Unit 2 AP HUGE
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
population distribution
pattern of human settlement—the spread of people across the earth
arithmetic population density
people per unit of land
physiological population density
people per unit of arable land
agricultural population density
farmers per unit of arable land
carrying capacity
number of people a region can support without damaging its environment
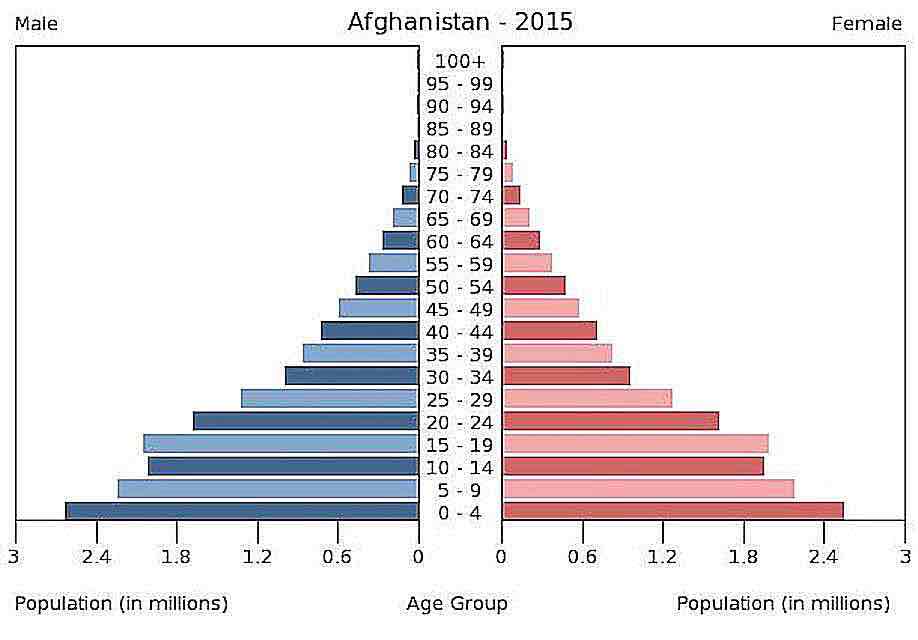
age-sex composition graph
also called a population pyramid, only displays age and gender data but can tell us a lot of information not on the graph
birth deficit
(1) a narrowed base or a dip in the youngest age cohorts, indicating fewer births than expected
baby boom
(2nd) spike of births caused when conflict ends
baby bust
(3rd) an echo of a baby boom where birth rates are lower until the boomers reach childbearing age
echo
a reflection of data from past events
potential workforce
group expected to be the society’s labor force
dependent population
everybody else besides the potential workforce, too young or old to be economically active
dependency ratio
comparison between the size of the potential workforce and the dependent population
migration
the permanent or semipermanent relocation of people from one place to another
voluntary migration
migration made by choice in pursuit of a better life
push factors
negative circumstances, events, or conditions present where they live that compels a person to leave
pull factors
positive circumstances or factors that attract migrants
immigrant
a person migrating across an international border with the intention to stay permanently
emigrant
from the perspective of the country the migrant is leaving, they are viewed as this
Lee’s model of migration
there are push and pull factors at both the source and destination. There are intervening obstacles in between.
intervening obstacles
barriers of any sorts that make migration difficult
intervening opportunities
opportunities that make migration difficult (EX: a migrant gets a job along the way)
distance decay
things near another are more closely connected than things far apart
gravity model of migration (+ formula)
model assuming the size and distance between two places will influence the amount of interactions between them ((population 1 x population 2)/distance²)
step migration
most migration occurs this way, migrants reach their destination through a series of smaller steps and moves
chain migration
when people move to a location because others from their community have previously migrated there.
most mobile population in the world
The United States
forced migration
involuntary migration, migrants are left with no choice but to move
refugees
forced migrants who migrate to another country, crossing international borders
internal migration
migrating inside a country, without crossing international borders.
transnational migration
migration to another country, crossing international borders
chain migration
when migrants decide to settle where their ancestors, friends, or family have resided in the past, creating a community (EX: Chinatown)
asylum
some refugees apply for this, protection granted from one country to an immigrant from another country, guaranteeing that they will not be harmed if they return
guest workers
transnational migrants who relocate to a new country to provide labor that isn't available locally
transhumance
process of herders moving with their animals to different pastures during different seasons
homestead act
U.S. government gave land to settlers willing to stay and farm for 5 years
xenophobia
a strong dislike of people of another culture
remittances
money sent to family and friends in the country an emigrate leaves
brain drain
when migration out of a country is made up of highly skilled people, this occurs to the country
ethnic enclaves
neighborhoods filled primarily with people of the same ethnic group (EX: Chinatown, Little Italy)
total fertility rate
average number of children born per woman in childbearing years in a country
(number) the replacement rate for a stable population
2.1
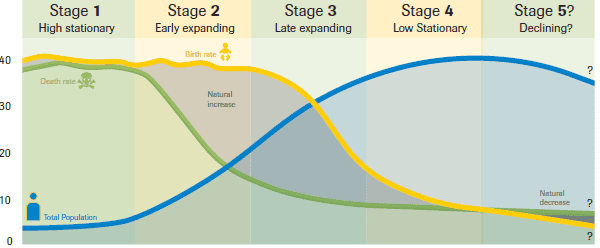
demographic transition model
a model showing 5 typical stages of population change that countries experience as they modernize
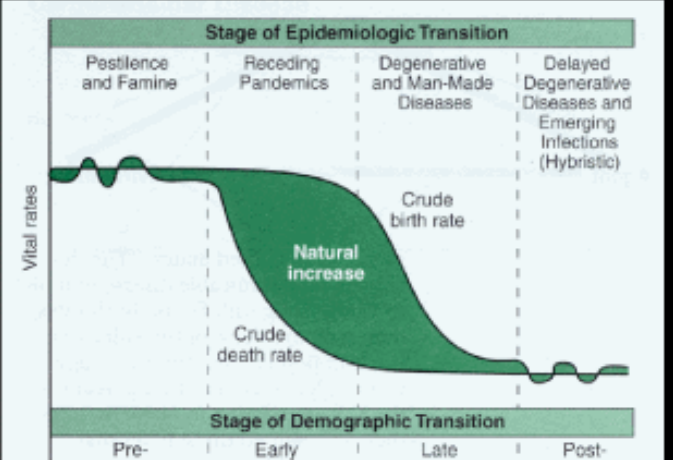
epidemiological transition model
an extension of the demographic transition model showing death rates and common causes of death within societies.

Malthusian theory
the theory that population will outgrow natural resources, specifically food, leading to widespread starvation.
neo-Malthusians
modern believers of the Malthusian theory who argue that population growth is a great threat.
conflict in Rwanda
Hutu v. Tutsi. During the German/Belgian occupation, Tutsi (minority) were favored, increasing tension between the groups. Post-independence, Hutus took power, and the RPF (Tutsi rebel forces) fought the government. Genocide sparked when the Hutu President was killed (4/6/1994). 100 days of mass killings (800,000+ killed; mainly with machetes). The RPF took back control, and the genocide ended in July of 1994.
Ravenstein’s laws of migration
1) most migrants go a short distance, 2) big cities attract long-distance migrants, 3) step migration, 4) most are rural to urban, 5) each migration produces a counterflow, 6) most migrants are single adults (families are less likely to move internationally), 7) most migrants are young adult males, 8) most migration for economic reasons, 9) migration increases with economic development
demography
the scientific study of demographics and human population, focusing on their size, structure, and distribution.