Pharmacokinetics Absorption and Distribution
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Drug disposition is divided into four stages designated by the acronym?
ADME
What does AD in ADME stand for?
A = Absorption of Drug from Site of Administration
D = Distribution within the Body
What does ME in ADME stand for?
M = Metabolism
E = Excretion
Pharmacokinetics is the study of?
Absorption, Distribution
Metabolism & Excretion
Cell membranes are selectively?
Selectively permeable membranes responsible for regulating cell volume.
intracellular pH and the correct concentration of intracellular ions and molecules.
Molecules such as glucose and amino acids are taken up from?
Extracellular Fluid
Molecules and ions move across the plasma membrane by?
Passive, Facilitated Diffusion
Active Transport Or
Endocytosis/Exocytosis
When does Lipid Diffusion occur?
Molecule is Small
Molecule is Uncharged
Molecule is Lipid Soluble
Lipid diffusion also depends on ?
Concentration of the molecule on either side of the Membrane.
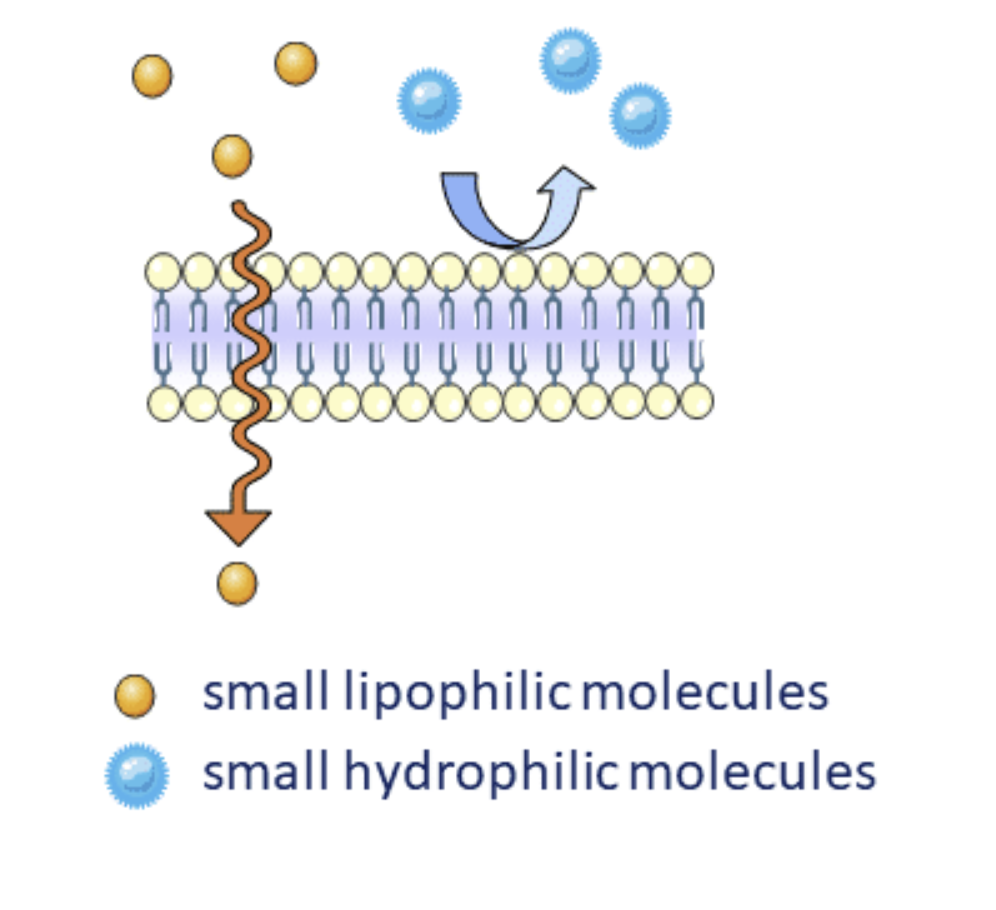
What Lipid Molecules will not pass efficiently through Diffusion?
