BIO B Unit 1 - Quiz #2 - DNA & Protein Synthesis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
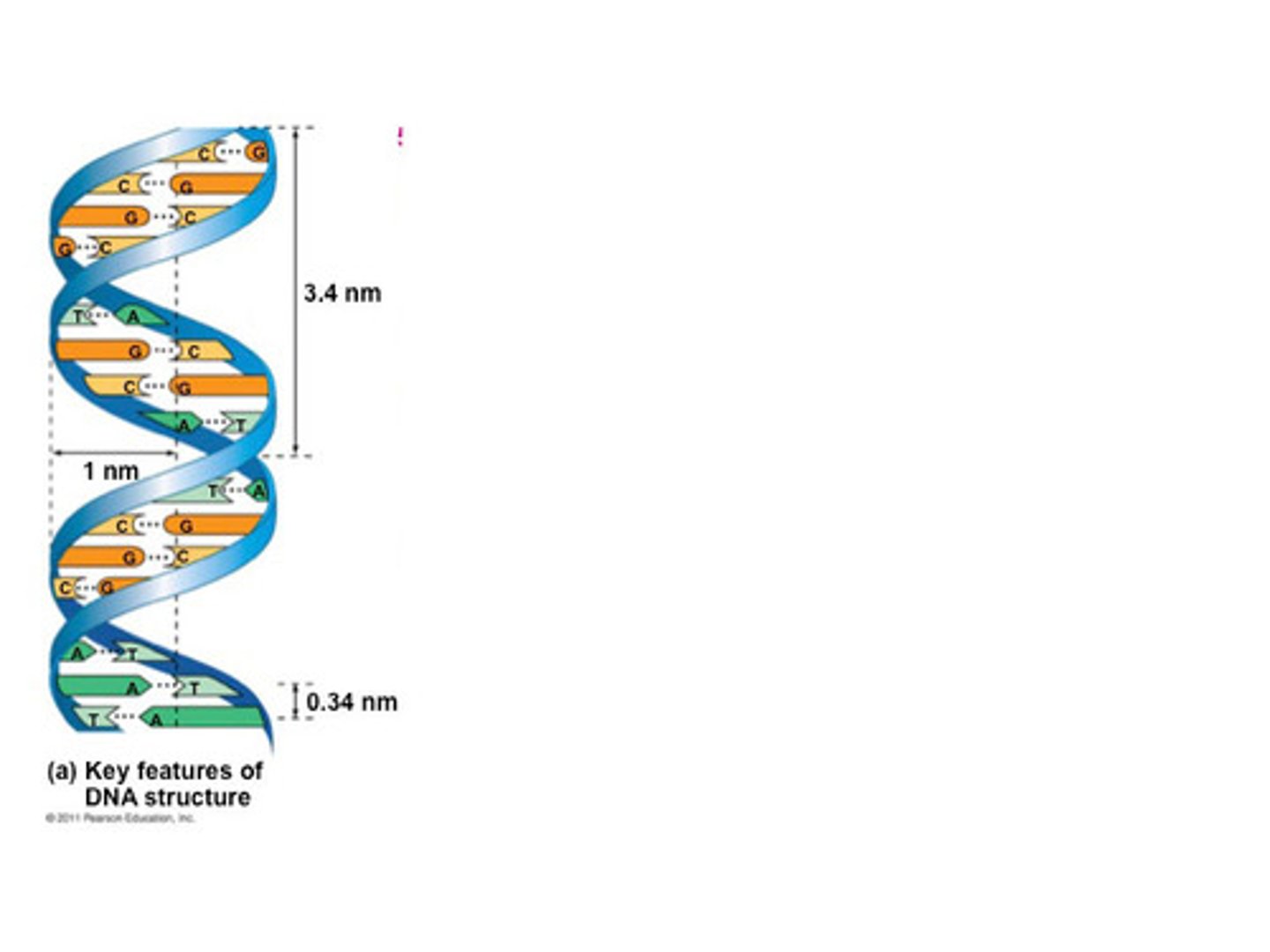
Describe the structure of DNA
double helix (twisted ladder)
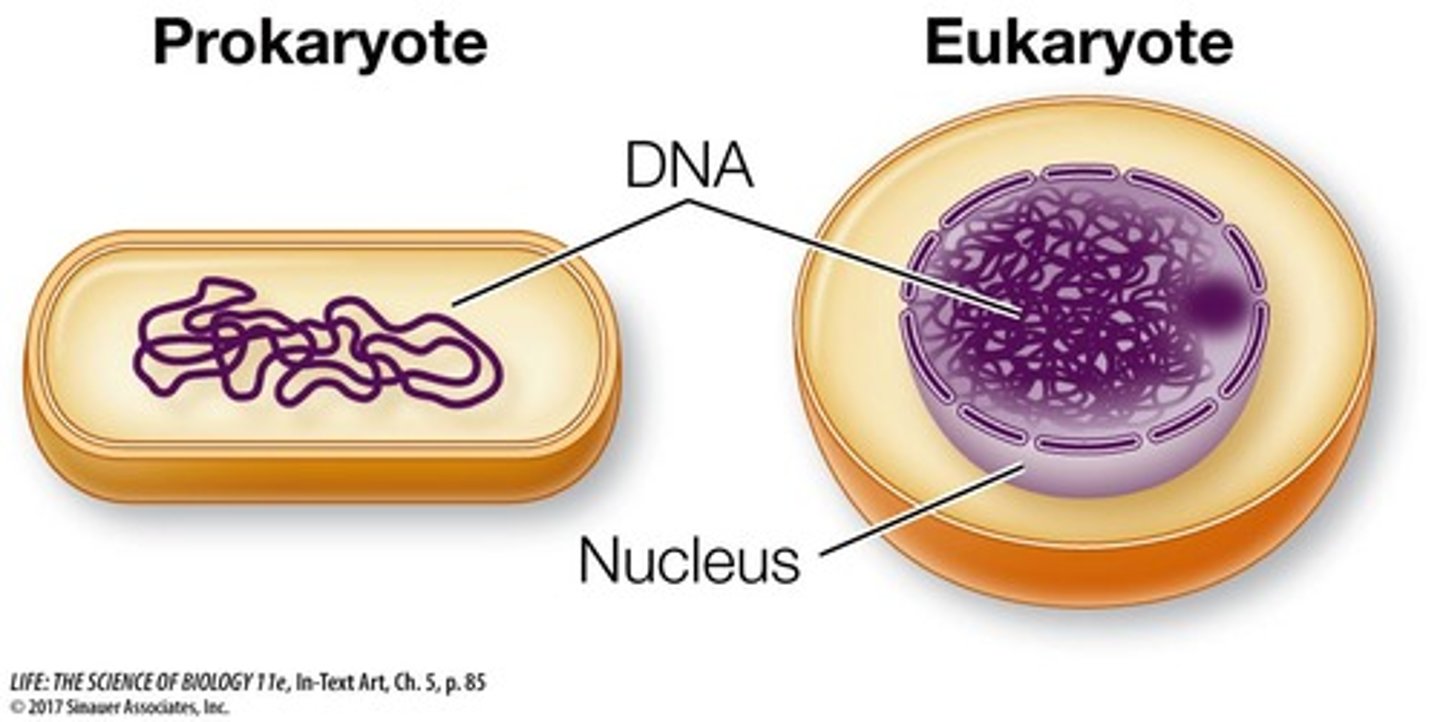
In eukaryotic cells, where is DNA located?
nucleus
What are the main functions of DNA?
-stores genetic information
-copies itself
-puts genetic info. to work
DNA is composed of smaller units called __________________.
