Psych exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:10 PM on 6/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
1
New cards
What is **Self-presentation**?
If one is trying to present himself as intelligent, they will be perceived as more intelligent if they do not conform
2
New cards
Theories why people kill?
Most killers report abuse as a child, The failings of police and official agencies, Poverty or social breakdown in the areas from which the victims came, Declining moral standards, Detrimental effects of promiscuous homosexuality, "Murder by homophobia”
3
New cards
What did B.F Skinner study?
repetition of responses is influenced by rewards or punishments.
4
New cards
What is anthropology?
The study of human cultures and their development
5
New cards
What is sociology?
The study of development, structure and human development
6
New cards
What is pyschology?
The scientific study of the human mind and its functions
7
New cards
What are the ethical guidelines used in research?
Unfair discrimination, Group work cooperation and mutual exchanges among social scientist are required, should act with a view to maintain the image and integrity of their own discipline, Must be aware that their assumptions have an impact on society, informed consent and do no harm
8
New cards
What is the little albert experiment?
Psychologist John Watson exposed Albert, a nine-month boy, to a variety of white objects, such as rabbits and cotton wool. He was then trained to be scared of these objects
9
New cards
Why was little albert unethical?
He was permanently affected by the research, and the mother may not have fully consented to the experiment
10
New cards
What is the milgrim study?
Psychologist **Stanley Milgram** conducted an experiment on obedience where a volunteer “teacher” who was told to provide shocks in increasing increments when the “student” (an actor who was part of the experiment) provided a wrong answer to word-pair questions.
11
New cards
Why was the milgrim study unethical?
Left the subjects feeling as though they killed someone, No informed consent as the couldn’t have known what was going to happen
12
New cards
What is the monster study?
**Wendell Johnson** of the University of Iowa conducted a speech experiment on 22 orphaned children with normal language development. Half were placed in the negative speech therapy group, where they were belittled for every speech error and told they stuttered.
13
New cards
Why was the monster study unethical?
Giving the children negative reinforcement, affected the children for the rest of their lives. The kids could not consent and no debriefing after the experiment. Also nobody stepped into help them
14
New cards
What is the david rimer experiment?
A botched circumcision when he was eight months old resulted in Bruce Reimer’s penis being burned off. Psychologist **John Money** recommended that his parents raise him as a female, “Brenda.”
15
New cards
What is unethical about the david reimer experiment?
He never got to make the decision, he was told how to grow up
16
New cards
What is the Stanford prison experiment?
The Stanford prison experiment was a study of the psychological effects of becoming a prisoner or prison guard.
17
New cards
Why was the prison experiment unethical?
There is **psychological** and **physical harm** being done to the prisoners
18
New cards
What are the four temperments?
Sanguine, phlegm, choler, melancholy
19
New cards
What did the four temperments tell us?
Different combinations of the temperaments caused different personality traits and illnesses
20
New cards
who is Hippocrates?
Called the father of modern medicine, studied people and noted that people with brian injuries acted differently. He concluded the brain was the source of ‘our pleasures, joys, laughter, sorrows, pain, grief, and tears.’
21
New cards
Who is Wilhelm Wundt?
He opened the first experimental psychology lab, it is thought to be the beginning of modern psychology. Known as the father of psychology
22
New cards
What is sensation?
The passive process of bringing information from the outside world into the body and the brain
23
New cards
What is preception?
The active process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting the information brought to the brain by the senses
24
New cards
What are literal optical illusions?
create images different form the objects that make them

25
New cards
What are Physiological optical illusions?
**are the results of our eyes receiving excessive stimulation of a specific type (brightness, color, movement.)**
26
New cards
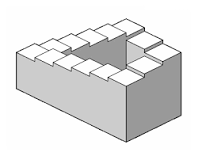
What are cognitive optical illusions?
results from the brain making unconscious inferences
27
New cards
Who is H.M?
H.M had his hippocampus removed to stop his seizures. After the sugery HM had lost his memory and had trouble remembering the simple tasks that he did throughout the day.
28
New cards
Who is clive wearing?
Cilve contracted a disease that attacked his central nervous system, he is unable to store new memories and has total amnesia
29
New cards
why is clives story so important?
Because of damage to the hippocampus he is unable to turn short term memory into long term memory
30
New cards
What are the three types of memory?
sensory, short term and long term
31
New cards
What is sensory memory?
Ultra-short term memory degrades 200-500 milliseconds after perception
32
New cards
What is short term memory?
A place to temporarily store information. Used while solving problems aka working memory
33
New cards
What is long term memory?
Information that is stored for 30-40 seconds to a lifetime
34
New cards
What are the two types of long term memory?
Implicit, explicit
35
New cards
What in implict procedural memory?
How to play golf, ride a bike , drive a car walk, talk
36
New cards
What is implicit priming memory?
