AP Comparative Government
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Start of UNIT 1
Comparative Government
Very literal: Analyzing and comparing different gov'ts
Government
The institution through which a society makes and enforces laws and policies
Political Systems
Comprise the laws, ideas, and procedures of a gov'tal authority
State (informally "Country")
Sovereign Entity
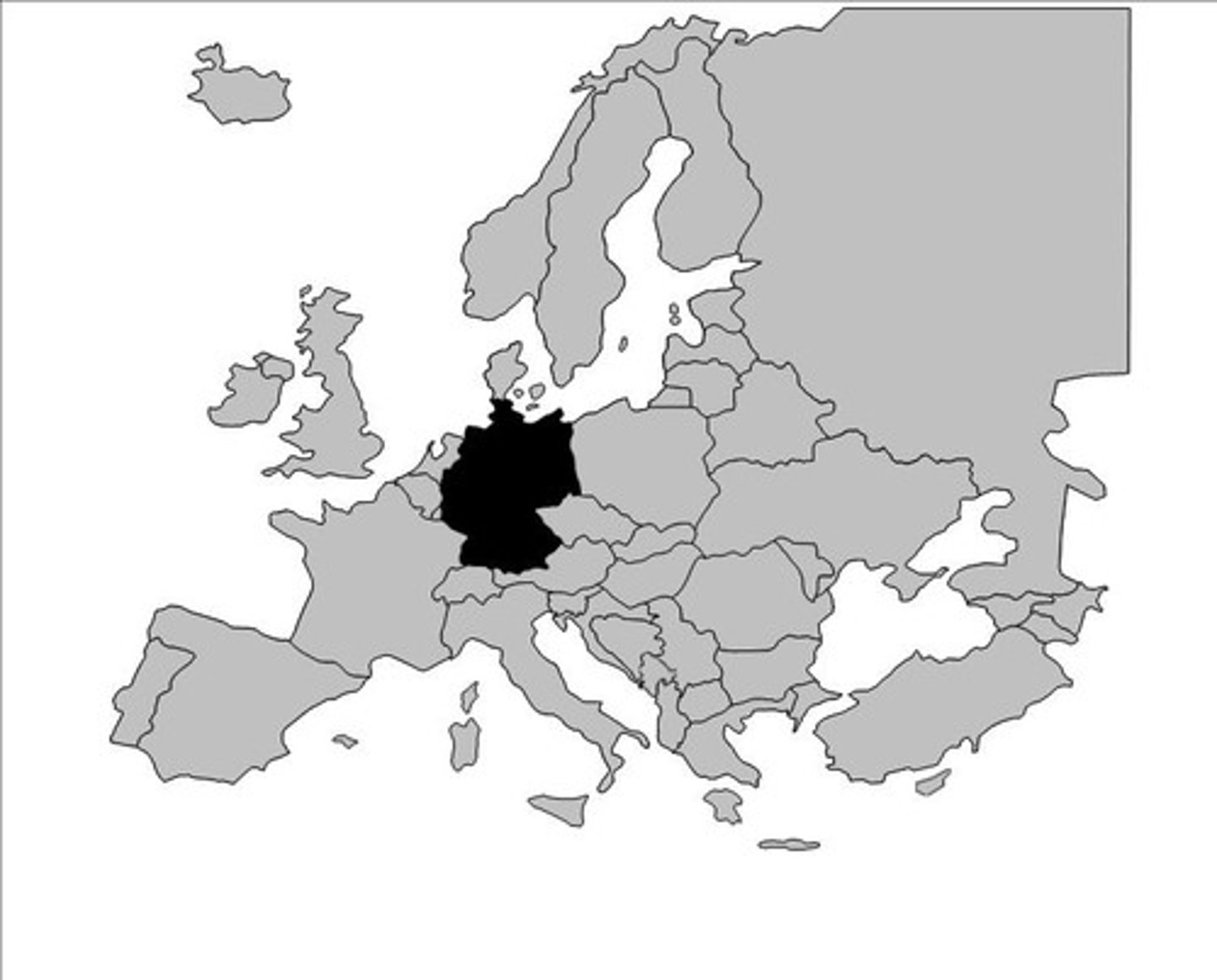
Nation
Different from states or countries
Self-identified cohesive groups of people.

