Electrocardiogram Lab Quiz
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
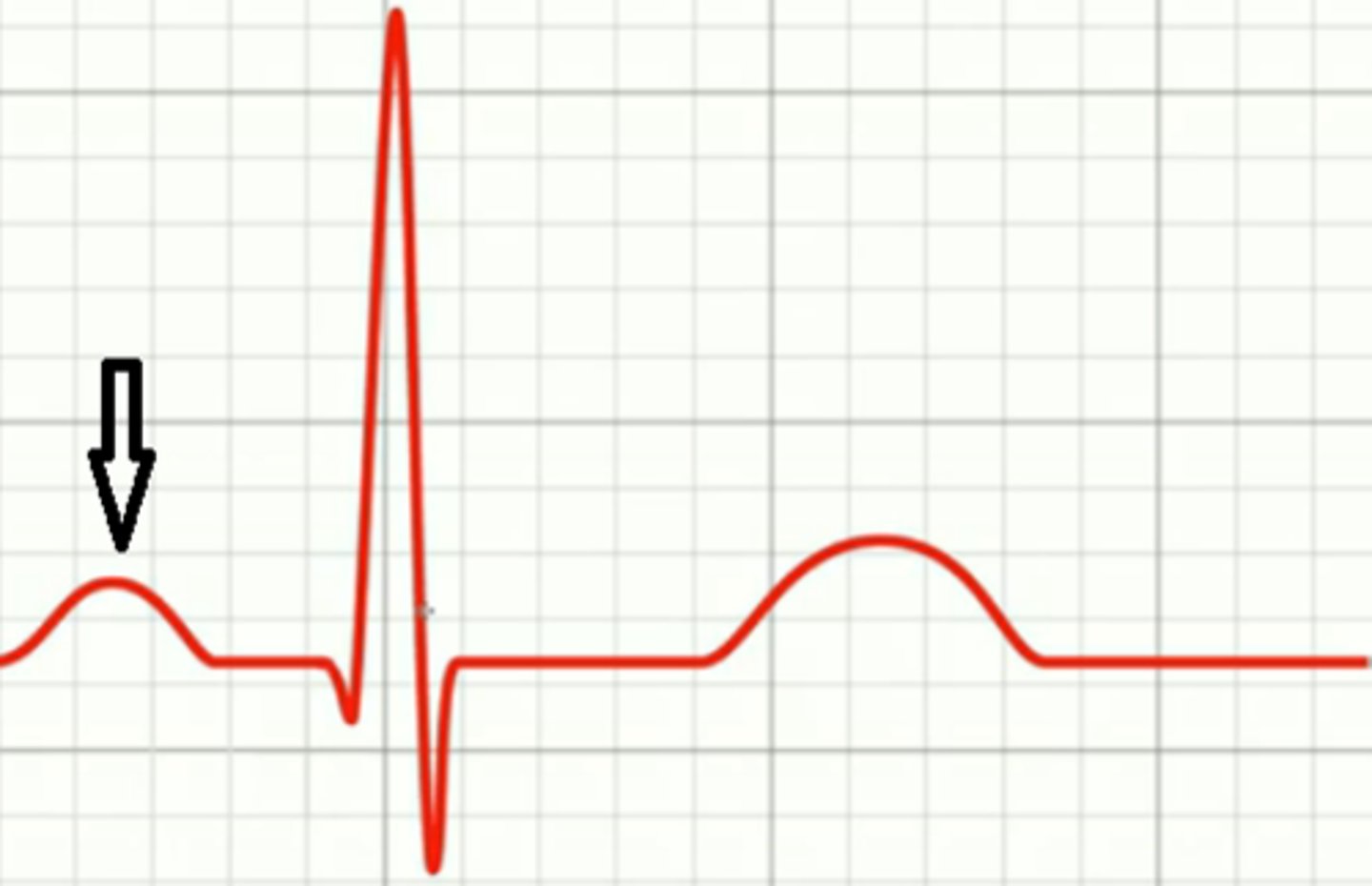
P wave, atrial depolarization
What wave is this and what occurs during it?
