Macromolecules
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:01 PM on 10/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Nucleic acid
- Built from nucleotides
- Two types:
1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): cellular database
2. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): needed to convert DNA info into polypeptide sequences
- Have one, two or three phosphate groups
- Two types:
1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): cellular database
2. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): needed to convert DNA info into polypeptide sequences
- Have one, two or three phosphate groups
2
New cards
Condesnsation reaction
- Involves the release of water (H2O)
- Joining together of two monomers by a covalent bond to form a polymer. Occurs in biosynthesis
- A-OH + B-H → A-B + H2O
- Joining together of two monomers by a covalent bond to form a polymer. Occurs in biosynthesis
- A-OH + B-H → A-B + H2O
3
New cards
Hydrolysis reaction
- Reverse of condensation
- Involves adding water to split a covalent bond, the release of two smaller molecules
- Occurs in digestion
- A-B + H2O → A-OH + B-H
- Involves adding water to split a covalent bond, the release of two smaller molecules
- Occurs in digestion
- A-B + H2O → A-OH + B-H
4
New cards
Building block of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
5
New cards
Functional group of carbs
- every carbon atom has H-C-OH, except one carbon atom that has a carbonyl group (C=O)
- Some sugars have an aldehyde group = aldose sugars (glucose), other sugars have keto group = ketose sugars (fructose)
- Some sugars have an aldehyde group = aldose sugars (glucose), other sugars have keto group = ketose sugars (fructose)
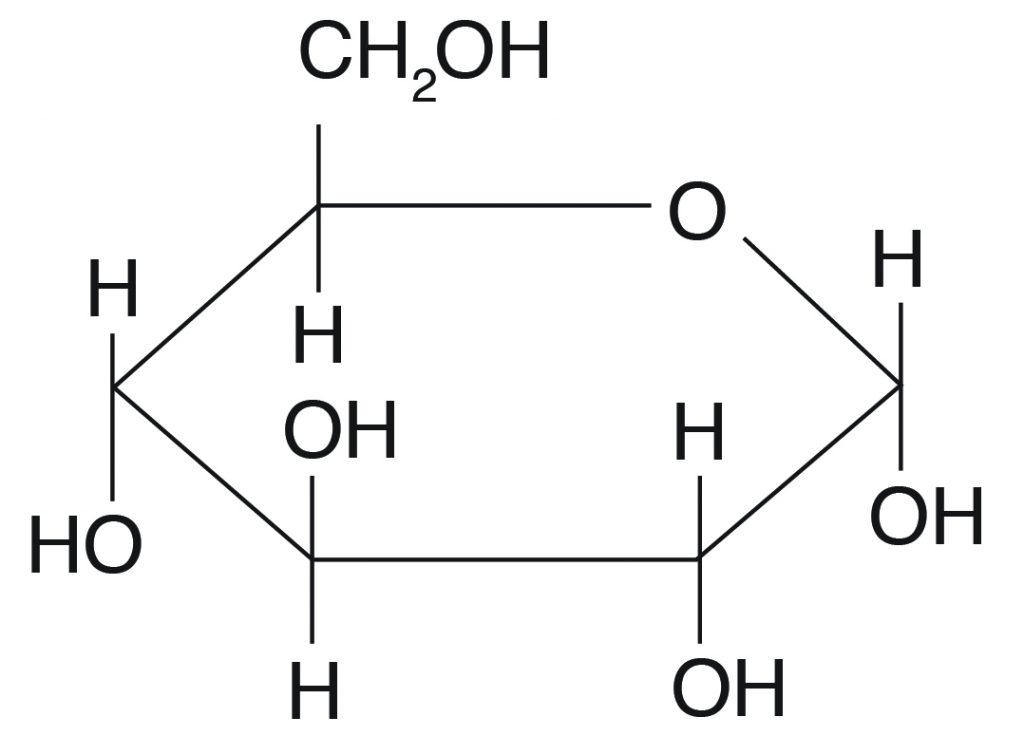
6
New cards
Importance of carbs
- Short-term energy source
- important substrate for building other needed molecules
- important substrate for building other needed molecules
7
New cards
Glycoproteins
- proteins with sugar tags
- Molecular “tags” on membrane proteins face outside of a cell, used for recognition of specific cells and molecules
- Molecular “tags” on membrane proteins face outside of a cell, used for recognition of specific cells and molecules
8
New cards
Monosaccharide
- simplest form (single sugar)
- most abundant sugars are the hexoses
- usually exist as ring structures when they dissolve in water
- most abundant sugars are the hexoses
- usually exist as ring structures when they dissolve in water
9
New cards
Common monosaccharides
Glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose (RNA), deoxyribose (DNA)
10
New cards
Glucose
- the most abundant sugar
- basis for polysaccharides
- produced in photosynthesis
- basis for polysaccharides
- produced in photosynthesis
11
New cards
Galactose
- found in lactose with glucose
- found in many plant polysaccharides
- found in many plant polysaccharides
12
New cards
Fructose
- found in fruits and vegetables
13
New cards
Disaccharides
- two monosaccharides joined together
- condensation reaction when created
- condensation reaction when created
14
New cards
Glycosidic bond