nucleotides
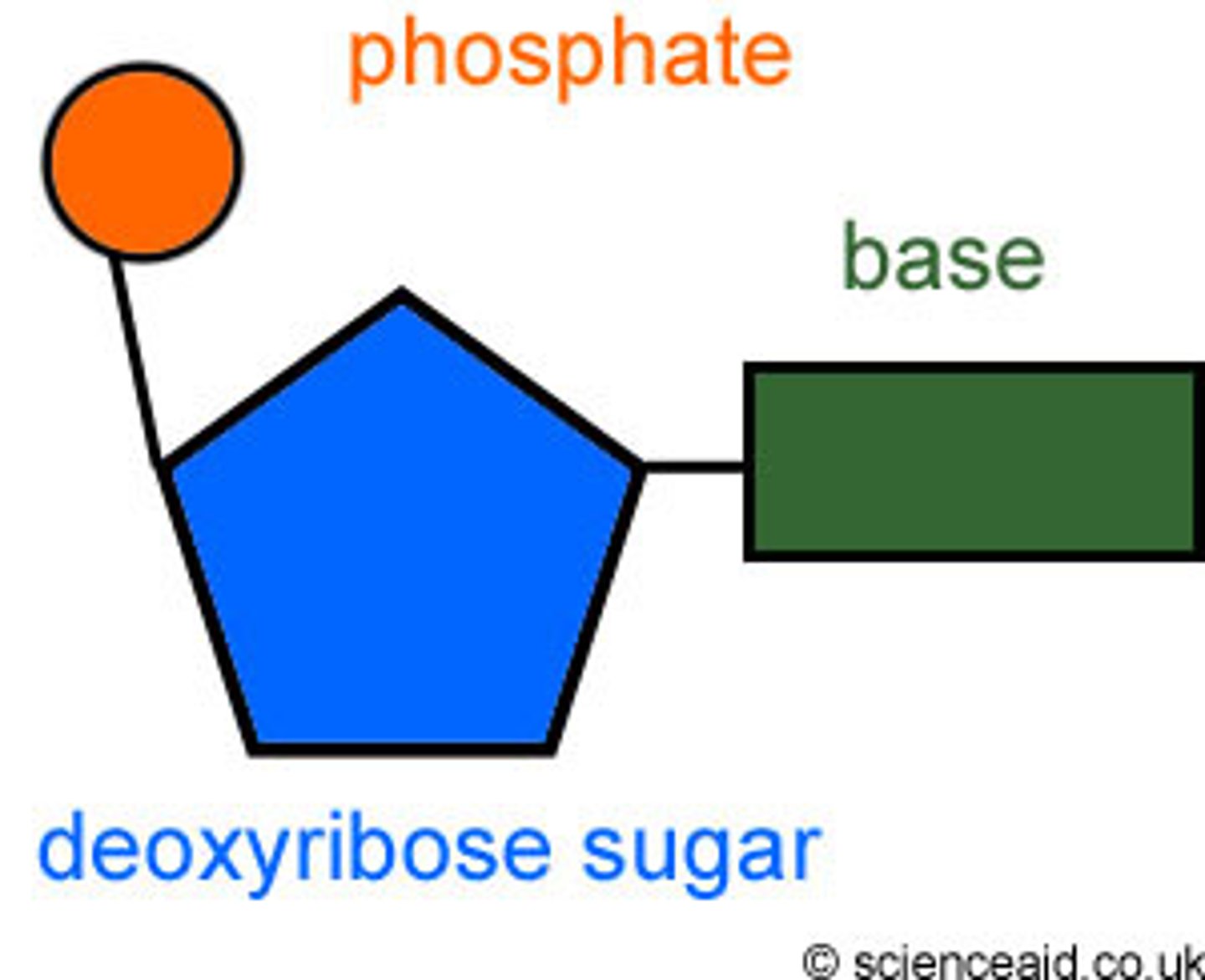
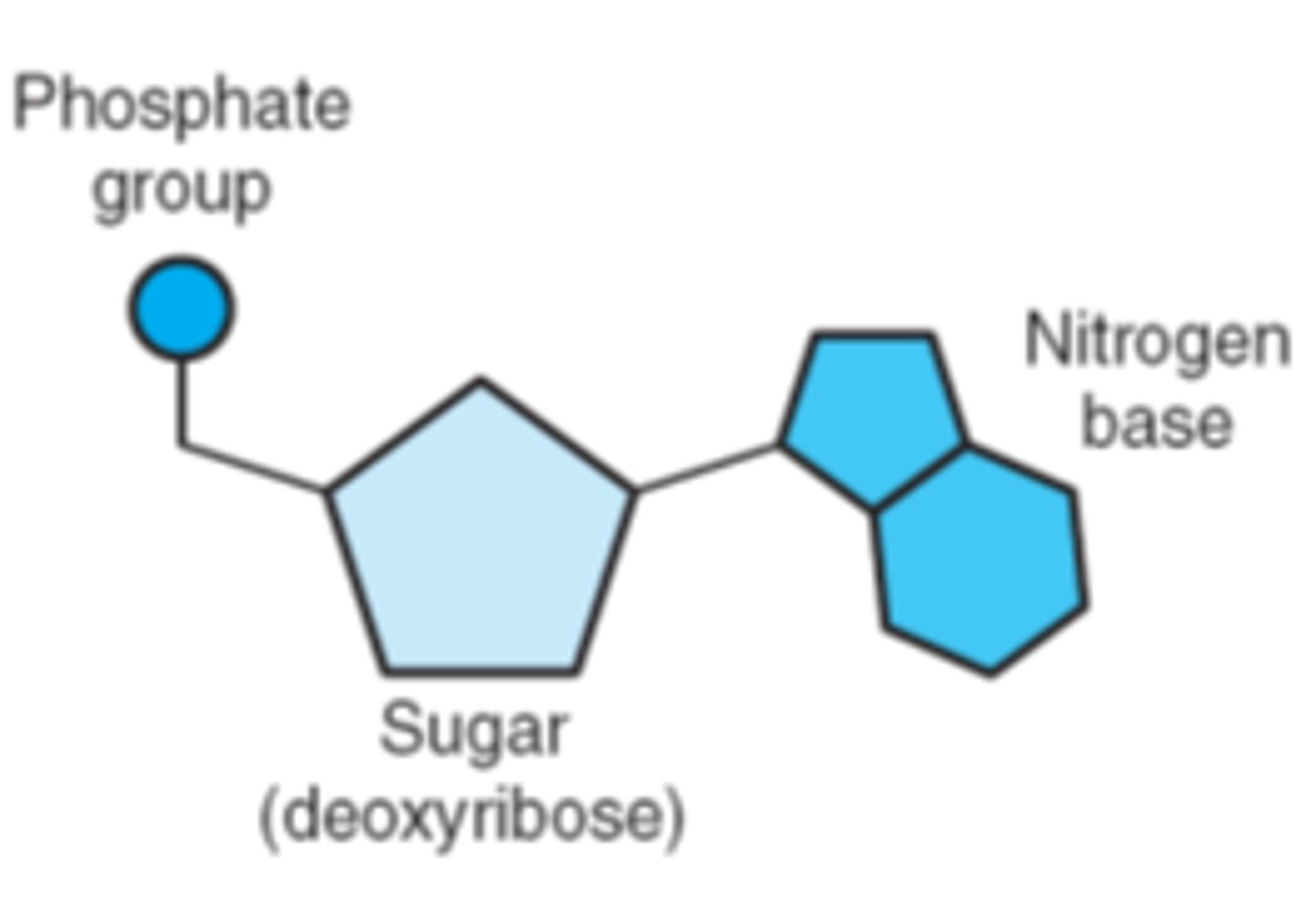
Label the 3 parts of a nucleotide
-Phosphate
-Deoxyribose sugar
-Nitrogen base
The nitrogenous bases are the genetic _______ to assemble proteins.
code
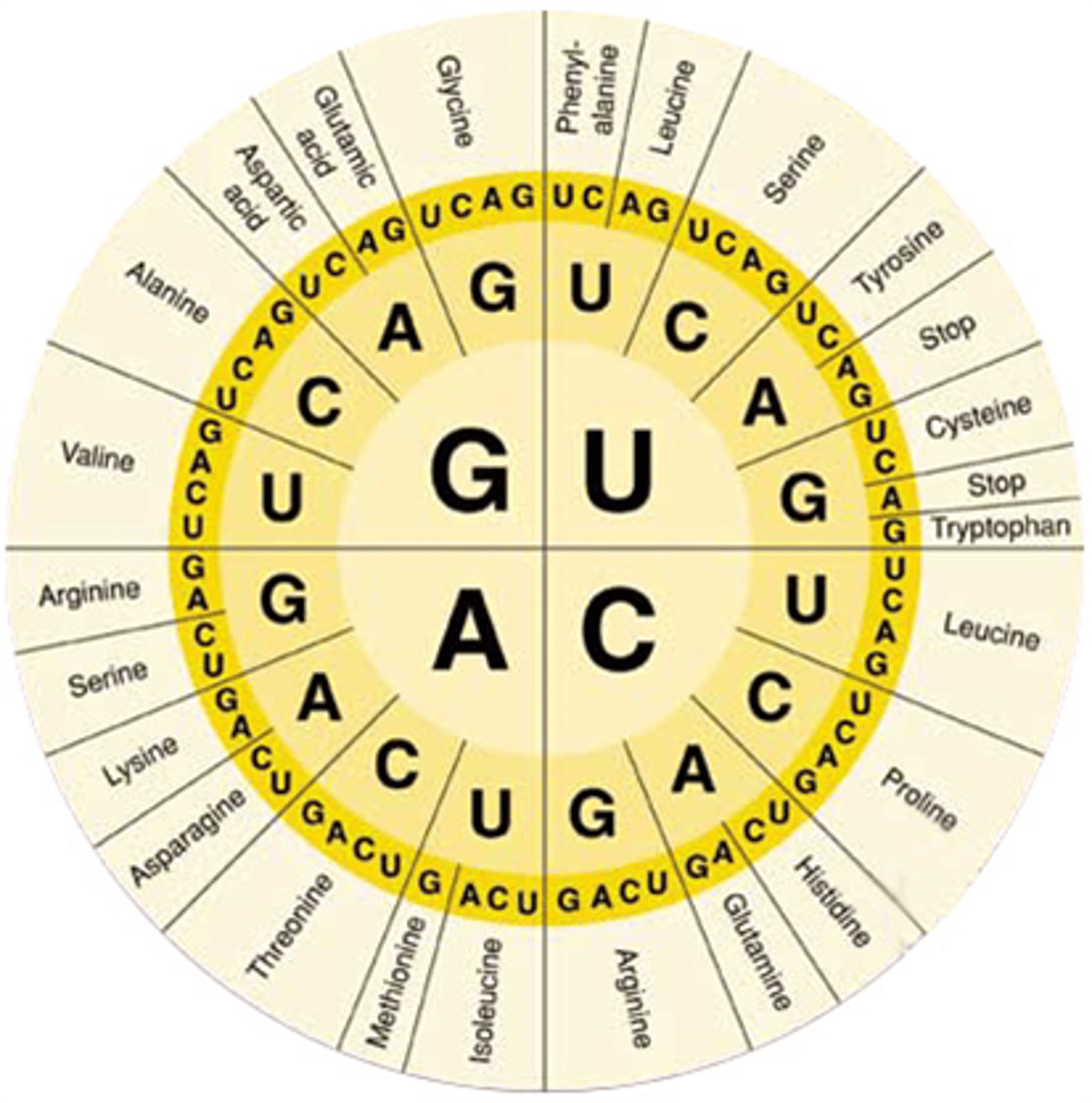
DNA relays information through the __________ of its nitrogenous bases.
