Pharm E3 (Carly's Comp Quizlet)
1/366
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
367 Terms
1. Endocrinology
1. Endocrinology
What is the minimum requirement for glucose that our bodies require just for survival?
190 mg of glucose/day
What are the secretory products produced by Alpha cells in the Pancreas?
Proglucagon
Glucagon
What are the secretory products produced by Beta cells in the Pancreas?
Proinsulin
Insulin
C-peptide
Amylin
Which type of diabetes is characterized by extensive and selective loss of B-cells from the pancreas?
Type 1 diabetes → autoimmune dz (type 1A) is MC
What is converted to insulin and C-peptide in golgi?
Proinsulin
How is Insulin cleared?
- hepatic = 60%
- renal = 40%
What is the mechanism of Insulin release?
1. Glucose enters pancreatic beta cells via GLUT-2.
2. Glucose is metabolized → ATP production increases.
3. ATP closes K+ channels, preventing K+ from leaving.
4. Cell depolarizes, opening voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels.
5. Ca²⁺ influx triggers insulin release via exocytosis.
6. Sulfonylureas enhance insulin release by blocking K+ channels.
What is the mechanism of Insulin action?
1. Stimulates glucose uptake into target tissues (GLUT4)
2. Initiates phosphorylation cascade within cells, translocated glucose transporters from inside cell to the cell surface
3. Glucose enters cell through facilitated diffusion
4. Glucose used for energy or stored
What are the stimulatory physiologic effect of Insulin on the Liver?
Storage as glycogen, conversion to fatty acids, VLDL then adipose
What are the inhibitory physiologic effect of Insulin on the Liver?
glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, conversion of fatty acids to ketones
What are the stimulatory physiologic effect of Insulin on Skeletal Muscle?
Storage as glycogen; storage of amino acids as protein (grow muscle)
What are the inhibitory physiologic effect of Insulin on Skeletal Muscle?
Protein degradation into amino acids
What are the stimulatory physiologic effect of Insulin on Adipose tissue?
Storage of fatty acids as TGs
What are the inhibits physiologic effect of Insulin on Adipose tissue?
Conversion of TGs to fatty acids
Which Insulins are ultra-short acting?
- Lispro
- Aspart
- Glulisine
Which Insulins are short acting?
Regular (Humulin, Novolin)
Which Insulin is intermediate acting?
NPH (contains protamine)
Which Insulin is long-acting?
Ultralente
Which Insulin is ultra-long acting?
- Glargine (lantus)
- Determir (levemir)
- Degludec (tresiba)
Which Insulin is inhaled?
Afrezza
What are the different insulin delivery methods?
Injection (conventional)
Portable pen injector (cartridges)
Continuous subq infusion (pump)
Inhaled Afrezza (dry powder)
What is the number one complication seen in patients taking Insulin?
Hypoglycemia
What is a drug that will increase hypoglycemic effects of insulin, but it blocks a lot of the physiologic signs of hypoglycemia?
Beta Blockers
Which type of insulin should be used in continuous subcutaneous infusions?
short acting
What type of insulin is the same as our own body's insulin?
Short-acting (regular)
When should you take rapid-acting insulin?
before meals (15-30 min onset)
What are the complications of insulin use?
hypoglycemia
immunopathology
lipodystrophy at injection site
weight gain
Which drugs may decrease the hypoglycemic effect of insulin (making it less effective, requiring more insulin)?
1. oral contraceptives
2. corticosteroids
3. dobutamine
4. epi
5. niacin
6. smoking
7. thiazides
8. thyroid hormone
Which drugs may INCREASE the hypoglycemic effects of insulin (making it more effective)?
1. alcohol
2. alpha blockers
3. anabolic steroids
4. beta blockers
5. MAO inhibitors
What are the indications for insulin?
1. All newly dx type 1 pts
2. Pregnant women with type 2 DM or women who develop gestational DM
3. Type II DM not controlled by diet, exercise, and oral meds
4. DKA
5. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketoic syndrome (HHNS)
6. Hyperkalemia
How does insulin treat Hyperkalemia?
pushes potassium K+ back into the cell
What are the pros and cons for more frequent Insulin administrations?
- Pro = Tighter glycemic control
- Con = Increased complexity
what are the pros and cons for less frequent insulin administrations?
