Neurologic Function Assessment Techniques
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Health history
Initial interview explores patient's neurologic condition.
Neurologic disease
Can be stable or progressive with symptom fluctuations.
Common symptoms
Includes pain, seizures, dizziness, visual disturbances.
Pain
Unpleasant sensory perception linked to potential damage.
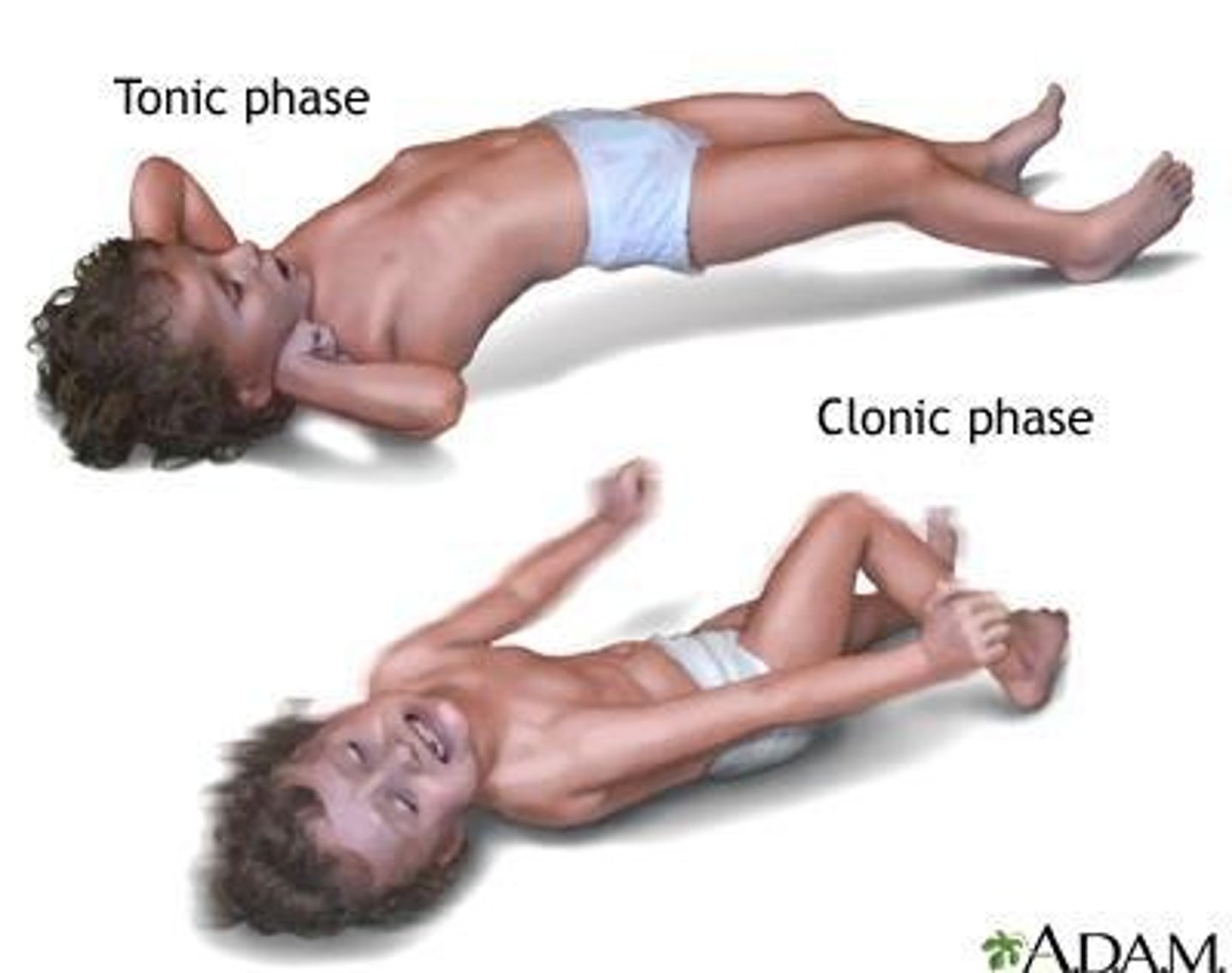
Seizures
Abnormal discharges in cortex altering sensation or behavior.
Dizziness
Abnormal sensation of imbalance or movement.
Vertigo
Illusion of movement, often due to vestibular dysfunction.
