7. Emulsions and microemulsions
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Emulsion
A mixture of immiscible liquids (not insoluble, still some degree of solubility, however usually different phases).
Examples:
– Oil-in-water (e.g mayonnaise) (continuous oil phase)
– Water-in-oil (e.g. butter)
– Double emulsions (e.g. oil-in-water-in-oil) (emulsion drops in the emulsion, drops have to be quite large to have drops inside of them)
• Droplet size: <100 nm to 100 μm
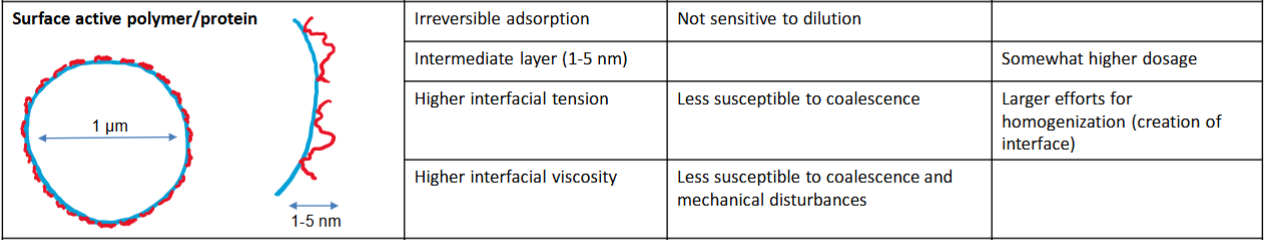
• Surface layer of adsorbed emulsifier (surface active) (protein or polymer) stabilizes
– Surface layer is typically very thin (1-3 nm)
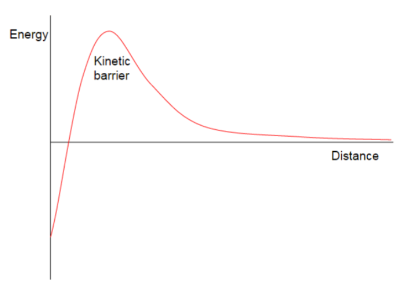
Emulsion instability
Emulsions are thermodynamically unstable (eliminating the dispersed phase)
A barrier needs to be created to prevent flocculation and coalescence
Add an emulsifier to create a barrier, stabilise by giving repulsive forces between oil drops (the main function of emulsifier, not to decrease surface tension)
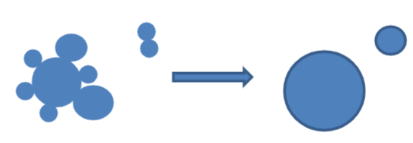
Coalescence
fusion of several small droplets to larger droplets
Emulsifier
The main role of the emulsifier is to prevent the immediate coalescence of droplets when the emulsion is formed, and to prevent flocculation and coalescence. The main role is not to lower surface tension that the liquids can mix.
In order to stabilize an emulsion the emulsifier should:
Give rise to repulsive interaction between droplets
Contribute to the interfacial viscosity (more rigid (higher viscosity) the interface better resistance to deformation)
Should be well anchored at the interface
Coalescence requires:
Requires that droplets are in close contact either through:
High dispersed phase volume fraction (φ) (e.g mayonnaise, the particles are not spherical, the maximum phase volume fraction is 0.57 for spherical particles)
Flocculation
Creaming/sedimentation
Requires deformation of the interface
Large droplets (larger flexible interface) are typically more susceptible to coalescence
Coalescence influenced by the adsorbed layer stability
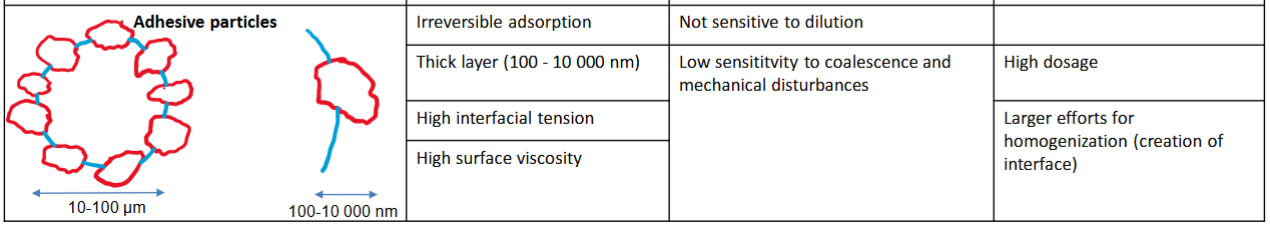
• Thick layer → more stable
• Rheological properties (viscosity) of the adsorbed layer and the dispersed phase
• The presence of other phases
• Solid particles wetted by the disperse phase can destabilize (example: fat crystals, can keep two oil droplets together called partial coalescence (e.g whipped cream and ice cream))
• The interfacial tension
• Low interfacial tension → work to deform interface lower → sensitive to
coalescence
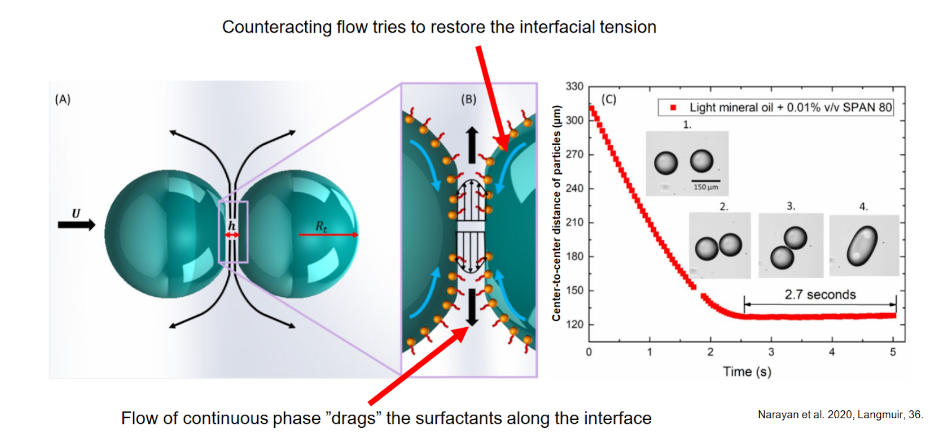
Deformation of the interfacial layer
Flow of continuous phase ”drags” the surfactants along the interface
Counteracting flow tries to restore the interfacial tension
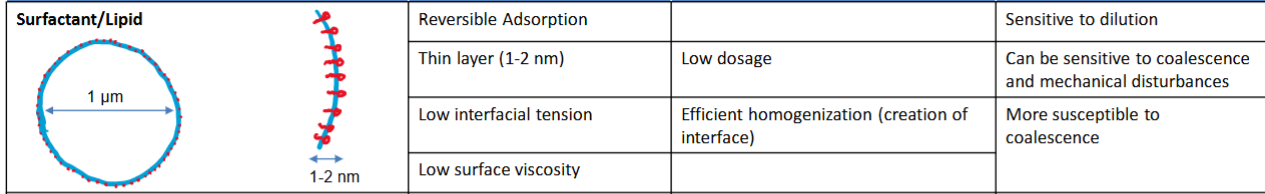
Different types of emulsifiers
Low MW surfactants/lipids
Marcomolecules (surface active polymers and proteins)
Adhesive particles (partial wetting - pickering emulsions)
Low MW surfactant/lipid
Surface active polymer/protein
Adhesive particles
Estimation of emulsifier dosage
Can also apply for other dispersions than emulsions
