Igneous Rocks Geological Oceanography
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Rocks
Solid aggregates of grains of one or more minerals (exceptions: Volcanic glass- obsidian, and coal)
Classifications
Generally reflect texture (size, shape, and mineralogical interrelationships) and mineralogy
Mineralogy
Igneous it gives info about cooling history
Sedimentary gives info about depositional history
Metamorphic gives info about the tectonic history
The Rock Cycle
Start with Igneous Rocks forming from cooling magma
Weathering, Erosion, deposition, and lithification (cementing the sediments together) forms sedimentary rocks
Heat and pressure on preexisting rocks change them into metamorphic rocks
Melting in the Earth forms magma
Start again!
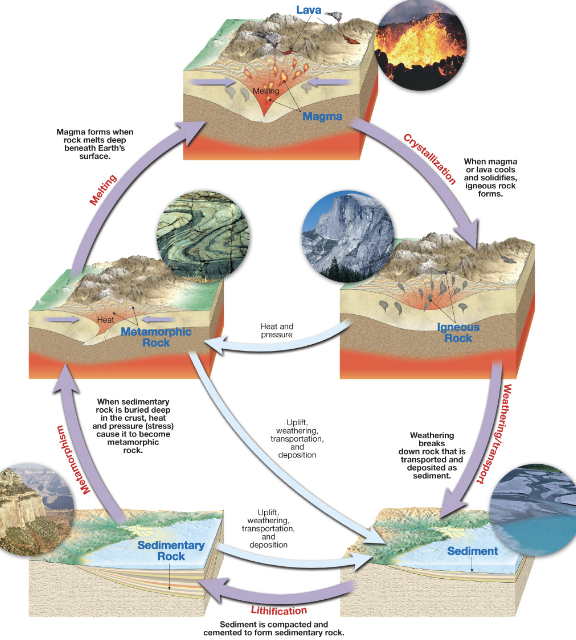
Formation of Igneous Rocks
Form as magma cools and crystalizes
If it occurs inside the Earth, these are termed plutonic rocks
Magma that makes it to the surface is called lava. These rocks are termed volcanic
2 major categories of igneous rocks:
volcanic: called extrusive
plutonic: called intrusive
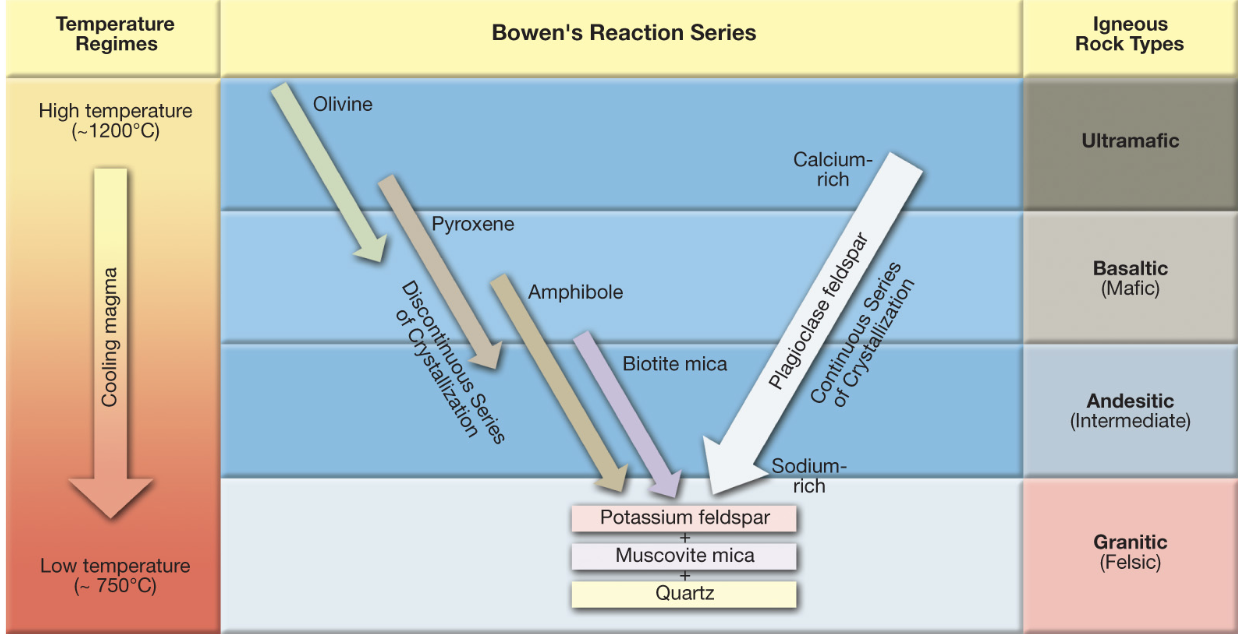
Bowen’s Reaction Series
From top to bottom of Bowen’s Reaction Series:
Decreasing temperature
Dark to light-colored minerals
Decreasing density
Increasing viscosity (increasing resistance to flow) (volcanic flow slows, it gets stuck; large amounts of silica cause this viscosity)
Start w/ Basaltic- the minerals in that section are what make salt (sometimes olivine can be included)
Andesitic- the rock type that these minerals form (biotite mica…)
Granitic- potassium feldspar, muscovite mica, quartz
Aphanitic
Crystals in the rock are fine-grained (smaller than the eye can see)
Texture indicates rapid cooling
Phaneritic
Crystals in the rock are coarse-grained (larger-sized)
Texture indicates slow cooling
Porphyritic
combo of aphanitic (fine-grained) & phaneritic (coarse-grained) textures
Fine crystals are called groundmass
Coarse crystals are phenocryst
this texture indicates slow then fast cooling
Pumice (glassy)
cools really fast, air bubbles mean rock didn’t have time to form crystals so it’s considered glassy, floats
Vesicular
Similar to pumice but heavier & less air pockets, doesn’t float
Ultramafic Rocks
Mostly composed of olivine and pyroxene
ex: peridotite & dunite
plutonic rocks that form deep in the Earth
Mafic Rocks
Rocks with mostly dark crystals
ex: magnesium and ferrum
contain some olivine, pyroxene, amphibole
includes: basalt (volcanic) & gabbro (plutonic)
Intermediate Rocks
both light & dark minerals
mostly plagioclase, some amphibole & pyroxene
includes: andesite (volcanic) & Diorite (plutonic)
Felsic Rocks
Light-colored minerals
quartz, muscovite, k-spar, biotite
includes: Rhyolite (volcanic) & granite (plutonic)