applied maths
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
define census, and give pros and cons
census: measures every member of a population
😊: accurate result
☹: expensive/testing may destroy
define sampling units and sampling frame
sampling units: individuals of a population
sampling frame: list of sampling units
define simple random sampling and how to do it, and give pros and cons
it means every unit has the same chance of being selected, you can use random number/lottery sampling - out of a hat
😊 bias free
☹ need sampling frame
define systematic sampling and how to do it, and give pros and cons
type of random sampling, take every kth unit, k = pop/sam, pick a random number been 1 and k for starting
😊 quick to use
☹ need sampling frame
define systematic sampling and how to do it, and give pros and cons
type of random sampling, sample represents groups (strata) of a population. sam/pop x strate for each strate, pick randomly.
😊 reflects population
☹ pop must be classified in strata
define quota sampling and how to do it, and give pros and cons
type of non random sampling, like stratified, but strata filled by interviewer/researcher
😊 no sampling frame required
☹non-random, potential bias
define opportunity sampling and how to do it, and give pros and cons
type of non random sampling, quota filled by those available at the time
😊 easy, cheap
☹unlikely to be representative
define the types of data
qualitative: non-numerical
quantitative: numerical
discrete: can only take certain values in a range
continuous: can take any value in a range
where are the uk weather stations
(alphabetical upwards apart from heathrow and hurn)
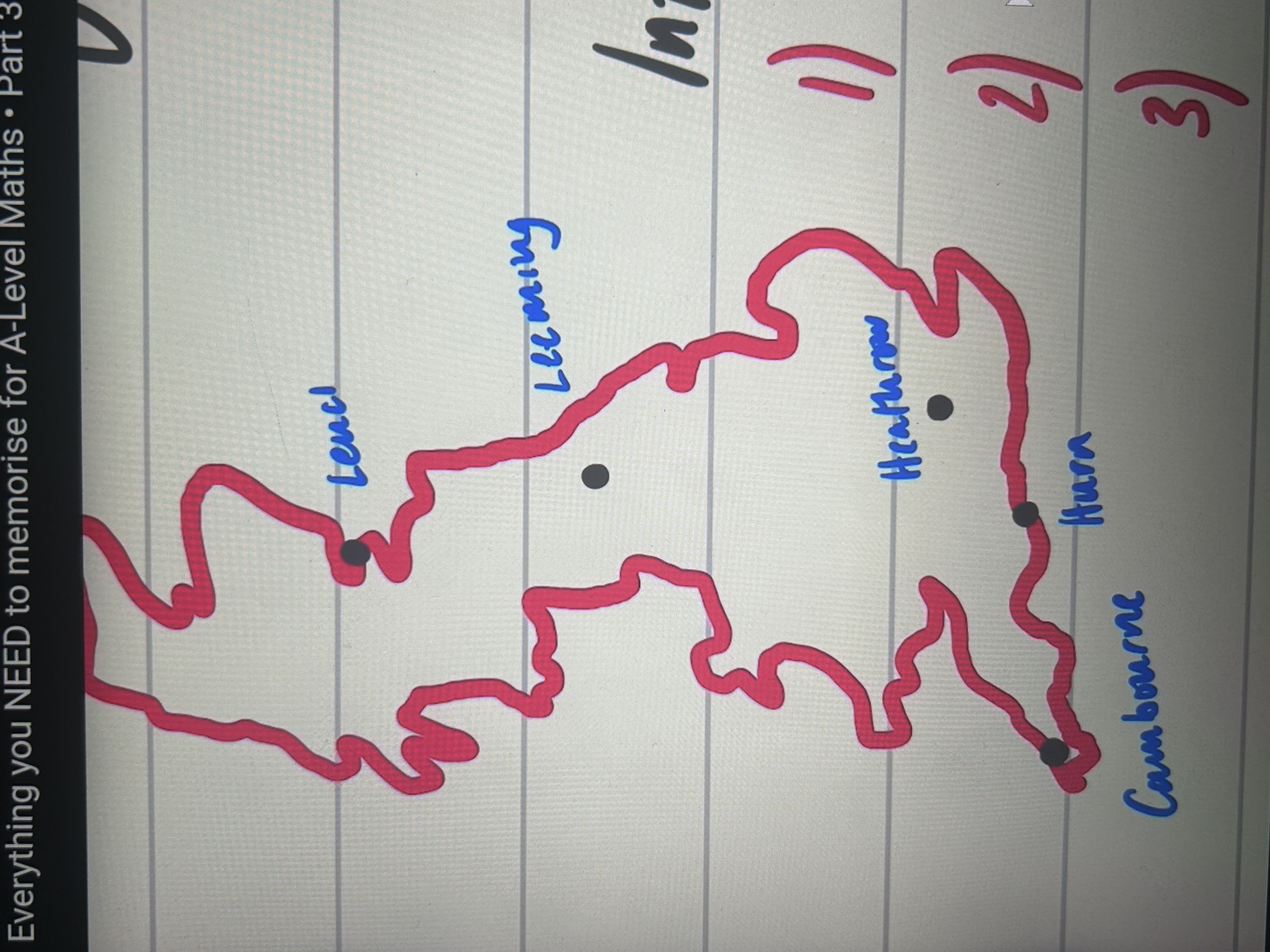
general rules for weather at uk stations
coastal: windier, wetter
south: warmer, more hours of sunshine
when is large data set recorded from?
may-oct ‘87 and ‘15 (only 6 months of year)
name the international stations and general weather rules there
perth, australia, summer and winter switched, very hot
beijing, china, very hot and rainy in summer, very cold in winter
jacksonville, florida usa, very hot, prone to hurricanes, hurricane in oct 87 and oct 15
what does tr mean in the rainfall data
trace, < 0.05mm, treat as 0 in calculations
what does n/a mean in lds
means reading is not available, so can’t use in sample
what is cloud cover measured in?
okras, discrete values integers 0-8 (9 values it can take)
what is max gust measured in?
knots, 1kn = 1.15mph, great storm oct 15th/16th ‘87.
formula for mean!

how to find LQ median and UQ in listed data
LQ = n/4
median = n/2
UQ = 3n/4
if a decimal, round up
if whole, use midpoint between that value and one above
how to find percentiles and deciles e.g
P(57) = 0.57 x n
D(3) = P(30) = 0.3 x n
do not round, use linear interpolation.
how to find IQR and interpretive range, and an advantage of these measures
IQR = Q3 - Q1
e.g 10th to 90th IPR = p(90) - p(10)
😊 ignores extremes
how to find variance and standard deviation

coding?