Visual disturbances
Defects range from decreased acuity to sudden blindness.
Muscle weakness
Common neurologic symptom affecting various muscles.
Abnormal sensation
Altered sensation indicating central or peripheral disease.
Mental status
Observing appearance and behavior for cognitive assessment.
Orientation
Evaluates awareness of time, place, and person.
Acute pain
Short-term pain signaling immediate harm.
Chronic pain
Long-lasting pain affecting daily life.
Cerebral cortex
Brain region involved in seizures and sensation.
Neuromuscular diseases
Progressive conditions causing muscle weakness.
Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movement affecting vision.
Diplopia
Double vision resulting from eye movement abnormalities.
Vestibular dysfunction
Disorder affecting balance and spatial orientation.
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar potentially causing seizures.
Emotional status
Assessment of mood and affect during evaluation.
Intellectual function
Cognitive abilities assessed through various tasks.
Language ability
Evaluates communication skills and comprehension.
Orientation
Awareness of time, place, and person.
Delirium
Acute confusion with hallucinations and delusions.
Intellectual Function
Ability to interpret proverbs and recognize similarities.
Judgment
Capacity to make decisions in situations.
Thought Content
Spontaneity and coherence of patient's thoughts.
Unusual Thoughts
Fixed ideas or preoccupations needing evaluation.
Emotional Status
Assessment of mood and affect during interaction.
Affect