Charged Lipids
Large Lipids
Water Soluble
What is Facilitated Transport?
Type of Passive Transport
It allows specific molecules or ions to move across the cell membrane with the help of transport proteins.
The process does not require energy (no ATP)
High Concentration → Low Concentration
No net buildup within the cell = Equilibrium.
Uses Carrier Proteins.
Facilitated Transport allows for what Vital Movement?
helps control the movement of vital molecules like glucose, amino acids, and ions into and out of cells.
What is Active Transport?
Uses Specific Transporters
Uses ATP
Allows accumulation of specific molecules against a concentration gradient.
Generally referred to as Pumps
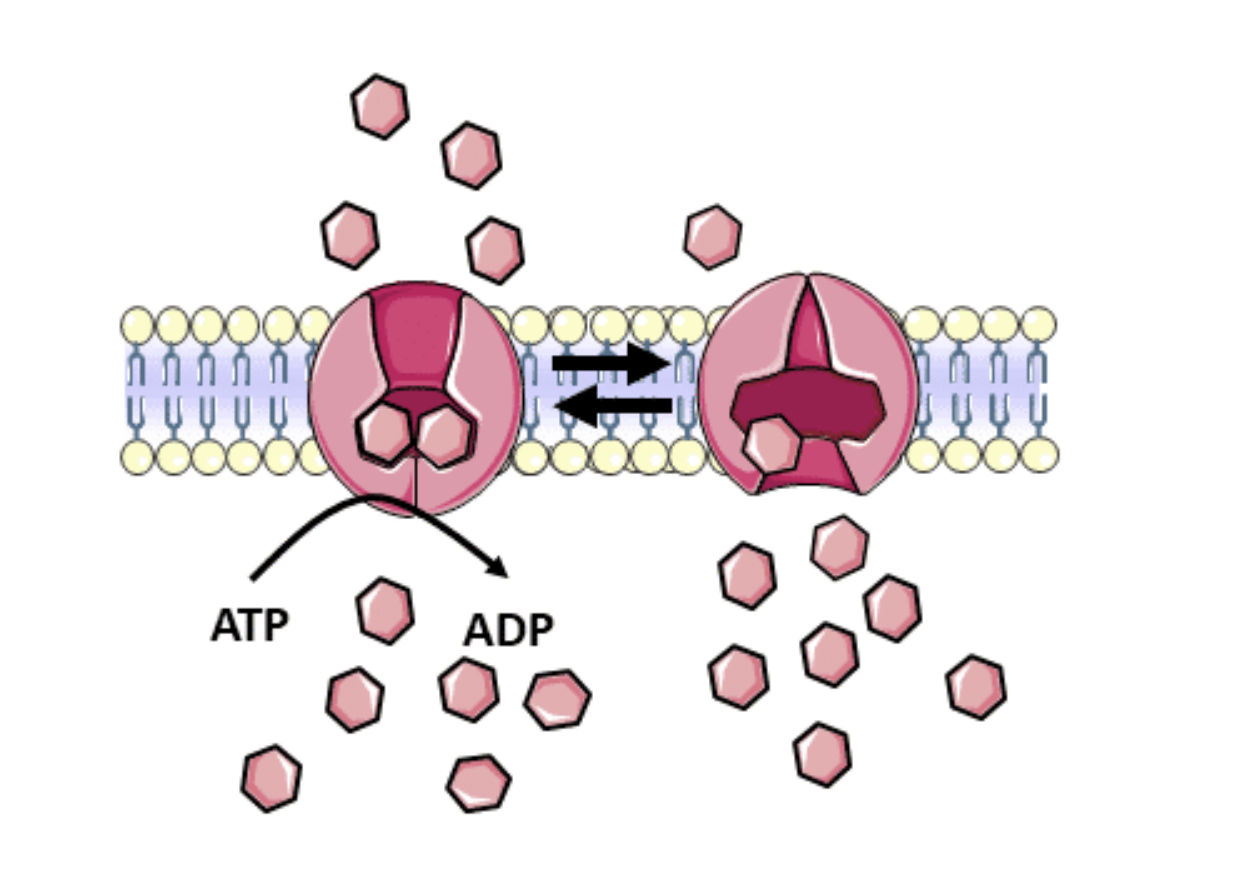
Macromolecules and some metabolites require?