order
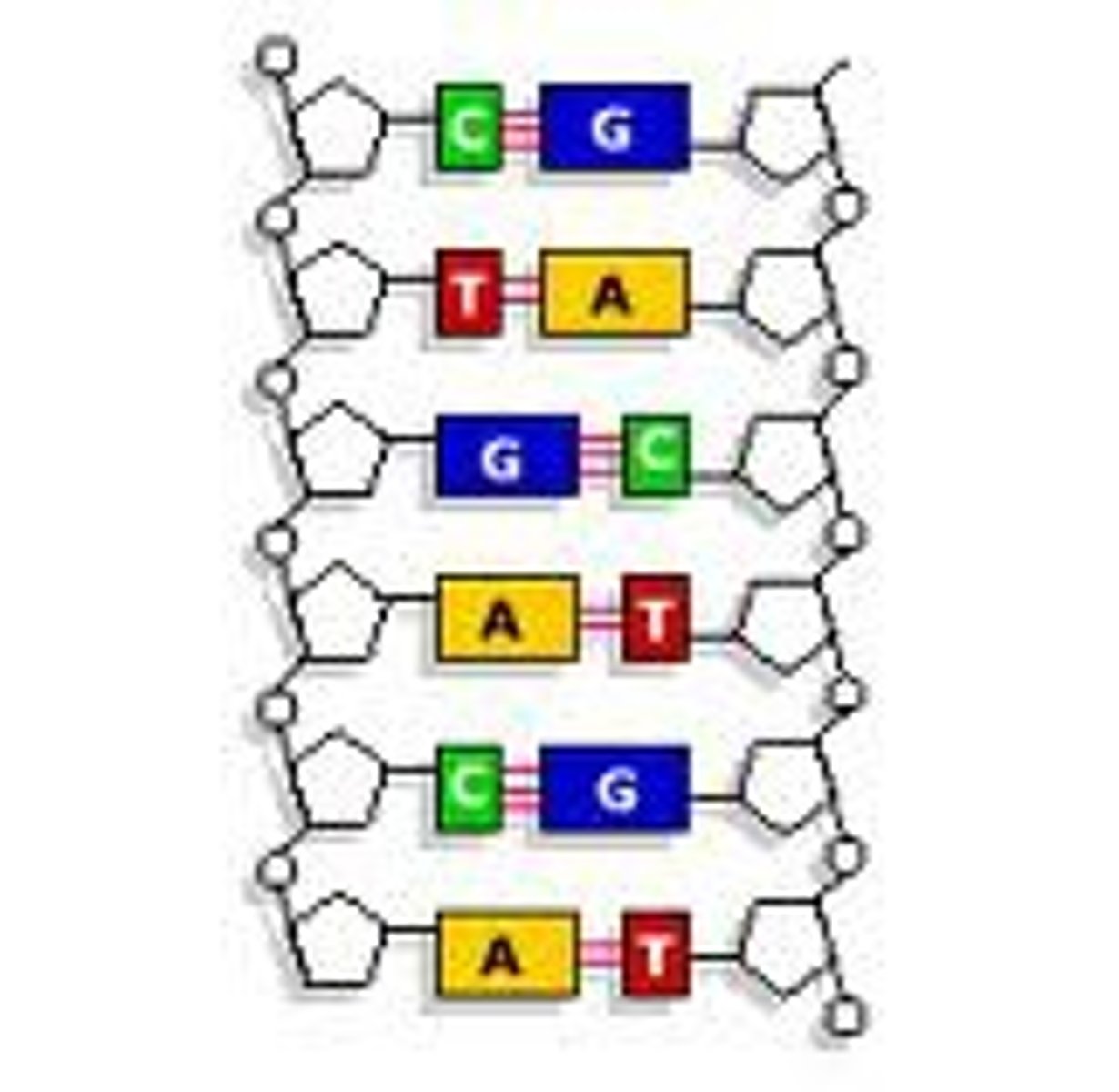
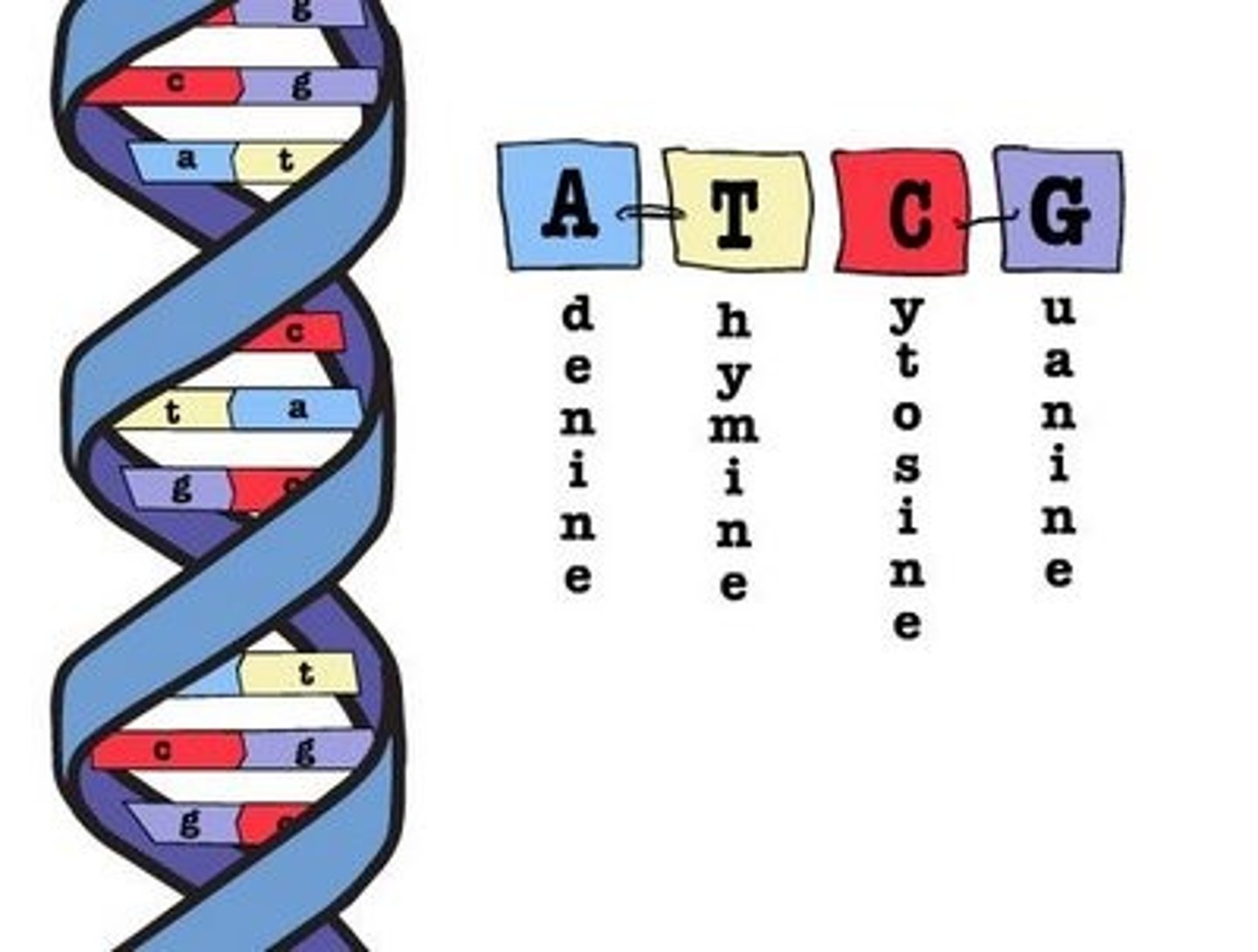
What are the DNA bases?
A - Adenine
T - Thymine
C - Cytosine
G - Guanine
Remember A goes with T, C goes with G!
DNA must be ___________ before cell division.