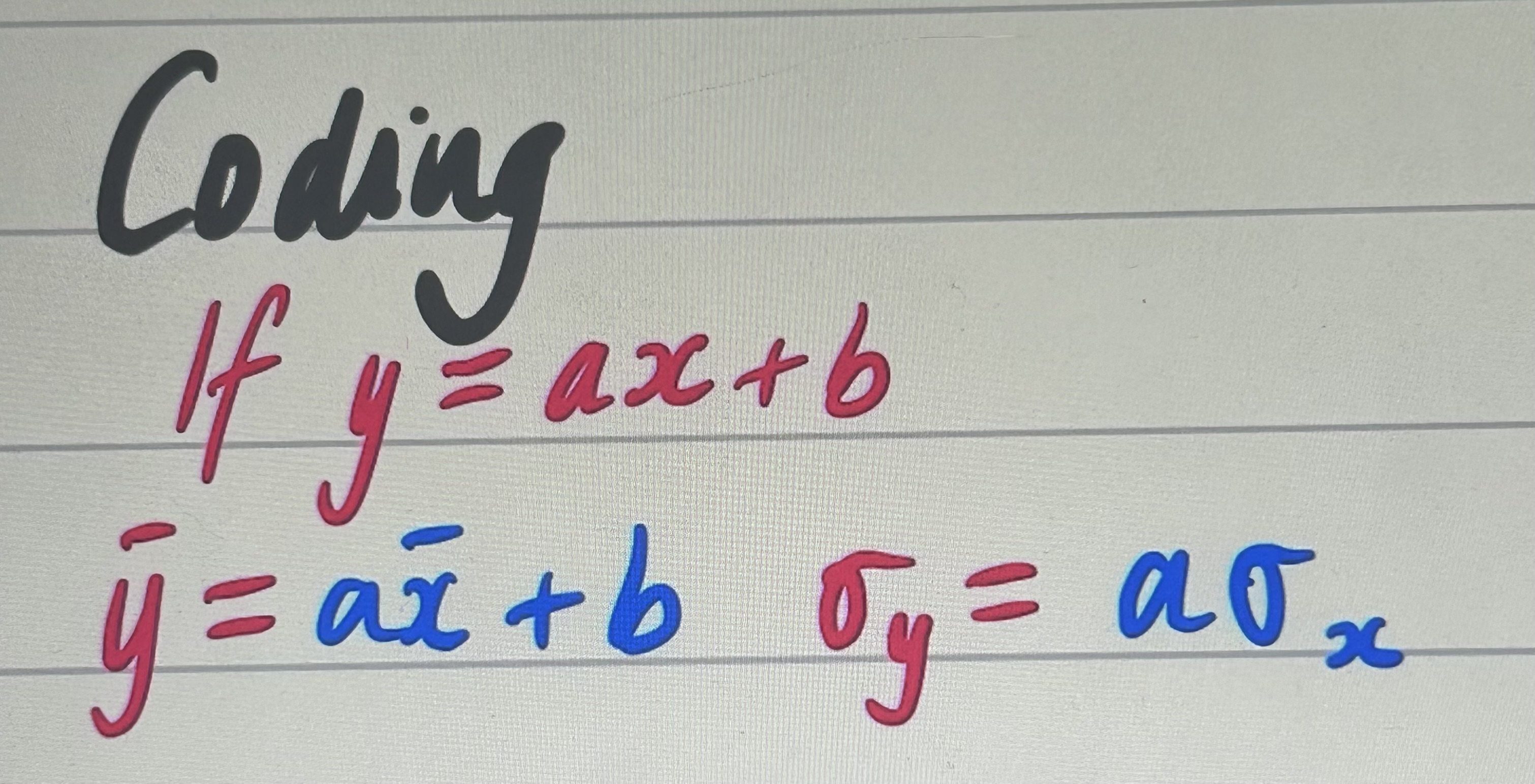
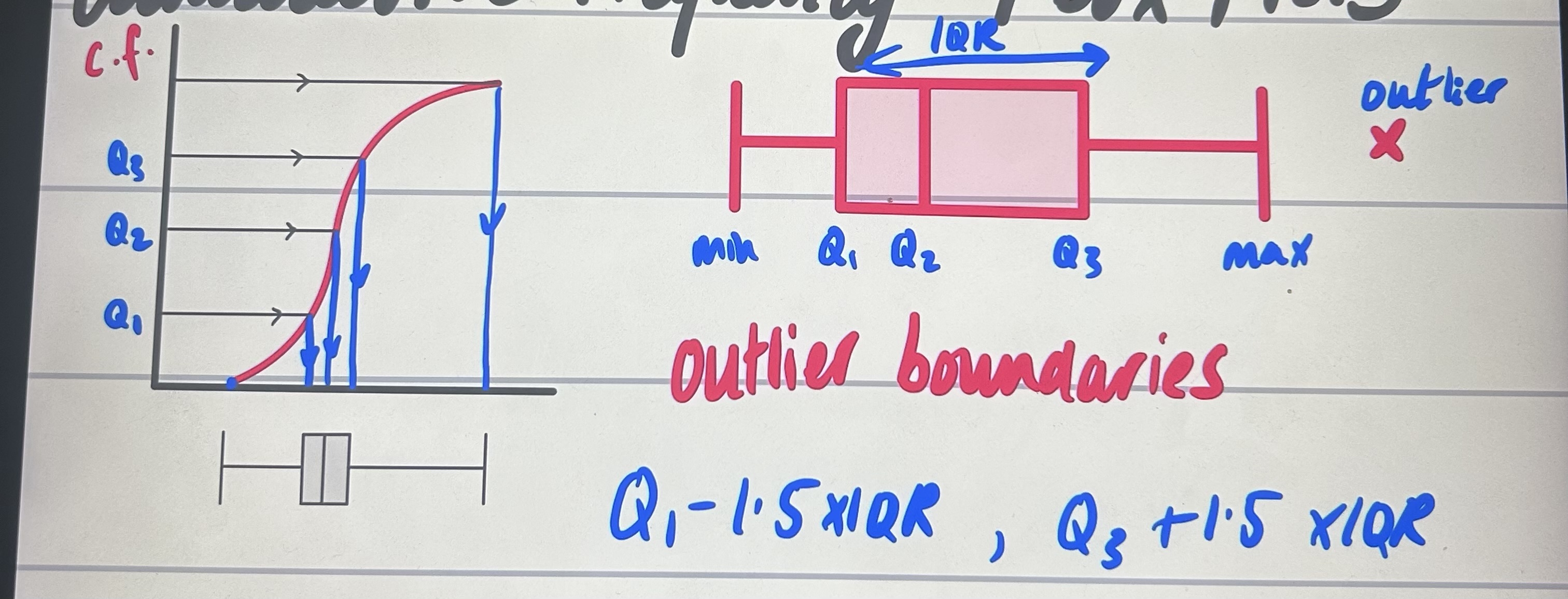
cumulative frequency diagrams/ box plots, and what are the outlier boundaries?
why should you use histograms, what is frequency density and what is the area?