Emotional expression matching verbal communication.
Language Ability
Understanding and communication in spoken/written forms.
Aphasia
Deficiency in language function affecting communication.
Sensory Aphasia
Inability to comprehend spoken or written language.
Auditory Aphasia
Loss of understanding sounds' symbolic content.
Visual Aphasia
Loss of understanding printed or written figures.
Motor Aphasia
Inability to express oneself through speech or writing.
Level of Consciousness
Patient's wakefulness and environmental responsiveness.
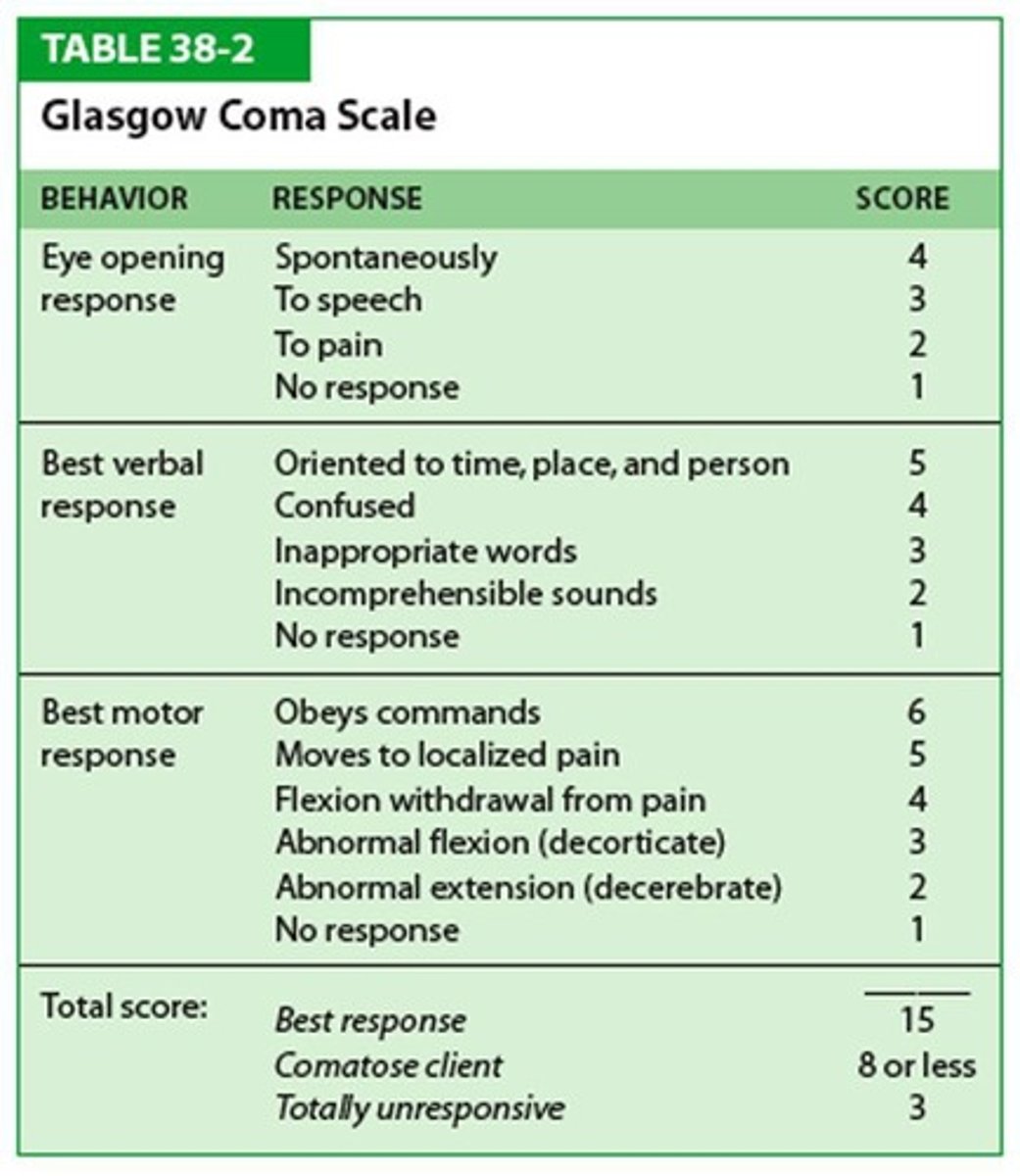
Glasgow Coma Scale
15-point scale assessing level of consciousness.
Reflex
Automatic body response to a stimulus.
Reflex Testing
Evaluating reflexes for symmetry and response quality.
Reflex Scale
0 to +4 grading reflex response intensity.
Biceps Reflex
Test of biceps muscle response to stimulus.
Triceps Reflex
Test of triceps muscle response to stimulus.
Patellar Reflex
Knee jerk response tested during physical examination.
Achilles Reflex
Ankle jerk response tested during physical examination.
Plantar Reflex
Superficial reflex, toes bend down normally.
Babinski Reflex
Positive response: toes spread, big toe upward.
Biceps Reflex
Tests spinal levels C-5, C-6; elbow flexion observed.
Triceps Reflex
Tests spinal levels C-7, C-8; elbow extension observed.
Brachioradialis Reflex
Tests spinal levels C-5, C-6; forearm flexion observed.
Patellar Reflex
Tests spinal levels L-2, L-3, L-4; leg extension observed.
Achilles Reflex
Tests spinal levels S-1, S-2; plantar flexion of foot.
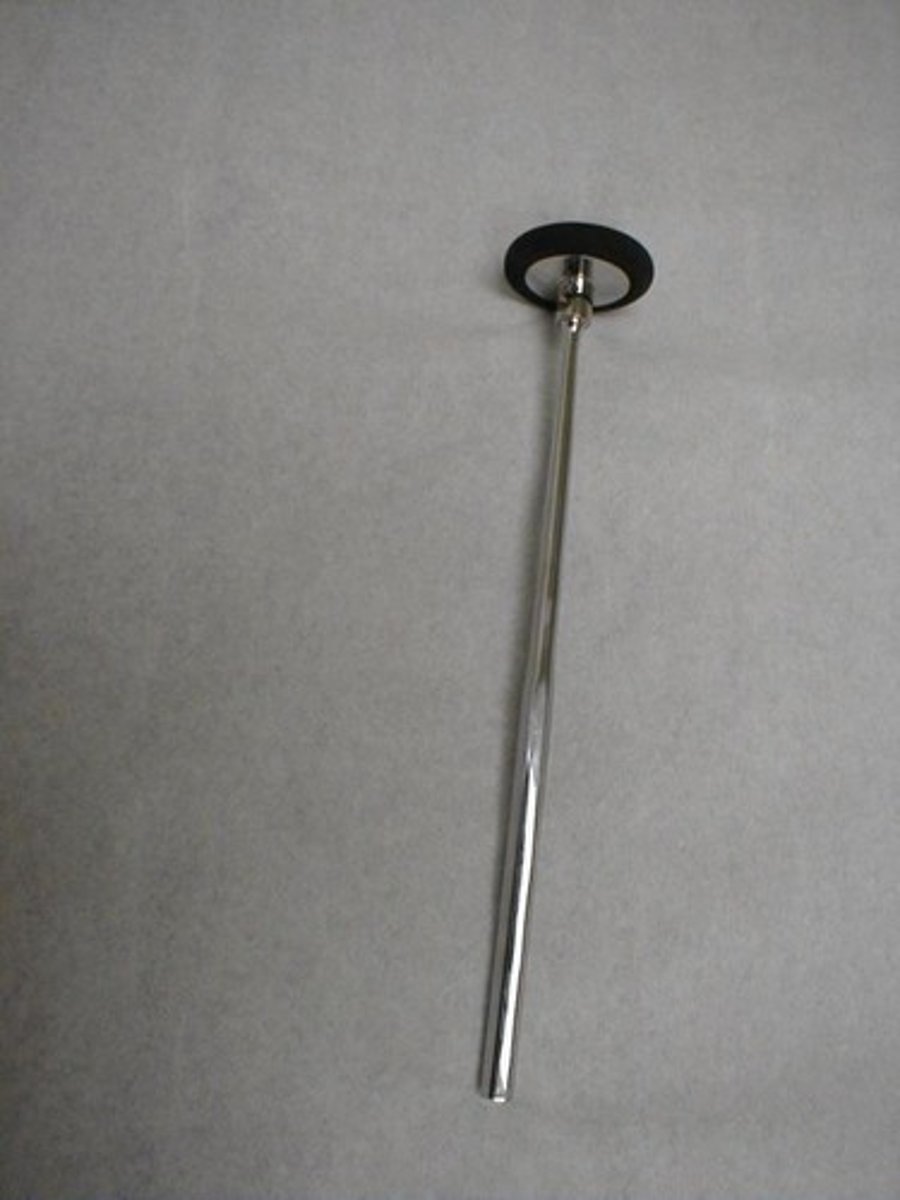
