Clinical practicum Final
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
identify a Digitally Reconstructed Image (DRR)
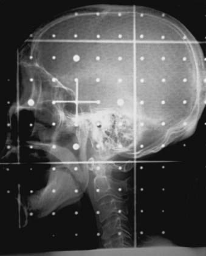
What type of image is this?
conventional sim film
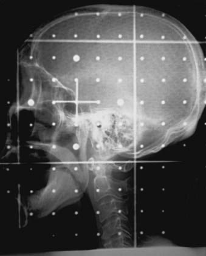
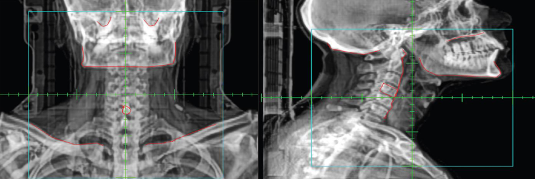
What type of image is this?
MV portal image
What type of image is this?
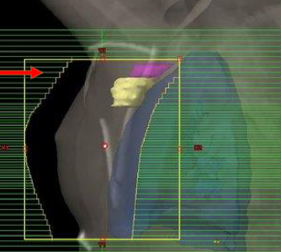
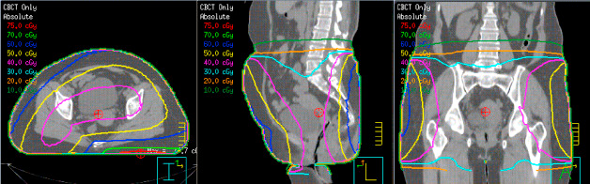
CBCT image
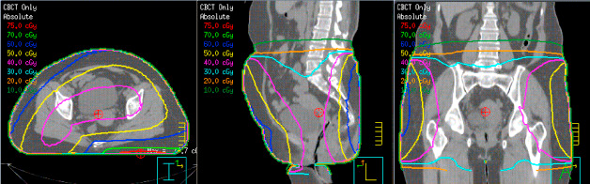
What type of image is this?
KV/KV
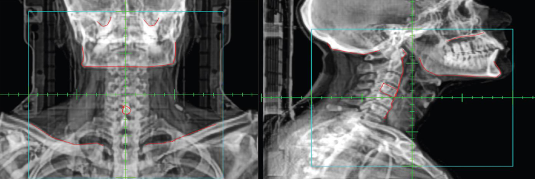
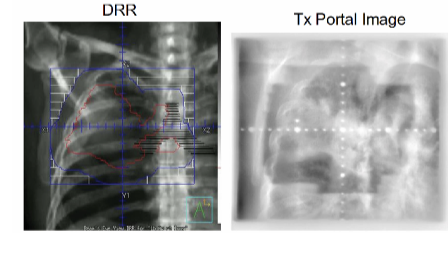
Differentiate between a DRR and a Port Image
What are positioning aids?
items used for comfort and positioning
doesn’t prevent patient movement
Examples of positioning aids
head rests/holders
pillows
rings
breast board
wing board
What are simple immobilization devices?
devices that restrict some movement
more cost effective
Examples of simple immobilization devices
velcro straps
rubber bands
bite blocks (tongue depressor)
hand to foot straps
What are complex immobilization devices
custom made devices
restrict the most amount of motion
more expensive
Examples of complex immobilization devices
vac-loks
aquaplasts
alpha cradles
How is the treatment field size denoted?
Width (X) times Length (Y)
What is Three-pointing?
the process of aligning to lateral and AP marks on a patient to align to isocenter before treatment
What is image-guided radiation therapy (IMRT)?
involves taking daily images prior to radiation treatment delivery
What is surface-guided radiation therapy (SGRT)?
using a system which looks at the surface of the patient’s body and compares that position to the planned position at time of simulation, to position patients prior to treatment
What is intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)?
type of treatment in which there are multiple beams of varying intensities where different parts of the tumor will receive different doses
uses different angles around the patient and use of MLCs
What is volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT)?
type of IMRT treatment where the gantry will rotate in a continuous arc around the patient as radiation is being delivered
What is stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)?
type of stereotactic treatment to places within the body (brain=SRS/SRT)
What is stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) also called??
stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR)
What does stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) use?
uses a highly focused and intense beam with high dose rates to target small amounts of tissue with high doses while sparring healthy tissue.
If a patient can’t stand or pivot what is required to transfer them?
hoyer lift
slider board
What is the process for patient oxygen delivery?
If a patient is on their own oxygen, you will typically hook them up to the oxygen that is
located in the treatment room.