Specific Transporters to Cross the Lipid BiLayer.
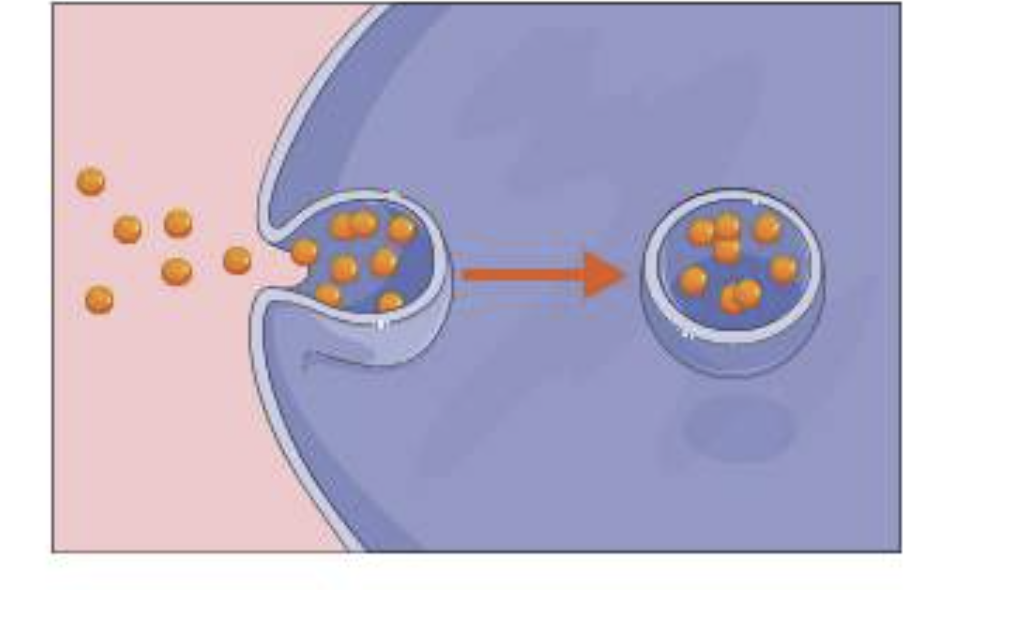
What is Endocytosis?
process whereby material at the cell surface is brought into the cell.
It allows large polar molecules to cross the plasma membrane into the cell.
The plasma membrane forms a pocket around the material in the extracellular environment.
then forms a vesicle that separates from the plasma membrane and migrates to the cell interior.
Exocytosis is?
The Opposite of Endocytosis
Describes the movement of material enclosed in membrane-bound vesicles from the interior of the cell to the plasma membrane where the contents are released to the exterior.
