glycolysis/ anaerobic cellular respiration
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
first step of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration
glycolysis
what is glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose
what does glycolysis break down
it breaks down one glucose molecule through a series of 9 chemical reactions
reactants and products of glycolis
glucose + 2 ATP,+2 NAD+ +2Pi ———> 2 pyruvic acids + 2 NADH + 2 ATP (net)
NAD+ & NADH
-NADH = reduced form
Pi
inorganic phosphates
how many carbons are in a pyruvic acid
3
where in the process is atp used
in the early reactions of gylcolysis 2 ATP’s are used
where in the process is ATP made
in the later reactions of glycolysis a total of 4 ATP are made but a net of 2
where in the process is NADH made
in the later reactions of glycolysis 2 NADH are made
what type of molecule is NADH
a high energy molecule; electron carrier
what is the potential energy in NADH used for
the potential energy is converted to atp during cellular respiration
what happens when there is no o2 to complete the breakdown of glucose
anaerobic cellular respiration occur
what process does anaerobic cellular respiration use to complete glycolysis
through lactic acid fermentation
-2 stages
why is the breakdown of glycolysis incomplete
because all the NAD+ was turned into NADH & glycolysis needs NAD+ to keep on running
how does oxygen turn NADH back to NAD+
it allows NADH can’t drop of electrons to the electron transport reverting it back into NAD+
how does fermentation/anaerobic cellular respiration complete glycolysis
by turning NADH back into NAD+, so glycolysis can keep making ATP.
-recycling
what does NADH carry
one hydrogen ion (H⁺)
how does anaerobic cellular respiration regenerate NAD
the H in NADH and the H+ it carries is given to pyruvate during lactic acid fermentation
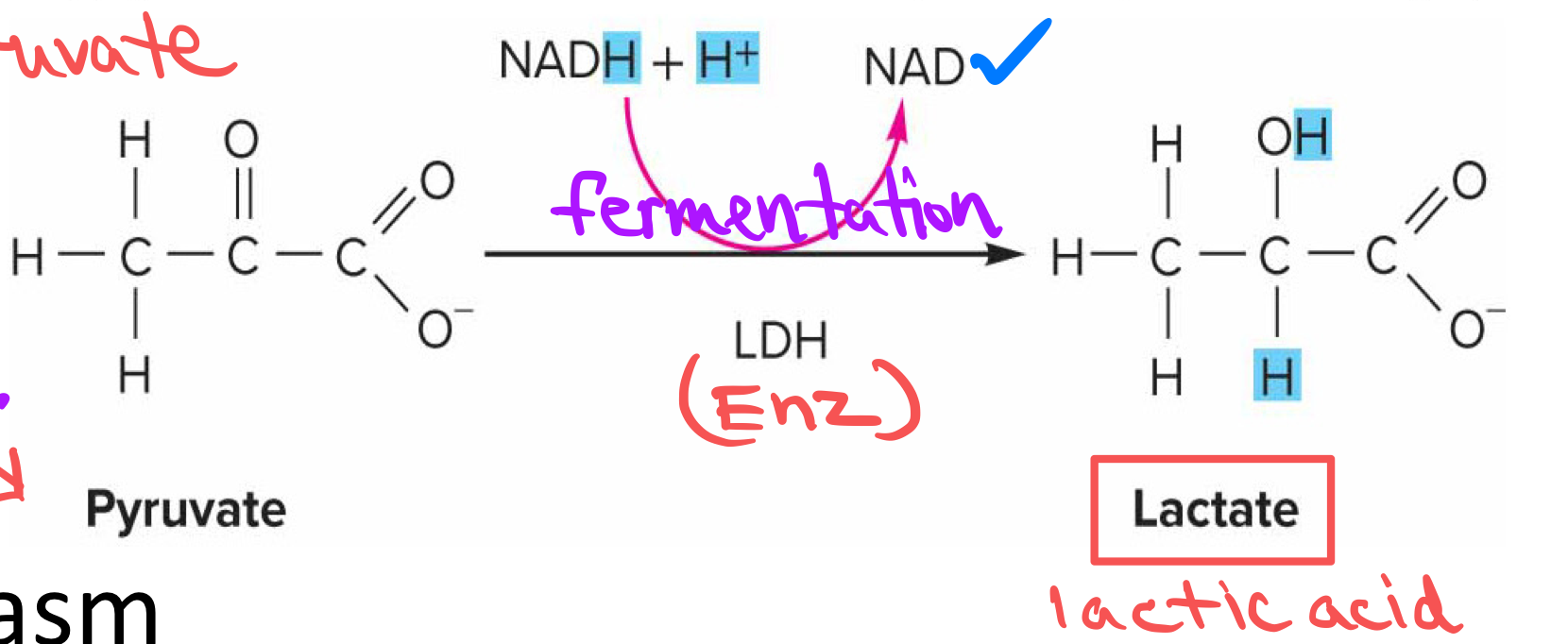
describe what happens to the functional groups of pryuvate
The carbonyl group is reduced to a hydroxyl group forming lactic acid
C=O → C-OH
what happens to pyruvic when it recieves the 2 H’s from NADH
it is converted to lactic acid/lactate
what enzyme is used in lactic acid fermentation
lactate dehydrogenase
why is NADH now NAD+
the H are gone and its + because it gave away electron so it is now cation
where does lactic acid fermentation mainly happen
in the cytoplasm
where else can lactic acid fermentation happen
in skeletal muscle cells
-excessive lactic acid formation and cause pain and muscle fatigue
net production for anerobic cellular respiration
-2 ATP
-2 Lactic acids
-2 NAD+