Cardiac Physiology: Electrophysiology & Excitation
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Electrophysiology
electrical activity that occurs in the heart
The mechanical activity (squeezing of the heart) is caused by...
changes in cardiac cell membrane polarity and the movement of ions
Cardiac cells are __________
polarized
polarization
the concentration of ions is different inside the cell and outside the cell
Transmembrane potential
The electrical potential difference (voltage) across a cell's plasma membrane
What is the resting potential of most cardiac muscle cells?
-80 to -90 mV
depolarization
an increase in the membrane potential caused by an influx of positive ions
Depolarization is mainly due to...
influx of sodium
repolarization
Return of the cell to resting polarized state
Repolarization is mainly due to...
exit of potassium
an action potential occurs when...
there is a reversal of the charge inside the cell from negative to positive
Three types of cardiac cells:
1.) cardiomyocytes
2.) Purkinje cells
3.) pacemaker cells
cardiomyocytes
contractile cells of the atrium and ventricle
Where are cardiomyocytes found?
myocardium (walls of atria and ventricles)
Purkinje cells
conduction cells of the heart that transmit electrical signals
Where are Purkinje cells found?
within the heart's conduction system
pacemaker cells
noncontractile cells that spontaneously depolarize to keep the heart beating
where are pacemaker cells found?
SA and AV nodes
The action potential of what cell type is responsible for initiating the cardiac cycle?
pacemaker cells
The action potential of what cell type is responsible for conduction within the heart?
cardiomyocytes
What cell types use Na channels for depolarization?
cardiomyocytes and Purkinje cells