the link between monosaccharide rings
15
New cards
Common disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
16
New cards
Sucrose
glucose + fructose
17
New cards
Lactose
glucose +galactose
18
New cards
Maltose
glucose + glucose
19
New cards
Polysaccharide
- long chains held togetehr by glycosidic bonds
- condensation reaction between each monosaccharide unit
- condensation reaction between each monosaccharide unit
20
New cards
Common polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose
21
New cards
Starch
- storage carb used by plants
- insoluble in water
- ex: potatoes
- polymer of glucose
- insoluble in water
- ex: potatoes
- polymer of glucose
22
New cards
Glycogen
- storage crab used by animals
- ex: liver and skeletal muscle
- ex: liver and skeletal muscle
23
New cards
Cellulose
- usd in plant cell walls to maintain their structure
- indigestible to all organisms except some bacteria
- polymer of glucose
- indigestible to all organisms except some bacteria
- polymer of glucose
24
New cards
Building block of lipids
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
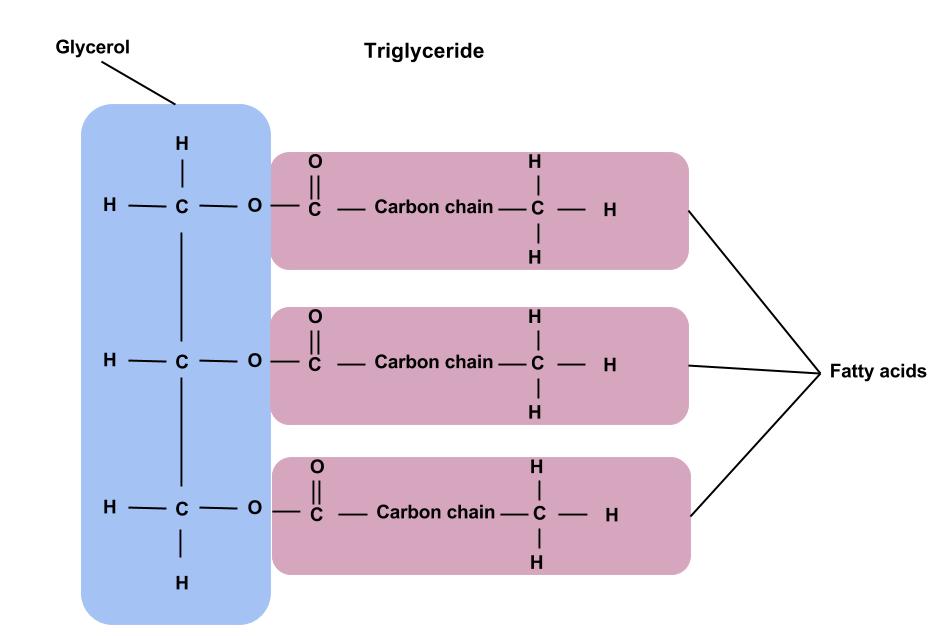
25
New cards
Functional groups in lipids
carboxyl and phosphate
26
New cards
Importance of lipids
- assebled through condensation
- structiral comonents of cell membranes
- long term energy
- vitamins and hormones
- insolation
- cushioning of organs
- structiral comonents of cell membranes
- long term energy
- vitamins and hormones
- insolation
- cushioning of organs
27
New cards
Saturated fats
all carbon bonds are singel bonds (more H = stiffer)
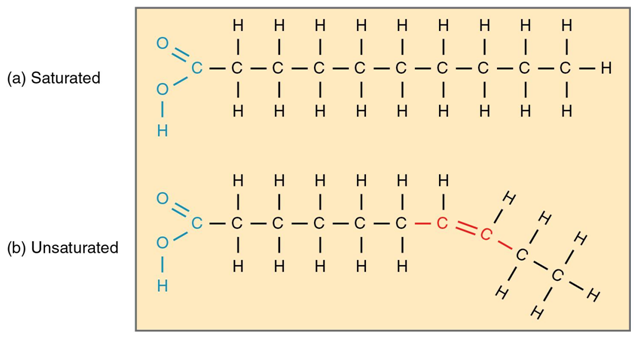
28
New cards
Unsatirated fats
some single, some double bonds
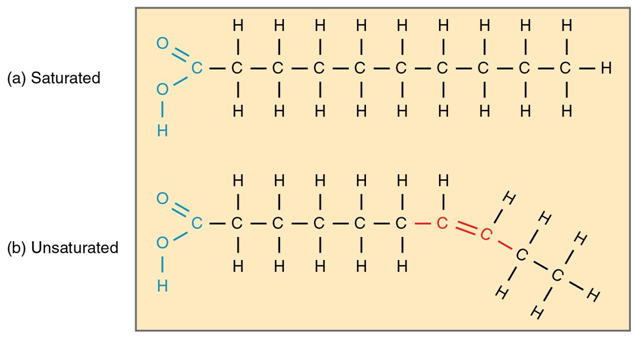
29
New cards
Omega-3
double bond between 3rd and 4th carbon
30
New cards
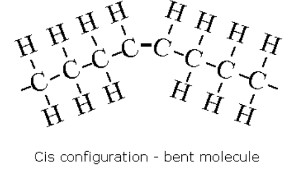
Cis fats
same side (most common fatty acids)
31
New cards
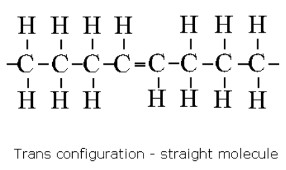
Trans fats
across or other side (toxic
32
New cards
Trans fatty acids
- double bonds are converted into single bonds
- Both these effects straighten out the molecules so they can lie closer together and mecome solid rather than liquid
- Both these effects straighten out the molecules so they can lie closer together and mecome solid rather than liquid
33
New cards
Tryglyceride
- Formed as a result of three condensation reactions involving the OH groups of the glycerol and the COOH groups of each fatty acid
- For each condensation reaction, an ester bond is formed
- For each condensation reaction, an ester bond is formed
34
New cards
Phospholipid
- similar to tryglycerides but one of the fatty acid molecules is replaced by a phosphate group
- lipid part is non-polar and hydrophobic (hates water)
- The phosphate part is polar and hydrophilic (loves water)
- If shaken up the phospholipids would form tiny spherical structures called micelles (like a circle). The hydrophobic tails turn inwards and become protected from the water by the hydrophilic heads
- lipid part is non-polar and hydrophobic (hates water)
- The phosphate part is polar and hydrophilic (loves water)