- Pro = less chance of hypoglycemia
- Con = looser glycemic control
How should insulin doses be changed according to diet?
change depending on carb intake and exercise
Which type of insulin doses are taken in the morning and evening (basal)? ***
Long Acting
Which type of insulin doses are taken around meals (bolus)?***
regular or ultra rapid acting
When would ultra-short acting insulin such as (lispro, aspart, glulisine) be used mainly?
Meal time
When would ultra-long acting insulin such as (glargine, detemir, degludec) be used mainly?
Basal insulin in the morning
Why do type 2 DM require larger doses of insulin?
Insulin resistance
What is the rule of 15 for?
To correct hypoglycemia
15g of simple carbs (8 oz of OJ or 4 glucose tabs)
check glucose in 15 mins
If BG <70, repeat!
How should you treat hypOglycemia if a pt is unconscious?
- Glucagon (GlucaGen)
- Dextrose IV
A diabetic patients suddenly passes out. An Accuckeck shows blood glucose of 35 mg/dL. How do you proceed?
Kahoot Q
1 mg Glucagon (Glucagen) IM
What adverse rxn may occur after a Glucagon (GlucaGen) injection?
N/V
What is another use for Glucagon (GlucaGen) besides hypoglycemia?
pass FB in esophagus → bc of smooth muscle relaxation in GI tract
What may high concentrations of Dextrose IV cause?
Thrombophlebitis
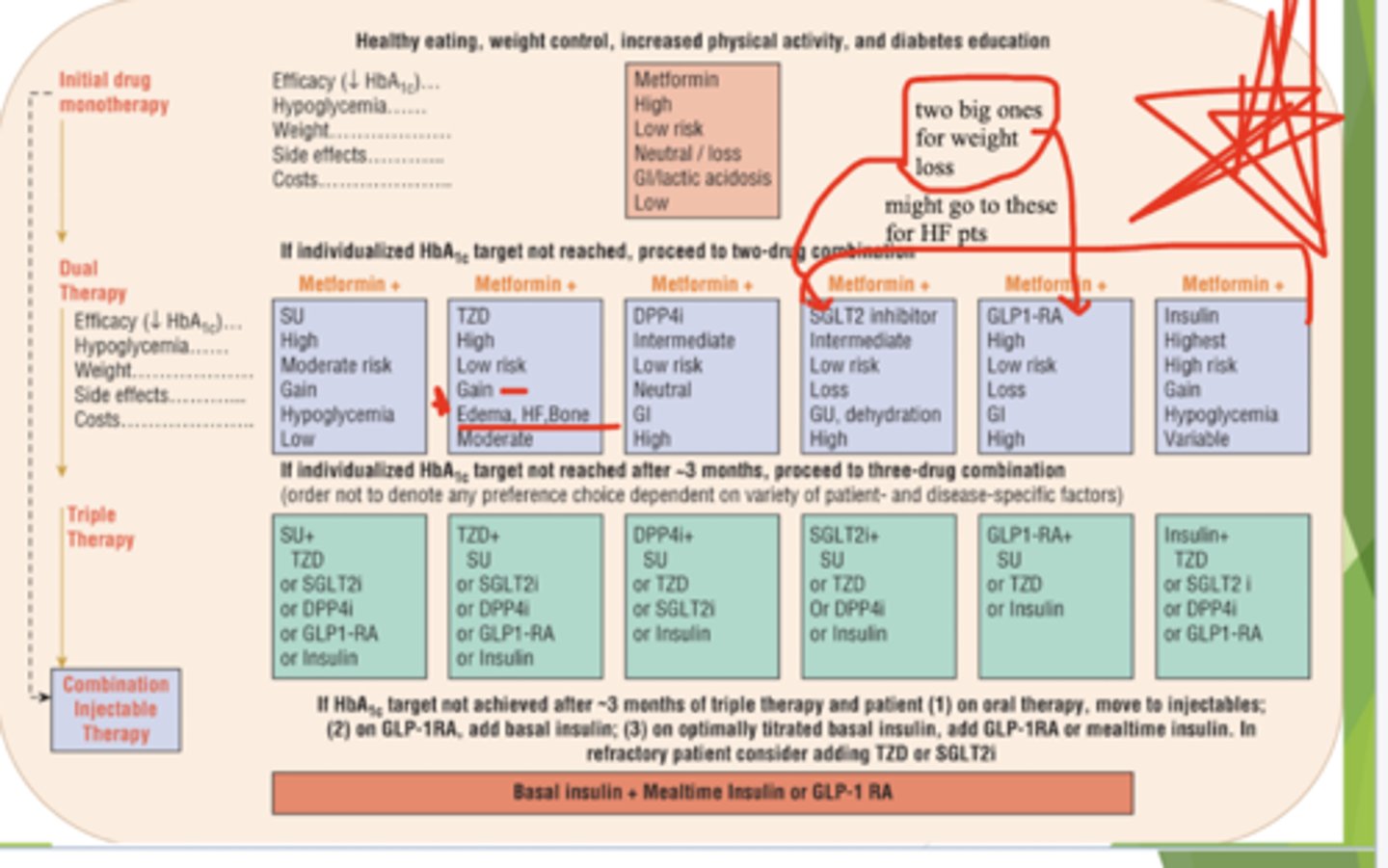
What is the treatment for Type 2 DM?