What cell types use the slow Ca current for depolarization?
pacemaker cells
Switch terms and definitions
Switch terms and definitions
cardiomyocytes and Purkinje cells
This is the action potential graph for what cell types?
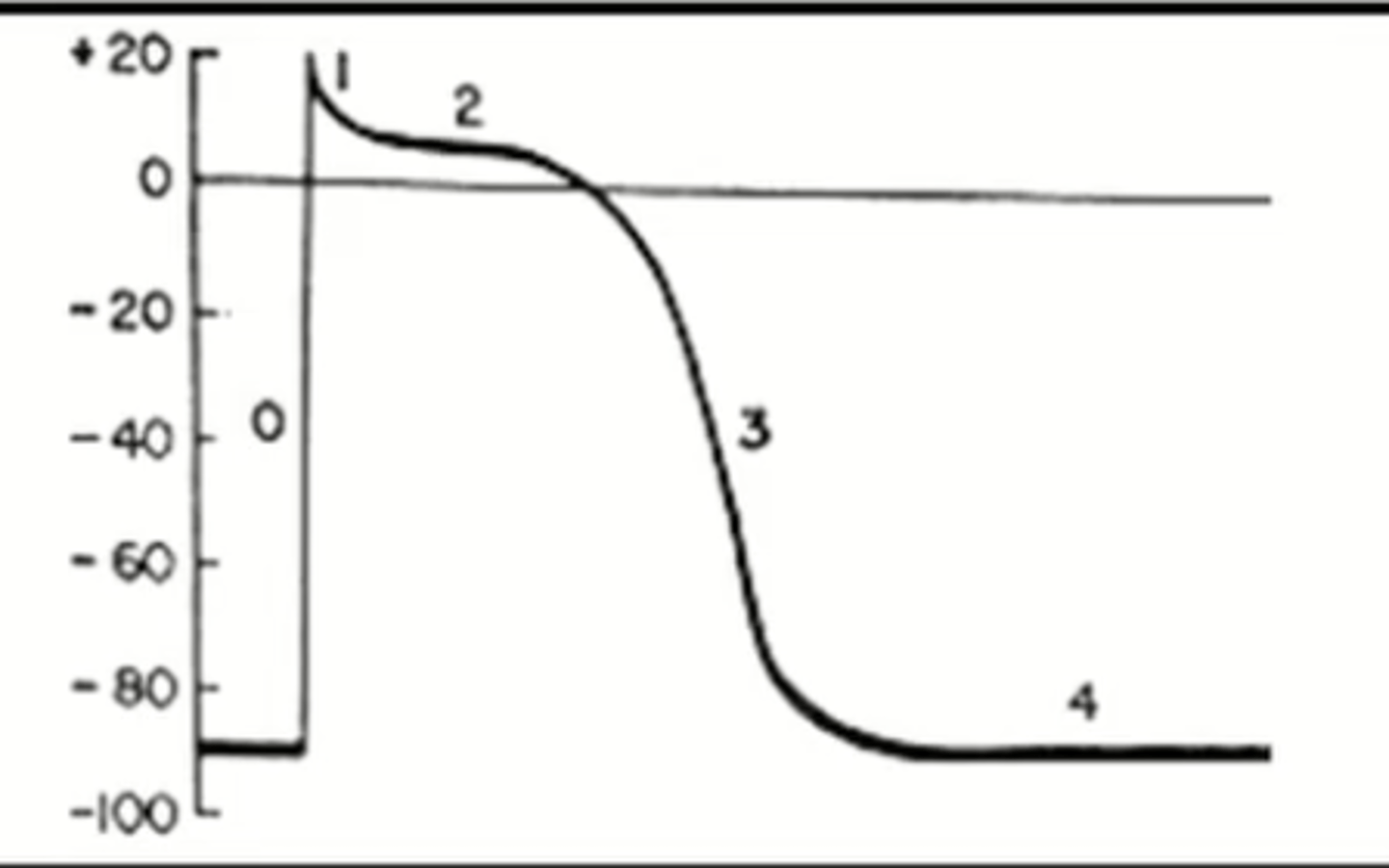
pacemaker cells
This is the action potential graph for what cell types?
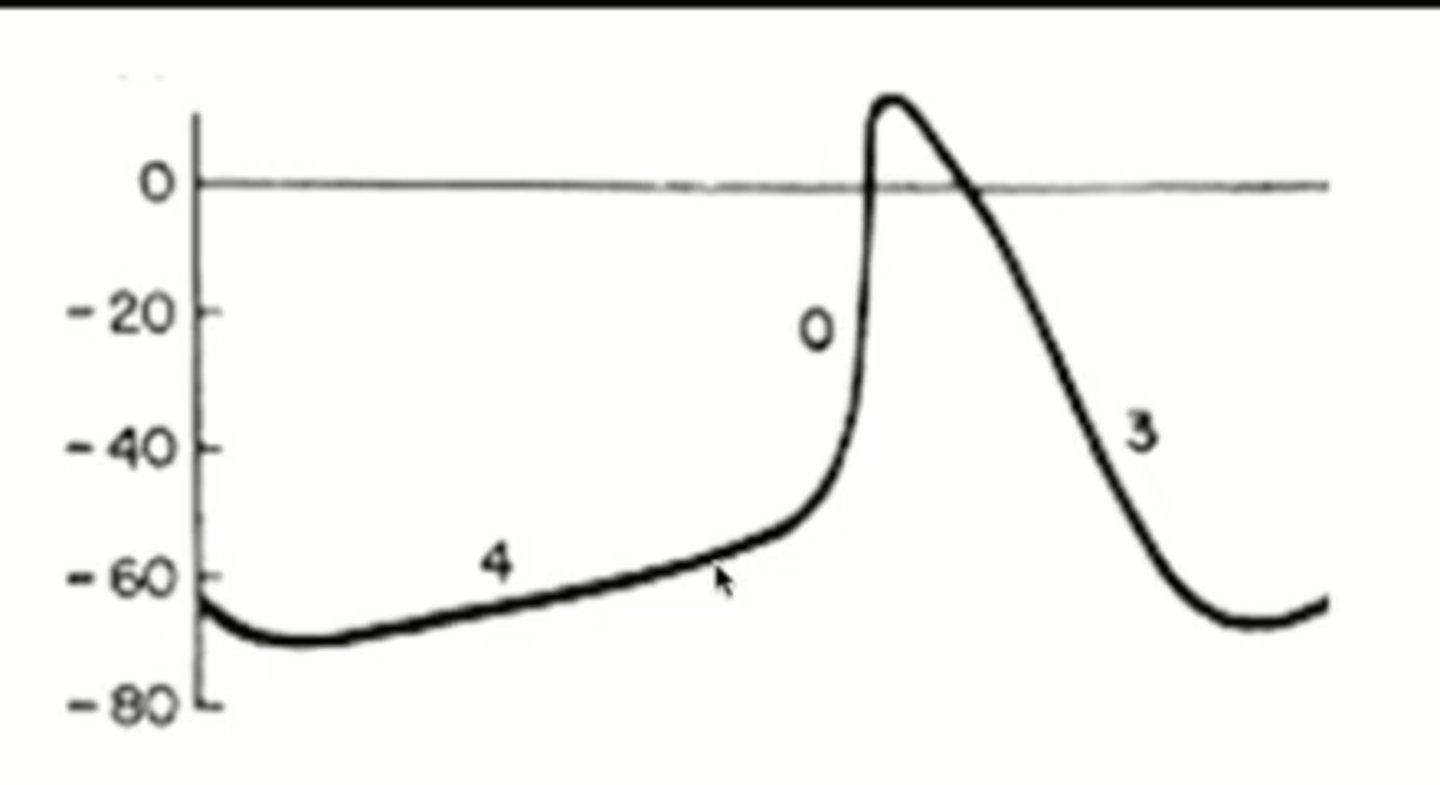
Switch terms and definitions back
Switch terms and definitions back
Five phases of the action potential in cardiac cells:
1.) phase 0
2.) phase 1
3.) phase 2
4.) phase 3
5.) phase 4
phase 0
depolarization
phase 1
brief, early repolarization
phase 2
plateau phase
phase 3
repolarization
phase 4
return to resting membrane potential
Pacemaker cells do not have a phase _____ or ____during their action potential
1 or 2 (brief repolarization and plateau)
Main ion channel that determines the resting membrane potential
sodium potassium ATPase pump
The Na/K ATPase pump moves _______ sodium ______ the cell and _______ potassium _______ the cell
3; out of
2; into
The Na/K ATPase pump creates a ________ charge inside the cell
negative
*the resting membrane potential
There is typically high concentrations of potassium __________ the cell and high concentrations of sodium _________ the cell
inside
outside
What takes place during phase 0 of the action potential (cardiomyocytes and purkinje cells)
Na channels open and allow Na to rush into the cell --> depolarization!
What is the stimulus that causes Na channels to open?
voltage change OR ligand binding to a receptor
What takes place during phase 1 of the action potential (cardiomyocytes and purkinje cells)
K channels open and K rushes out of the cell --> brief repolarization
