the ear- labelling and functions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
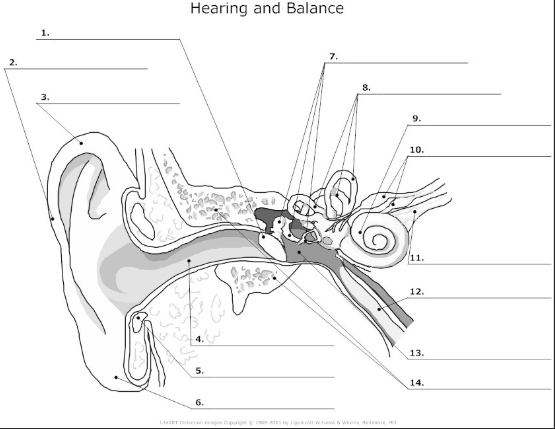
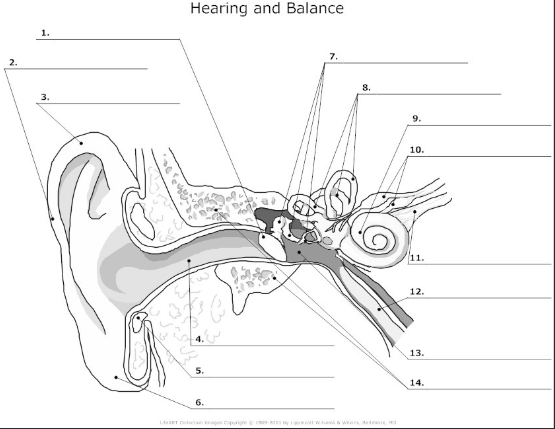
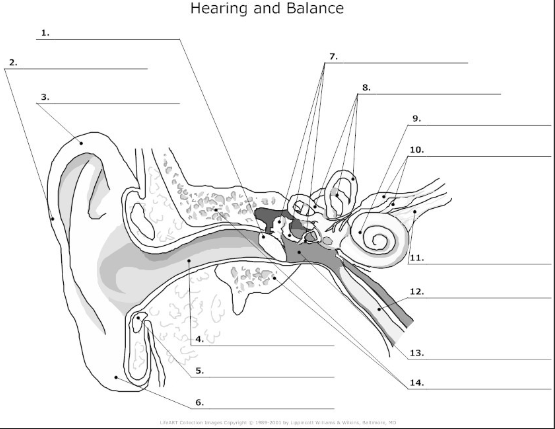
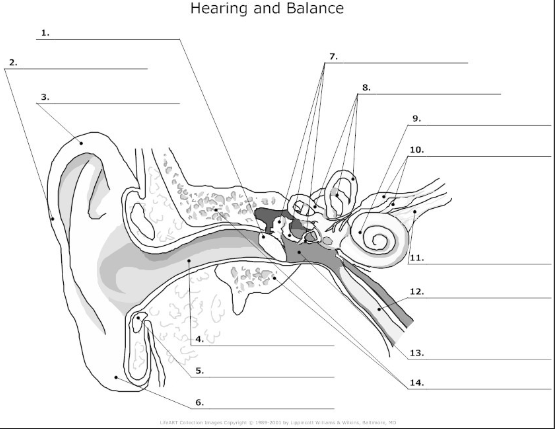
functions of the ear
used for hearing and balance
what 3 areas is the ear divided into
external ear, middle ear, inner ear
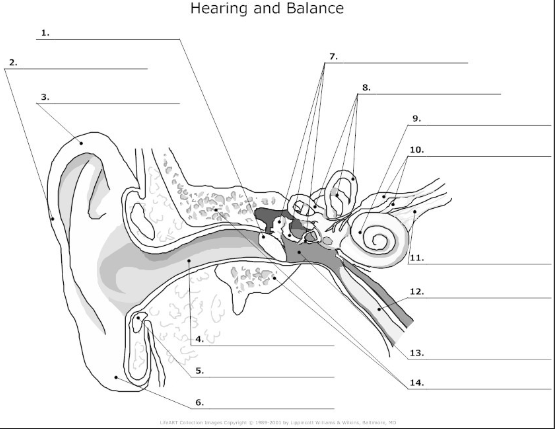
1
tympanic membrane- also known as the ear drum, flat membrane at the end of the auditory tube that vibrates in response to pressure from sound waves
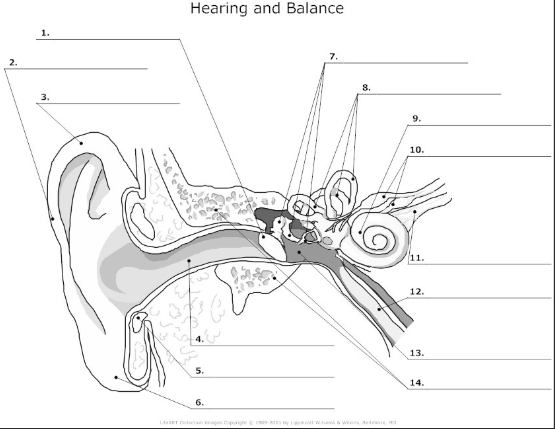
2-
pinna/auricle- the visible part of the ear that acts as a funnel for sound waves to the auditory tube
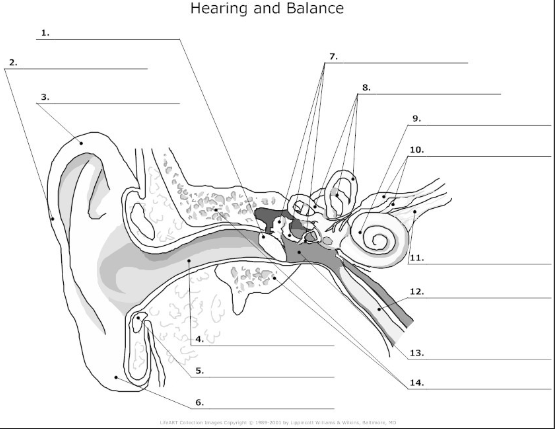
3
helix- curved cartilage that is part of the pinna/auricle and involved in sound collection
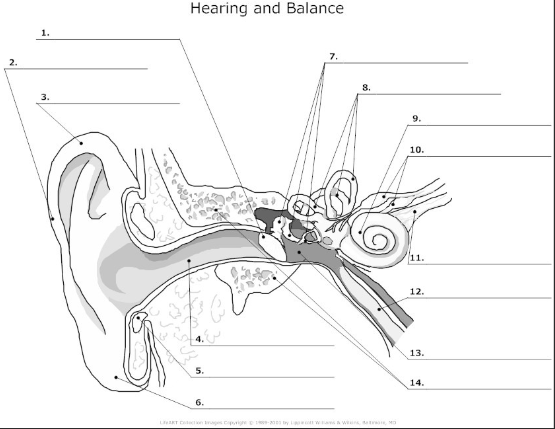
4
auditory canal- transmits sound from the pinna/auricle to the tympanic membrane
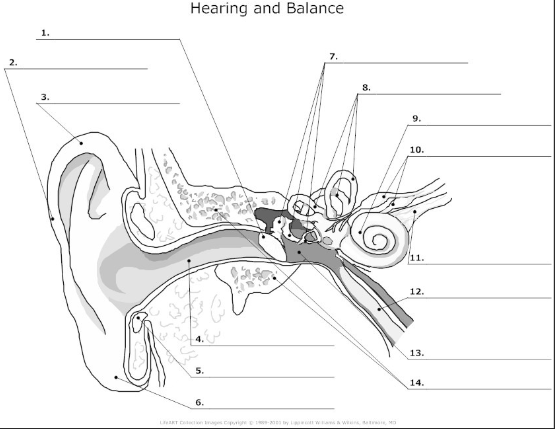
5
cartilage
6
auricular lobe- soft, fleshy part of the outer ear
7
auditory ossicles(malleus, incus, stapes)- bones in the middle ear that transmit and amplify incoming sound before transmitting to the inner ear
8
semicircular canal- 3 fluid filled tubes containing hair cells that detect fluid movement and send impulses to the brain, responsible for equilibrium in the ear
9
cochlea- small fluid filled spiral where sound is converted from sound waves to electrical impulses
10