Ensure that tubing is long enough for any couch kicks and ensure it is not in the way of the imaging panels or gantry
What are the 6 responsibilities of a radiation therapist?
complete sims (include starting IV)
daily QA
accurate daily treatments
helping monitor side effects and educate on things like skin care
placing TLDs on patient if needed for treatment
completing charting/records of treatment delivery
What are the 4 responsibilities of a dosimetrist?
reviewing scans from CT/MRI/PET for planning purposes
contouring organs and tissues on scans
calculating optimal doses and angles for the radiation beams
developing the treatment plan
What are the 4 responsibilities of a physicist?
conducting monthly and annual QA on linear accelerator
complete any necessary QA testing for individual patients/plans
treatment planning
provide TLDs for treatment (therapist will place them, while physicists will provide them and gather the readings)
What are the 5 responsibilities of a physician?
consulting with patients and determining appropriate treatment plan
completing weekly visits with current patient and follow-ups with established patients
approving plans created by the dosimetrist/physicist and helping contour/ create treatment plans
approving daily images
providing patient prescriptions
What are the responsibilities of a nurse?
patient education
monitoring and managing side effects
help with weekly follow-up visits and consults
taking vitals
What are the two things to remember when making an isocenter shift?
First, the lasers in the room all converge on isocenter.
Second, when you move the table and patient, you are moving the patient to the lasers, not the lasers to the patient.
TRUE/FALSE: your isocenter shift will be in the opposite direction of where you move your table
TRUE
If you need to shift the isocenter 5 cm inferior, what do you do with the table?
You would move the table 5 cm superior.
If you need to shift the isocenter 2 cm anterior, what do you do with the table?
You would move the table down (posterior) 2 cm.
If you needed to shift the isocenter 3 cm to the patient’s right, what do you do with the table?
You would move the table 3 cm to the patient’s left (or 3 cm to the right, viewing it from the foot of the table from the view of the therapist).
What are the components of the radiation therapy prescription?
total doses and fractionation (dose per treatment)
protraction (time treatment is to be delivered in number of treatments)
anatomic site of treatment
beam energy
treatment technique (protons v. electrons, 3D or IMRT)
any beam modifiers or bolus,
Does the prescription need to list information about patient immobilization devices?
No, this is determined by therapists, dosimetrists, and/or physician at the time of simulation and each patient’s individual needs (mask, vac, etc.).
What is a bolus?
a substance that mimics tissue and brings the dmax closer to the skin surface
When is the bolus commonly used?
when the tumor is very close or on the skin surface
5 Examples of when a bolus would be used
skin cancer
chest wall
vulvar
soft tissue
other treatments where tumor is relatively surface level
What are two important QA tests that the therapist runs daily?
Checking for door interlock
AV (audiovisual) system functionality.
Should treatment proceed if the door interlock or AV system is not functional?
No, you would not treat if either of these is not functional.
What are some additional QA tests therapists check daily?
Checking beam output
laser alignment
ODI
imaging coincidence.
What should you do if additional QA tests are not functional?
Likely repeat testing to see if it was an error in setting up the test, then report issues to your physicists.
Where are emergency off buttons located in a radiation therapy vault?
These buttons are located in several places within the vault and console area
on the couch
on the walls in the vault/console area
on the Linac stand
on the console.
Where are emergency off buttons not located?
in general public areas
other areas of the radiation oncology department, such as nursing stations, exam rooms, or receptionist areas.
When should you use an emergency off button?
In case of extreme emergency, such as
fire
major technical or safety issues
or being trapped in the room while the beam is running.
If a patient is moving, having a medical issue, or needs to get off the table, do you use the emergency off button?
No, you would typically just stop the beam and enter the room – the emergency off button is rarely needed in situations like this.
What should you do if audio-visual devices are not working in the treatment room?
You may NOT treat if you cannot see or hear the patient, for safety reasons.
This must be resolved before treating again.
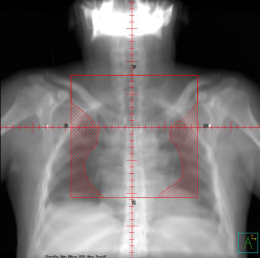
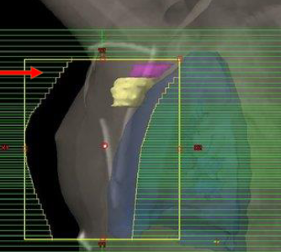
On which patients is flash mainly checked?
Flash is mainly checked on breast patients, especially if you are treating tangents and are not imaging daily.
Why is flash checked on breast patients?
It is a visual way of checking that all breast tissue is within the treatment field.
On which other patients may flash be checked?
Flash may also be checked on whole brain patients.
Why is flash checked on whole brain patients?
Traditionally, you would not image whole brains daily and treat with parallel-opposed fields, so therapists set up to marks on the mask and check the field visually.
When would you treat a patient with a full bladder?
most commonly used for prostate and GYN treatments
sometimes rectum
When would you treat a patient with a empty bladder?
treating the bladder itself
What type of radiation can we treat with on a linear accelerator?
the linear accelerator is capable of treating with
photons
electrons