We’ve heard it a lot or rehearsed it. Its associated with other things we remember
37
New cards
what is explict semantic memory?
Memory for facts and information
38
New cards
What is explicit episodic memory?
Autobiographical memory of personal experiences
39
New cards
What was freuds theory of the mind?
Freud thought early childhood experiences, especially sexual connections strongly influenced adult personality, and is the base of adult emotional problems
40
New cards
What are the 3 aspects of the human mind?
**Conscious:** (The thoughts and perceptions)
**Preconscious:** (Memories and stored knowledge)
**Unconscious:** (immoral urges, selfish needs, irrational wishes)
**Preconscious:** (Memories and stored knowledge)
**Unconscious:** (immoral urges, selfish needs, irrational wishes)
41
New cards
What is the ID?
is the primitive and instinctive component of personality. It consists of all the inherited components of personality present at birth. (Every wishful impulse should be satisfied)
42
New cards
What is the super ego?
Incorporates the values and morals of society which are learned from one's parents and others. From the age of 3-5. (Controls the IDs decsion making)
43
New cards
What is the ego?
Mediates between the desires of ID and demands of the superego. It is the decision making component and takes into consideration the rules and means of society
44
New cards
What is psychoanalysis?
a process whereby patients discuss their background feelings and experiences with a trained psychologist.
45
New cards
What is **Freud’s Theory of Psycho-sexual Development?**
Failure to progress smoothly through a particular stage can cause **fixation** – a tendency to continue to engage in behaviours associated with that stage.
46
New cards
What are the 5 stages of frueds theory?
Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency ,Genital
47
New cards
What is the oral stage?
This occurs from birth to about 1 year, and the libido is focused on the mouth. **Gratification from oral behaviours**, such as sucking, biting, and chewing.
48
New cards
What happens if you get fixated on the oral stage?
an excessive use of oral stimulation, such as cigarettes, drinking or eating.
49
New cards
What is the anal stage?
Gratification from defecation. This period occurs about age 2 and 3 yrs. **Conflict over toilet training. First encounter with rules.**
50
New cards
What happens if you become fixated on the anal stage?
Fixation at this stage can result in stinginess, stubbornness, or orderliness, as well as messiness.
51
New cards
what is the phallic stage?
This period starts about age 4-5 years.Gratification from genital stimulation. Resolution of the Oedipus Complex
52
New cards
What is the Oedipus Complex?
a conflict between the child’s sexual desire for the parent of the opposite sex and fear of punishment from the same-sex parent.
53
New cards
What is the latency stage?
This lasts from about the age of 7 until puberty, and this is a period of rest where there are no developmental events. Sexual impulses are repressed and Development of friendships
54
New cards
what is the genital stage?
Begins at puberty involves the development of the genitals, and libido begins to be used in its sexual roleGratification from **genital stimulation,** Development of **intimate relationships**
55
New cards
What is regression?
Abandonment of regular coping mechanisms and fall into habits of their younger self. Ex. a person fixated on an early developmental stage ight cry or sulk hearing unpleasant news
56
New cards
what is Intellectualization?
Avoids thinking about the situation and only focuses on the intellectual components. Ex. If someone ends a relationship the victim will think about ways to spend more time with friends rather than the emotional concepts
57
New cards
what is displacement?
involves taking out our frustrations, feelings, and impulses on people or objects that are less threatening. Ex. after a bad day, taking your emotions out on friends or family
58
New cards
what is sublimation?
Allows us to act out unacceptable impulses by converting these behaviors into a more acceptable form. Ex. a super angry person might take up kickboxing
59
New cards
What is projection?
Involves taking our own unacceptable qualities or feelings and ascribing them to other people. Ex. If you have a strong dislike for someone you might believe that they don’t like you.
60
New cards
What is rationalization?
Involves explaining an unacceptable behavior or feeling in a rational or logical manner, avoiding the true explanation for the behavior. Ex. if someone is turned down for a date they might rationalize the situation by saying they never found the other person attractive
61
New cards
What is reaction formation?
Taking up the opposite impulse or behavior.Ex. treating someone you strongly dislike is friendly.
62
New cards
What is the cognitive component of emotion?
The mental feeling of being happy sad or angry
63
New cards
What is the physical component of emotion?
**the physical components of feeling emotion, tense muscles or pounding heart**
64
New cards
What is the behavioural component of emotion?
**Withdrawal, body language or facial expression**
65
New cards
What are the 3 skills of emotion?
Emotional awareness, Harness emotions and apply them to thinking and problem solvin, Managing emotions
66
New cards
What did Harlow study? What was his experiment design?
He studied monkey reactions, to a cloth mother and a mother with a bottle. He would put the monkeys through different tests and see what would happen
67
New cards
What did Harlow’s experiments reveal?
The importance of mothers' love for childhood development. Without the love of a proper mother the monkeys would not fit in many different aspects.
68
New cards
Ways we learn?