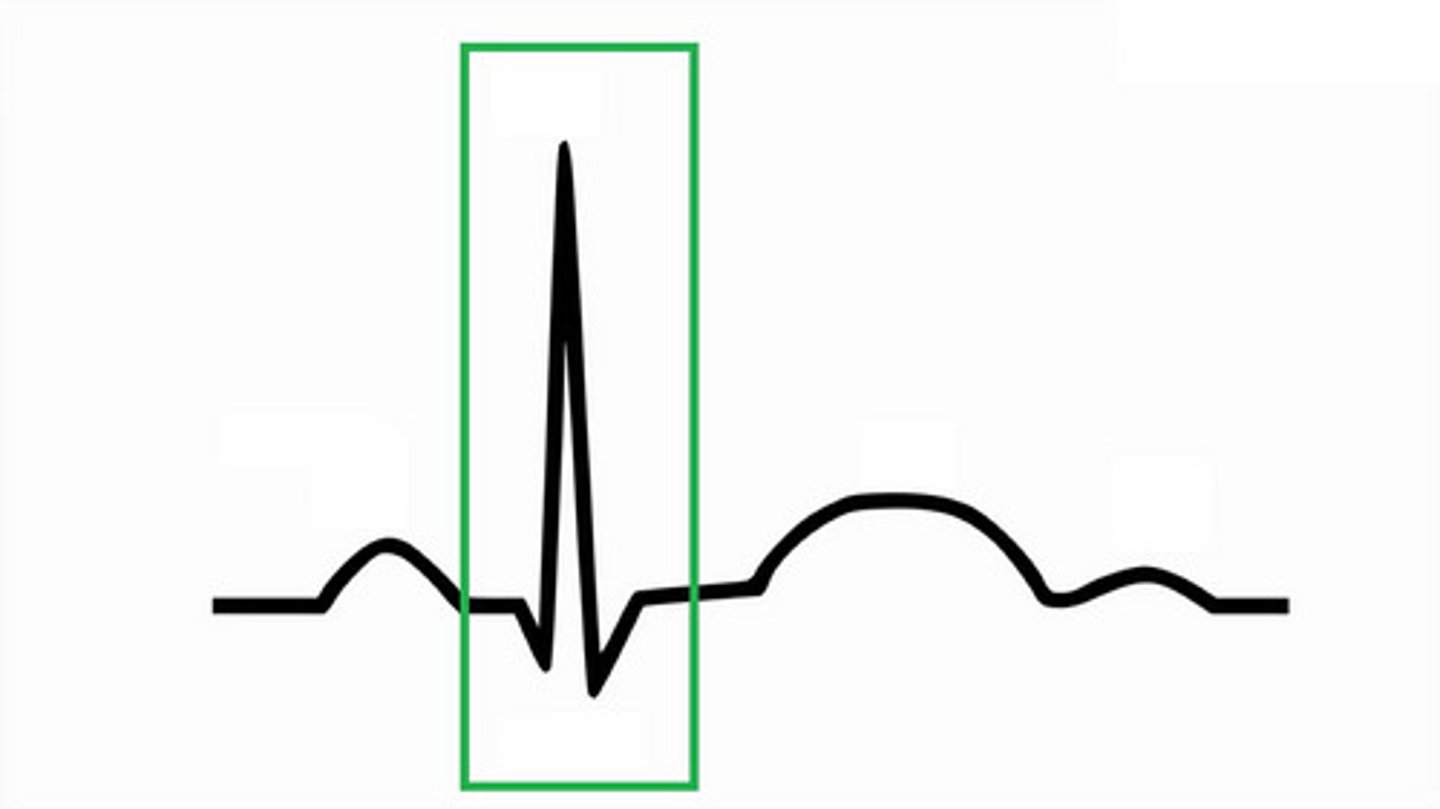
QRS complex, ventricular depolarization (atrial repolarization)
What wave is this and what occurs during it?
