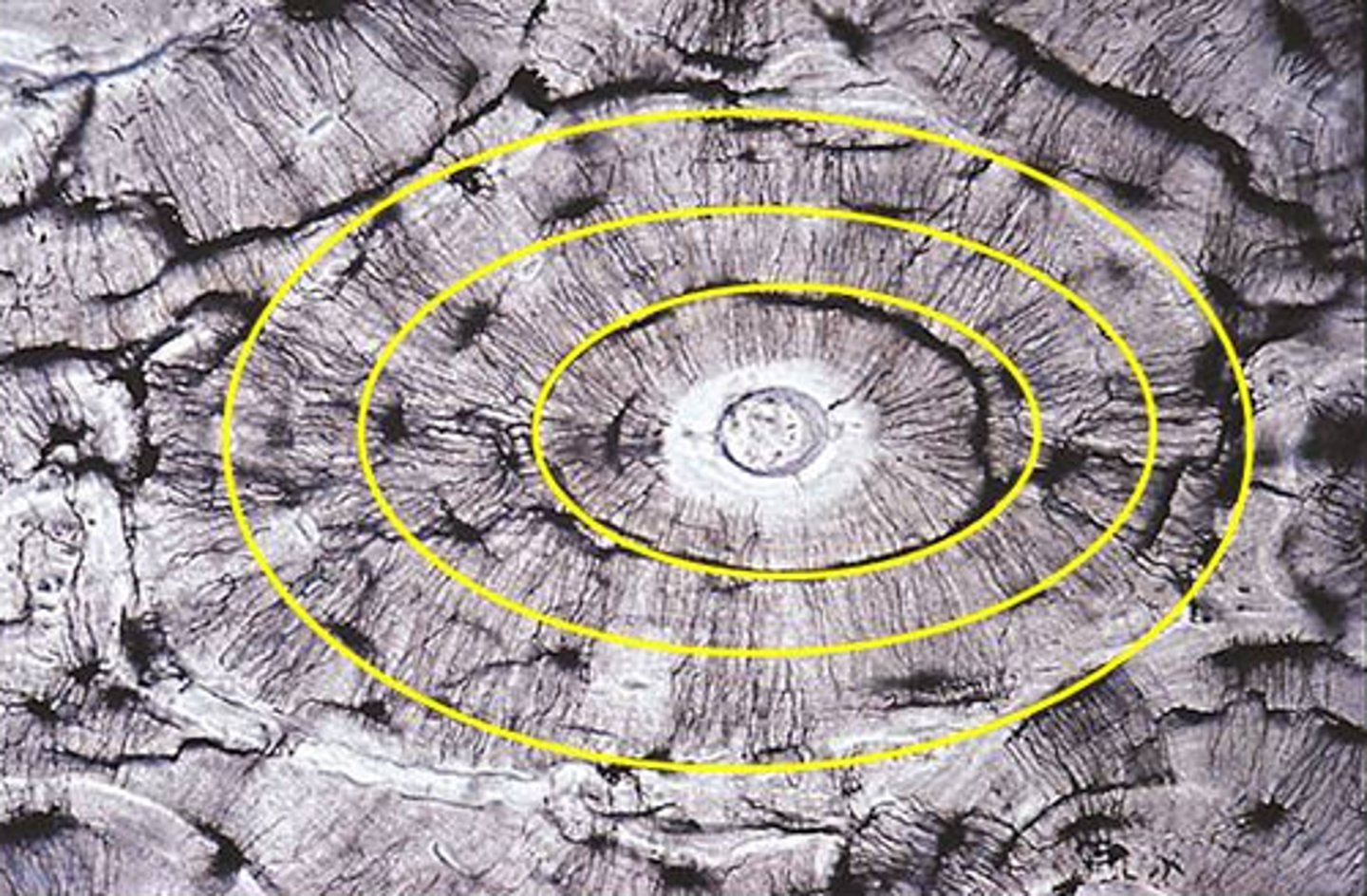
Canal where blood vessels run through in compact bone
Central canal
Calcified ECM that forms rings of osteon
Concentric Lamellae
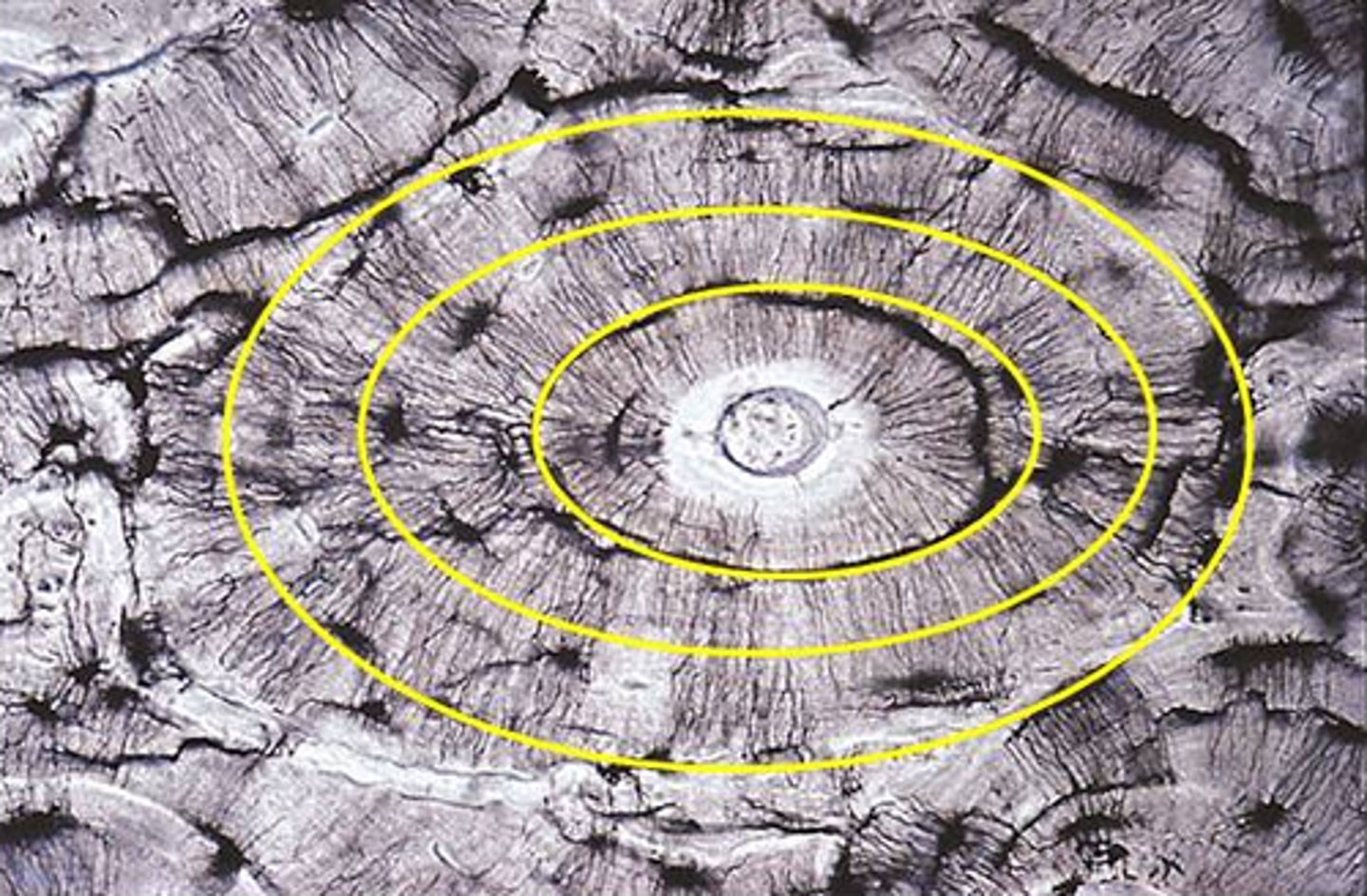
Go around entire bone circumference, don't form osteons
Circumferential Lamellae
Longitudinal canal that connects different osteons together
perforating Canal
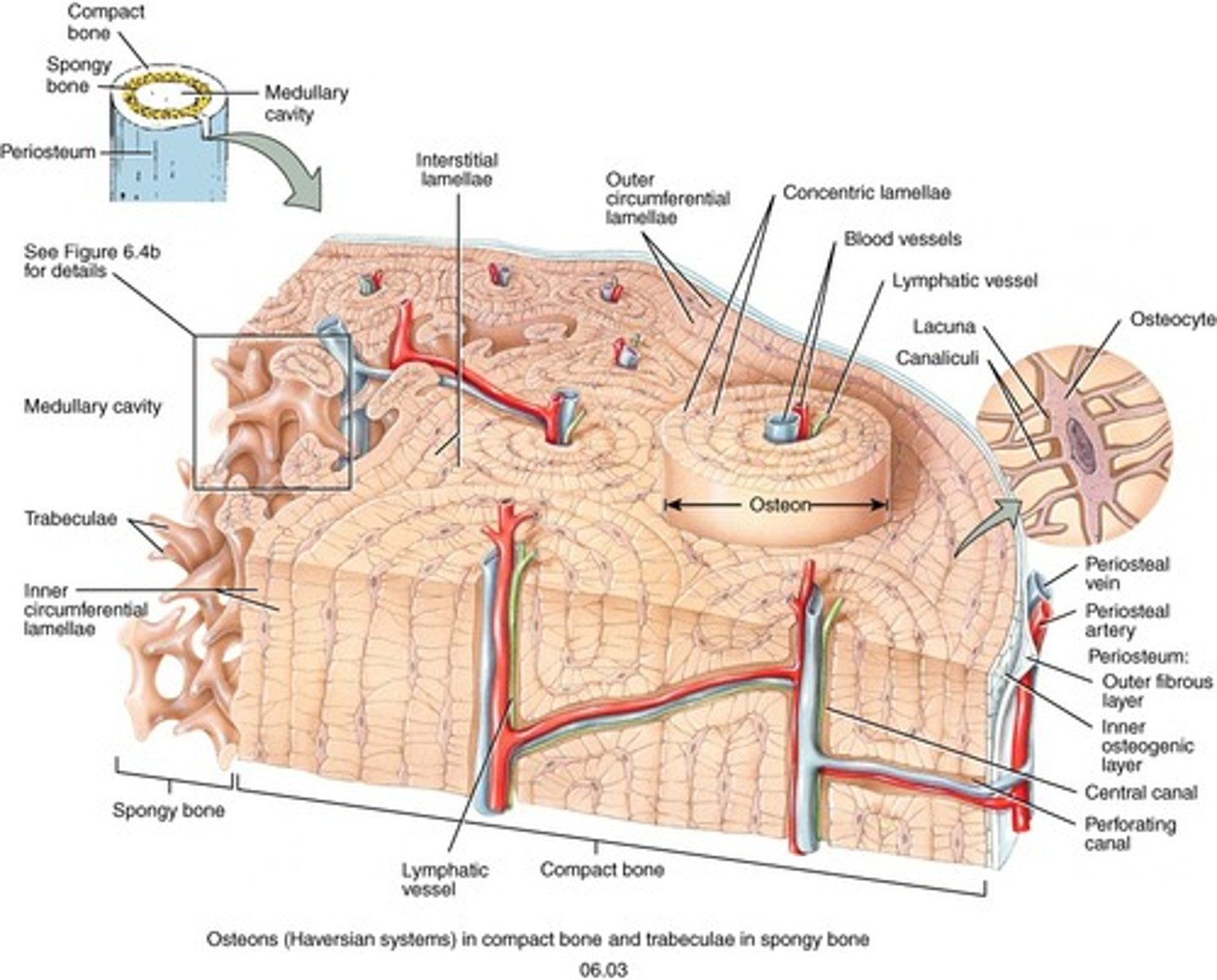
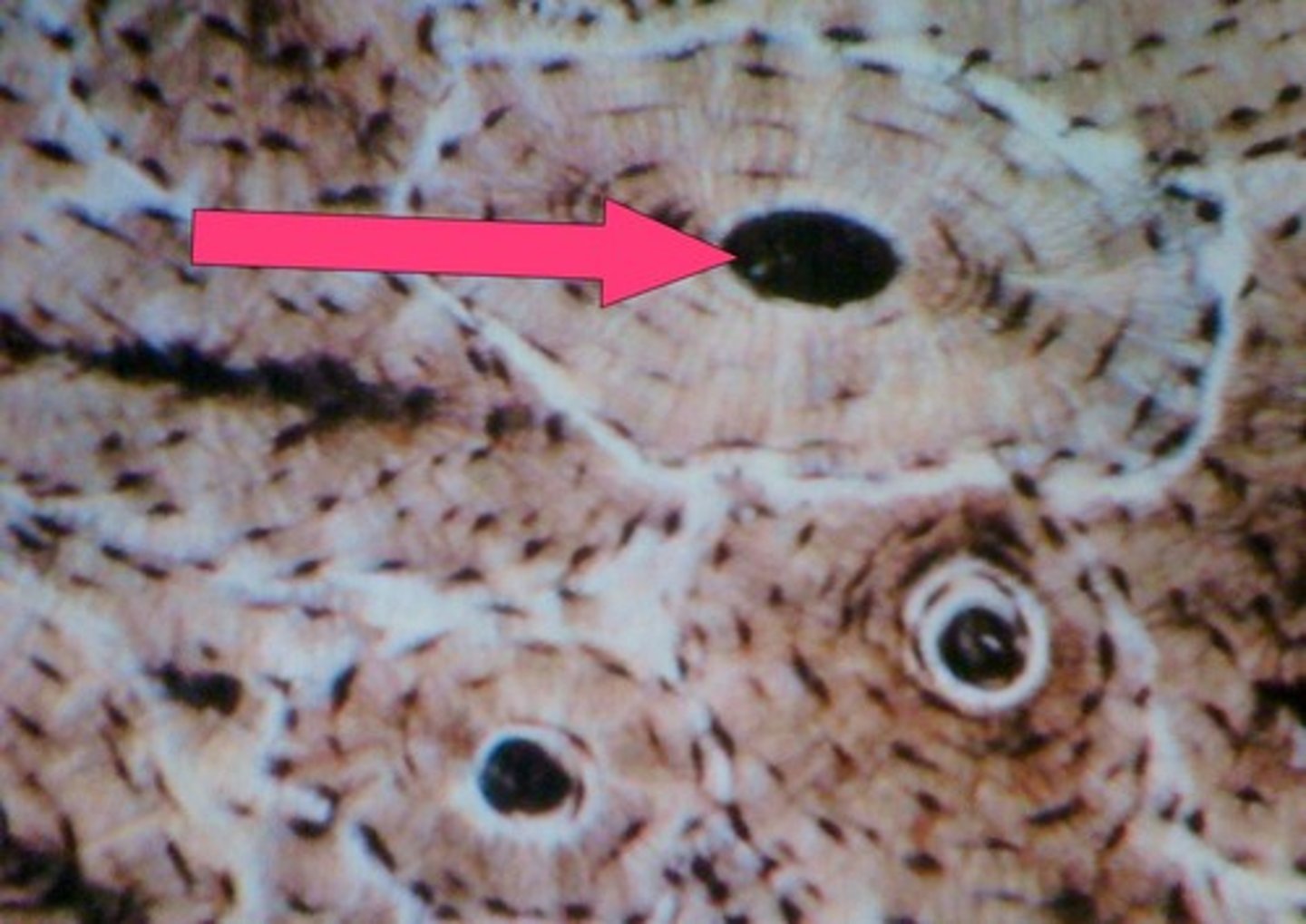
Tunnels that run through Lamellae, osteocytes run through these to reach other osteocytes for nutrients
Canaliculi
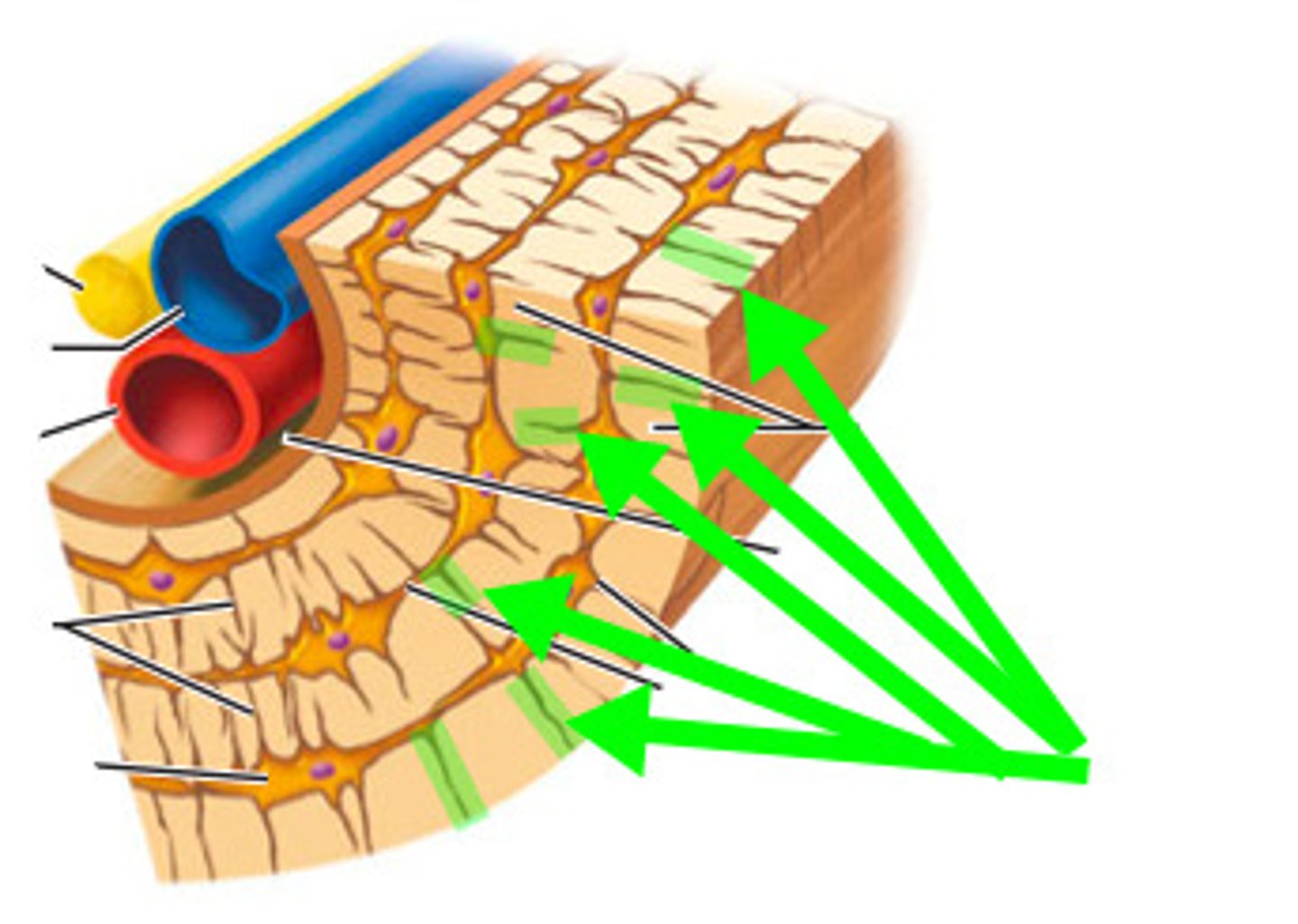