replicated
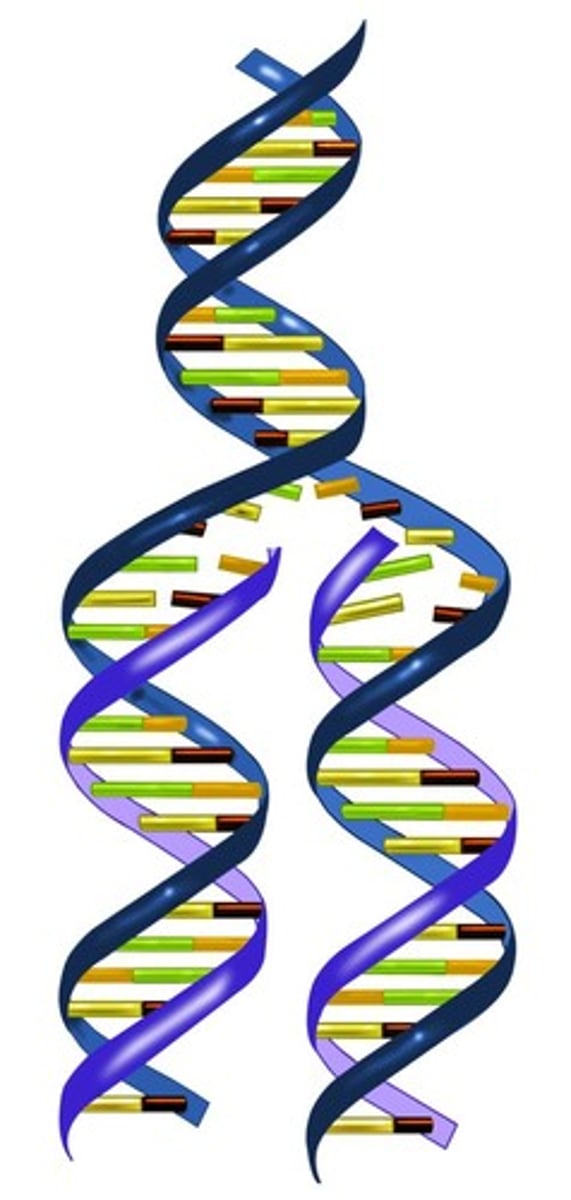

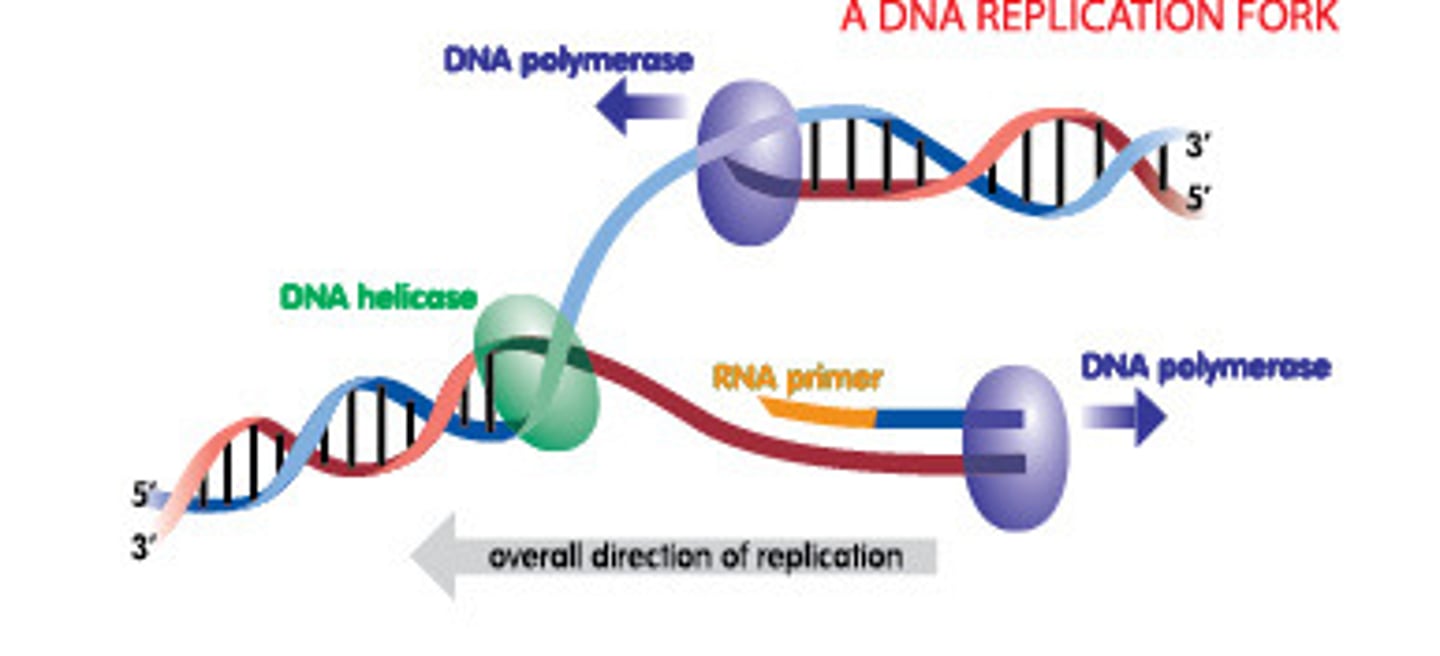
What unzips the DNA during replication?
DNA helicase (H = cuts in HALF)
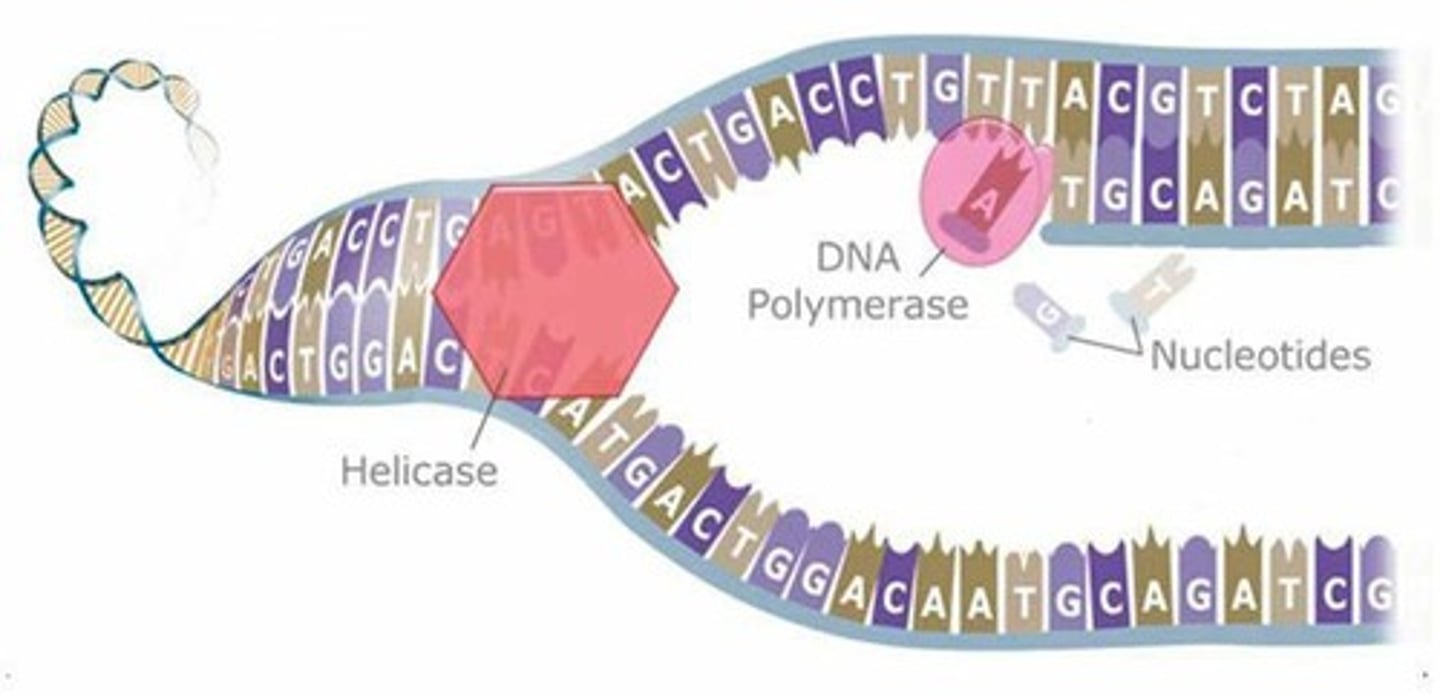
What connects the new bases to the old strand during DNA replication?