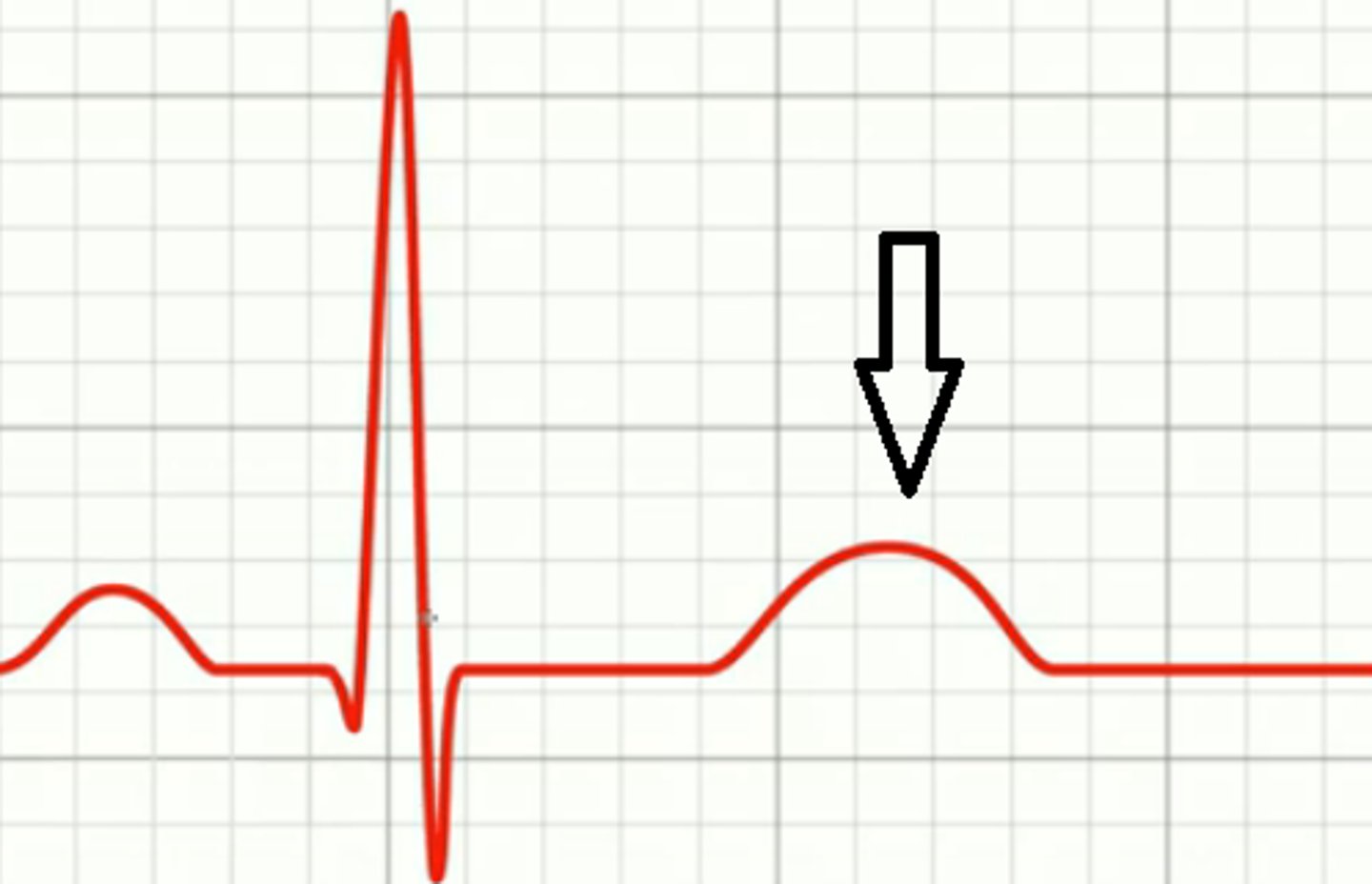
T wave, ventricular repolarization
What wave is this and what occurs during it?