Pits in tissue where cells are found
Lacunae
Lamellae filling in gaps between osteons, calcified ecm
Interstitial Lamellae
Run through Lamellae with each section running in different directions
Collagen fibers
Allows bone to resist twisting forces
Collagen fibers
The "little beams" that make up spongy bone are called
trabeculae
Solid, fed nutrients from surround Endosteum
Trabeculae
Found in spaces between trabeculae
Red bone marrow
Process by which bones forms
Ossification or Osteogenesis
Bone genesis can happen in 4 situations
- formation of bone in uterus
- normal growth through adulthood
- recycling of bones throughout life
- repair of fractures or injuries
Has good regenerative capacity
Bone
Bone forms from mesenchyme arranged in layers that resemble membranes
Intramembranous Ossification
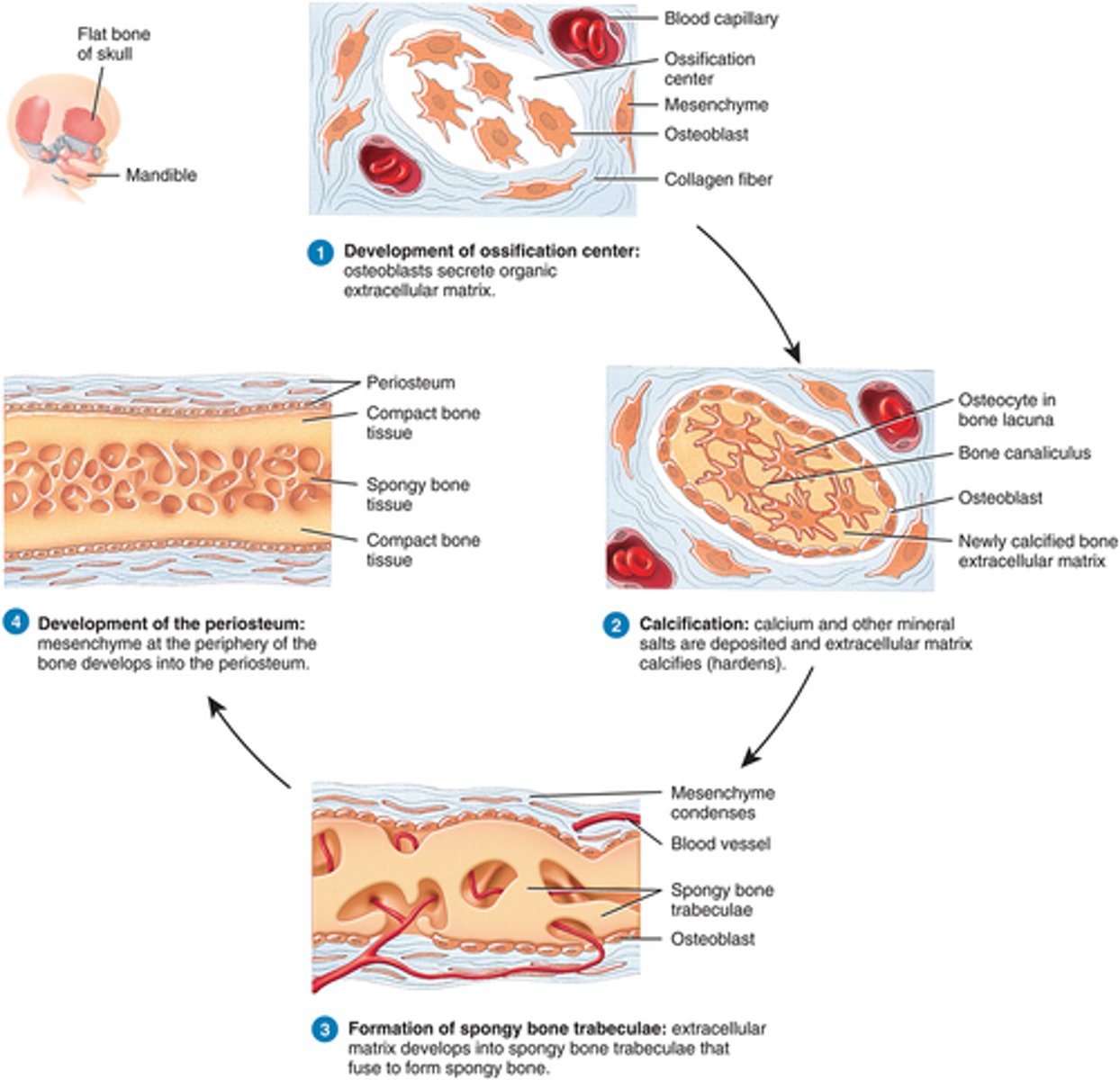
Ossification found in skulls and clavicles
Intramembranous
Bone replaces hyaline cartilage
endochondral ossification
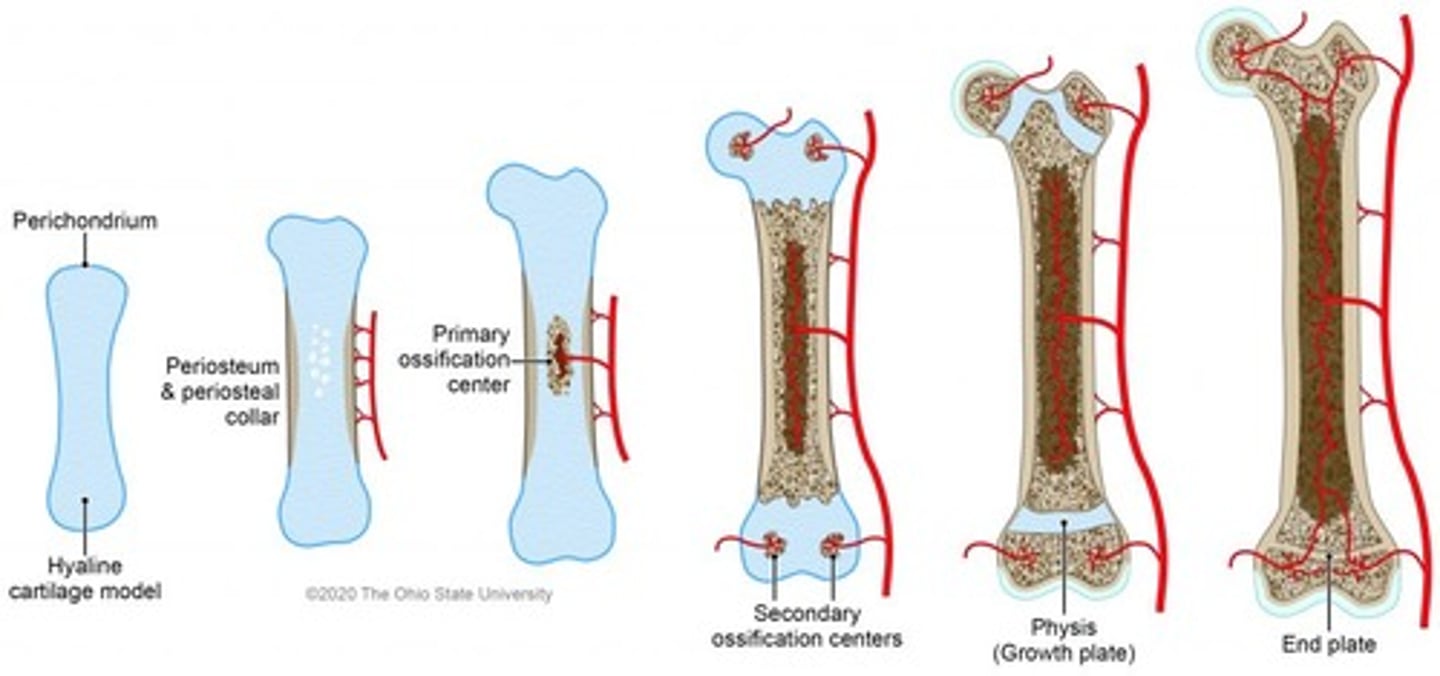
Ossification found in all other bones then skull and claviciles
Endochondrol Ossifcation
mesenchymes form into osteoblasts which then calcify to form compact bone on both sides and periosteum
Intermembranous Ossification
endochondral ossification