Rough estimation based on mass to cover interface
Length of surfactant molecule ~ 1 nm (i.e. thickness of adsorbed layer)
Density of surfactant molecules ~ 1000 kg/m3
10-9 * 1000 = 10-6 kg/m2 → 1 mg/m2
Calculate the total surface area in the emulsion/dispersion and compare with the mass of
emulsifier present
Estimation from thickness of emulsifier layer
Gives emulsifier amount relative to the dispersed phase
VE= Volume of emulsifier
VD= Volume of droplet
cE= Volume of emulsifier (in relation to the dispersed phase)
A= Area of droplet
d= diameter of droplet
Δ= thickness of emulsifier layer (length of emulsifier molecule)
Bancroft rule
The phase in which the emulsifier is most soluble in will be the continuous phase
Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) concept
Emulsifier with a HLB value < 7 forms an oil continuous emulsion
Emulsifier with HLB > 7 forms a water continuous emulsion
Emulsification and stability
• For emulsification we need unstable interfaces
• For stability we need stable droplets
What should the emulsfication process accomplish?
• Create new interface (more and smaller droplets)
Energy cost: A*γ (surface area*surface tension)
• Overcome the viscous resistance of the disperse phase
Dynamic viscosity η
• Create a deformating force gradient over the droplets (intensive treatment to get small particles)
Phase inversion in emulsions
switch phase continuous phase becomes dispersed
• Spontaneous phase inversion
• Can occur at a high volume fraction (φ > 0.7) of dispersed phase
• Can also occur at a lower volume fraction
• For instance by increasing T in oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by an ethoxylated surfactant (sensitive to high temperature, hydrophilic drastically decreases → wants continuous phase rather polar)
• Phase inversion can also occur due to intense mechanical treatment
• Can be an approach to disperse very viscous oils
For example: Cream → butter
Different HLB value in relation to phase inversion
High HLB emulsifiers are hesitant to form water-in-oil emulsions
Low HLB emulsifiers are hesitant to form oil-in-water emulsions
Phase inversion is most likely when emulsifier has an intermediate HLB (get bicontinuous system, any of phases can become continuous)
Microemulsions
• Contains oil, water, surfactants and co-surfactants (can be a fatty alcohol (not surface active on its own))
• Gives additional lowering on the interfacial tension
• Requires relatively high amounts of surfactant
• Can be O/W, W/O or bicontinuous
• Are disordered
Properties of microemulsions
• Relatively low viscosity
• Solubilize both hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules
• High diffusion of both oil and water soluble components (move quite freely)
• Low interfacial tension (close-packing of surfactant and co-surfactant)
Winsor classification of microemulsions
Winsor 3: The middle phase (M) can be a bi-continuous microemulsion
Winsor 2: W/O
Winsor I: O/W
Properties of microemulsions are changed by
Ionic strength (applied for ionic surfactants)
Temperature (applied for non-ionic ethoxylated surfactants)
Marcoemulsion vs microemulsions
M