Multination State
State comprising of multiple nations - most states
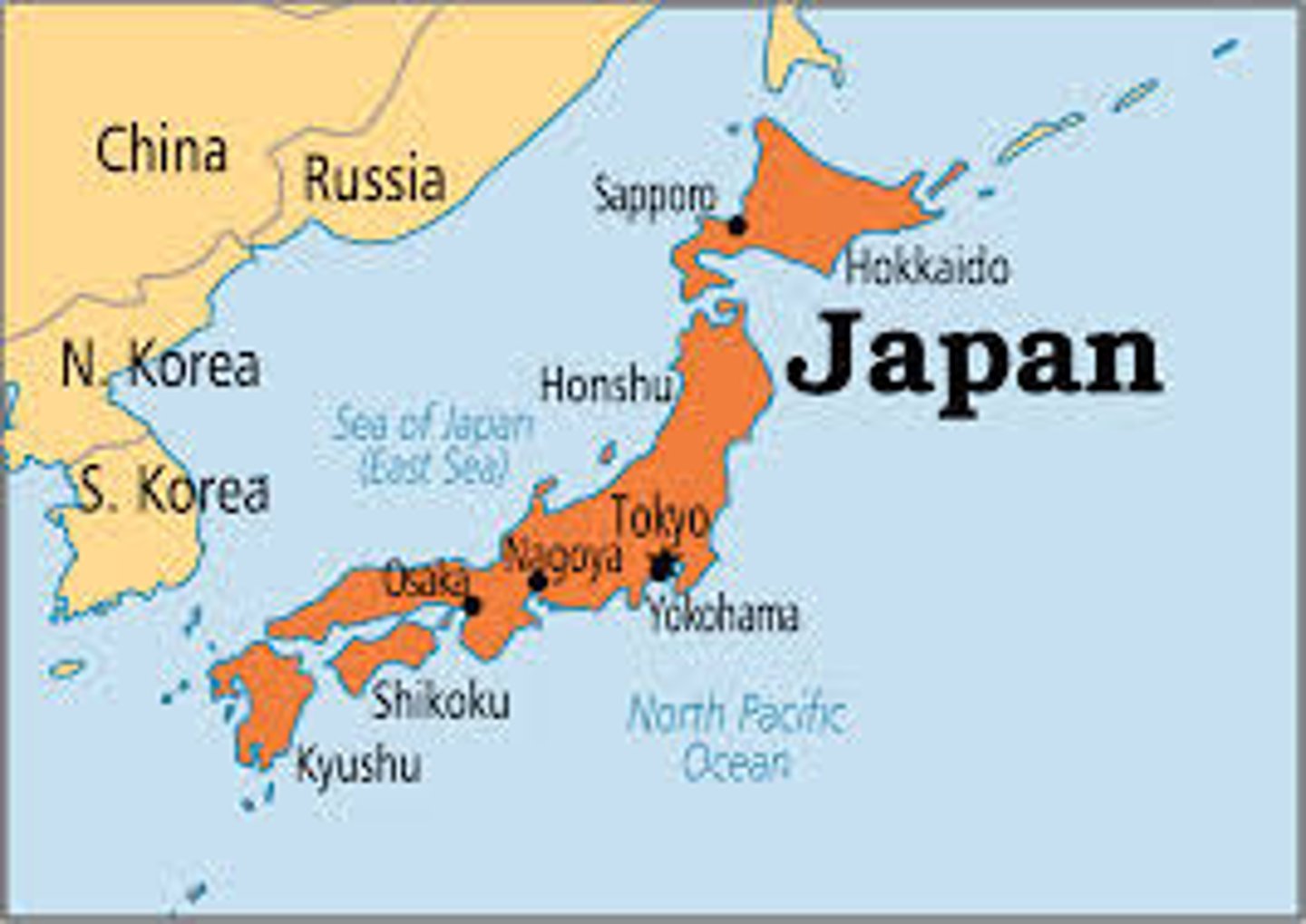
Nation-State
A state whose citizens or subjects are mostly contiguous with a specific nation. Could be a specific nation or simple homogeneity within a state.
e.g. Japan, Ireland
Sovereignty
Self-government and determination for a state
Requirements for statehood (Montevideo Convention, 1933)
1. Permanent population (e.g. can't be nomadic)
2. Established territory/boundaries (e.g. Need to have an agreed upon, uncontested border)
3. Working, sovereign gov't (needs functional gov't with authority and power)
4. International Relations (must be able to trade and be recognized by other states)
Regime
The type of government in power
Authoritarian Regimes
The power comes from sources other than the people: could be religion, military, fear, etc.
e.g. China, which gets its power from its status as a police state.
Democratic Regimes
The power comes from the people. The gov't relies on public support to give it authority.
Power vs. Authority
Power is the ability to do something, while authority is the right to do it
Political Culture
Widely shared beliefs, values, and norms that define how the public and the gov't interact.
Regimes vs. Gov'ts
Regimes don't change often; they represent the underlying structure and foundation of a state's gov't.
Gov'ts are the current face of a regime, and change frequently, due to coups, elections, etc.