vestibular nerve- transmits sensory information eg)balance and spacial orientation from the inner ear to the brain
11
cochlea nerve/auditory nerve- transmits sound information from the cochlea to the brain

12
Eustachian tube- tube that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and helps maintain the pressure within the middle and outer ear
13
tympanic cavity- air filled space in the middle ear
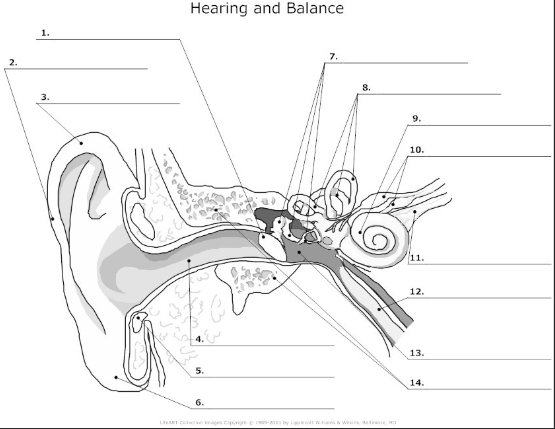
14
temporal bone
what is the basilar membrane
tissue within the cochlea containing cilia that respond to different sounds and frequencies due to characteristics of the cilia eg) thickness, length, width etc
what is the organ of corti
in the basilar membrane, contains singular rows of inner and outer hair cells that turn vibrations into electrical impulses
describe the process of hearing in steps 1-8
1) sound waves are carried and funneled to the pinna
2) the sound is then carried along the auditory tube to the tympanic membrane
3) the tympanic membrane vibrates in response to the pressure from the sound waves
4) the malleus is connected to the tympanic membrane and transmits sound waves to he incus
5) the incus receives the vibrations and transmits it to the stapes
6) the stapes transmits the vibrations to the cochlea
7) the vibrations reach the cochlea and the hair cells within transform the sound waves to nerve impulses
8) the nerve impulses are carried to the brain stem along the auditory tube
9) the brain can then interpret these as sounds