Heart block
What does a longer P-Q interval suggest?
Enlarged ventricle
What does a longer QRS interval suggest?
60-100
What is a normal heart rate
tachycardia
What is a heart rate over 100bpm called?
bradycardia
What is a heart rate under 60bpm called?
exercise causes hypertrophy causing heart to contract slower
Why do athletes commonly have bradycardia?
lead
What is a measurement of the electrical difference between two points on the body?
heart abnormalities
What does the 12 point lead help diagnose?
arms
Lead 1 measure electrical differences between what two body parts?
right arm and left leg
Lead 2 measures electrical differences between what two body parts?
left arm and leg
Lead 3 measures electrical differences between what two body parts?
increases heart rate
How does increasing sympathetic info affect the heart?
decreases heart rate
How does increasing parasympathetic info affect the heart?
increases impulse conduction
How does increasing sympathetic HOROMONES affect the heart?
adrenal glands
Where are sympathetic hormones released?
shorter
How is the cardiac output affected after exercise compared to normal?
QRS axis
What is the average direction impulses move through the ventricles called?
lead with the tallest R wave
How do you determine which lead to use for the direction of the heart?
strength of impulse as it travels vertically
What does the lead aVF measure?
-30
What angle does lead aVL mean?
0
What angle does lead 1 mean?
60
What angle does lead 2 mean?
90
What angle does lead aVF mean?
120
What angle does lead 3 mean?
-150
What angle does lead aVR mean?
halfway between
How do you determine the position angle if two leads have equal magnitude?
hearts anatomical axis
What is the QRS axis of healthy individuals?
changes in breathing
What can change the position of the heart?
different than actual position
How is the QRS axis affected if there's a heart abnormality?
no
Can ECG alone determine the actual position of the heart?
sinus rhythem
What is the ECG tracing of a normal heartbeat called?
arrhythmias
What is the ECG tracing of an abnormal heartbeat called?
no
Does everyone die from arrhythmias?
yes
can arrhythmias be symptomatic OR asymptomatic?
heart disease, alcohol, drugs, infection, present at birth
What are some causes of arrhythmias?
one or more chambers
Where are artificial pacemakers impulses administered to after arrhythmias?
near clavicle under fat
If artificial pacemakers are implanted after arrhythmias where are they placed?
autorhythmic areas
What are other areas of the heart that can initiate impulses other than the SA node?
Junctional Rhythm
What is the abnormality resulting from the AV node initiating impulses instead of SA node?
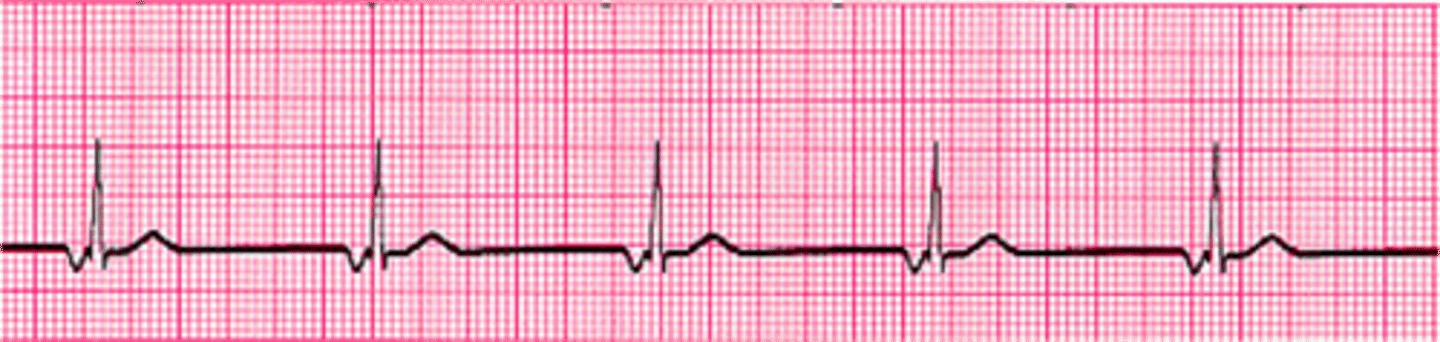
junctional rhythm
What heart abnormality is this?
fibrillation
What is the abnormality resulting in the uncoordinated contracting of heart muscles?
ventricular
What type of fibrillation is a medical emergency?
thrombus and embolus
untreated atrial fibrillation increases the risk of what?