area = frequency x k

what two things do you need to compare if asked to compare two diagrams
1) measure of location
2) measure of spread
put in context
what does the PMCC measure and what values can it take
measures strength and +/- of correlation
-1 <= r =< 1
what is a regression line, what form does it often take and what does it mean, and what to do if model is non linear
line of best fit, y = a + bx
a is y when x = 9
b is how much y changes when x increases by one
if y = ab^x or y= ax^n: take logs to make linear
what is interpolation and extrapolation, and are they reliable
interpolation: estimating inside data range, reliable
extrapolation: estimating outside data range, unreliable
what are unions and intersections

tree diagrams
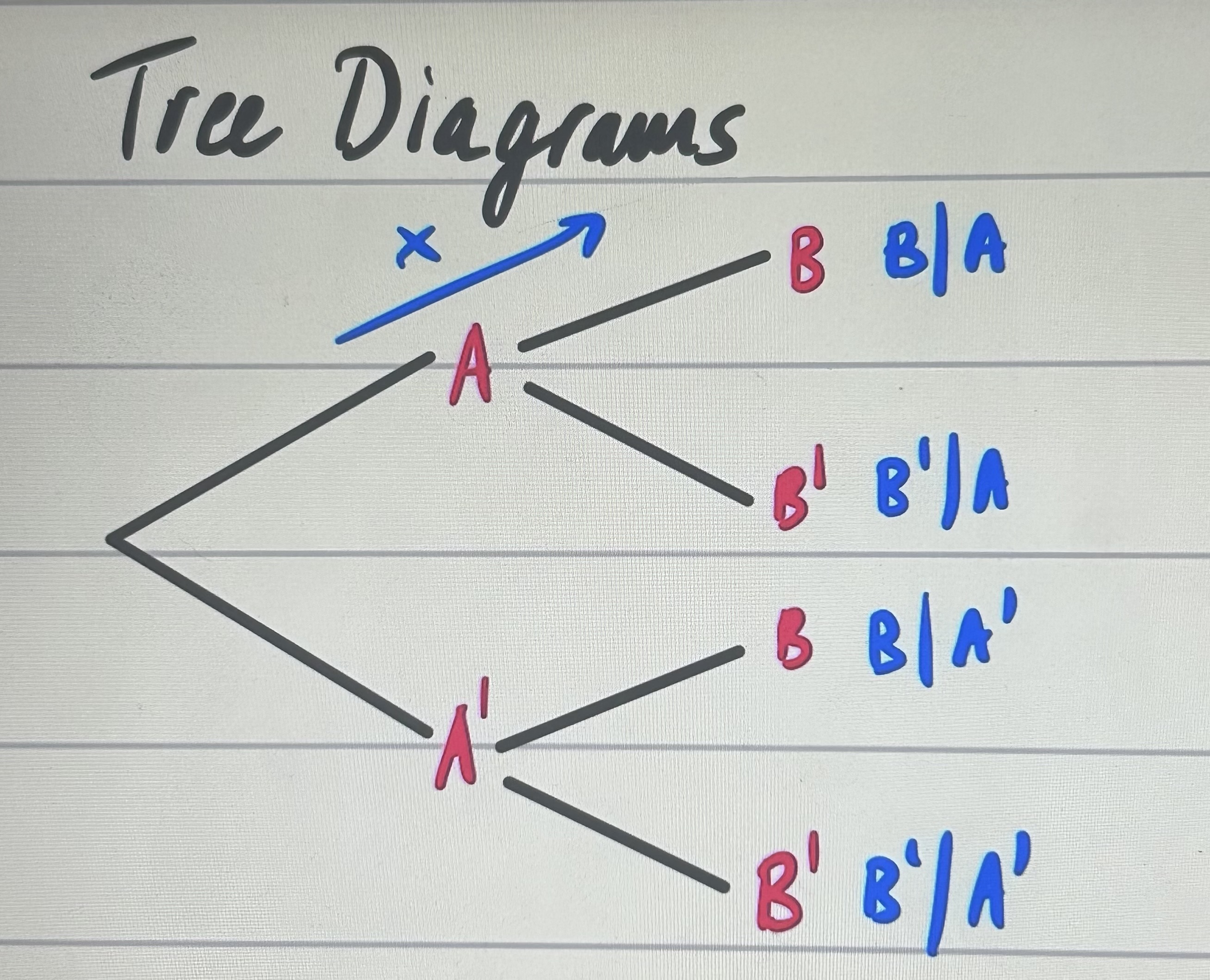
if a and b are mutually exclusive?
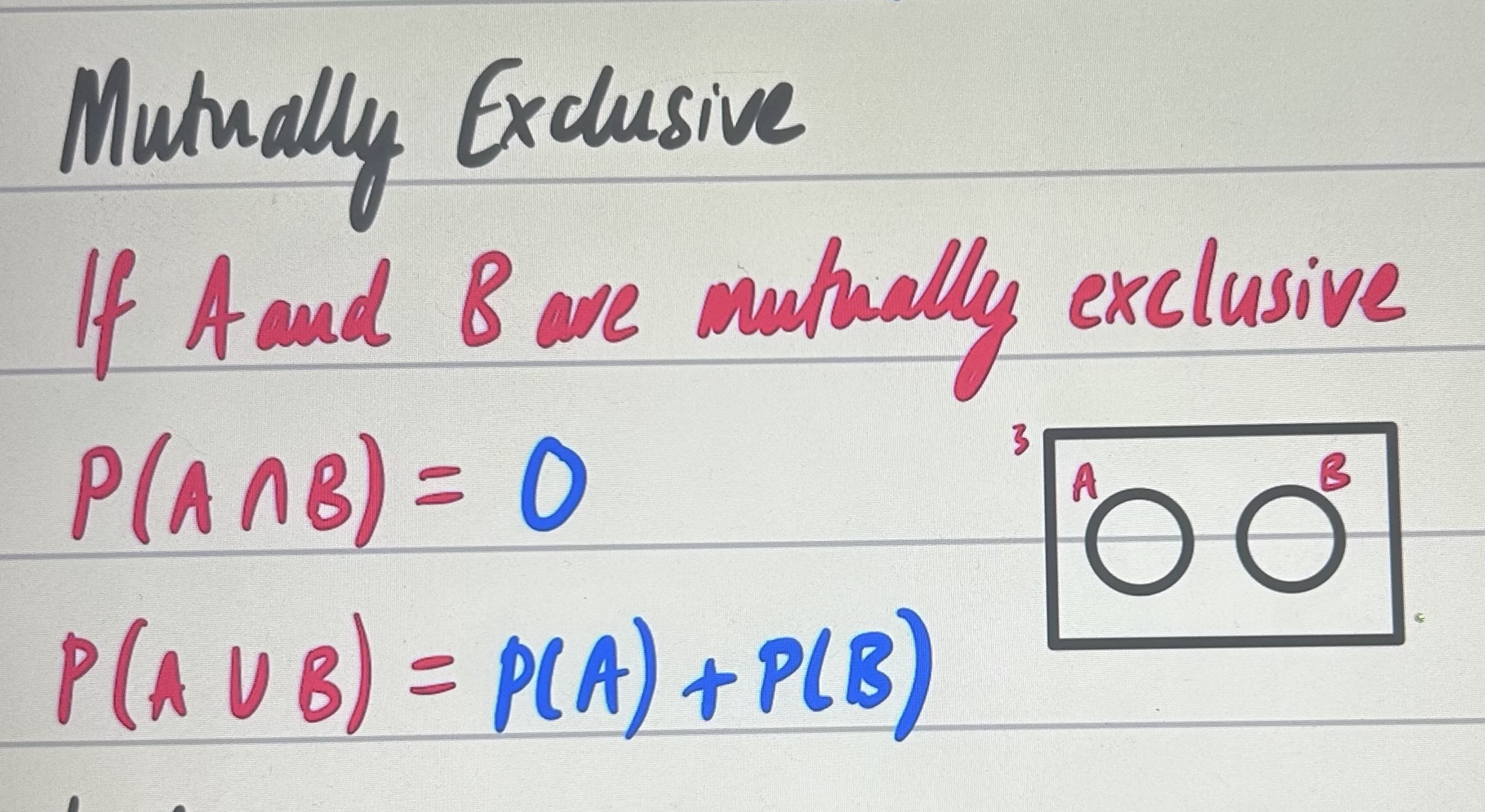
if a and b are independent?