Life style changes → Monotherapy → Combo therapy (Oral drugs only) → Combo therapy (Oral with insulin)
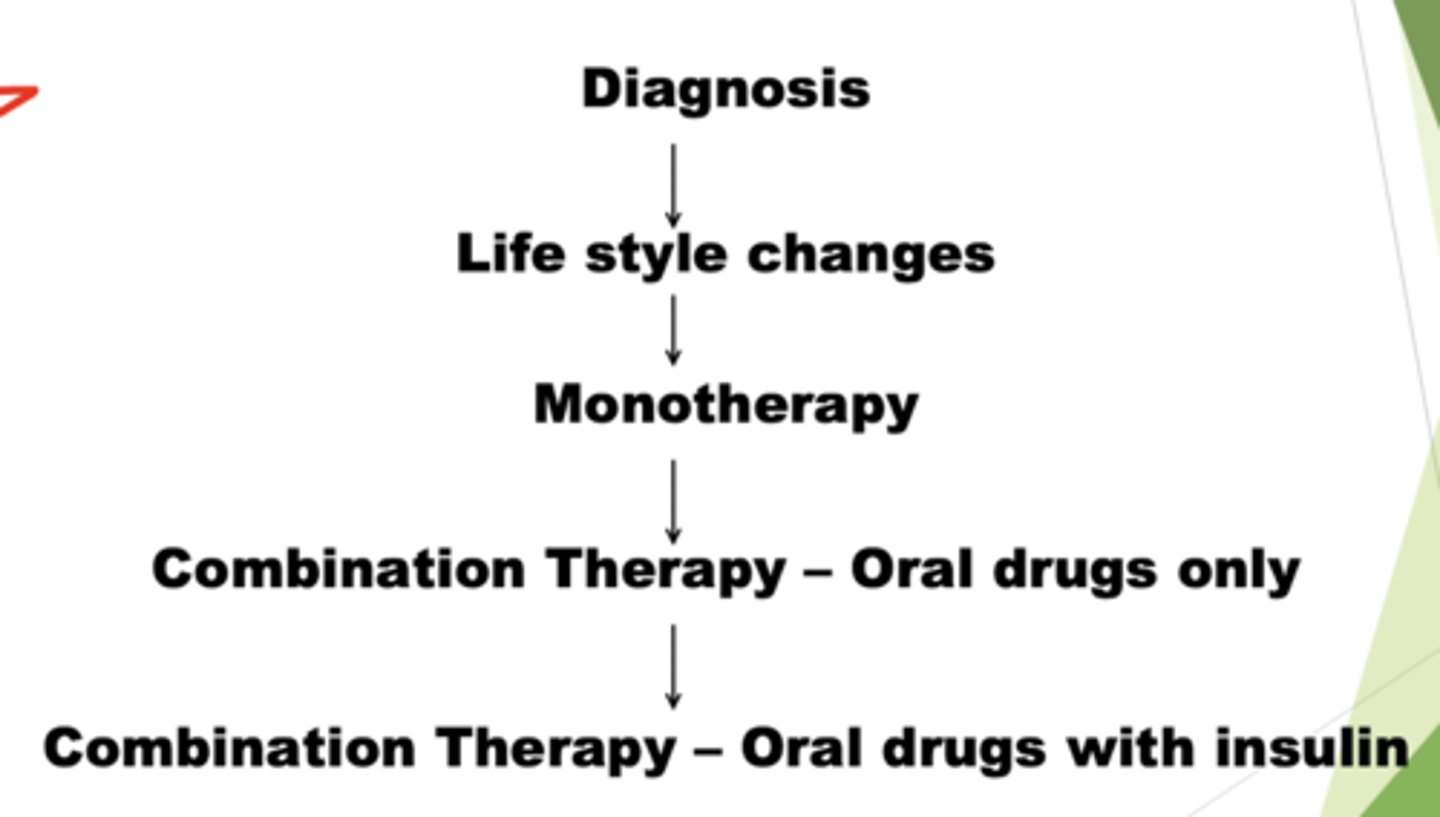
What is the first line of treatment for DM2?