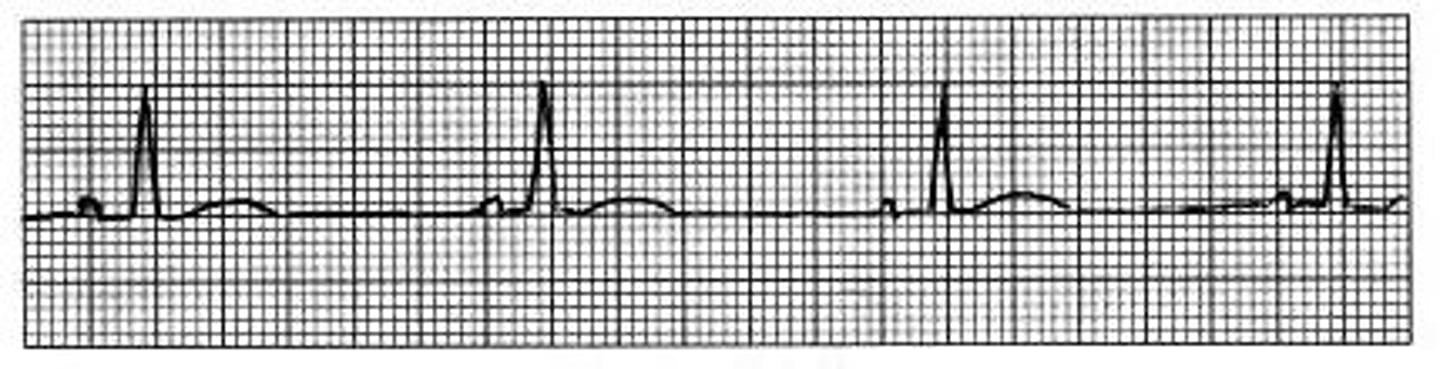
atrial fibrillation
What heart abnormality is this?
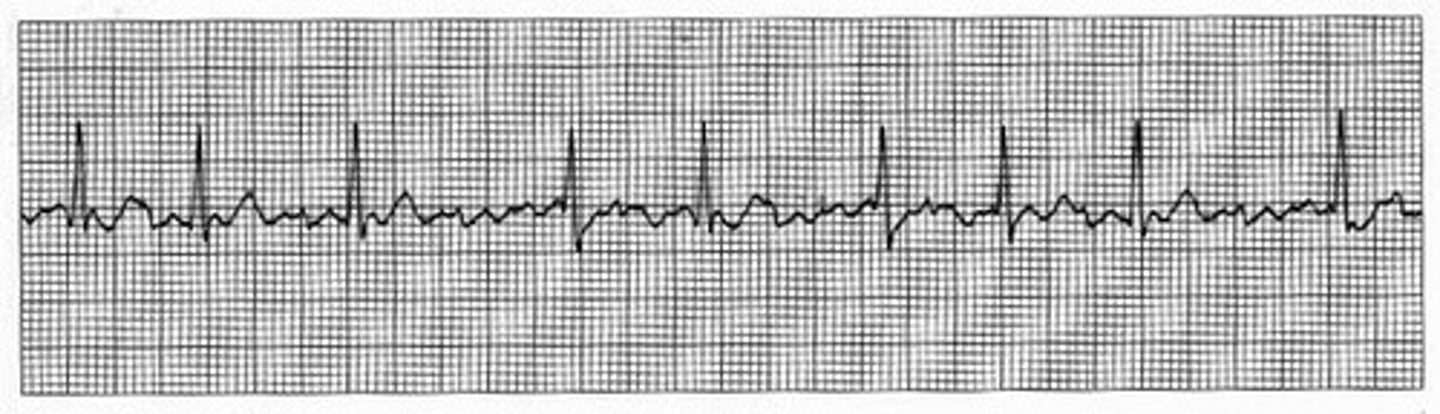
tachycardia
What heart abnormality is this?