Illiberal Democracies/Hybrid Regimes
Put up a facade of legitimate democracy, but are truly authoritarian regimes. Have elections which are not fair or free, and control people in other ways (e.g. Censorship) E.g. Russia

One-Party States
Dominated by a single controlling political party
E.g. China

Theocracies
Religion plays a critical rule in gov't
E.g. Iran

Totalitarian Gov'ts
Total government
Control over personal lives as well as internal affairs
E.g. Nazi Germany, USSR, CCP under Mao

Military Regimes
Military used to solidify control
E.g. Nigeria in the 90's
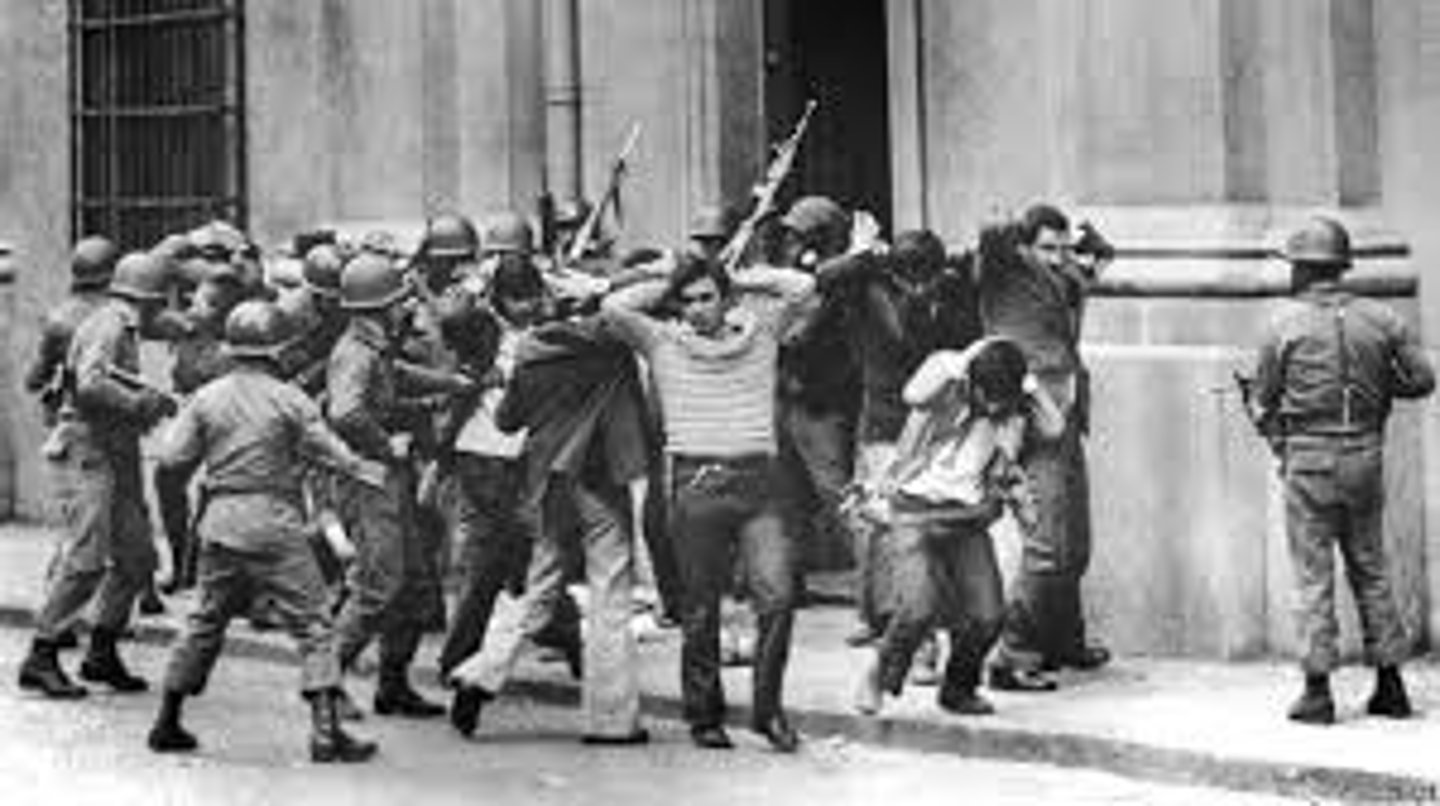

Democratization
A transition from authoritarian to democratic regime
Democratic Consolidation
A state of solidified democracy where the country is highly unlikely to revert to an authoritarian regime on its own
Authoritarian Consolidation
A state of solidified authoritarian status where a country is unlikely to revert to a democratic regime
Helpful/Detrimental to Democratization
Helpful:
- Diverse electoral systems
- Multiparty competition
- Independent judiciaries
- Protections of civil liberties
- Separation of powers
Detrimental:
- Political corruption
- Voting restrictions
- Marginalization
- Excessive Consensus or polarization between parties
Coups v. Revolutions
A coup is typically led by the elite, and it uses violence or threat of the same to replace a regime
Revolutions are not always violent, they can be peaceful. They are generally supported by a greater portion of the public, not just by elites.