Lifestyle Changes
Which drugs can stimulate the pancreas to make more insulin?
- Sulfonylureas
- Meglitinides
Which drugs may sensitize the body to insulin and/or control hepatic glucose production?
- Thiazolidinediones (TZD)
- Biguanides
Which drugs may slow the absorption of starches?
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
Which drugs suppress glucagon, decrease gastric emptying, and decrease food intake?
Incretins (glucagon-like peptides)
Which drugs may decrease reabsorption of glucose from renal tubules?
SLGT2 inhibitors
What are the First Generation Sulfonylureas?
chlorpropamide (diabinese)
What are the second generation Sulfonylureas?
Note: (~100 x more potent, less SE’s)
- Glimepiride (Amaryl)
- Glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL)
- Glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase, Micronase)
What drugs block ATP potassium channels which causes depolarization and insulin increase?
Sulfonylureas (Oral Hypoglycemics)→ Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide
How are Sulfonylureas (Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide) metabolized and excreted?
metabolized in liver
excreted in urine
use caution in liver/renal failure
Do Sulfonylureas (Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide) cross the placenta?
YES! → may deplete insulin from fetal pancreas
Can we use Sulfonylureas (Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide) during pregnancy?
NO
Which drug may cause Disulfiram like reaction with alcohol?
Chlorpropamide → also avoid in elderly
Which Sulfonylureas are more likely to produce hypOglycemia?
- Chlorpropamide
- Glyburide
What Sulfonylureas when combined with insulin, may decrease dose of insulin required?
Glimepiride (Amaryl)
What are 2 big adverse reactions to watch out for when prescribing Sulfonylureas (Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide) to patients?
Weight gain
HypOglycemia
What are the contraindications for Sulfonylureas (Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide)?
DKA
T1D
pregnancy/breastfeeding
What interactions may occur with Sulfonylureas (Chlorpropamide, Glimepiride, Glipizide, and Glyburide)?
Protein binding
Hyperglycemic drugs decrease effectiveness
Disulfiram- like rxn
Which drugs are Meglitinides?
- Repaglinide (prandin)
- Nateglinide (starlix)
What drugs Blocks ATP potassium channels which eventually increases insulin but ONLY in response to *glucose* in the bloodstream?
Meglitinides
--Repaglinide (prandin)
--Nateglinide (starlix)
What are the adverse effects of Meglitinides (Repaglinide, Nateglinide)?
hypoglycemia
weight gain
HA
Nausea
joint pain
use in caution w/ liver probs (hepatic metabolism)
Which drugs are Biguanides (oral antihyperglycemics)?
Metformin (glucophage)
What sensitizes insulin to work better and has limited hypOglycemia?
Biguanides (Metformin (glucophage))
What are the contraindications of metformin?***
- renal disease (GFR <30)
- metabolic acidosis or hypoxia
- hepatic disease
- cationic drugs compete for tubular excretion
- should be stopped before surgery d/t lactic acid
Does Metformin (glucophage) cause weight gain?
no → may be useful in obese pts with insulin resistance and HLD
How is Metformin (glucophage) excreted?
unchanged in urine → don't use in renal impairment (GFR <30)
What are the adverse effects of Metformin (glucophage)?
- GI effects (anorexia, constipation, heartburn, diarrhea)
- lactic acidosis
- rash
- megaloblastic anemia (dec. B12)
Why might someone with renal impairment not want to take Metformin (glucophage)?