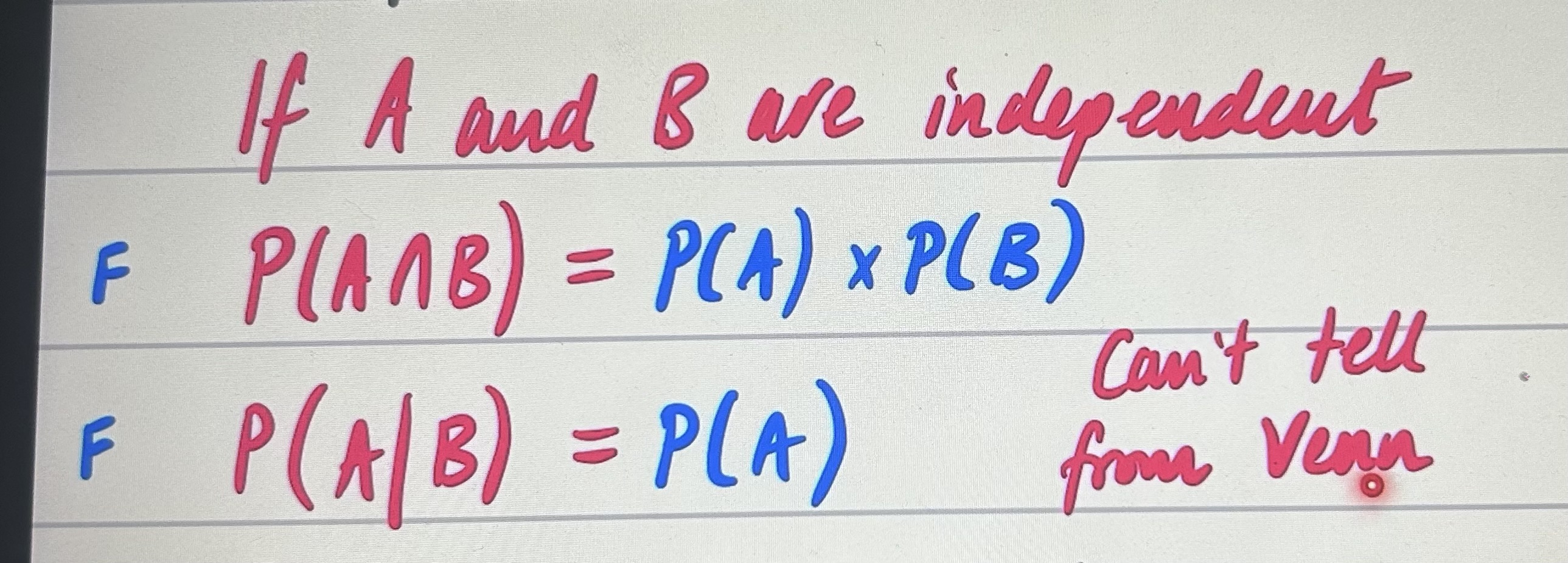
conditional probability formula?

addition law for probabilities?

what does it mean for a distribution to be discrete and uniform
probabilities of outcomes are all equal
when should you use binomial distribution
FFIT:
Fixed number of trials, n
Fixed probability of success, p
Independent trials
Two outcomes, success/failure
normal distribution? where is p.o.i and where does the data lie
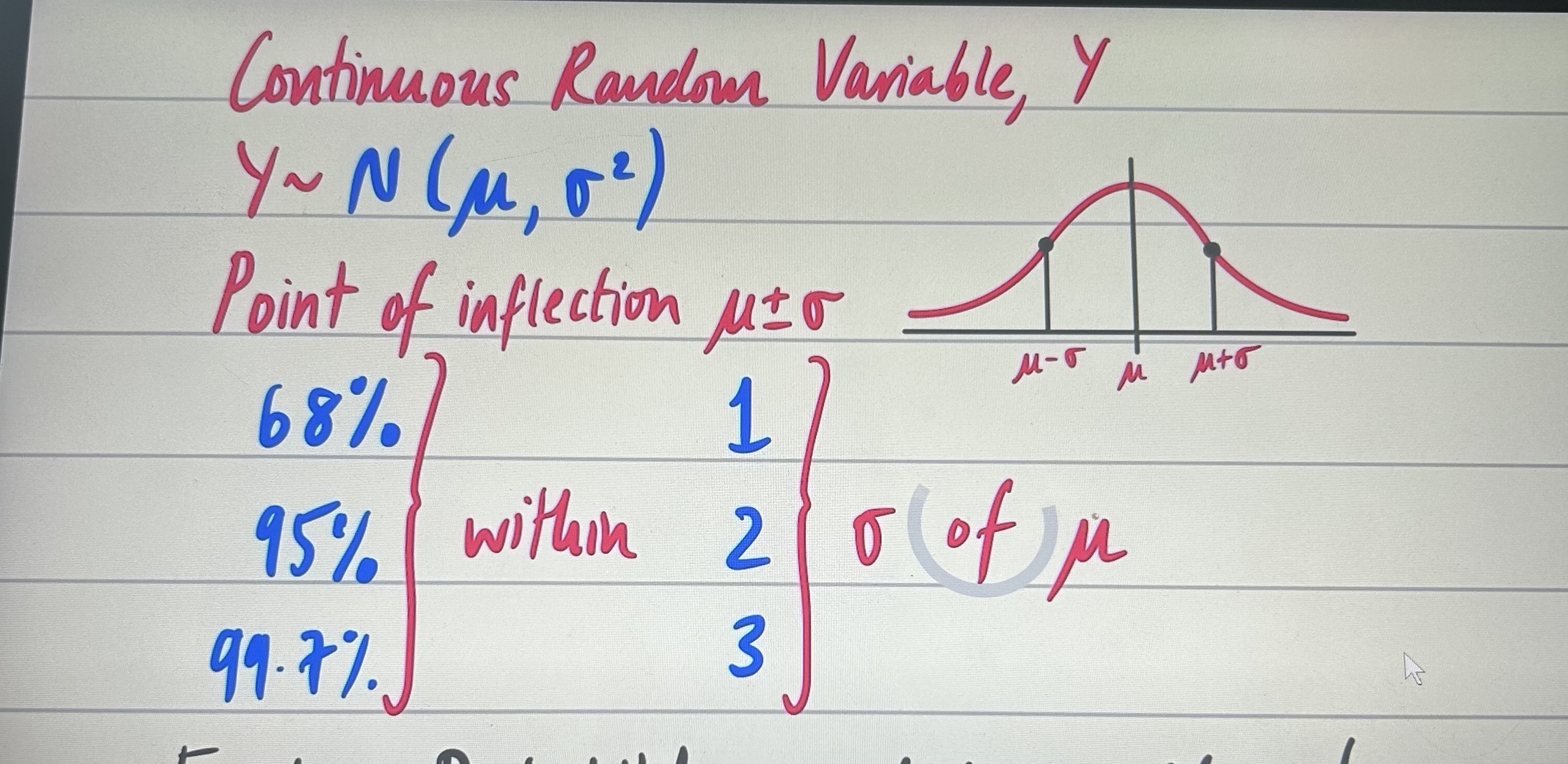
standard normal distribution? what is the coding?