process in which bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage
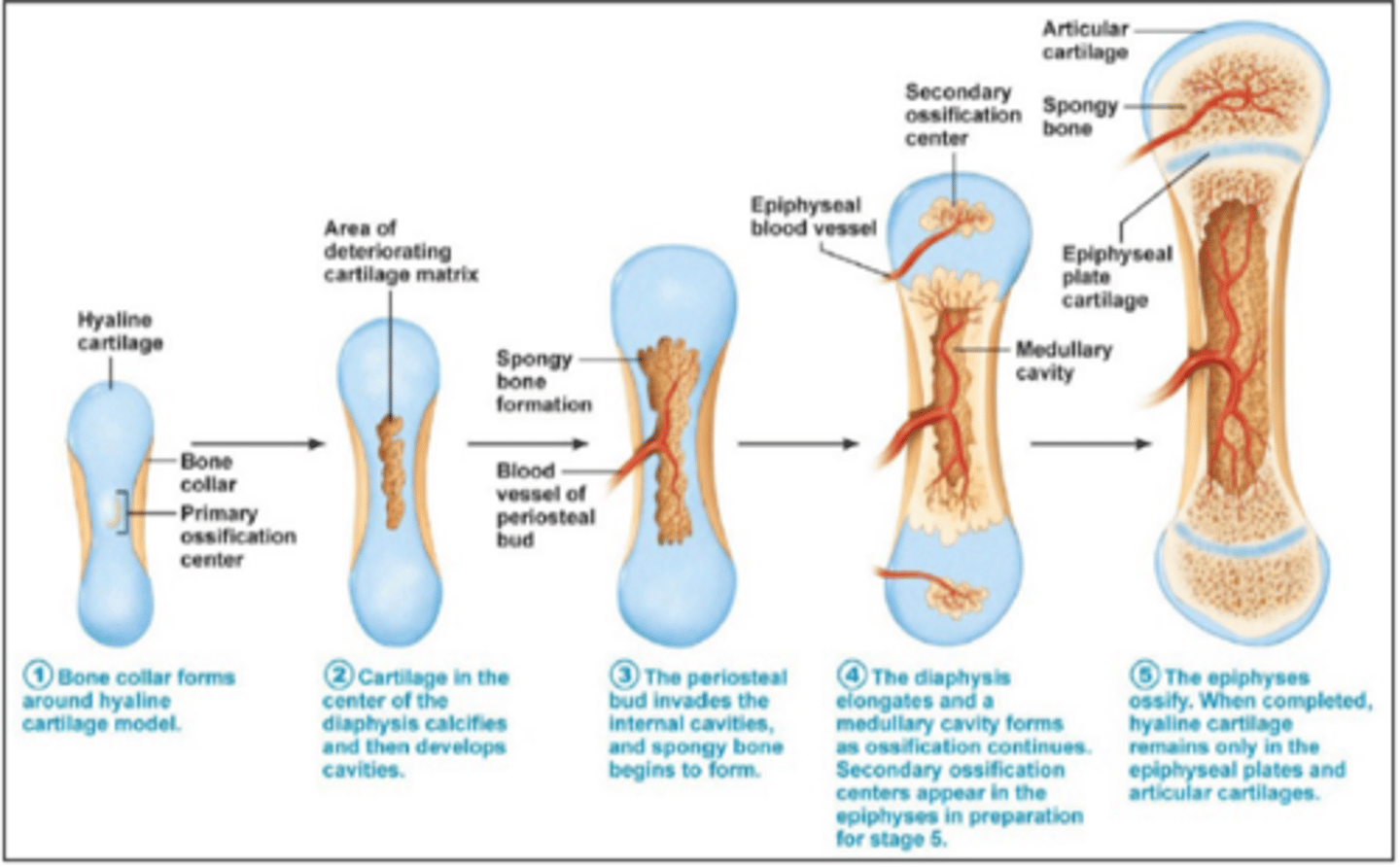
allows for bone growth by growing more caritlage and replacing old cartilage with bone tissue by calcifying it
Epiphyseal Plate
when you stop growing the entire plate calcifies and becomes bone:
Epiphyseal Line
bones get wider by
osteoblasts adding more circumferential lammellae to outer side
ostesoclasts remove bone from inner wall:
about the same rate as osteoblasts add to outside
_______ widens not bone
medullary cavity
taking away bone tissue via osteoclasts
Bone Resorption