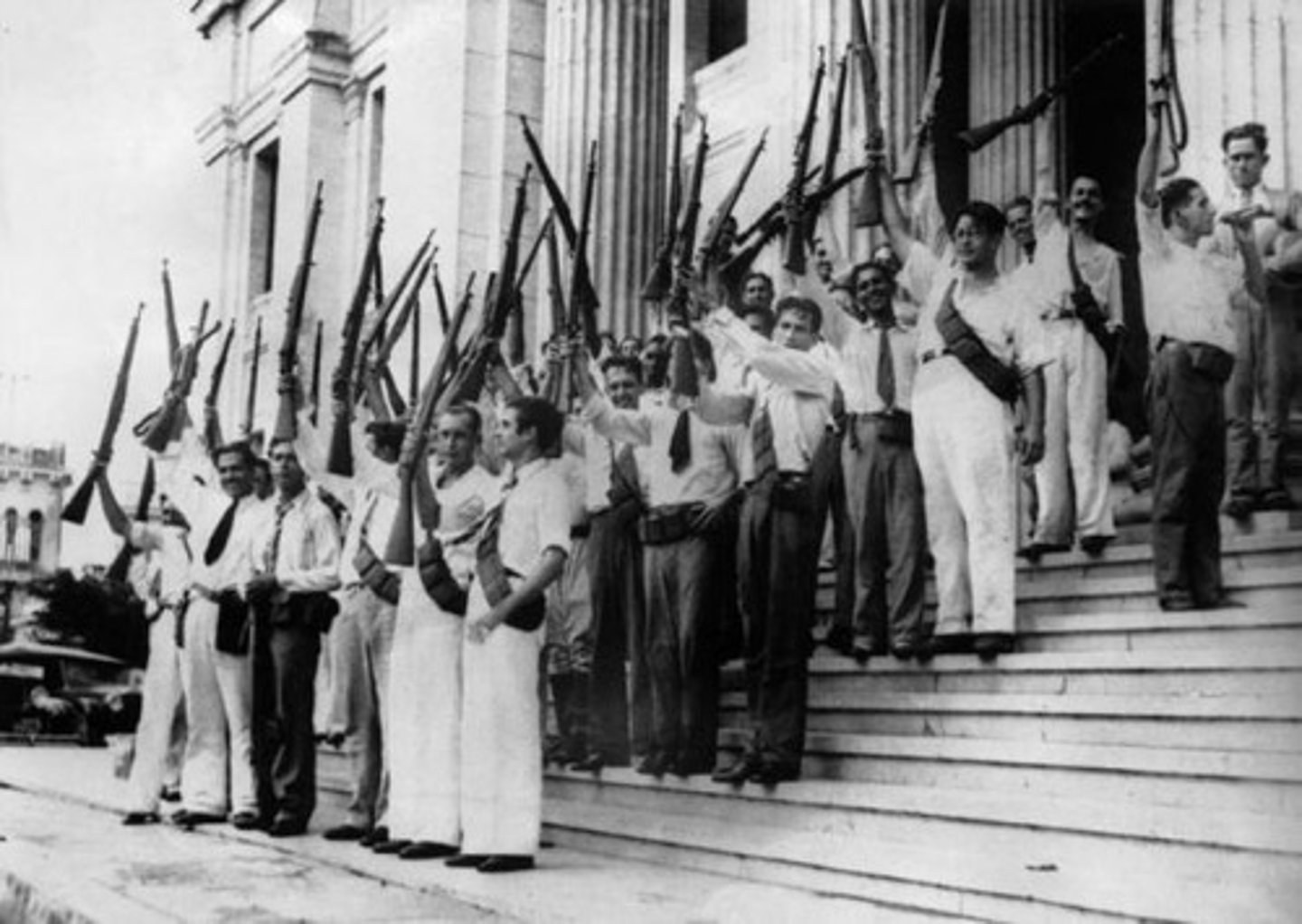

Federal System
Delegates some powers to regional and state branches
Unitary Systems
All power is concentrated in the central gov't
Can still have branches of gov't, but they lack authority
Devolved Unitary Systems
A unitary system in which certain powers are temporarily granted to lower branches
Asymmetric Federal System
A federal system in which certain powers are unconstitutionally taken away from lower branches of gov't
Political Legitimacy
Public acceptance to the gov't's authority
Do the people recognize the gov't's power and authority?
Sources of political legitimacy
Popular elections
Constitutionalism.
Nationalism
(Perceived) Political Efficacy
Economic Growth
Can an authoritarian regime be legitimate?
Yes, provided that the people accept the gov't's authority
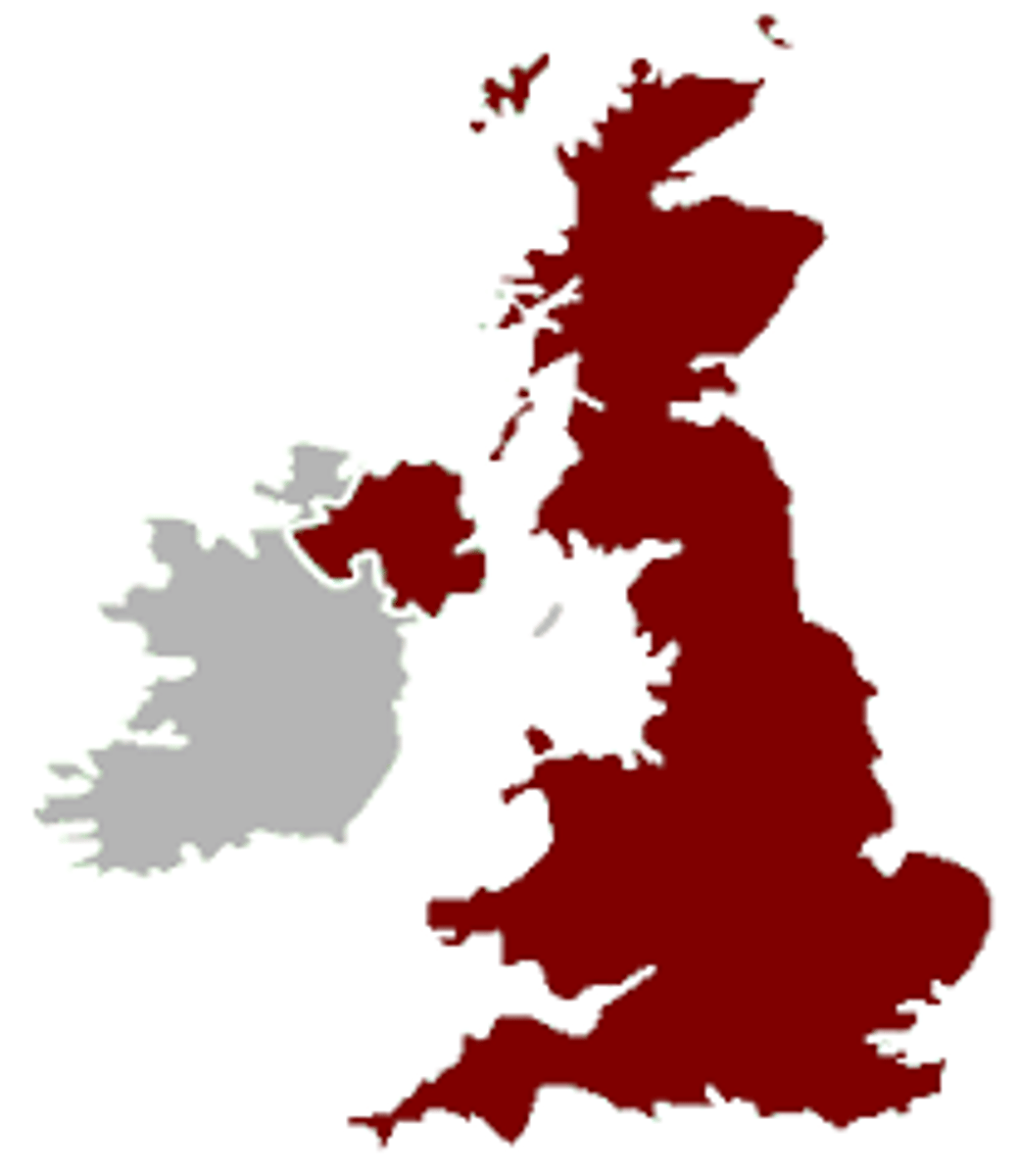
UK Gov't
Constitutional Monarchy, but without an official written constitution
- Instead, reliant on tradition and precedent
- Has an official state religion, the Church of England
Two legislative houses:
- Hereditary House of Lords
- Elected House of Commons
Consists of England, Wales, Northern Ireland, and Scotland
Is a devolved unitary gov't
Consists of three branches
- Centered in London
Human development Index (HDI)
Indicator of level of development for each country, constructed by United Nations, combining income, literacy, education, and life expectancy
Ranges from 0-1, highest quality of life being a 1.00.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total measurable market in a country. All goods and services output, typically in one year.
GDP Per Capita
GDP divided by population, can give us more accurate scales of how well off a population is.
GDP Growth Rate
Shows how quickly an economy is developing
Gini Coefficient
A measure of income inequality within a population, ranging from 0 (complete equality), to 1 (total inequity)