what conditions needed to approximate binomial as normal

continuity correction for approximating binomial as normal
going from discrete to continuous, increase range by 0.5

define null hypothesis
what we assume to be true, H0
define alternative hypothesis
H1, what would be true if H0 is wrong
define significance level
the given threshold of likeness, alpha
when do you do one-tailed test/ two-tailed test
one-tailed: when H1: p > k or p < k
two-tailed test: when H1: p ≠ k → halve s.l for each tail
how do you do correlation testing

how to do binomial testing

how to do normal hypothesis testing of a sample mean

what formula to use when a = 0
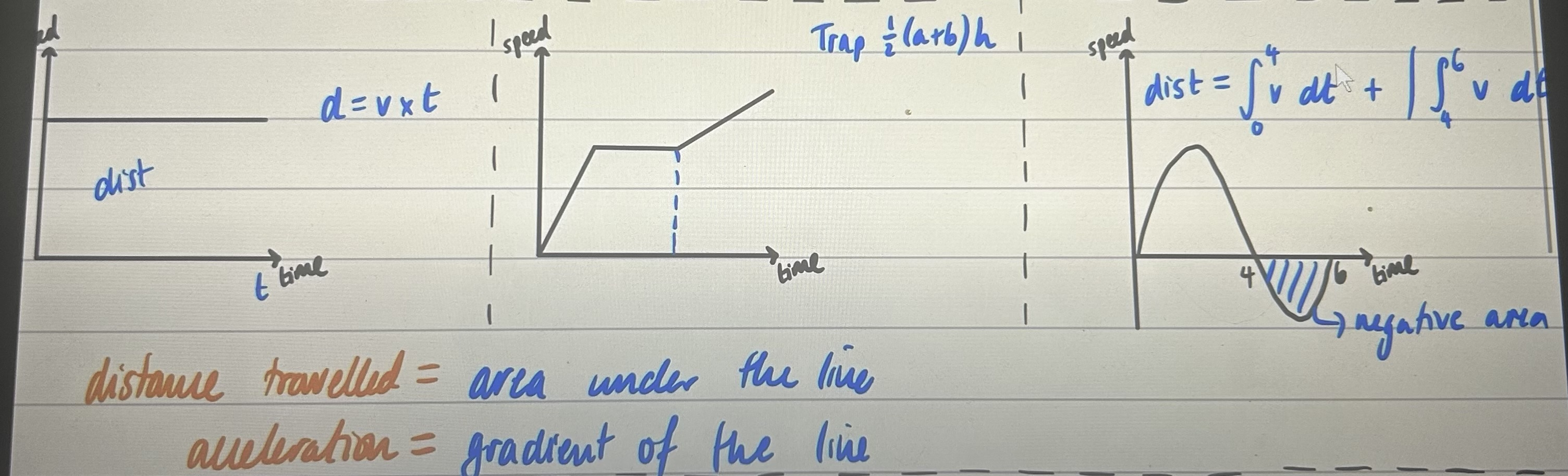
distance = speed x time
suvats
v = u + at
s = ut + 1/2at²
s = vt - 1/2at²
v² = u² + 2as
s = (u + v)t
variable acceleration
can tell it’s variable acceleration when expressed in terms of t
s differentiates to v which differentiates to a (with respect to time) integration opposite
speed-time graphs
distance travelled = area under the curve
vector motion when
a. no acceleration
b. constant acceleration
c. variable acceleration
a. r = r(0) + vt
b. v = u + at,
r = r(0) + ut + 1/2at²
r = r(0) + vt - 1/2at²
c. r differentiates to v differentiates to a, differentiate i and j components separately
projectiles are a and b. connected by t.
what does it mean for a vector to be ‘moving in the direction’
parallel to it, e.g moving in the north direction = k(0,1)
what effect do each of these modelling assumptions have on calculations
smooth pulley:
light string:
inextensible string:
particle:
rod:
smooth pulley: tension on either side of the pulley is equal
light string: tension is equal
inextensible string: both particles have same acceleration
particle: ignore air resistance and ignore rotational effects
rod: rigid, so it doesn’t bend, it has no thickness.
what does it mean when described as:
static/at rest
on the point of slipping/limiting equilibrium
constant speed
vector forces f1 + f2 + f3 = 0
in equilibrium, forces are balanced: down forces = up forces, left forces = right forces.
what does it mean and what to do when forces not in equilibrium
it is accelerating/decelerating, resolve using F=ma, in the direction of motion.
