comp 3 part 2
1/298
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
299 Terms
If you feel resistance in the spring test, it’s a
Positive spring test
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome:
One mutant allele inherited → only one more hit needed → sarcomas, breast cancer, leukemia, brain tumors.
MYC
Transcription factor
Burkitt lymphoma (t(8;14))
Amplified in many cancers
Upregulates telomerase
RAS
Most common abnormality of proto-oncogenes
Permanently activated (GTP-bound)
Seen in colon, pancreas (KRAS), bladder (HRAS)
Words Associated With Malignancy
Anaplasia
Pleomorphism
Hyperchromasia
↑ N/C ratio
↑ mitotic rate
Loss of polarity
Necrosis
Invasion/infiltration
Definitive Criterion for Malignancy
Ability to metastasize.
Primary vs Secondary Intention
Primary: Clean surgical wound, edges apposed.
Secondary: Large wounds, must fill in + contract.
24–48 hrs:
Epithelial migration, macrophages predominate.
5–7 days:
Granulation tissue (new vessels, macrophages, fibroblasts).
Weeks 1–2:
↓ edema, ↓ WBC.
1–2 months:
Pale, avascular scar
Why does swelling occur?
Na enters cell → water follows → hydropic change.
What causes ↓ ATP?
Mitochondrial damage → ↓ oxidative phosphorylation.
Time to irreversible damage?
~20–30 minutes
What is preserved in coagulative necrosis
Cell outlines remain (“ghost cells”).
What do neutrophils pierce?
Basement membrane
Acute inflammation main cell?
Neutrophils
Chronic inflammation main cells?
Macrophages, lymphocytes, eosinophils.
Tumor Types
Benign epithelial: Adenoma
Benign mesenchymal: Lipoma
Malignant epithelial: Adenocarcinoma, SCC
Malignant mesenchymal: Sarcomas (liposarcoma, osteosarcoma)
The glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) innervates one muscle, the:
Stylopharyngeus
Foramen rotundum
CN V2 enters the pterygopalatine fossa through this, but doesn’t exit the skull here.
A surgeon accidentally cuts the nerve that provides motor innervation to all intrinsic muscles of the larynx except the cricothyroid.
Inferior (recurrent) laryngeal nerve
____ nerve innervates cricothyroid, the only intrinsic laryngeal muscle not innervated by recurrent laryngeal.
External branch of the superior laryngeal nerve
Damage to which nerve would cause inability to ABduct the vocal folds, leading to breathing difficulty?
Inferior (recurrent) laryngeal nerve
A patient has difficulty elevating the soft palate. All of the following muscles would be affected EXCEPT the one that is NOT innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X).
Tensor veli palatini.
During a neurologic exam, a patient is asked to protrude their tongue. The tongue deviates toward the right side.
Right hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
A newborn presents with a midline neck mass that elevates when the infant protrudes their tongue. Imaging shows a cystic structure located just inferior to the hyoid bone. Which developmental structure failed to properly regress?
Thyroglossal duct
A branchial fistula (or branchial cyst) is caused by a persistent __, which is formed from pharyngeal clefts 2–4.
cervical sinus
Between which two muscles does CN IX pass?
Superior and middle pharyngeal constrictors
During the early phase of acute inflammation, which mediator is most responsible for increasing vascular permeability by causing endothelial cell contraction?
Histamine
patient with a right CN IV palsy complains of vertical diplopia. To compensate, the patient tilts their head:
To the left
Tongue deviates to the right →
lesion of right hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
During a cranial nerve exam, a physician moves a patient’s eye into an adducted position, then asks the patient to look up. The patient is unable to elevate the eye in this position. Which muscle is most likely affected?
Inferior oblique
During the H-test, a patient’s right eye fails to abduct when asked to follow the examiner’s finger to the far right. Which nerve is most likely affected?
Abducens nerve (CN VI)
During an H-test, a patient cannot depress the left eye when it is in the adducted position. Which muscle is most likely affected?
Superior oblique
A patient suffers blunt trauma to the face. CT reveals herniation of orbital contents into the maxillary sinus. Which bony structure is most likely fractured?
Orbital floor
A researcher administers a peptide that regulates growth hormone secretion and also has major inhibitory effects in the central nervous system.
Somatostatin
A 72-year-old man presents with fever, neck stiffness, and confusion.
Lumbar puncture shows elevated neutrophils and low glucose.
Gram stain reveals Gram-negative diplococci.
He has no drug allergies.
Which beta-lactam is the most appropriate first-line treatment?
Ceftriaxone
At equilibrium binding analysis:
Drug X has a Kd of 1 μM,
Drug Y has a Kd of 10 nM,
and both have similar Emax values.
Which of the following statements is most accurate about these findings?
Drug Y has greater affinity and is more potent than Drug X.
In which situation do you have effect modification (not confounding)?
A medication reduces migraines more in women than in men
A study finds an odds ratio of 1.0. What does this mean?