DNA polymerase (P = PUTS it together)
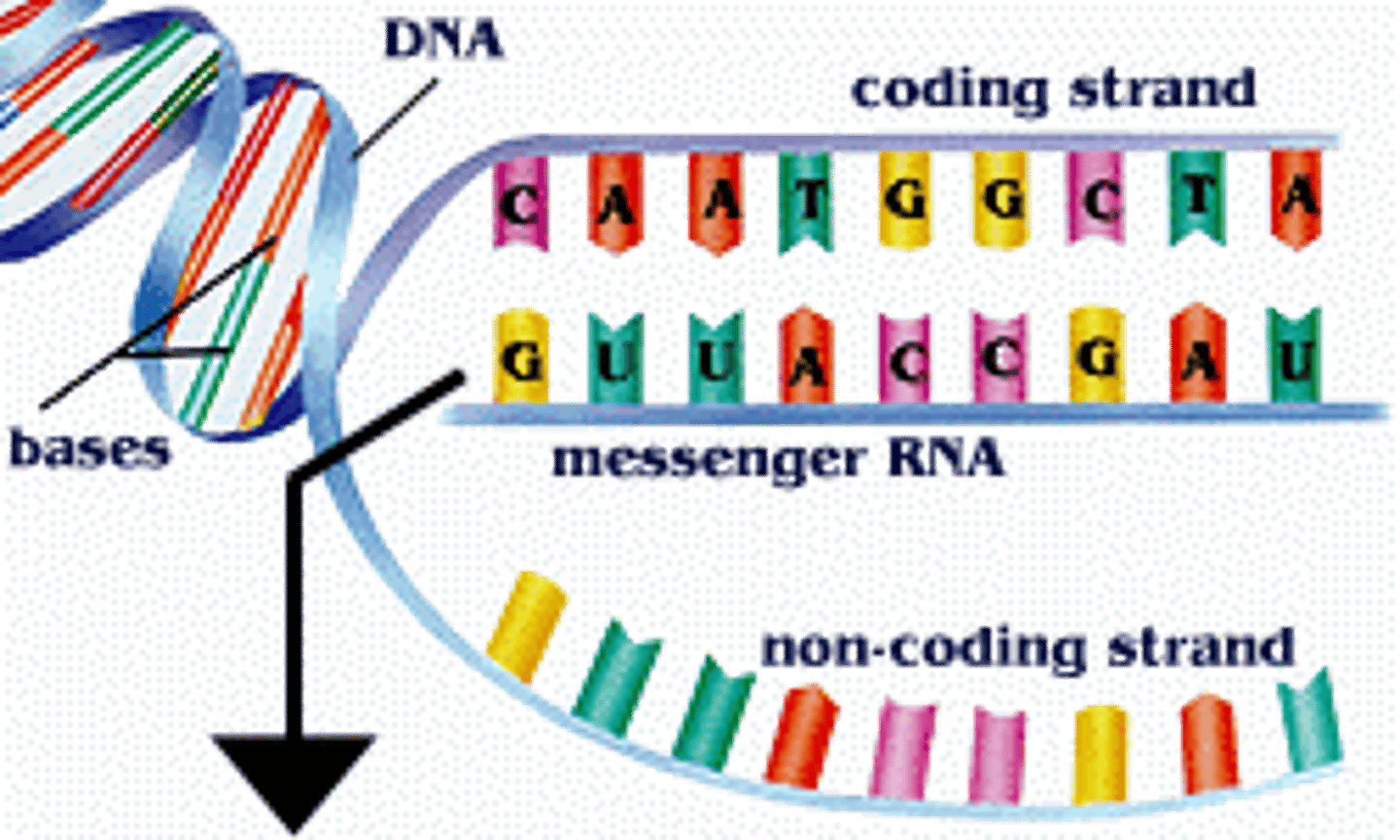
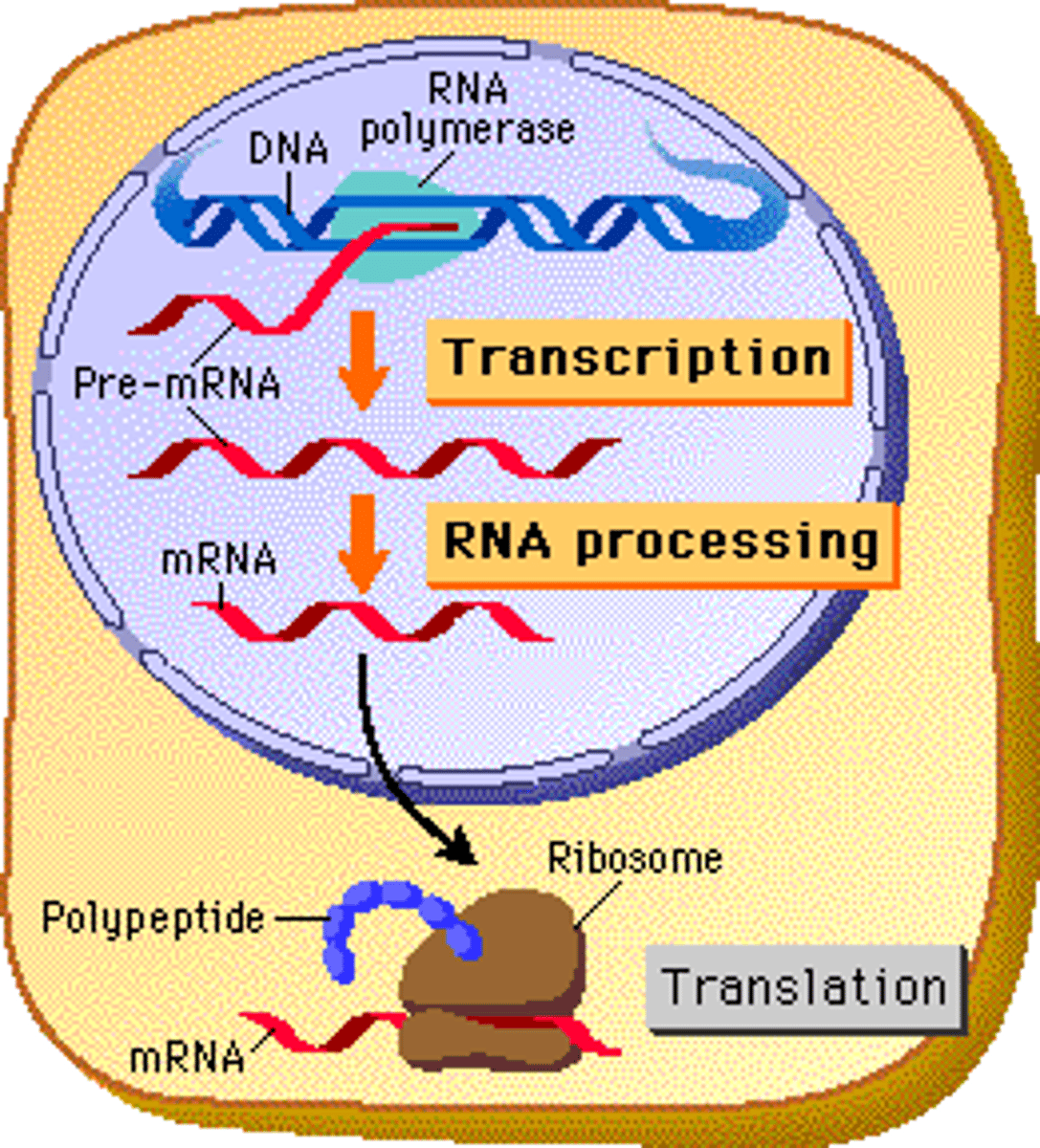
A _______ of the DNA is made through the process of transcription.
copy
Where does Transcription occur?
nucleus
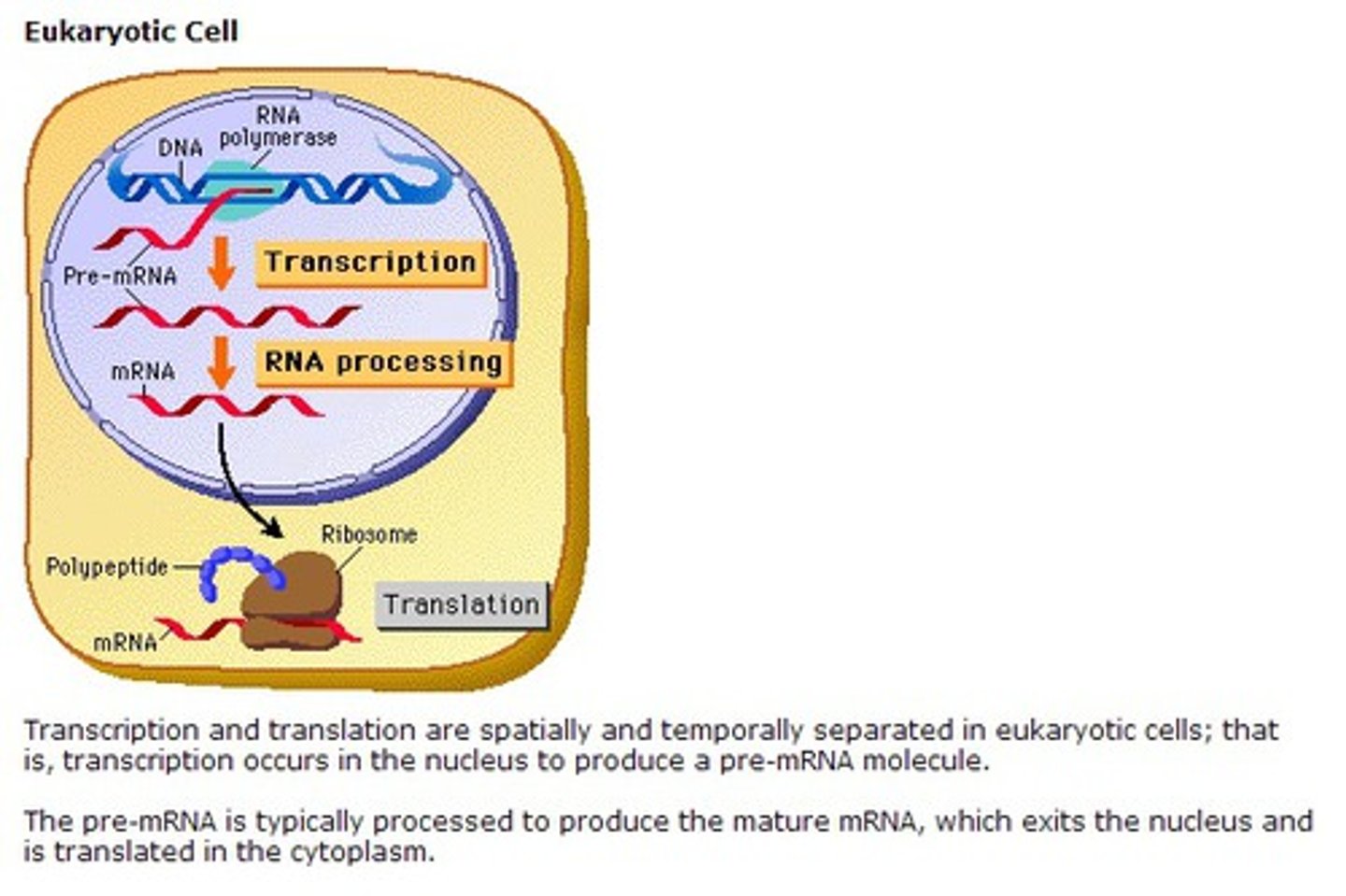
What is mRNA?