Vectors: use F=ma where F is the resultants R
friction
always opposes the direction of motion/it’s about to move in
if static, Fr <= muR
if limiting equilibrium/dynamic Fr = muR
0 <= mu (mu is generally < 1, < 4)

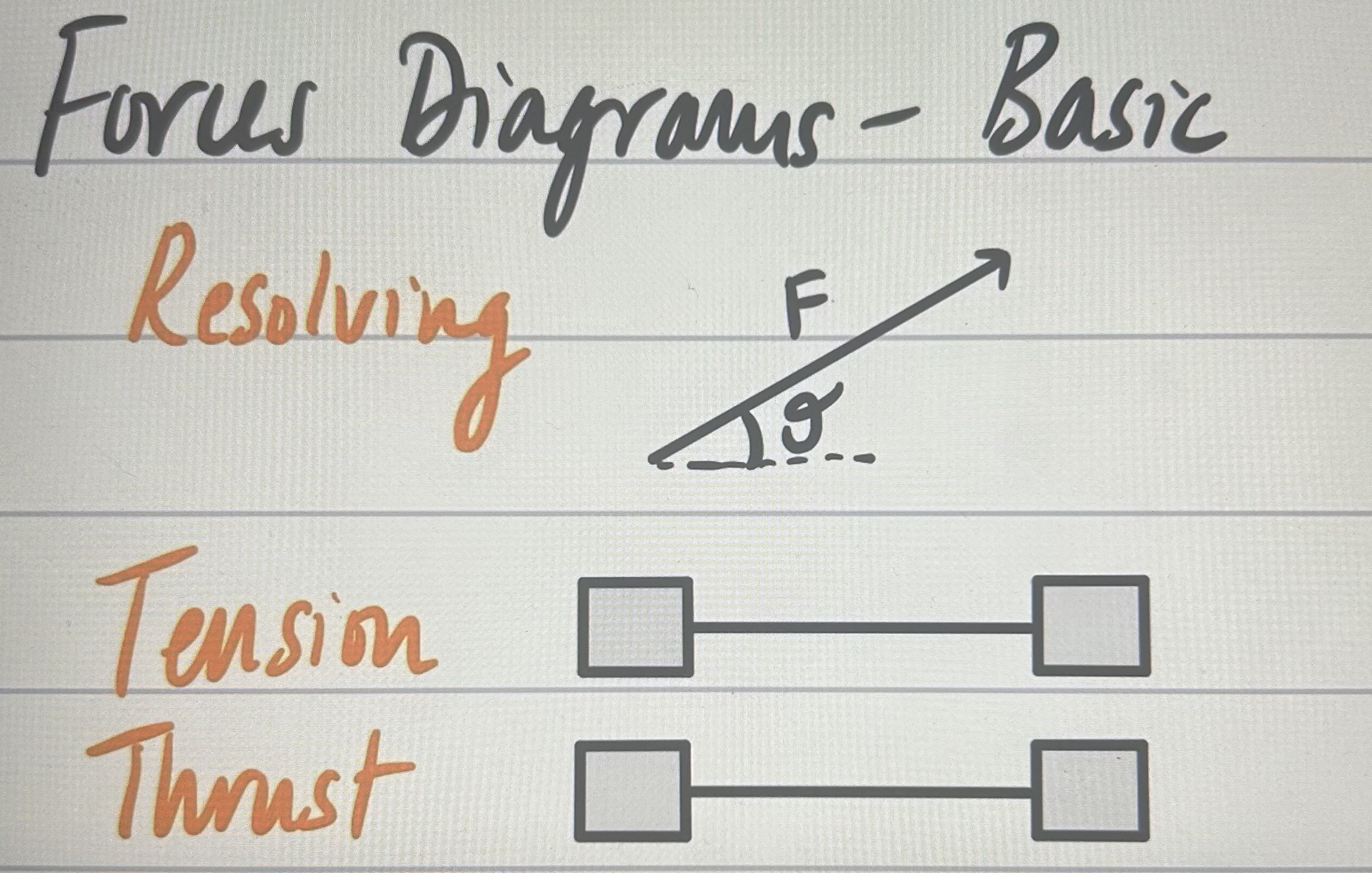
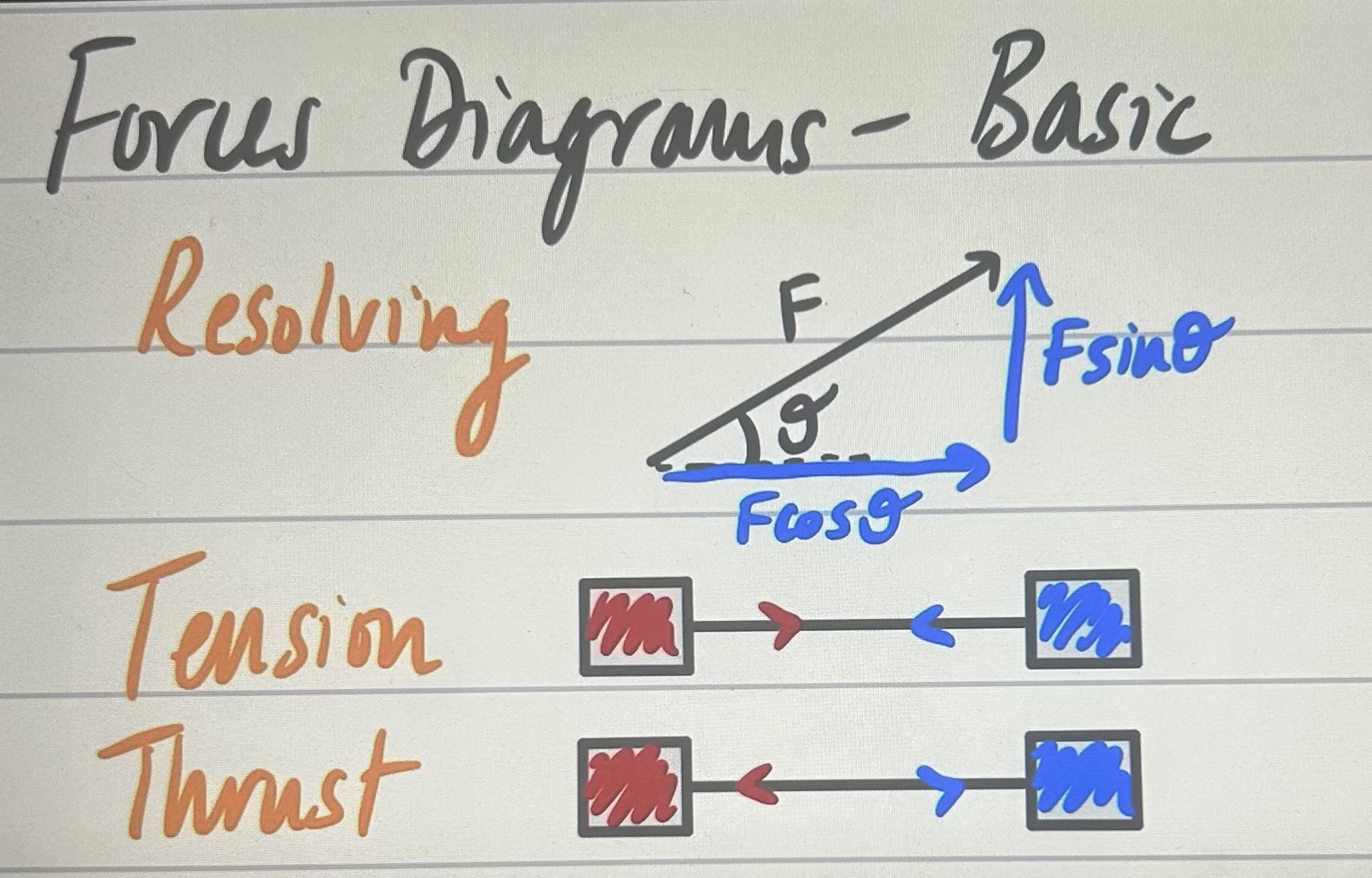
resultant force on pulley?