There is no association
Which study is best for studying a rare exposure?
Cohort
Increases risk
Would require OR > 1.
Decreases risk
Would require OR < 1.
“Gram-positive diplococci, lancet shaped”
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Culture grows Bacteroides fragilis. According to the lecture, which antibiotic is the most appropriate choice for this infection?
Cefoxitin
Blood culture shows Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
The isolate is oxacillin-sensitive.
What is the correct first-line beta-lactam?
Nafcillin (MSSA)
Two intravenous drugs are given at the same dose.
Drug A remains mostly in the plasma.
Drug B distributes widely into tissues.
Both are cleared by the same elimination mechanisms and have the same clearance rate.
Which statement best explains which drug has the longer elimination half-life?
Drug B, because it has a larger volume of distribution (Vd), which increases the elimination half-life.
A mutation in the voltage-gated Na⁺ channel’s inactivation gate keeps the channel open longer than normal.
Which clinical outcome is most likely?
Epilepsy
A 58-year-old man reports gradually progressive muscle weakness that improves temporarily after exertion.
He also has dry mouth and reduced sweating. EMG shows decreased presynaptic Ca²⁺ entry at the neuromuscular junction.
Autoantibodies against voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels
A patient with hypertension has been taking propranolol (a nonselective β-blocker) for several months.
He abruptly stops taking the medication. Within 24 hours, he experiences palpitations, chest pain, and a severe increase in blood pressure.
Upregulation and supersensitivity of β-adrenergic receptors
Emax is reduced but EC₅₀ is unchanged
Shifts downward
What is the MAIN weakness of case-control studies?
They rely on past information and are prone to bias
Which study gives you PREVALENCE, not incidence?
Cross-sectional
Which statement about RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS is TRUE?
Their analysis is the same as a cohort study
Which scenario is an example of EFFECT MODIFICATION (not confounding)?
A drug lowers blood pressure much more in women than men
His eye exam shows normal abduction and adduction, but he has difficulty depressing the eye when it is adducted.
Trochlear n
Which antibiotic is most appropriate for surgical prophylaxis according to the lecture?
Cefazolin
Weakness of depression of the adducted eye is caused by dysfunction of which muscle?
Superior oblique
Which measure can you calculate in both cohort studies and RCTs?
Relative risk
A study finds that smokers have a relative risk of 3.0 for developing pneumonia compared to non-smokers. What does this mean?
Smokers are three times more likely to develop pneumonia
A lesion of the precentral gyrus would cause which deficit?
Loss of voluntary motor control
A patient with a lesion in the postcentral gyrus would most likely present with:
Loss of proprioception and touch
A 70-year-old man develops progressive difficulty with balance and coordinated movement, but his strength and sensation remain normal. MRI shows atrophy of a brain structure with two hemispheres.
Which structure is affected?
Cerebellum
A lesion of the lateral sulcus would most likely disrupt which major functional region?
Primary auditory cortex
Which cephalosporin is excreted in the bile rather than the kidneys and therefore does not require renal dose adjustment?
Ceftriaxone
Which cephalosporin should NOT be used in neonates
Ceftriaxone
“This is the classic pattern seen in myocardial infarction (heart, kidney, solid organs).
The cell outlines remain preserved for a while, but nuclei disappear and cytoplasm becomes deeply eosinophilic due to protein denaturation.”
Coagulative necrosis
Ketamine works on the
N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor
Which antibiotic is preferred over ceftriaxone for treatment of meningitis in neonates due to safety?
Cefotaxime
Which cephalosporin can cause hypoprothrombinemia and a disulfiram-like reaction with alcohol?
Cefotetan
Streptococcus pyogenes. First line treatment?
Penicillin V
A patient with infective endocarditis grows Enterococcus faecalis. He has no drug allergies.
Best initial therapy?
Ampicillin + gentamicin
A 7-year-old with exudative pharyngitis and +rapid strep test.
No allergies. Can tolerate oral meds.
Best first-line treatment?
Amoxicillin (but not in adults)
“CYP1A2, 3A4 inhibitor, OAT substrate”
Ciprofloxacin
Levofloxacin Is mostly excreted in
Urine
Folate inhibitors (sulfa drugs) are metabolized by
Hepatic
CYP2C9 and NAT2
(N-acetylation)
_____ STIMULATE growth of Rickettsia.
Sulfonamides
Active against many gentamicin- and tobramycin-resistant strains
Amikacin and Plazomicin
Taste buds are mainly on the
Lingual papilla
Where does the chords tympani exit the skull
Petrotympanic fissure
Which cranial nerves is taste conveyed along?