Freedom House Score
A score out of 100 that assesses personal freedoms, rights, and civil liberties in a state.
Transparency International Score
Measures corruption and crime in a country, from 0-100 (higher is worse)
Rule of Law
No one is above the law. Gov't enforces law, not the other way around.
Rule by Law
The law is subjective, and manipulated for political purposes. The law backs the gov't up, not the other way around.
Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power
Capitalism (Reference)
An economic system centered around the concept of "survival of the fittest."
Each person looks out for his/her own interests exclusively.
e.g. The USA
Democracy (Reference)
Style of gov'tal headship which places power in the hands of the people
e.g. Switzerland
Autocracy (Reference)
A gov't which places power exclusively or nearly exclusively in the hands of one person.
e.g. Russia
Oligarchy (Reference)
A government ruled by a few powerful people (not necessarily nobles)
Aristocracy (Reference)
A government in which power is in the hands of a hereditary ruling class or nobility
Socialism (Reference)
A theoretical gov't where all citizens share and redistribute wealth (usually via the state) equally.
No examples. This form of gov't is easily corrupted, typically into Communism
Communism (Reference)
A theory or system of social organization based on the holding of all property in common, actual ownership being ascribed to the community as a whole or to the state.
Generally very corrupt.
e.g. formerly the USSR, the CCP
Dictatorship (Reference)
A form of government in which the leader has absolute power and authority.
e.g. the Nazi Regime
Monarchy (Reference)
A government ruled by a king or queen
e.g. many medieval states
Constitutional Monarchy (Reference)
A King or Queen is the official head of state but power is limited by a constitution.