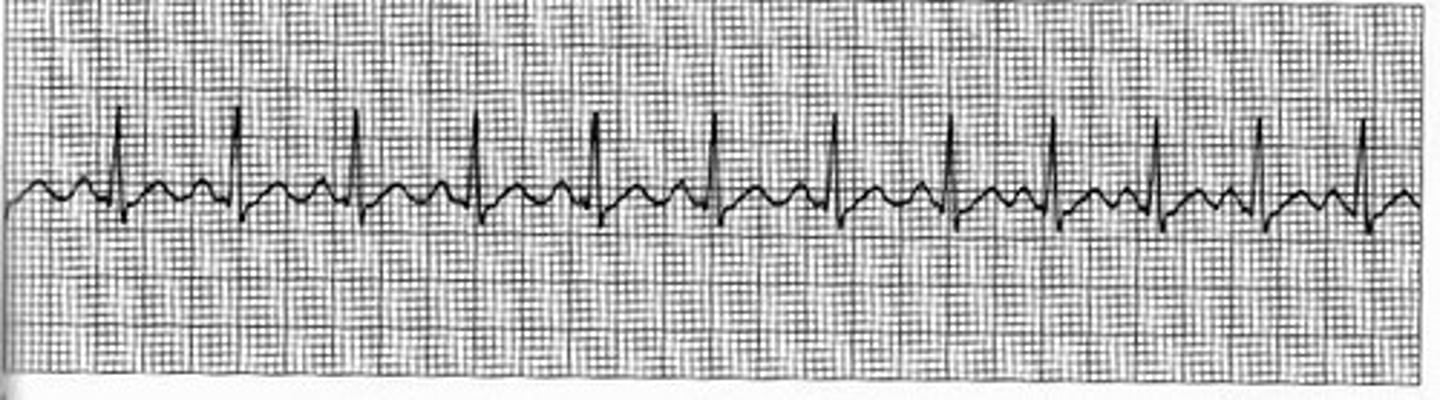
Bradycardia
What heart abnormality is this?
death
untreated ventricular fibrillation increases the risk of what?
anticoagulents
What is the treatment for atrial fibrillation?
defibrillation asap
What is the treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
shocks heart to stop impulses
What is the function of defibrillation?
automated external defibrillators (AED)
What type of defibrillators are available in public places?
diagnose arrhythmias and treat by resetting heart rhythm
What is the function of automated external defibrillators (AED)?
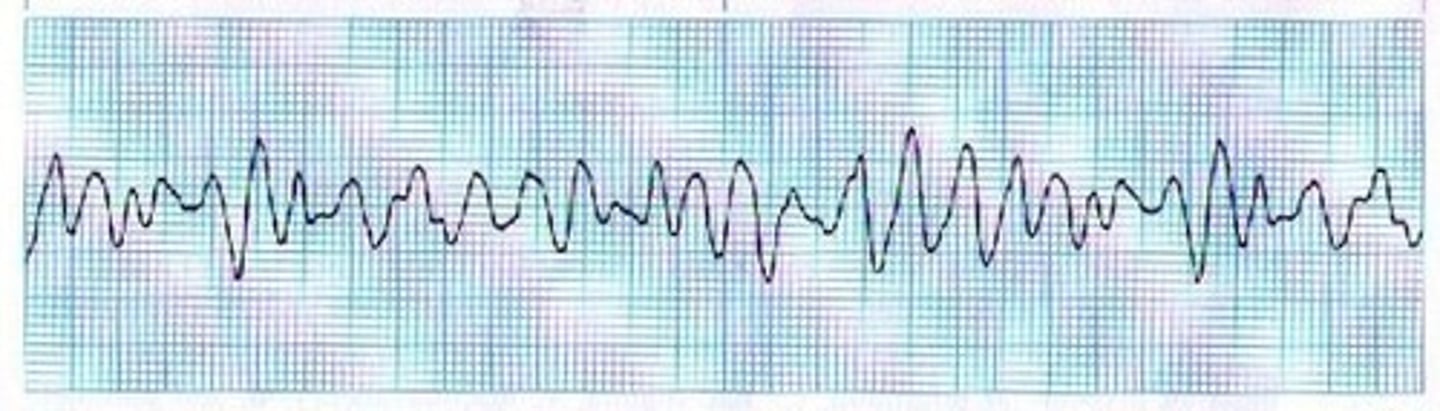
ventricular fibrillation
What heart abnormality is this?