- If shaken up the phospholipids would form tiny spherical structures called micelles (like a circle). The hydrophobic tails turn inwards and become protected from the water by the hydrophilic heads
35
New cards
Steroids
- Insoluble in water
- 4 ring structure with various side chains
- Human steroids are synthesized from cholesterol
- 4 ring structure with various side chains
- Human steroids are synthesized from cholesterol
36
New cards
Hydrogenation
- process which combines gaseous H and oil
- destroys essential fatty acids and replaces them with trans fatty acids
- destroys essential fatty acids and replaces them with trans fatty acids
37
New cards
Building block of proteins
amino acids
38
New cards
Functional gorups in protein
- each amino acid has an amino group and a carboxyl group joined by a single carbon atom
- Also has a side chain (R group) that differentiates them
- Also has a side chain (R group) that differentiates them
39
New cards
Main functions of proteins
Structurally: muscle tissue, connective tissue, skin, hair, and nails, plus many others
Functionally: enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions (used in all biochemical reactions)
Functionally: enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions (used in all biochemical reactions)
40
New cards
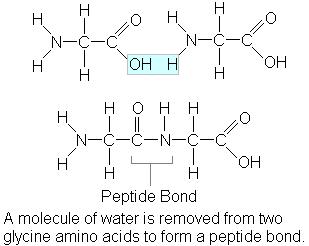
Peptide bond
- strongest of covalent bonds
- betweeen the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl hroup of another
- condensation reaction
- betweeen the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl hroup of another
- condensation reaction
41
New cards
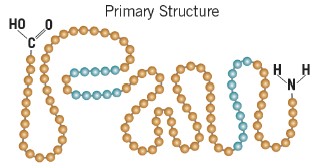
Primary structure
the sequence of amino acids in the chain
42
New cards
Secondary structure
- how r groups interact with each other
- the first level of folding of polypeptides
- alpha helix and beta-pleated helix held together by hydorgen bonds
- the first level of folding of polypeptides
- alpha helix and beta-pleated helix held together by hydorgen bonds
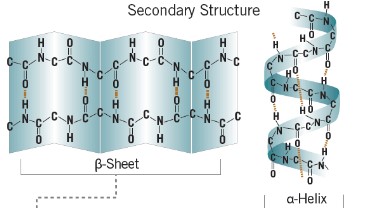
43
New cards
tertiary structure
- becomes active proteins
- the shape the molecule takes when the helix twists and folds around itslef
- the shape the molecule takes when the helix twists and folds around itslef
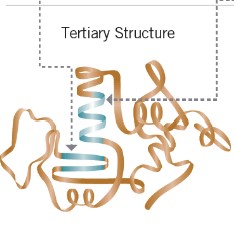
44
New cards
quaternary structure
- The linking together of a number of polypeptide chains
Ex: hemaglobin (has 4 subunits)
Ex: hemaglobin (has 4 subunits)

45
New cards
Denatiration
when bonds are disrupted and the protein unfolds
46
New cards
renaturation
the reverse of denaturation
47
New cards
Globular proteins
- Compact molecules
- Polypeptide chains “roll up” into spherical shape
- Water soluble (amino acids around R group), unstable
- Metabolic fucntion
- Ex: hemoglobin, enzymes
- Polypeptide chains “roll up” into spherical shape
- Water soluble (amino acids around R group), unstable
- Metabolic fucntion
- Ex: hemoglobin, enzymes
48
New cards
Fiborous proteins
- Polypeptide chains form long strands
- Stable, insoluble and strong
- Ex: collagen in bone or keratin in hair
- Stable, insoluble and strong
- Ex: collagen in bone or keratin in hair