e.g. modern UK
Start of UNIT 2
Three Branches of Gov't
Legislative Branch - Makes laws
Executive Branch - Enforces laws
Judicial Branch - Interprets laws
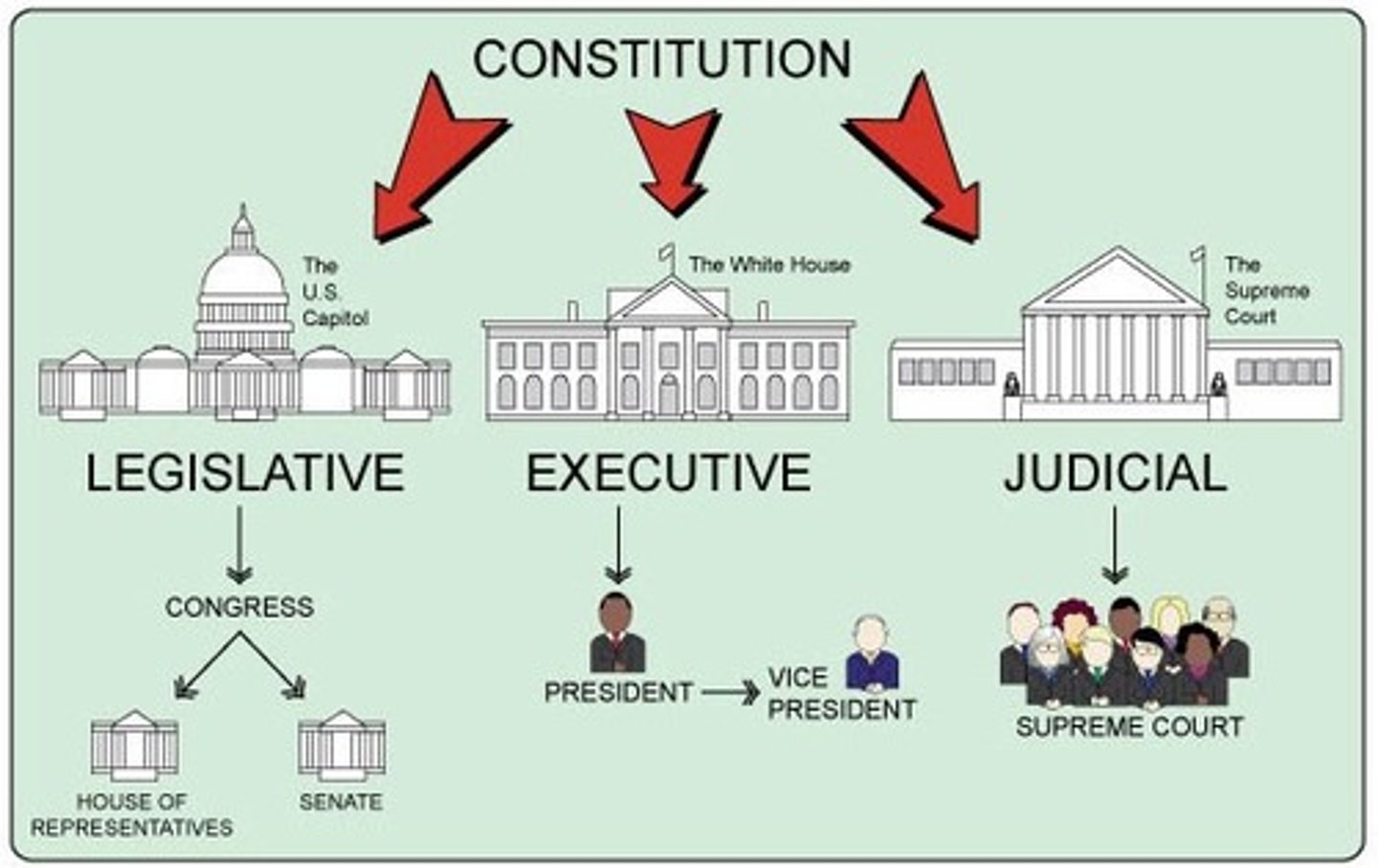
Separation of Powers
Division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches
Head of Gov't
Executive tasked with running government.
e.g. Presidents, PM's

Head of State
The executive role that represents the people both nationally and internationally.
e.g. Presidents, monarchs

Parliamentary Systems
Citizens vote for legislative representatives which in turn select the leaders of the executive branch.
Legislature and Executive are fused.
Voters select MP's (Members of Parliament), who in turn select the PM (Prime Minister) who will lead the gov't (but is not the head of state)
Policymaking is more efficient, because the majority rules.
e.g. the UK
Presidential Systems
Governments with strong presidents as both the head of state and the head of government.
The Executive and Legislative are separated.
The President is directly elected.
Is designed to have some gridlock, and passing laws is intentionally difficult.
Semi-Presidential System
The voters select a president and legislature in separate elections.
The PM is then nominated by the president and confirmed by the legislature.
There is both a PM and a president, with the latter nominating the former.