What takes place during phase 2 of the action potential (cardiomyocytes and purkinje cells)
Ca channels open and Ca rushes into the cell --> plateau
Why does a plateau occur during phase 2?
result of K ions leaving the cell during phase 1 (brief repolarization) and Ca ions entering the during phase 2
What is the role of Ca entering the cell?
it will help trigger a cascade of events that promote more calcium to enter the cell and ultimately stimulate myocardial contraction
What takes place during phase 3 of the action potential (cardiomyocytes and purkinje cells)
K channels open and K rushes out of the cell --> repolarization
What takes place during phase 4 of the action potential (cardiomyocytes and purkinje cells)
Na/K pump returns cell to resting membrane potential
What takes place during phase 0 of the action potential (pacemaker cells)
calcium channels open and allow calcium in --> depolarization
What takes place during phase 3 of the action potential (pacemaker cells)
K channels open and K rushes out of the cell --> repolarization
What takes place during phase 4 of the action potential (pacemaker cells)
the cell reaches its resting membrane potential through the "funny current"
funny current
spontaneous automatic drift towards the resting membrane potential due to slow influx of Na AND K
The funny current causes the membrane potential to become more _________
positive
*towards resting membrane potential
Once the funny current causes the cell to reach its membrane potential, what happens?
Ca channels open, triggering phase 0 depolarization
The resting membrane potential of cardiomyocytes and purkinje cells is ____ mV
The resting membrane potential of pacemaker cells is ____ mV
-80 to -90 mV
-50 mV
What causes depolarization in cardiomyocytes/purkinje cells?