secrete hydrochloric acid and lysozomal enzymes to break down bone
osteoclasts
bones break down into this which then get sent to blood stream for reuse
calcium
remaining collagen fibers and osteocytes are removed via
phagocytosis
have ruffled border and multiple nuclei
osteoclasts
creation of bone tissue when needed
Bone Deposition
essential ions and nutrients needed for this to occur
Bone Deposition
Osteoblasts become ____ once calcified
osteocytes
Interchangeable with joints
Articulation
Bones meet at joints however not all joints are
Bone to bone
Meeting site for 2 or more rigid elements
Joint or Articulation
Joints are classified both
structurally and functionally
Criteria for structural classification
- Presence of Synovial Cavity
- types of connective tissue binding rigid elements together
Bones held together by dense collagen fibers with no synovial cavity
Fibrous Joints
Bones held together by cartilage with no synovial cavity
Cartilaginous Joints
Bones held together by ligaments with a synovial cavity
Synovial Joints
Encapsulated space between 2 rigid elements
Synovial Cavity
Based on type and degree of movement allowed
Functional Classification
Immovable joints
synarthroses
Slightly mobile joints (limited)
Amphiarthroses
Free mobile joints (unlimited)
Diarthroses
Only in skull, bones held together by short interconnecting fibers (immobile: synarthroses)
Suture
Joint held together by ligament, no synovial cavity, fibrous tissue length varies (Amphiarthroses)
Syndemosis
Relates to tooth, peg in socket fibrous joints, periodontal ligament holds pegs in socket, no synovial (syntharioses)
Gomphosis
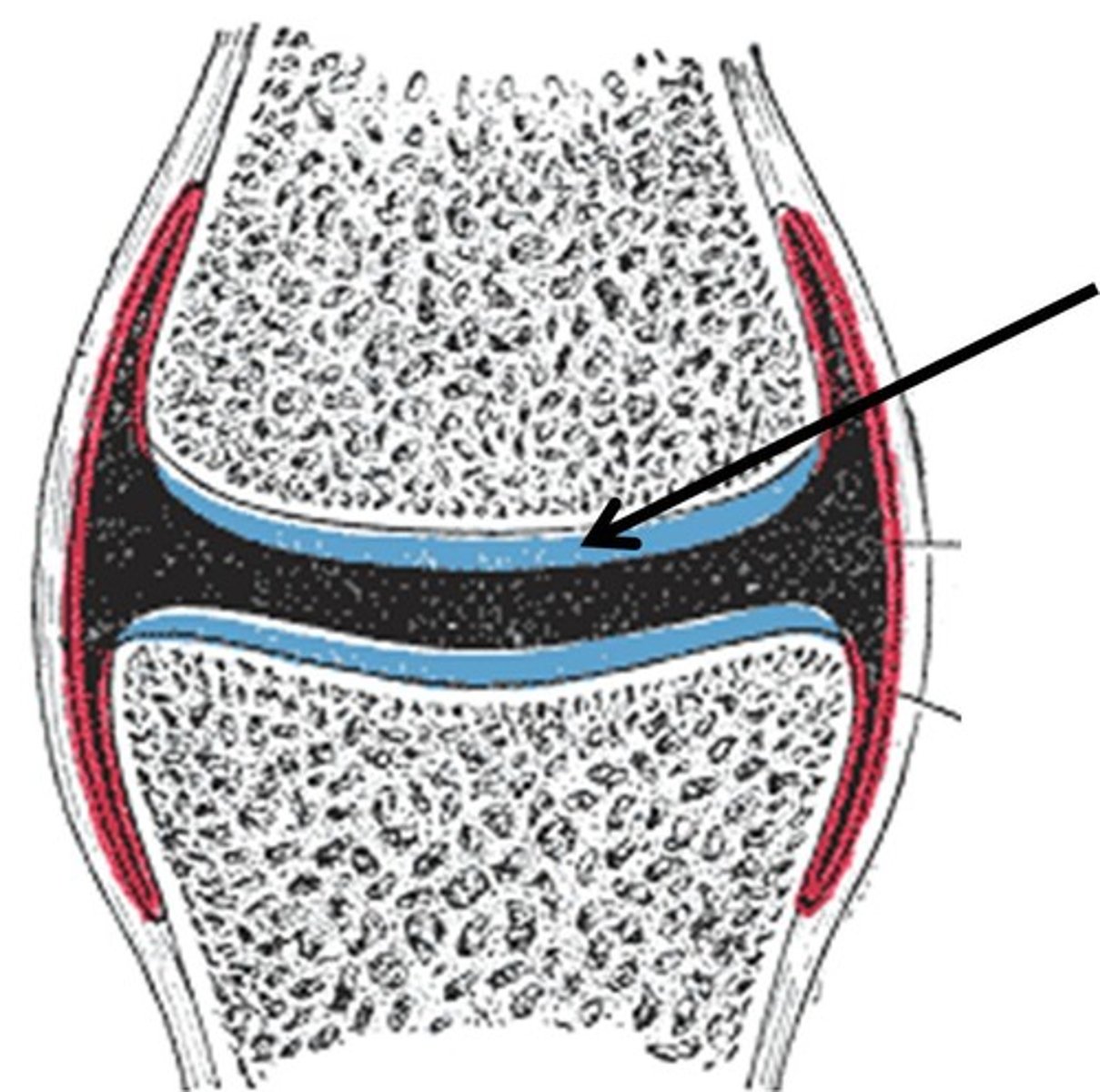
Bones united by hyaline cartilage (areas of high possible friction) (synarthroses)
Syndochondroses
Bones united by fibrocartilage (areas of high possible impact) (Amphiarthroses)
Symphyses
All are freely mobile (diarthroses)
Synovial Joints
Ligaments hold bone together with a synovial cavity present, makes up most joints of body
Synovial Joints
Connects rigid elements together in synovial joints
Ligament
Capsule that encapsulates joint cavity
Articular Capsule
Continuous with periosteum, made of dense irregular ct proper and functions as a strengthening joints
Fibrous Layer of Articular Capsule
Covers insides of any synovial cavity, loose ct that secretes synovial fluid (not present where Articular cartilages is present)
Synovial Membrane
Ends where Articular cartilage begins
Periosteum