E.g. Russia: Presidential elections for a president, who appoints the PM
UK Executives
Head of State: King Charles III
Largely Ceremonial
Some role in foreign relations
Head of Gov't: PM Starmer
Commander in Chief
Cabinet Appointments
Laws, proposals and approvals, but the King approves
Treaties
Foreign Relations policy, with King being the public face
Mexico Executives
Head of State: President Steinbaum
Commander in Chief
Cabinet Appointments
Laws, proposals and approvals
Treaties
Foreign Relations
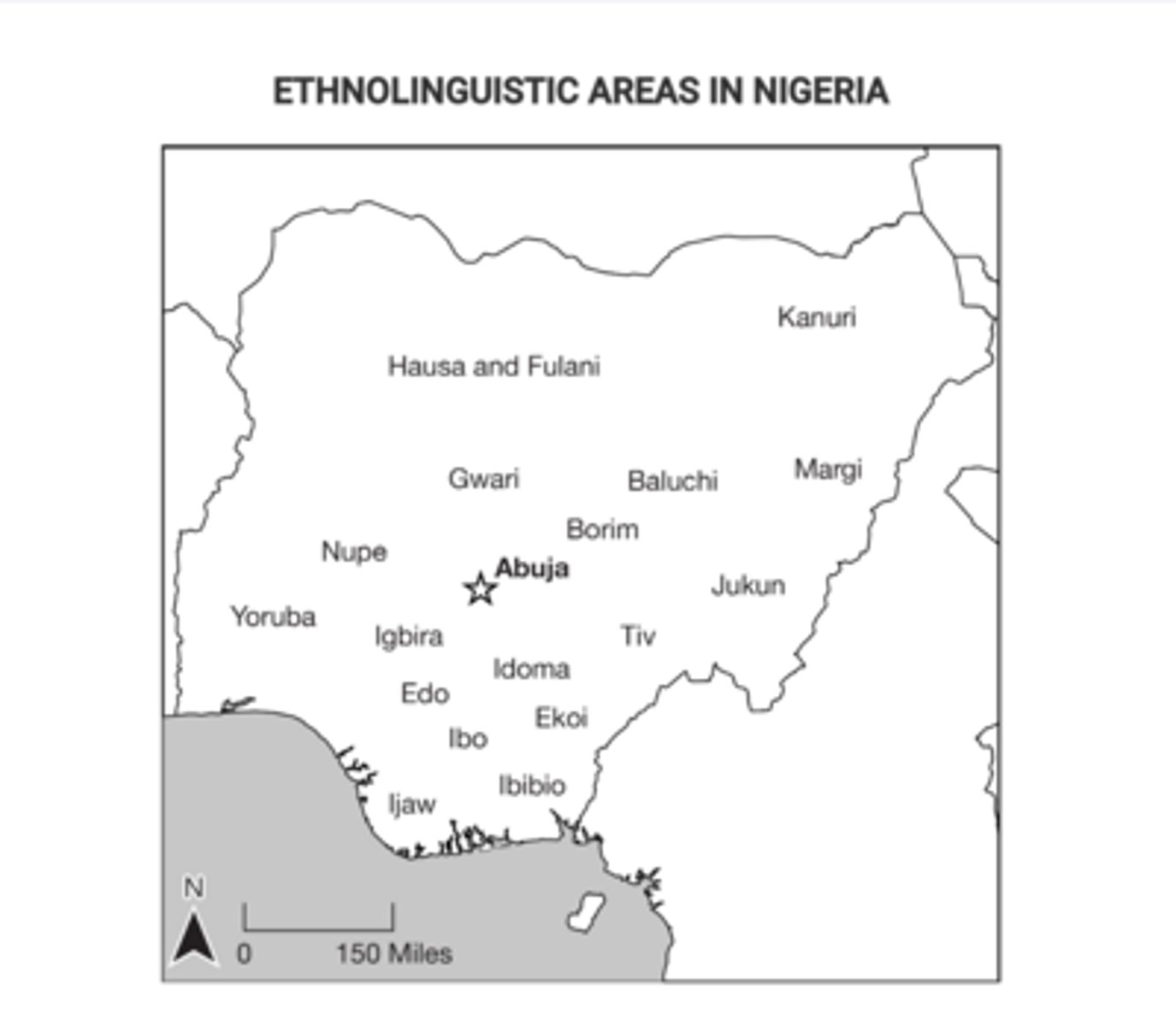
Nigeria Executives
Head of State: President Tinubu
Commander in Chief
Cabinet Appointments
Laws, proposals and approvals
Treaties
Foreign Relations
Russia Executives
Head of State: President Putin
Commander in Chief
Cabinet Appointments - Putin and PM
Laws, proposals and approvals, but the PM proposes domestic legislation
Treaties
Foreign Relations
Head of Gov't: PM Mishustin
Some role in cabinet appointments
Some role in domestic affairs, so that if things go wrong in the Russian interior, the people blame the PM, not the President
Sits there and smiles.
China Executives
Head of State: President Xi
Commander in Chief
Treaties
Foreign Relations
Head of Gov't: Premier Li
Cabinet Appointments (but the premier is appointed by...you guessed it: the president)
Laws, proposals and approvals: Premier (must be approved by NPC)
Iran Executives
Head of State: SL Khamenei
Commander in Chief
Appoints most high-up politicians
Head of Gov't: President Rouhani
Cabinet Appointments, but SL appoints everyone else
Laws, proposals and approvals
Treaties
Foreign Relations
Single Member District Plurality (First Past the Post)
An electoral district in which voters choose one representative or official.
The candidate with the most votes represents the whole district
Executive Term Limits
Caps on how long a President or PM can stay in office.