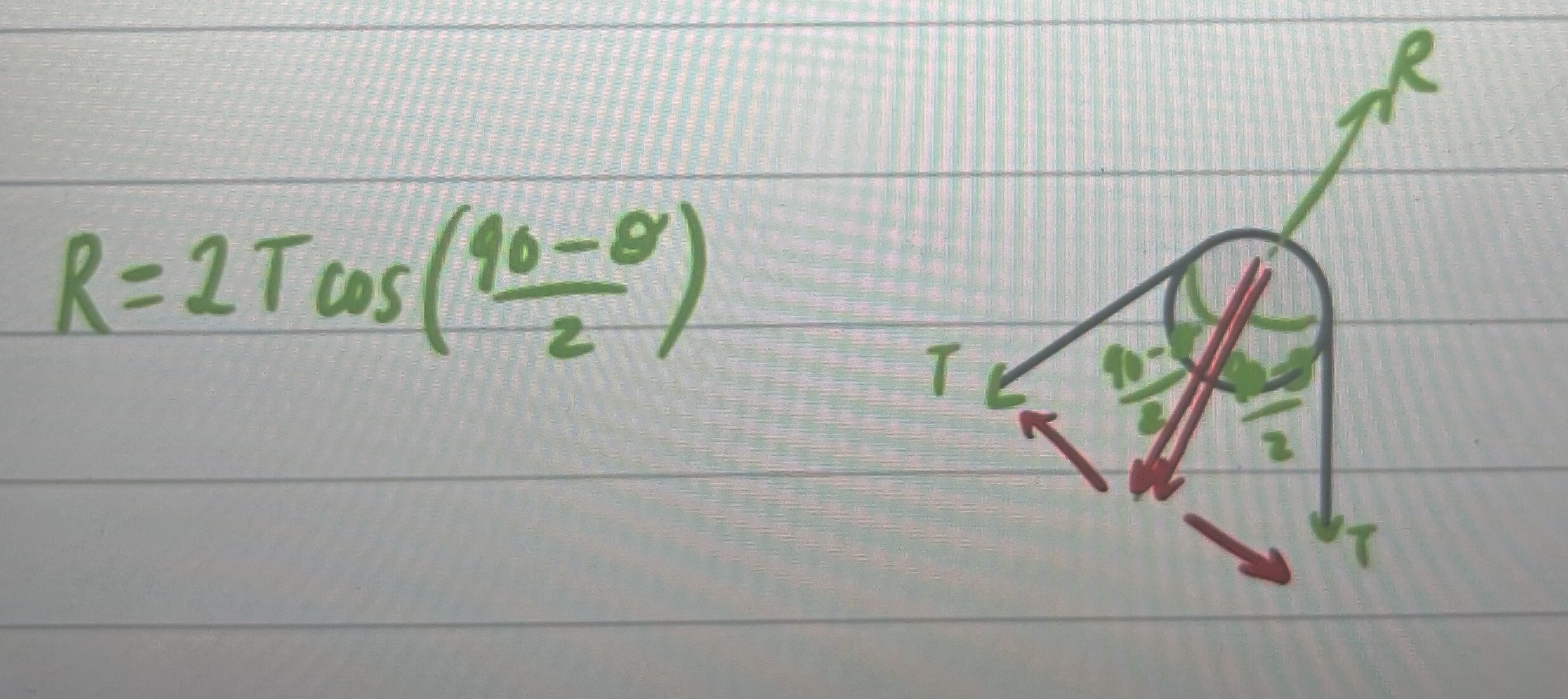
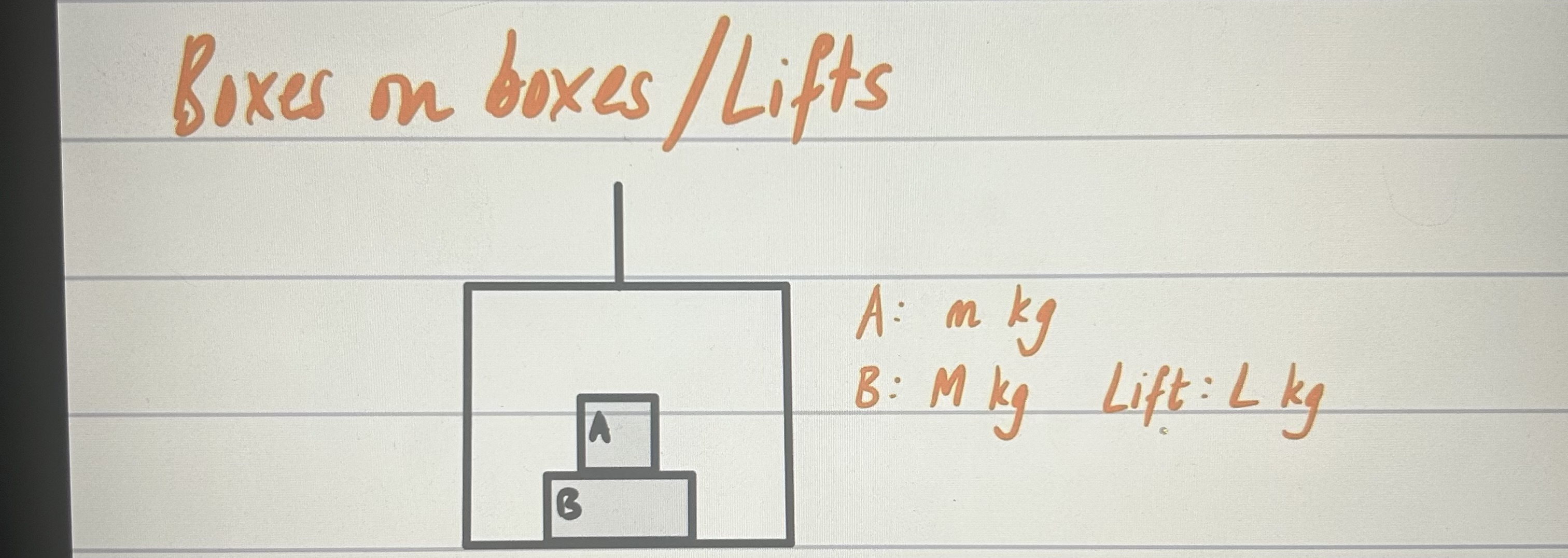
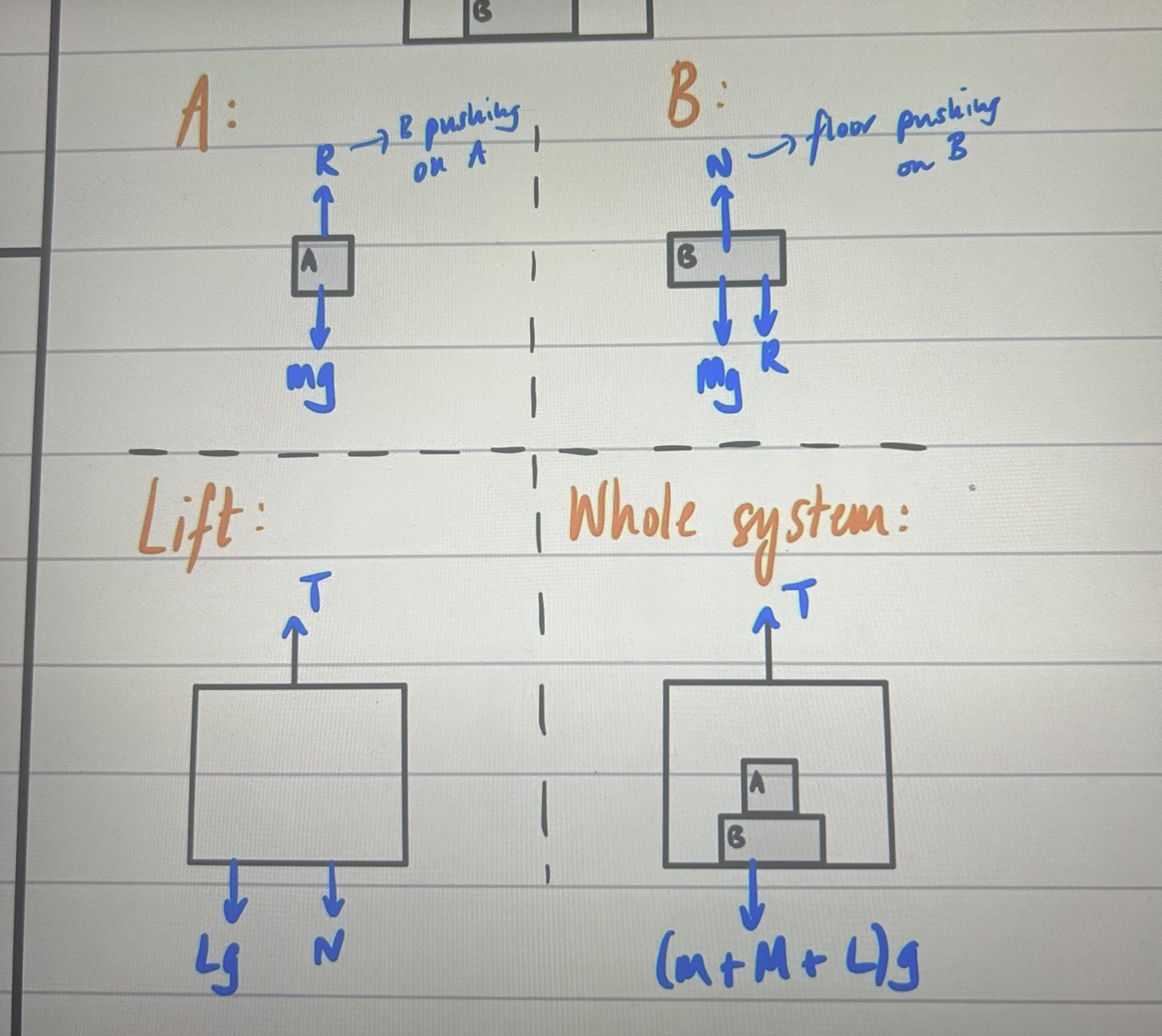
method for connected particles
1) F = ma
2) F= ma
3) Sim Equations
4) SUVAT, find v → u after string breaks after particle hits floor
5) New acceleration, T = 0
6) More SUVAT, use new a and u will be v from before
what do these terms mean for calculations:
uniform:
non-uniform:
on the point of tilting about A:
uniform: weight acts at centre