mRNA is the COPY of DNA instructions
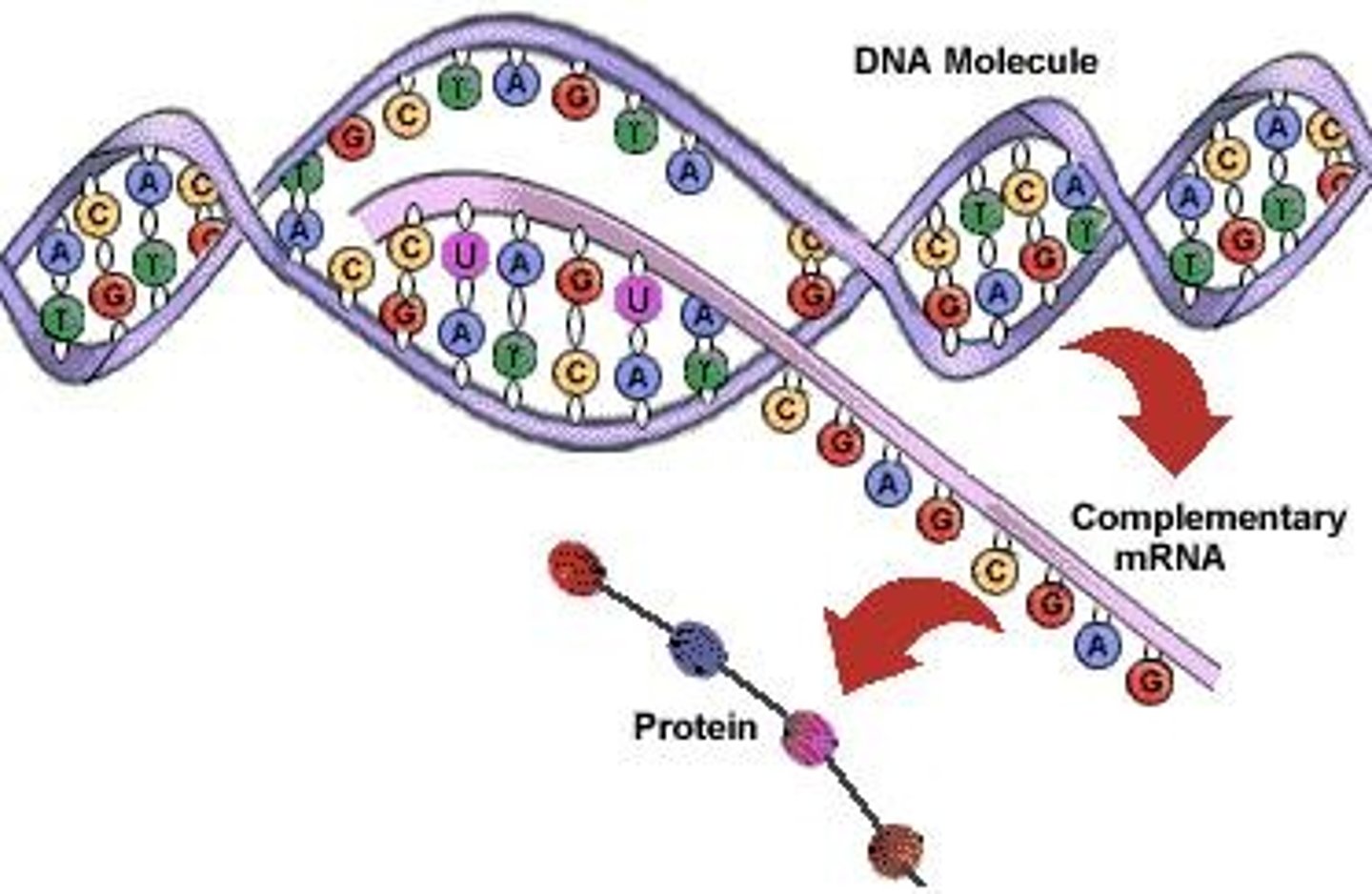
Why doesn't DNA leave the nucleus?
DNA is too large and too important to leave, that's why the copy (mRNA) is made.
__________ is small enough to fit through the nuclear pores.
mRNA
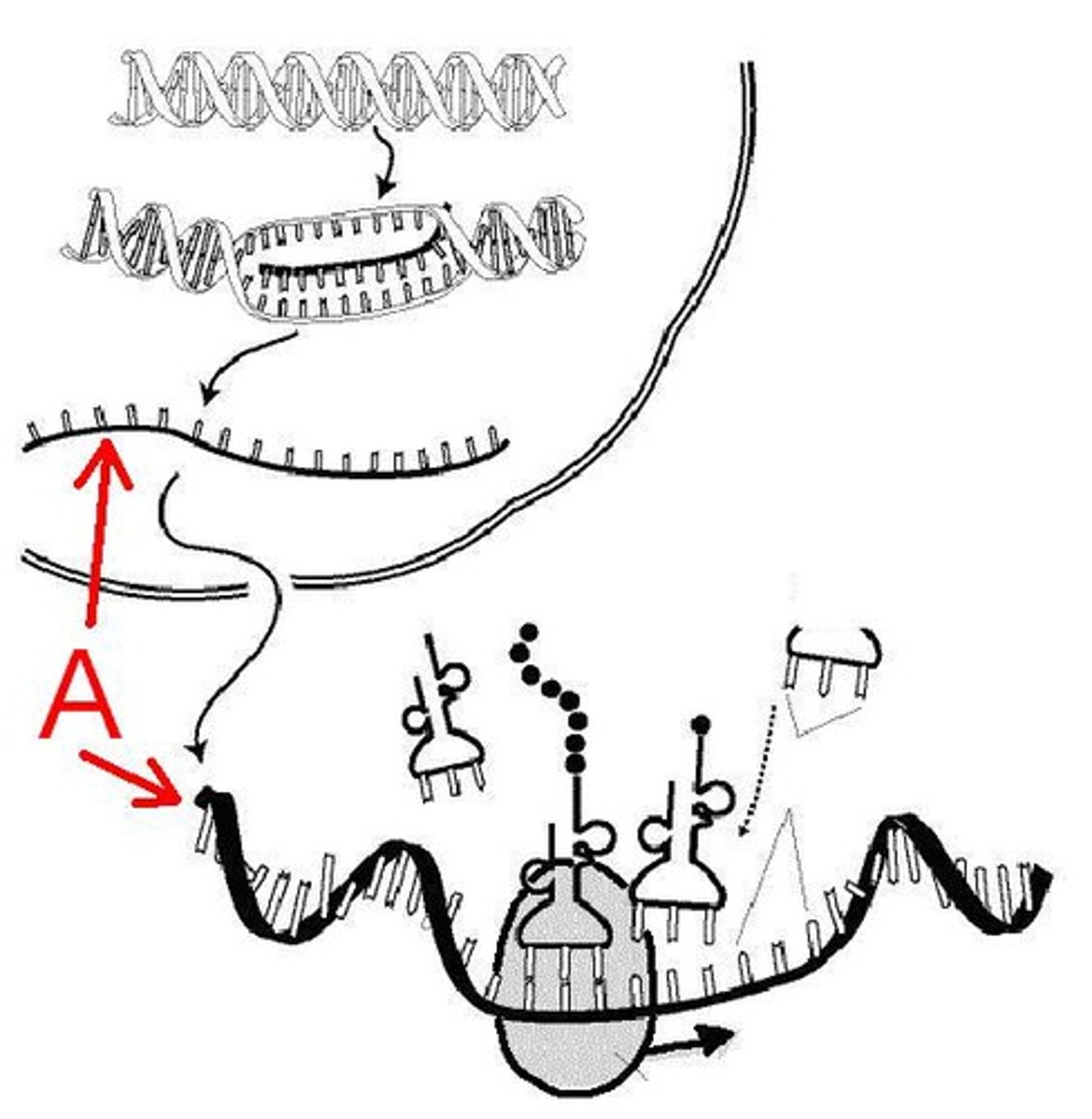
Where does the mRNA go after transcription (after it's copied?)