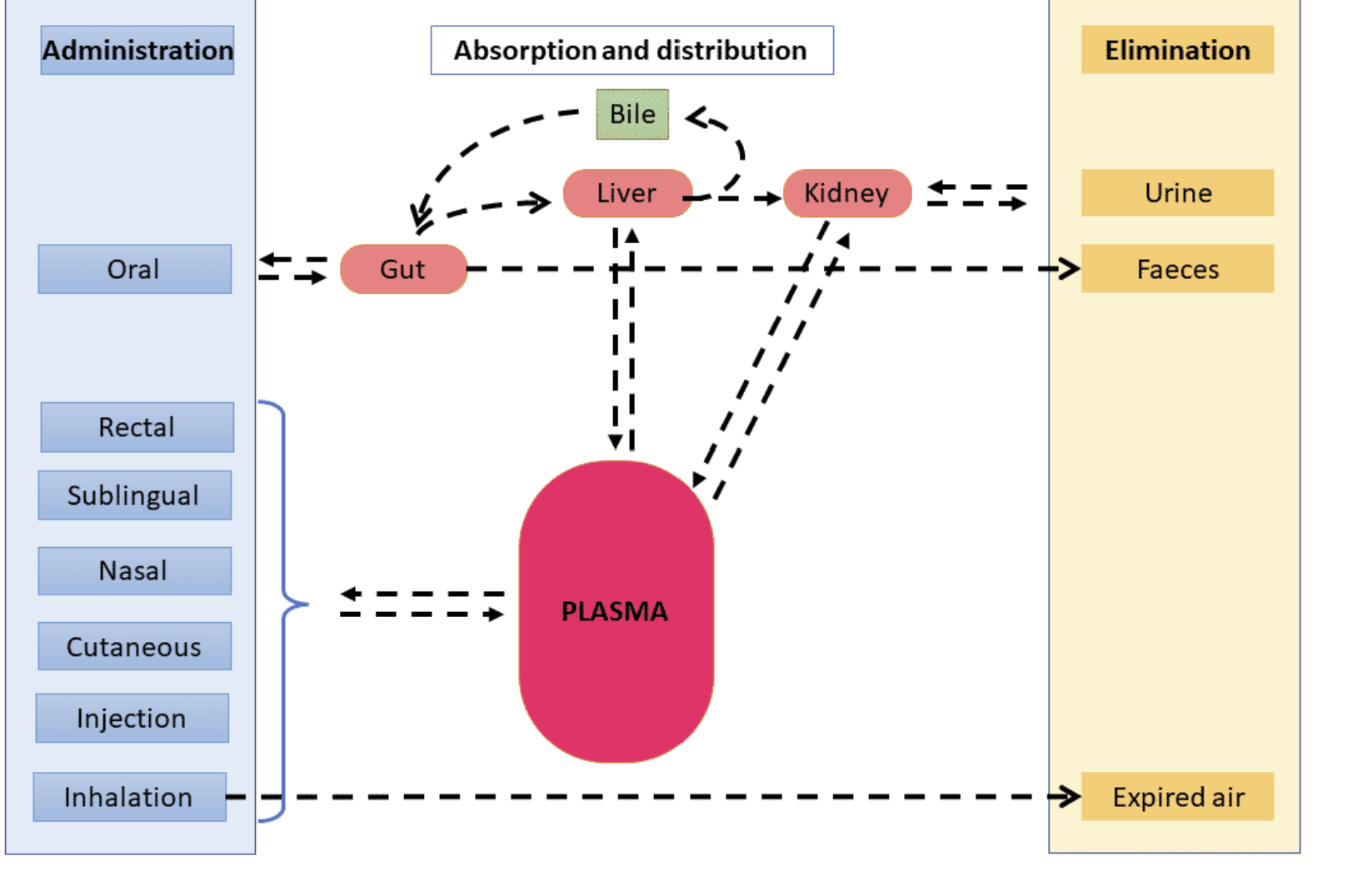
drugs must often move across?
Membrane Barriers to be Absorbed, and Distributed. To reach Site of Action
Passive diffusion through lipid cell membrane, facilitated transport and active transport are the?
Important Mechanisms
The lipid solubility and ionisation of the drug is a?
Major Determining factors in the permeability of the cell membrane to the compound.
Drugs which resemble endogenous substrates for transporter…?
Transporter Proteins can move across the Cell Membrane.
Endocytosis is important for?
Large Molecules.
Absorption is the?
passage of a drug from the site of administration into the plasma.
What is the only route where Passage is not as important?