non-uniform: weight doesn’t have to act at centre
on the point of tilting about A: all other R = 0
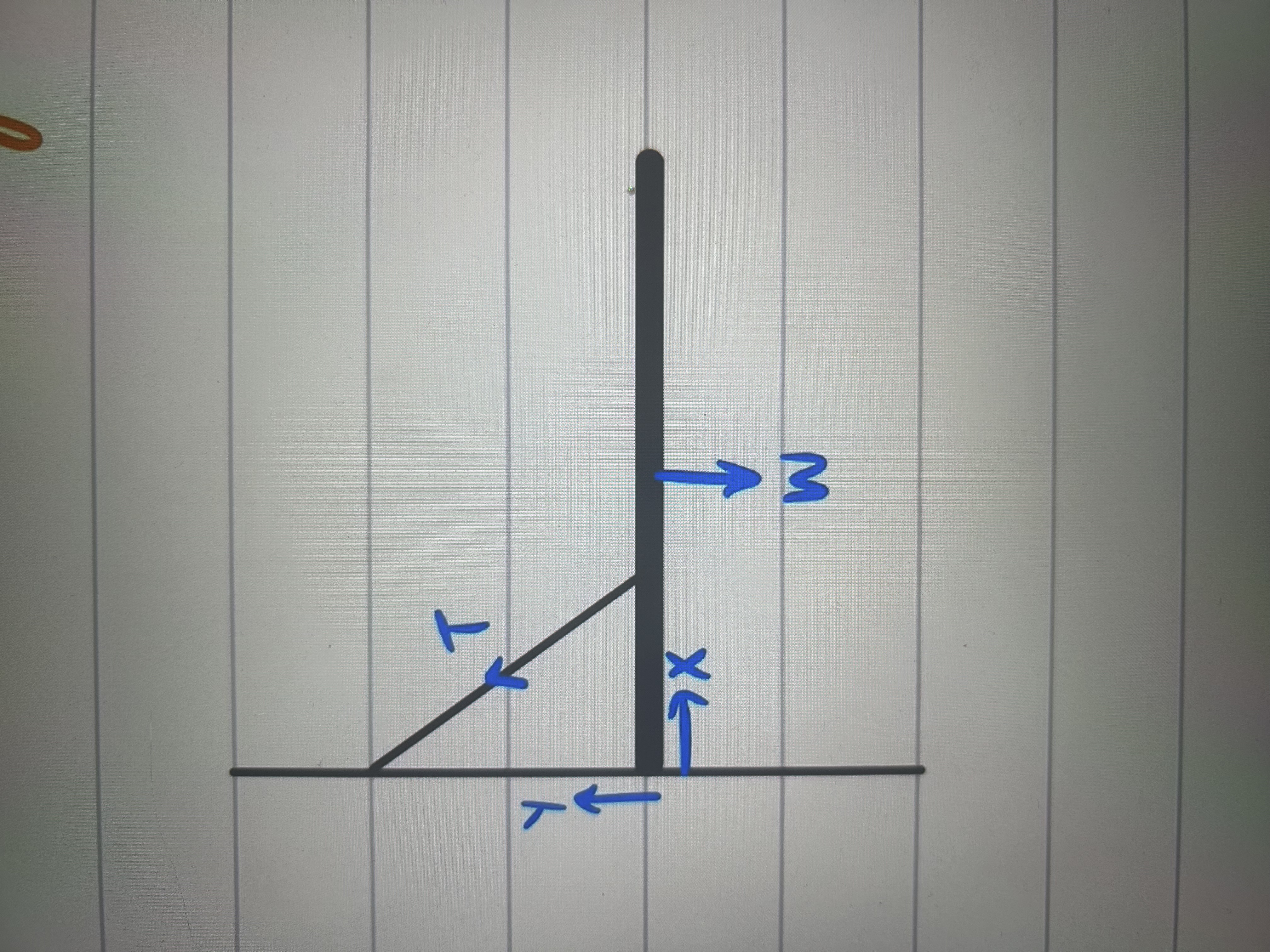
rod suspended by string
y can be up or down

rod resting on peg
use pythagoras to find R
formula for moment
moment = force x perpendicular distance
or
moment = perpendicular force x distance
if moment is in equilibrium
anticlockwise moment = clockwise moment
general method for moments
1) resolve up/down
2) resolve left/right
3/ take moments