Ribosome
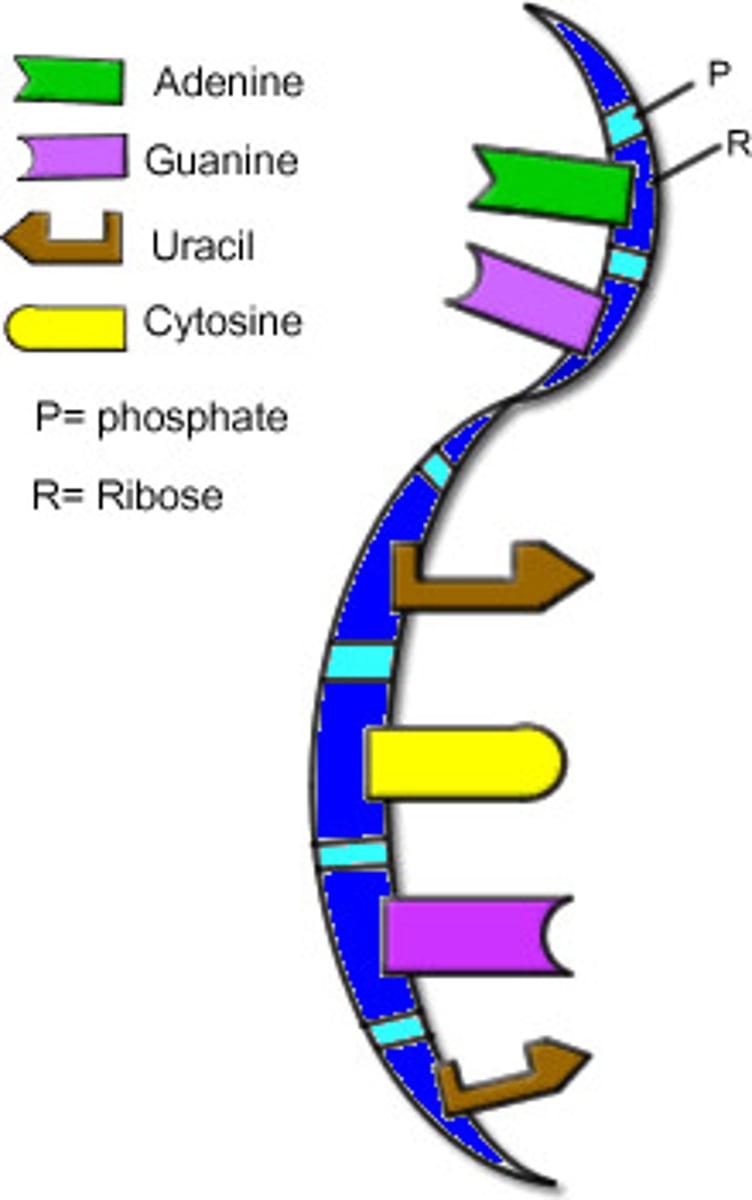
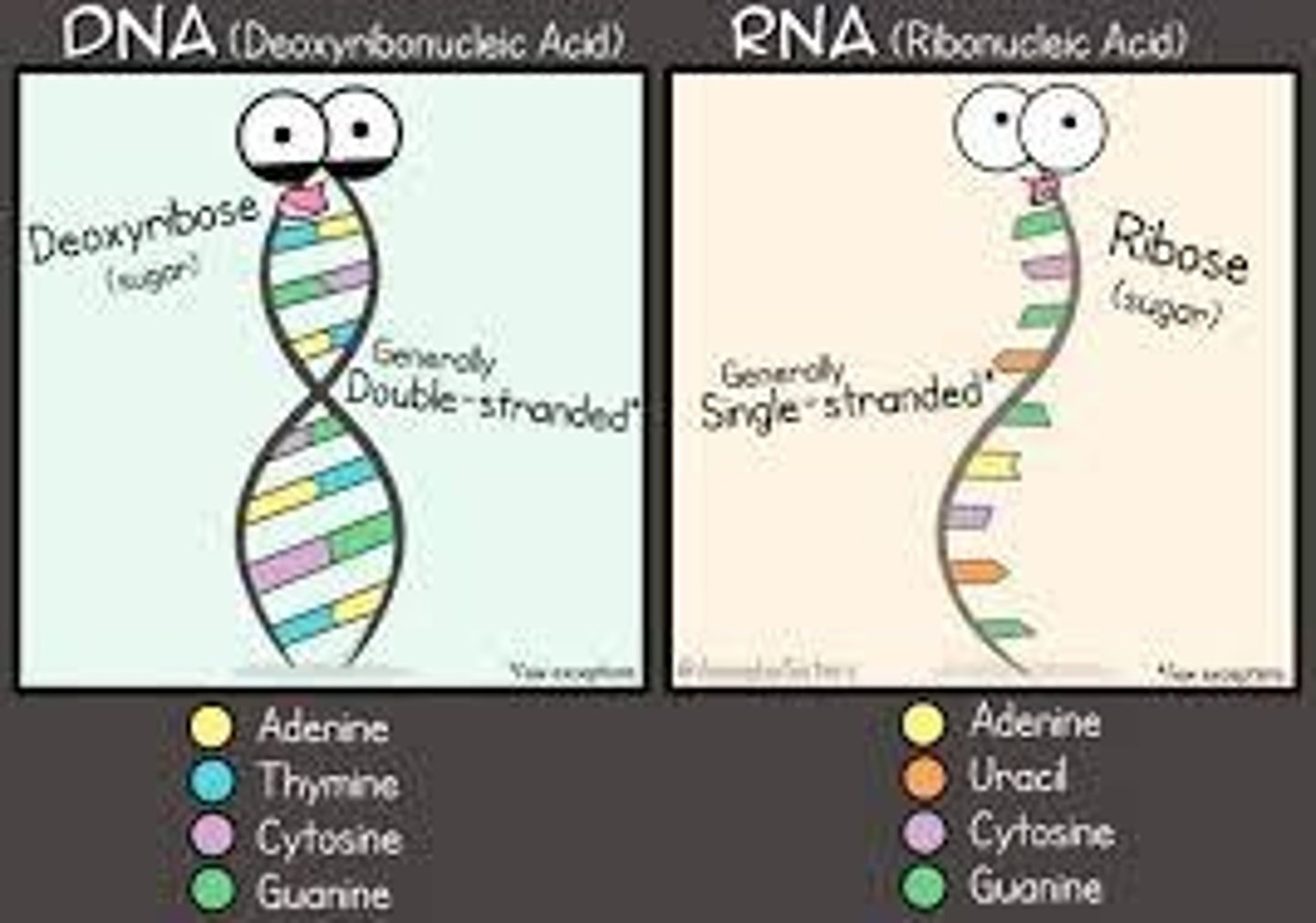
Differences between DNA & RNA - DNA is double stranded and RNA is ________ __________.
single stranded
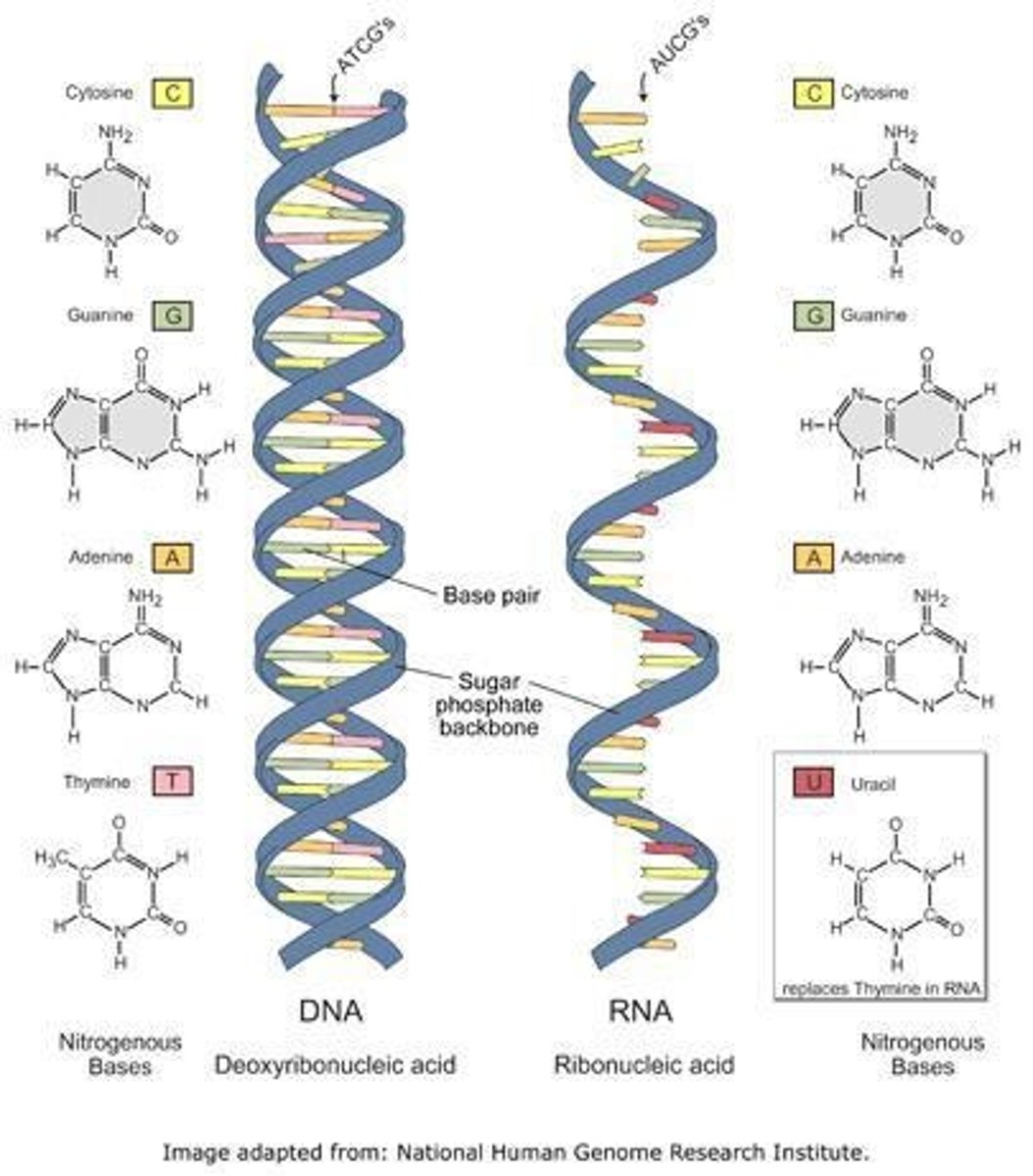
DNA has a double helix, and RNA has a _______________ ______________.