Can cause lactic acid to build up in the liver as a result of the kidney not filtering properly
NOTE: Fatal lactic acidosis can occur as a result
How long should metformin be stopped before surgery?
48 hours prior
Which drugs are Thiazolidinediones (Oral antihyperglycemics)?
Note: metabolized in liver
✨The - gilitazones ✨
- Pioglitazone
- Rosiglitazone
- Troglitazone (removed d/t liver tox)
What are PPAR-g agonist which increases transcription of insulin responsive genes?
Thiazolidnediones
--Pioglitazone
--Rosiglitazone
Which major adverse effect can be from Thiazolidnediones (Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone)?
Which organ should be monitored for this drug?
Worsened heart failure → monitor liver function and liver enzymes q2 months
Increase HDL, LDL, variable TG
Which drugs are Alpha-glucosidase Inhibtors?
- Acarbose (Precose)
- Miglitol (Glyset)
What are competitive inhibitors of a-amylase and a-glucosidase enzymes in intestinal brush border → decrease glucose absorption?
Alpha-glucosidase Inhibtors
--Acarbose (Precose)
--Miglitol (Glyset)
What drugs stops the breakdown of carbs and decrease glucose absorption?
Alpha-glucosidase Inhibtors
--Acarbose (Precose)
--Miglitol (Glyset)
What is a major adverse effect in using Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors (Acarbose and Miglitol)? Hence why we don't use it as often
There is an extreme increase in flatulence 💨💨💨 from undigested carbs
How is Acarbose metabolized?
intestinal bacteria?
How is Miglitol excreted?
unchanged via kidneys
In which Sx are use of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors (Acarbose and Miglitol) contraindicated?
IBD
GI obstruction/ulceration
chronic intestinal disease
What are the Incretins?
- Exenatide (Byetta)
- Liraglutide (Victoza)
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
- Albiglutide (Tanzeum)
- Semaglutide
- Tirazepatide
Which Incretin is derived from the saliva of a Gila Monster?
Exenatide (Byetta)
How do Incretins work?
GLP-1 suppresses glucagon levels after meal, glucagon increases during fasting, increase glucose production → decreases gastric emptying and slows peak glucose absorption → increased satiety
How do Incretins work with type 2 diabetes?
They mimic Glucagon-like-peptide 1 which helps increase insulin release, decrease glucagon release, and increase satiety causing weight loss
What are the adverse effects of Exenatide (Byetta)?
- n/v
- hypoglycemia with sulfonylureas
- delay absorption of other oral meds
- weight loss
- pancreatitis
Which drugs are DPP-4 Inhibitors?
- Alogliptin (Nesina)
- Sitagliptin (Januvia)
- Saxagliptin (Onglyza)
- Linagliptin (Tradjenta)
What drugs have Peptidase involved in the breakdown of GLP-1 and GIP as well as several peptides: including peptide YY, Neuropeptide Y, Growth Hormone releasing
hormone?
- Also involved in T-cell activation (CD 26)
DPP-4 Inhibitors
--Alogliptin (Nesina)
--Sitagliptin (Januvia)
--Saxagliptin (Onglyza)
--Linagliptin (Tradjenta)
Which type 2 diabetes drug class has risk for Stevens Johnson?
DPP-4 Inhibitors
--Alogliptin (Nesina)
--Sitagliptin (Januvia)
--Saxagliptin (Onglyza)
--Linagliptin (Tradjenta)
Which drugs are SGLT2 inhibitors?
- Canagliflozin (Invokana)
- Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
- Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
What drugs inhibits SGLT2 in proximal renal tubules, inhibits reabsorption of filtered glucose →increased RENAL elimination of glucose → lowered blood sugar and body weight?
-- Works in the kidneys to inhibit glucose reabsorption and so you pee out the glucose --
SGLT2 inhibitors
--Canagliflozin (Invokana)
--Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
--Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
Why might SGLT2 inhibitors cause fungal UTIs?
From all the glucose in the bladder
Can a patient on SGLT2 inhibitors be at risk for DKA?
Yes, and it will be euglycemic (normal blood sugar)
Which type 2 diabetic drug class would we avoid in someone with recurrent UTIs?
SGLT2 inhibitors
--Canagliflozin (Invokana)
--Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
--Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
KNOW THIS - ignore the crazy writing on the picture lol