Pacemaker cells?
fast inward sodium current
slow inward calcium current
For each cell, when the resting membrane potential is reached, this triggers...
depolarization to occur
conductance
the ease with which ions flow through a channel and in what direction; aka permeability
Membrane conductance ________ throughout an action potential
varies
Four things that cause the opening of an ion channel:
1.) voltage changes
2.) time duration
3.) concentration gradients
4.) ligand binding
Three ligands that open channels in the heart:
1.) norepinephrine
2.) epinephrine
3.) acetylcholine
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are released by...
sympathetic nerves and adrenal glands
Norepinephrine and epinephrine bind to...
beta-adrenergic receptors
beta-adrenergic receptors
cause an increase in the force of contraction of the heart, an increased heart rate, and bronchial dilation
acetylcholine is released by...
the vagus nerve
acetylcholine binds to...
muscarinic receptors (M2)
muscarinic receptors
modulate channel conductance; decrease the force of contraction in the heart and lower heart rate
In resting cardiomyocytes, the cell membrane has high conductance to ________ and low conductance to _______ and ___________
potassium; sodium and calcium
Because the resting membrane of cardiomyocytes is highly permeable to potassium...
this ion is constantly drifting out of the cell along its concentration gradient (remember potassium is high within the cell and low outside of the cell)
Because the resting membrane of cardiomyocytes has low permeability to sodium...
little sodium crosses the membrane, despite an enormous concentration gradient for entry
Channelopathies
diseases and disorders that are the result of ion channel dysfunction; can cause arrhythmias
Anti-arrhythmic drugs
block ion channels to help treat arrhythmias
Example of anti-arrhythmic drug
lidocaine --> Na channel blocker
ionophores
lipid soluble chemicals that act as a carrier of ions across the cell membrane; sometimes added to animal feeder as growth promoters
Problem with ionophores
when ingested in excessive amounts by cattle or when fed to unintended species (especially horses and camelids), the compound can be highly toxic to the heart causing arrhythmias, heart failure, and even death
Three main ion channels in the heart:
1.) Na channels
2.) Ca channels
3.) K channels
Na channels are found in what cardiac cell type?
cardiomyocytes and Purkinje cells
Role of Na channels
fast sodium influx that depolarizes the cell during phase 0
What causes activation of Na channels?
when transmembrane voltage increases to -60 to -70 due to spontaneous depolarization of pacemaker cells in the SA node
The slope of phase 0 determines the conduction _________ from cell-to-cell
velocity
The Na channel is both ________ gated and _________ dependent
voltage gated and time dependent (shuts down milliseconds after opening)
Na channels are aka...
fast channels since they open and close so quickly
Ca channels are found in what cardiac cell type?
all cardiac cells
Ca is required for __________ of muscle cells
contraction
Two functions of Ca channels in pacemaker cells:
2.) important for depolarization in pacemaker cells
3.) contributes to the spontaneous pacemaker currents of SA node cells
Functions of Ca channels in cardiomyocytes:
responsible for the plateau phase of the action potential, resulting in calcium influx into the cell
Calcium influx into the cardiomyocyte is important for...
calcium-induced calcium release within the cell that helps lead to myocardial contraction
Two types of Ca channels based on activation
1.) voltage gated
2.) ligand gated
Two types of Ca voltage gated channels in the heart:
1.) T-type
2.) L-type
T-type Ca channels
open at low voltages and allow for short bursts of Ca entry
Where are T-type Ca channels found?
pacemaker cells (SA node)
*help initiate muscle contraction in late phase 4!!
L-type Ca channels
open at high voltages and allow for sustained Ca entry
Where are L-type Ca channels found?
cardiomyocytes (cause plateau phase) and pacemaker cells (slow depolarization)
Two types of Ca ligand gated channels in the heart:
1.) norepinephrine gated
2.) epinephrine gated
Norepinephrine and epinephrine bind to...
beta-receptors
What happens when Norepinephrine and epinephrine bind to beta-receptors?
causes Ca influx, which leads towards greater heart contraction and faster heart beat
K channels are found in what cardiac cell type?
all cardiac cells
Three functions of K in cardiomyocytes:
1.) phase 1 brief repolarization
2.) phase 2 plateau (as Ca enters, K leaves, creating plateau)
3.) phase 3 repolarization
Two functions of K in pacemaker cells
1.) phase 3 repolarization
2.) facilitates funny current
Repolarization is mainly due to _____ channels letting this ion go ______ of the cell
K; out of
K channels determine the ________ of repolarization
speed
effective refractory period
phase in which cells are incapable of depolarizing (occurs during repolarization)
A faster repolarization will _________ the effective refractory period
decrease