From experiences, Innate drive and instinctive reactions
69
New cards
What is stimuli learning?
Objects or events that produce a response from a person or other living thing.
70
New cards
what was Ivan pavlov interested in studying?
Learning to transfer a natural response to on stimulus to another, Classical conditioning
71
New cards
What did Albert Bandura think?
You learn by observing people who act of models of our behavoir (observational learning)
72
New cards
What are the four processes of observational learning?
* **ATTENTION** - pay attention to the behaviour of others.
* **RETENTION** - you store a mental representation of what you observe in your memory (what worked well).
* **REPRODUCTION** - Put stored memory into action (practice).
* **MOTIVATION** - you must be motivated to practice skills (believe that the skill is useful or important)
* **RETENTION** - you store a mental representation of what you observe in your memory (what worked well).
* **REPRODUCTION** - Put stored memory into action (practice).
* **MOTIVATION** - you must be motivated to practice skills (believe that the skill is useful or important)
73
New cards
What did this experiment teach us about learning that was in opposition to the ideas of Pavlov and Skinner?
Learning isn’t all about conditioning, it can be about observing someone's behavior
74
New cards
What is the bobo doll experiment?
A woman beat up the doll while a kid watched. The kid would mimic what they saw
75
New cards
What stage of sleep do most of our dreams occur in?
During REM sleep is where most of our dreams occur, most memorable dreams occur in this stage too
76
New cards
What links does stress have to our dreams?
Stress can lead to an increase in REM sleep due to a problem regulating the stress hormone
77
New cards
What are the perpose of dreams?
They increase problem solving and adi memories
78
New cards
What are the 5 stages of the sleep cycle?
Light Sleep in NREM: eyes move slowly, and muscle activity slows
NREM: the body prepares for deep sleep, the body temperature drops and heart rate slows
Deeper Sleep in NREM: this is deep sleep, this is where nightmares, sleep talking occurs
REM: rapid eye movement, increased blood pressure, heart rate and brain activity, and majority of dreams happen in this stage
NREM: the body prepares for deep sleep, the body temperature drops and heart rate slows
Deeper Sleep in NREM: this is deep sleep, this is where nightmares, sleep talking occurs
REM: rapid eye movement, increased blood pressure, heart rate and brain activity, and majority of dreams happen in this stage
79
New cards
Information Processing Theory as to why we dream?
sort out and process the day’s events and store them into memory
80
New cards
Physiological Function Theory as to why we dream?
result of neural development and preserves pathways by providing brain stimulation
81
New cards
Cognitive Development Theory as to why we dream?
draw on our knowledge and understanding of the world, mimicking reality
82
New cards
Neural Activity Model as to why we dream?
REM sleep triggers neural activity and dreams are a side
83
New cards
History of mental illness?
\
* **Middle Ages (5th - 15th Century): Exorcism**
* **15th & 16th Century: burned on the stake as witches**
* **18th Century: Confined to asylums**
* **1793: Patients in asylums were aloud to roam**
* **19th and 20th century: Medical drugs became available so did therapy**
* **Middle Ages (5th - 15th Century): Exorcism**
* **15th & 16th Century: burned on the stake as witches**
* **18th Century: Confined to asylums**
* **1793: Patients in asylums were aloud to roam**
* **19th and 20th century: Medical drugs became available so did therapy**
84
New cards
What were/are the types of treaments for mental illness?
Shock therapy, isulin coma, lobotomy, pills
85
New cards
what is todays approch to mental illness?
Today we have counseling and various forms of therapy in combination with specific medication for specific illnesses. We are even trying psychedelics for some patients.
86
New cards
Medical care of mental illness?
Psychological disorders have **physiological causes that can be diagnosed** on the basis of symptoms, treated, and even cured!
87
New cards
Biopsychological care of mental illness?
This approach advocates for the necessity of treating and thinking about illnesses by including the social and behavioural factors that play a role in overall health
88
New cards
Physiological care of mental illness?
Certain disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and autism fit the biological model in a very clear-cut sense.
89
New cards
non-physiological care of mental illness?
or other conditions, such as depression or anxiety, the biological foundation is more unclear.
90
New cards
Where is the insular lobe located?
under all four other lobes
91
New cards
Where is the frontal lobe located?
Front of the head
92
New cards
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
Reasoning, planning, movement and emotions
93
New cards
Where is the motor section loctated?
At the back of the frontal lobe
94
New cards
Where is the sensory area located?
In front of the parietal lobe
95
New cards
Where is the parietal lobe located?
Top of your head
96
New cards
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
Recives sensory input (touch pressure, temperature and pain)
97
New cards
Where is the temporal lobe loctaed?
Sides of your head above your ears
98
New cards
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
Speech preception, hearing and memory
99
New cards
Where are the occipital lobes located?
Back of the head
100
New cards
What is the function of the occipitcal lobes?
receives input from the eyes