Reflex Hammer
Tool used to elicit deep tendon reflexes.

Cranial Nerves
Nerves assessed for brain stem or PNS issues.
Cranial Nerve 1
Olfactory nerve; tests smell with aromas.
Cranial Nerve 2
Optic nerve; tests vision and visual fields.
Cranial Nerve 3
Oculomotor nerve; assesses eye movements and pupils.
Cranial Nerve 4
Trochlear nerve; controls superior oblique muscle.
Cranial Nerve 5
Trigeminal nerve; tests facial sensation and motor function.
Cranial Nerve 6
Abducens nerve; controls lateral eye movement.
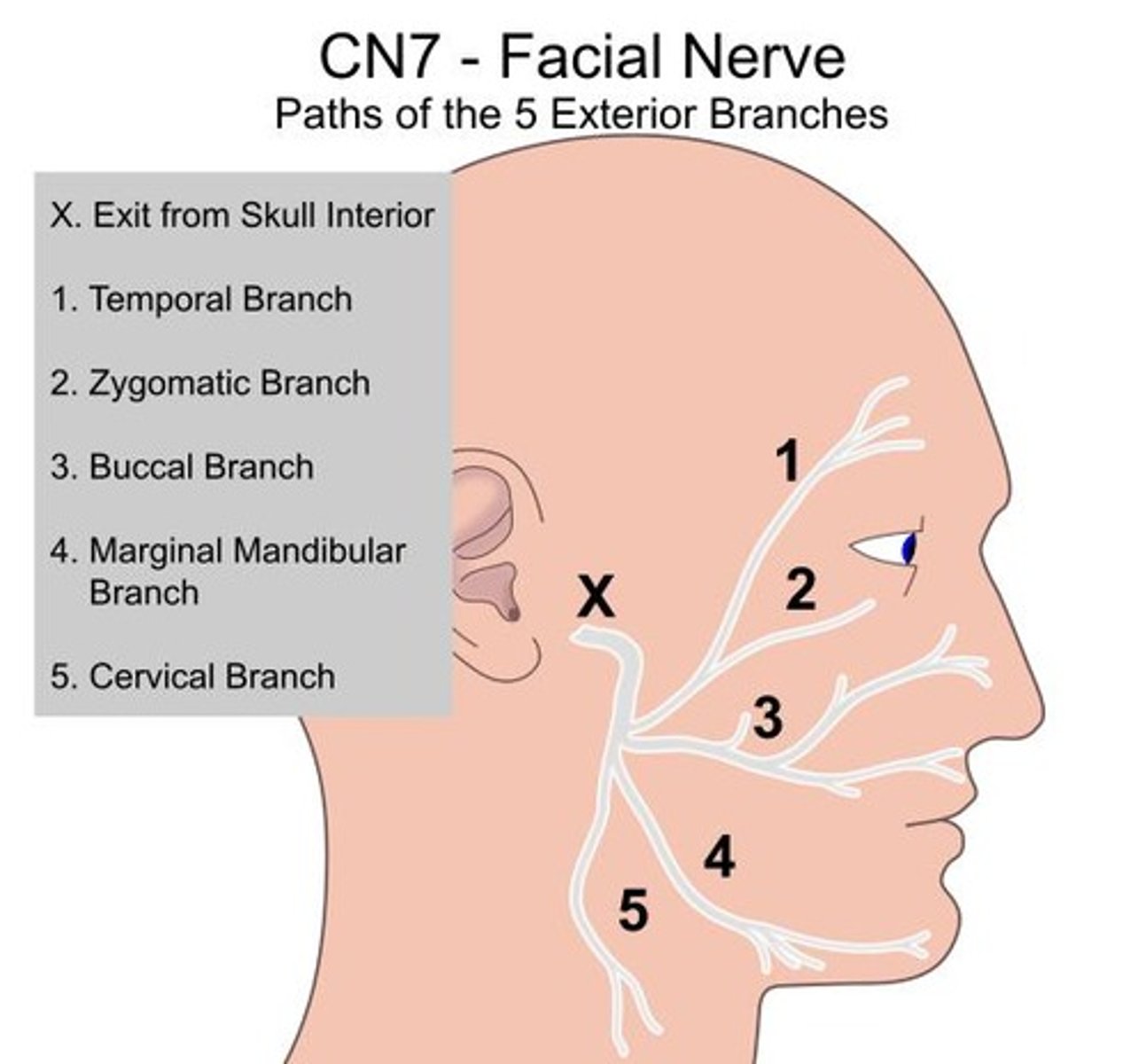
Cranial Nerve 7
Facial nerve; tests facial expressions and taste.
Cranial Nerve 8
Acoustic nerve; assesses hearing and balance.
Cranial Nerve 9
Glossopharyngeal nerve; tests taste on posterior tongue.
Cranial Nerve 10
Vagus nerve; controls autonomic functions.
Romberg's Test
Balance test assessing vestibular function.
Ophthalmoscopic Examination
Visual inspection of the retina and optic nerve.
Confrontation Test
Checks visual fields by direct confrontation.
Vagus Nerve (X)
Assesses speech for hoarseness.
Accessory Nerve (XI)
Controls shoulder shrug and head turning.
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Controls tongue movement and protrusion.
Gross Motor Tests
Evaluate overall motor function and balance.
Walking Gait
Client walks across room; posture and balance assessed.
Normal Gait
Upright posture, steady gait, arm swing present.
Gait Deviation
Poor posture, unsteady, irregular, wide stance.
Romberg Test
Balance test with eyes closed on one foot.
Normal Romberg Findings