CN 7, 9, 10 (facial, gustatory, vestibular cochlea)
Absolute contraindications to HVLA techniques
No somatic dysfunction
● No consent
● Patient intolerance or pain during set-up (unless promptly resolved with adjusting your technique set-up)
● Osteoporosis; Osteomyelitis; Fracture
● Cancer in the bone (can get pathologic fractures)
● Any “hardware” in the joint or fusion of the joint
● Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis and other inflammatory arthritis
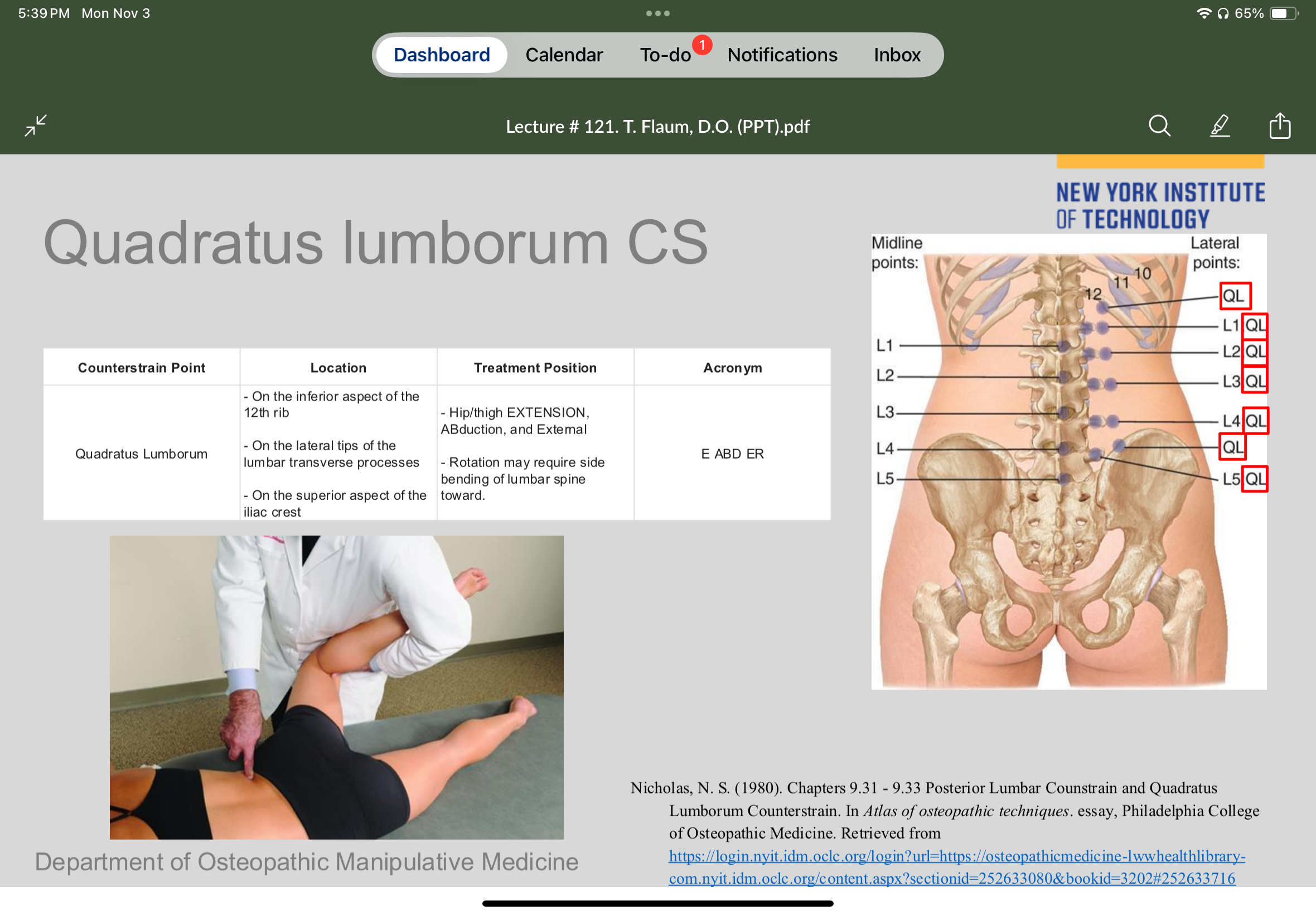
Set up for quadratus lumborum Counterstrain
Major synthetic cycling
Tigecycline
Doxycycline has a ____ affinity for calcium
Low
List of macrolides
Erythromycin, clarithromycin, and azithromycin
The only oxazolidinone we need to know
Linezolid
When do conjugation reactions occur that produce a hydrophilic metabolite?
Phase 2
Oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis; polar functional groups exposed —when do they occur?
Phase 1
UGT1A1 function
Transfers a glucuronic acid from the cofactor uridine diphosphate (UDP) glucuronic acid
Examples of passive transport
Paracellular transport; diffusion; facilitated diffusion
First-pass effect
A fraction of an oral dose may be inactivated by drug-metabolizing enzymes in
the GI tract and liver before reaching the systemic circulation.
Redistribution
The change in plasma drug concentration significant enough to alter or terminate the CNS effect of the drug.
Partial agonists
Mostly bind to Ra and a little to Ri