heart block
What abnormality does the SA node transmit impulses, but ventricles don't receive them?
heart block
What heart abnormality is this?
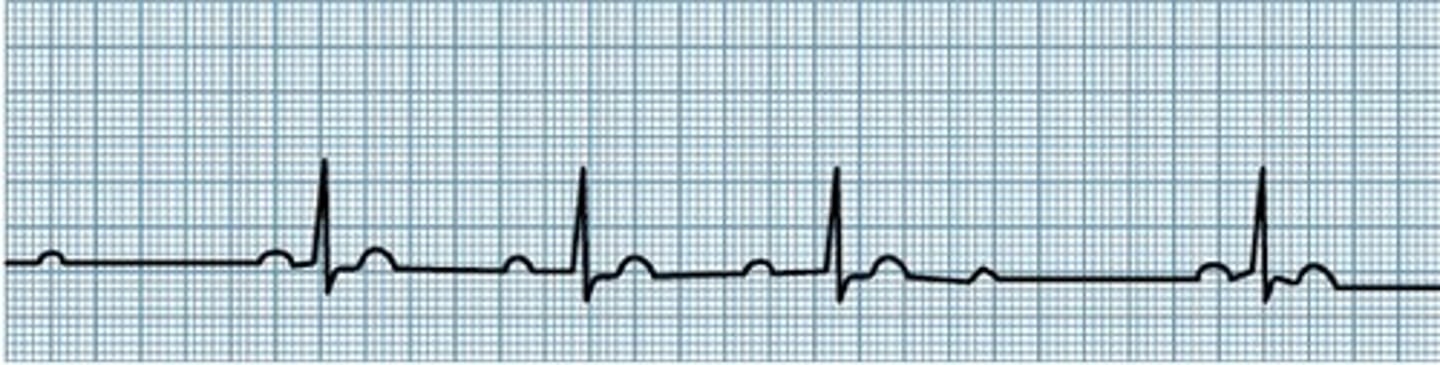
20-60
What is the normal heartbeat produced by an artificial pacemaker?
decreased blood flow or AV node damage
What is the cause of heart blocks?
artificial pacemaker
What is the treatment for heart blocks?
stops impulse and decreases blood flow
How does the blow to the chest actually cause commotio cordis?
commotio cordis
What is the rare heart abnormality caused by a blow to the chest
ascending part of T wave
When does the blow the chest have to occur to cause commotio cordis?
opens mechanical K channels causing ventricular fibrillation
What occurs after commotio cordis?
commotio cordis
What is the second leading cause of death in athletes?
96%
What percent of commotio cordis victims are male?
14
What is the average age of commotio cordis victim?
15
What percent of commotio victims survive?
lack of diagnosis or defibrillator
Why do so many commotio victims die after the trauma occurs?
0
What percent do chest protectors reduce the risk of commotio cordis?
diaphragm contracts increasing thoracic cavity space
Why is the heart more horizontal during inhale?
vertical
During forceful EXHALE is the heart more vertical or horizontal?
horizontal
During forceful INHALE is the heart more vertical or horizontal?