IV/IO
For some drugs absorption to the plasma is not required, such as?
Topical / Inhalation
Absorption & Distribution Diagram
Drugs need to be stable at acidic…?
Acid pH to pass through the Stomach
Absorption may begin in the mouth and stomach but most drugs are usually absorbed from?
The Small Intestine
Orally administrated drugs must pass through the?
Gut Wall
Transported To Liver
Before entering the Bloodstream
Most drugs administered orally are susceptible to?
First Pass Metabolism
Or Pesystemic metabolism in the gastrointestinal tract and the liver
Describe First Pass Metabolism?
Most drugs are usually absorbed from the small intestine.
A proportion of the drug will undergo metabolism in the cells of the gut wall.
The drug is transferred from the intestine to the liver via the portal vein.
A proportion of the drug will undergo metabolism in the liver.
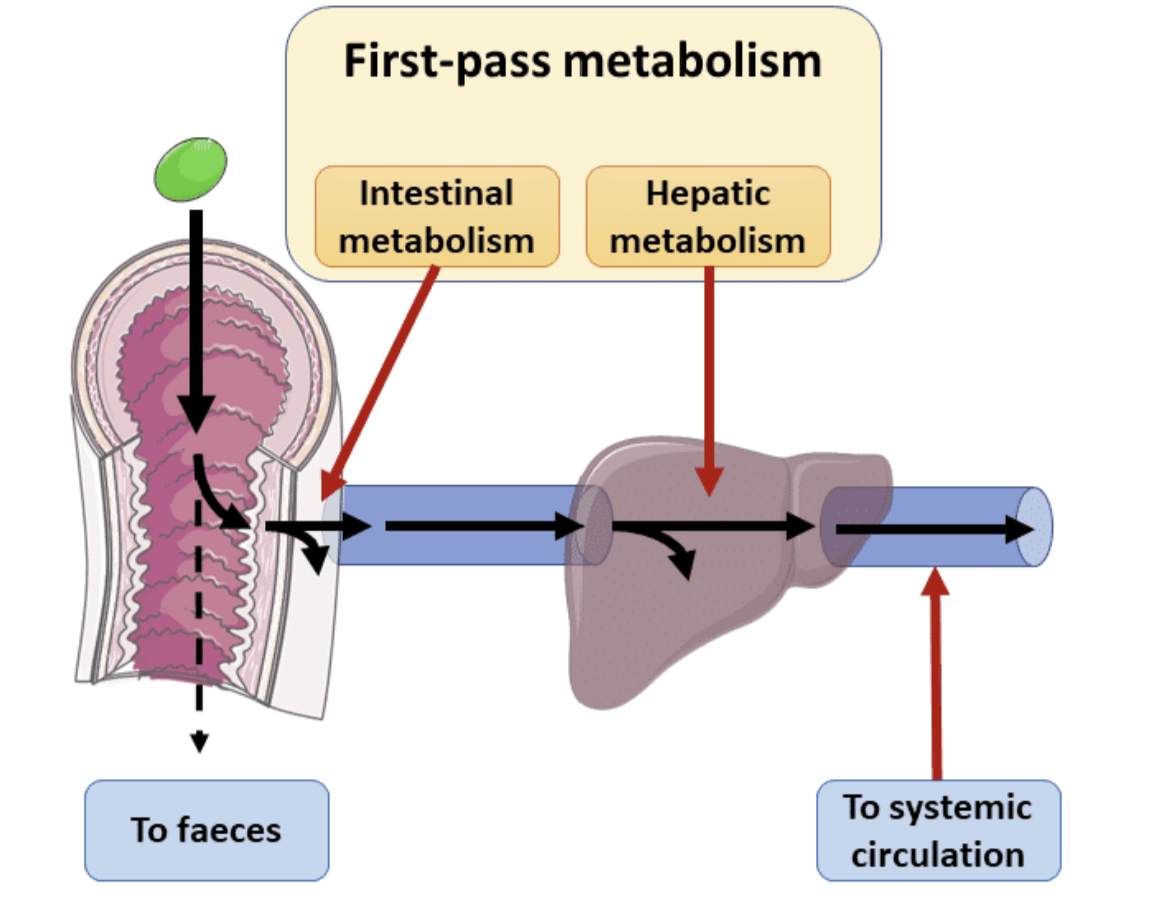
If the Drug is Rapidly Metabolized in 1st Pass Metabolism then?