China Legislature
Lower House: Nat'l People's Congress
Elected
Party controlled
Elects President + Approves the Premier
Legitimizes Executive's Policies
*Is Constitutionally the most powerful institution, but is Party-controlled
Iran Legislature
Lower House: Majles
Elected
Approves legislation
Makes Budget
Confirms Presidential appointments
*Acts under the supervision of the Guardian Council and therefore religion
Nigeria Legislature
Lower House: House of Representatives
Elected
Approves legislation
360 members
Higher House: Senate
Also elected
Approves legislation as well
Confirmation/impeachment power
109 members
Mexico Legislature
Lower House: Chamber of Deputies
Elected
Approves legislation
Levies taxes
Verifies election outcomes
Upper House: Senate
Again, elected in
Treaties
Legislation
Confirms Supreme Court Justices
Approves Federal intervention in state matters
UK Legislature
Lower House: House of Commons
Elected
Approves legislation
Includes the PM
Upper House: House of Lords
Appointed and Hereditary
Reviews and amends bills
Can delay implementation
Very little effective power
Russia Legislature
Lower House: The Duma
Elected
Passes legislation
Confirms the President's PM pick
Upper House: Federation Council
Appointed
Approves budget
Confirms judicial nominees
Approves military actions
China Judiciary
Tiered court system
CCP appointments
Rule by Law
No Judicial Review
Not independent; CCP-controlled
Iran Judiciary
Islamic Sharia Law must be upheld
The judiciary exists to ensure that the legal system is based on Sharia Law
Head of the Judiciary nominates the other half of the GC, but is appointed by the SL
Judicial Review exists, in the scope of Sharia Law, not the Constitution
Not independent; it is a political tool
Mexico Judiciary
Another tiered court system
- Has a Supreme Court
- Has judicial review
- Magistrates in the Supreme Court are nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate for 15-year terms
Has been undergoing reforms in the post-PRI era
Semi-independent; still influenced by organized crime
Nigeria Judiciary
Tiered system
Judicial Review is present
Sharia Courts are present in the North
Judges are recommended by Judicial Council, appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate
Recent reforms trying to reduce corruption in the branch.
Semi-independent; heavily influenced by the President
Russia Judiciary
Tiered system
Judicial review in theory but not in practice
Judges are nominated by the President and approved by the Federation Council
Is often used to target opposition
Not independent; a political tool, dependent on the President
UK Judiciary
Not a unified system
Common Law is relied upon to enforce Rule of Law
While each area has its own courts, there is still a Supreme Court that acts as the highest circuit.
No official judicial review, but the Supreme Court does sometimes check the other branches
Independent, because it upholds Rule of Law and supports Checks and Balances
Start of UNIT 3
Civil Society
Associations that aren't gov't-backed. These organizations are typically focused on providing some skill of lobbying for a political change.
Civil Society is often but not always politically focused.
- e.g. NGO's, media outlets, business associations
NGOs (Non-Governmental Organizations)
Self-explanatory; any organization that isn't gov'tal

What strengthens Civil Society?
More free regimes
Fewer gov'tal limits on civil liberties and political freedoms
Effects of Civil Society
Promotes democratization
Monitors the gov't and holds them accountable
Expose gov'tal issues and flaws
Represent people's interests
Restrictions on Civil Society
Could include:
Gov't censorship
Regulations on things like protests and freedoms
Restrictions on NGOs
Silencing/harassing journalists, political opponents, protestors, etc.
Gov'ts restrict Civil Society to maintain power and minimize threats.
Political Culture
Widely shared beliefs, values, and norms that define how the public and the gov't interact.
What can form political culture?
Geography - Japanese culture was very unique due to how the island isolated the population
Religious Traditions - Iran uses Sharia Law, with Islam defining the political culture
History - Nigerian tribes have long histories of animosity, which makes it harder for them to collaborate today.
Political Socialization
The ways that we transmit political culture throughout a society. Methods:
Family is most important in influencing political culture
School and childhood peers
Media
Religious institutions and authorities
Overall society
In authoritarian regimes, the gov't generally plays more of a role
Political Ideologies
Driving beliefs and principles behind gov't and politics. These are more broad and conceptual than political culture is.
Individualism (Political Ideologies)
Prioritizes civil liberties and individual freedom over gov't restrictions.
e.g. Many Right-leaning Americans, who prioritize individual rights
Neoliberalism (Political Ideologies)
Belief that limited gov'tal intervention in the economy is good, but things should be otherwise free from gov't influence. Values privatization, free trade, deregulation, and elimination of subsidies
e.g. The overall net of American opinions, where some gov't support is generally welcomed, but people reject excessive involvement.
Privatization
Private ownership rather than public shareholding
Nationalization
The antithesis to Privatization, going from private to public, gov'tal ownership.
Subsidies
Gov't grants to achieve specific goals through financial incentives
Communism (Political Ideologies)
Belief in complete elimination and abolition of private property. Support for near-total economic gov't control.
No strong examples - In reality, "Communist" regimes are a lot more controlling than this.
Socialism (Political Ideologies)
Not to be confused with Communism
Belief in the reduction of disparities and inequalities, typically through wealth redistribution.
Support for nationalization of major industries
No strong examples - we haven't seen a successful socialist regime in history
Wealth Redistribution
Taking money from taxes, especially from the rich, and giving it to lower classes to reduce wealth disparity.

Fascism (Political Ideologies)
Extreme nationalist ideology that favors authoritarian rule and ethnic homogeneity
supports marginalization of minorities
e.g. Nazi Germany, Italy during WWII
Populism (Political Ideologies)
Support for the interests of the working class, rather than the elites.
Post-Material Values
Values beyond the material
Includes self-expression, Quality of Life, etc.
More post-material values lead to more public pressure on the gov't