Maintains stance for at least 5 seconds.
Romberg Deviation
Cannot maintain balance for 5 seconds.
Heel-Toe Walking
Walks straight line, heel in front of toes.
Normal Heel-Toe Walking
Maintains straight line without wider stance.
Heel-Toe Deviation
Assumes wider gait to maintain balance.
Toe Walking
Client walks several steps on toes.
Heel Walking
Client walks several steps on heels.
Normal Toe or Heel Walking
Able to maintain balance on toes and heels.
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle wasting due to inactivity or injury.
Intrinsic Hand Muscles
Control fine motor movements in the hand.
Finger-to-Nose Test
Client touches nose alternately with fingers.
Normal Finger-to-Nose Performance
Touches nose repeatedly and rhythmically.
Finger-to-Nose Deviation
Misses nose or responds slowly.
Alternating Supination and Pronation
Client pats knees with palms and backs alternately.
Normal Supination/Pronation Performance
Can alternate rapidly without clumsiness.
Supination/Pronation Deviation
Slow, clumsy movements with irregular timing.
Fingers to Fingers Test
Client brings fingers together at midline.
Normal Fingers to Fingers Performance
Coordinates rapidly with eyes open and closed.
Normal Performance
Accurate and rapid execution of tasks.
Deviations in Movement
Slow movement; inconsistent finger coordination.
Fingers to Thumb Test
Touch each finger to thumb rapidly.
Heel Down Opposite Shin Test
Run heel down opposite shin; assess coordination.
Normal Heel Test Result
Bilateral equal coordination demonstrated.
Deviation in Heel Test
Tremors; heel moves off shin.