The amount of unchanged drug entering the systemic circulation is decreased.
What is Bioavailability?
The fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation
What is the Bioavailability of Gtn and Naloxone?
GTN = 1%
Naloxone = 2%
Drugs with high first-pass metabolism are generally administered by?
By routes Such as
Sublingual, Nasal, Injection (Paranetral)
Up to ….% of a drug can be absorbed within 1-3 hours.
75%
What are the 4 Main Factors affecting GI Absorption?
GI Motility
Sphlachnic Blood Flow
Particle Size
Physiochemical Factors
The sublingual route results in?
Rapid Absorption
And Enters Bloodstream Immediately.
E.G GTN
Drugs administered as nasal spray must be transformed into?
Tiny Droplets in Air (Atomized)
Nasal Administration is absorbed through?
through the thin mucous membrane that lines the nasal passages.
Once absorbed, the drug enters the bloodstream and avoids first-pass metabolism.
Works Quickly
Lipid-soluble drugs can be administered through stick?
Stick on patches.
Causing Systemic Effects.
Inhalation administration, The Lungs serve as both…?
Absorption & Excretion
Inhalation is used to administer?
This method is used for gaseous and volatile drugs
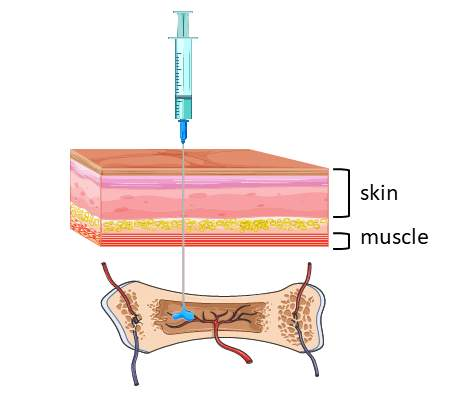
Administration of drugs by injection is used for drugs that are?
Poorly absorbed in the GI Tract, Or unstable.
4 Types of Injection
IV Can be administered either?
The drug can be administered by a bolus injection
or by slow infusion (by gravity or infusion pump).
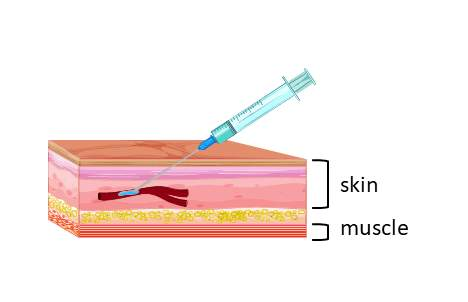
The addition of adrenaline to a local anaesthetic reduces the?
the absorption of the aesthetic into the general circulation
, thus prolonging the anaesthetic affect locally.
IM is the preferred Route for?
Drugs with a large volume
Rate of Absorption is dependent on Blood Volume.
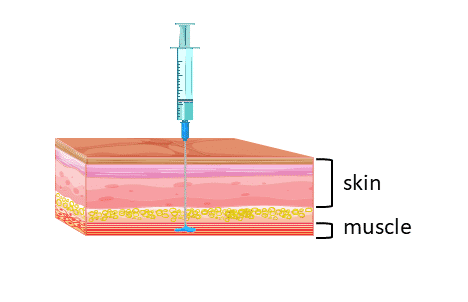
IO provides a non?
Non Collapsable Entry Point To the Venous System