single helix
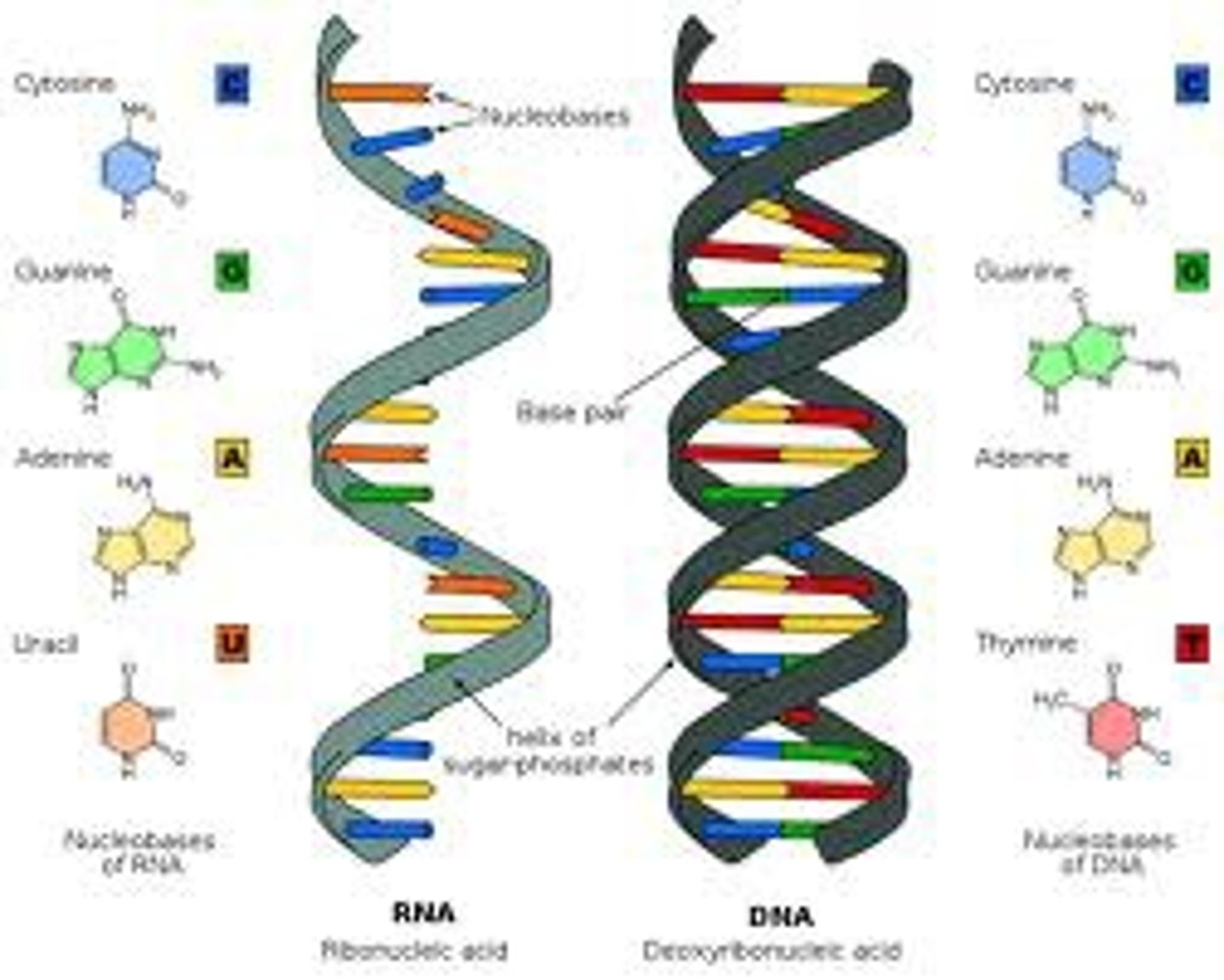
DNA has deoxyribose sugar and RNA has ___________ sugar.
ribose
(D = deoxyribose, R = ribose)
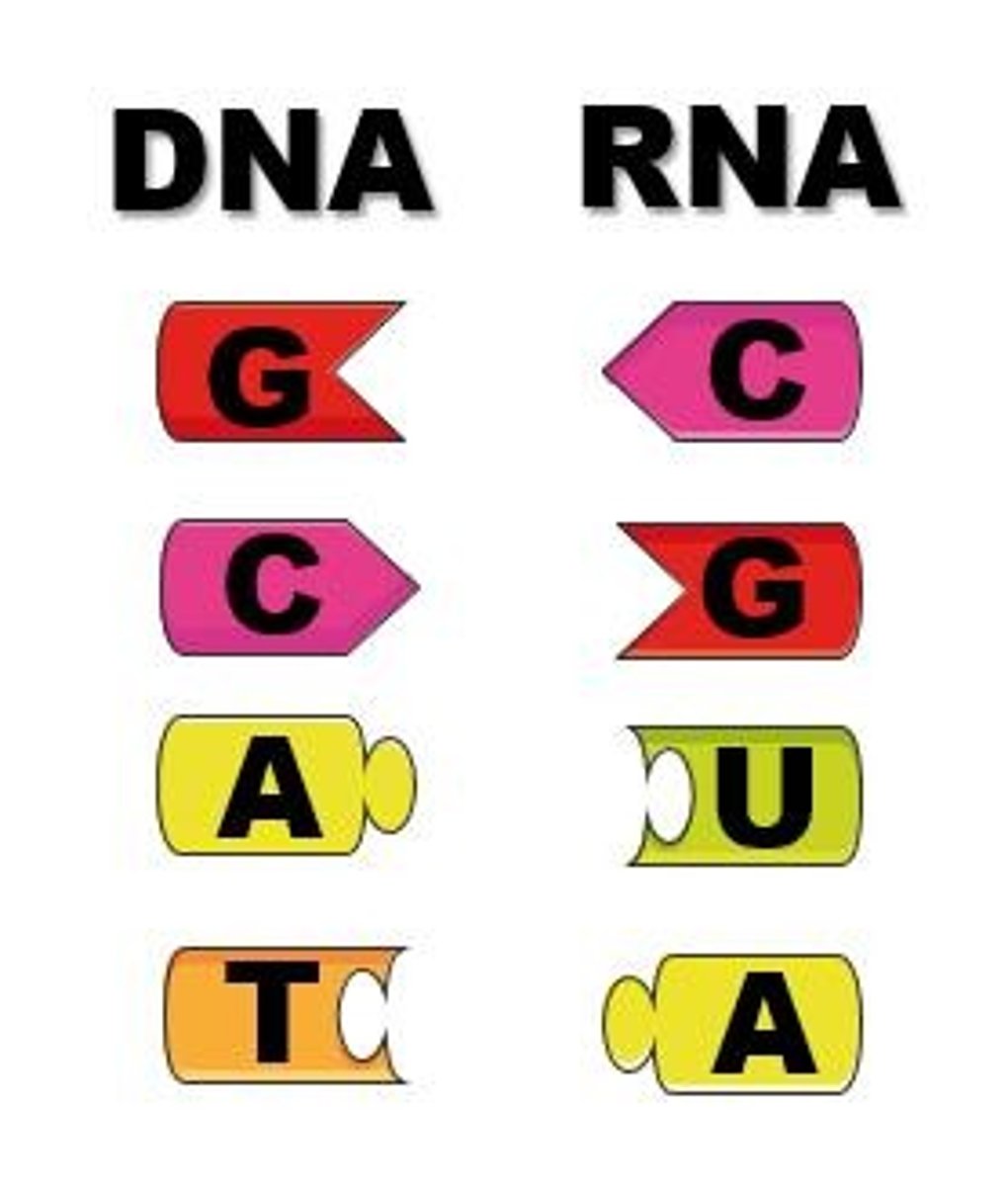
Nitrogen bases - DNA has A,T,C,G and RNA has __, __, __, __.
A,U,G,C
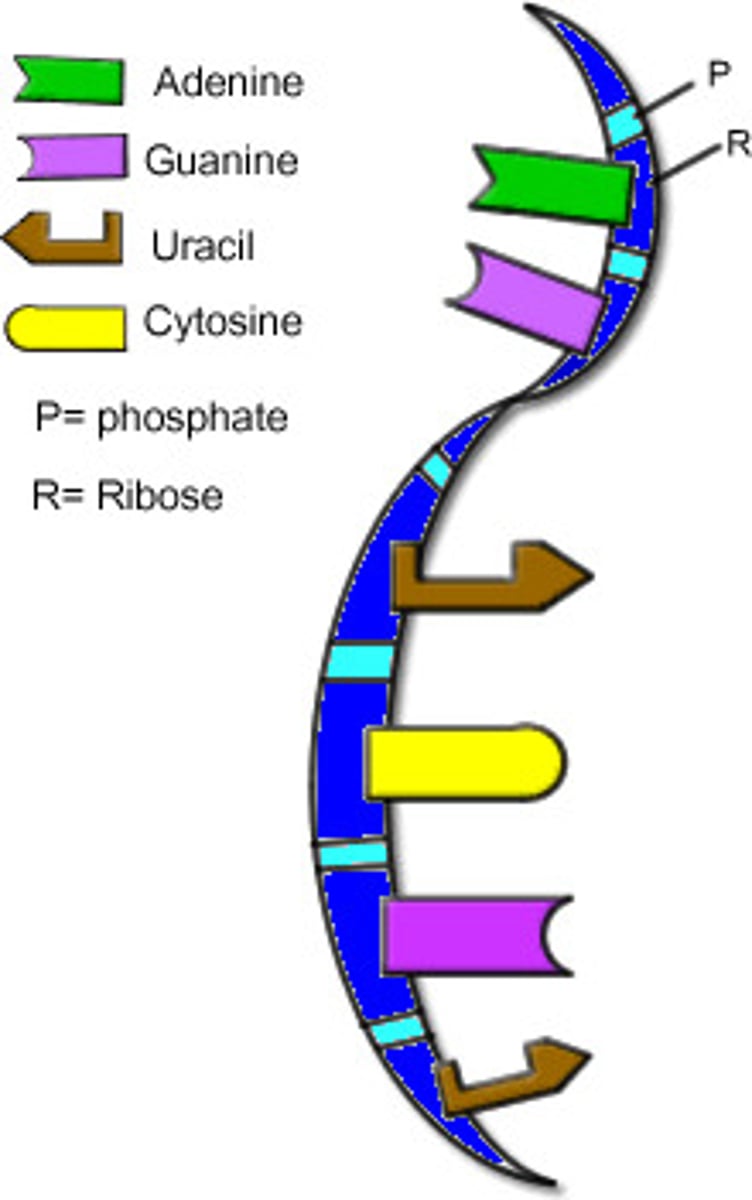
Base pairing - Transcription
A (Adenine) connects to _________
T (Thymine) connects to _________
G (Guanine) connects to ________
C (Cytosine) connects to ________
A -----> U (Uracil)
T -----> A
G ----> C
C ----> G
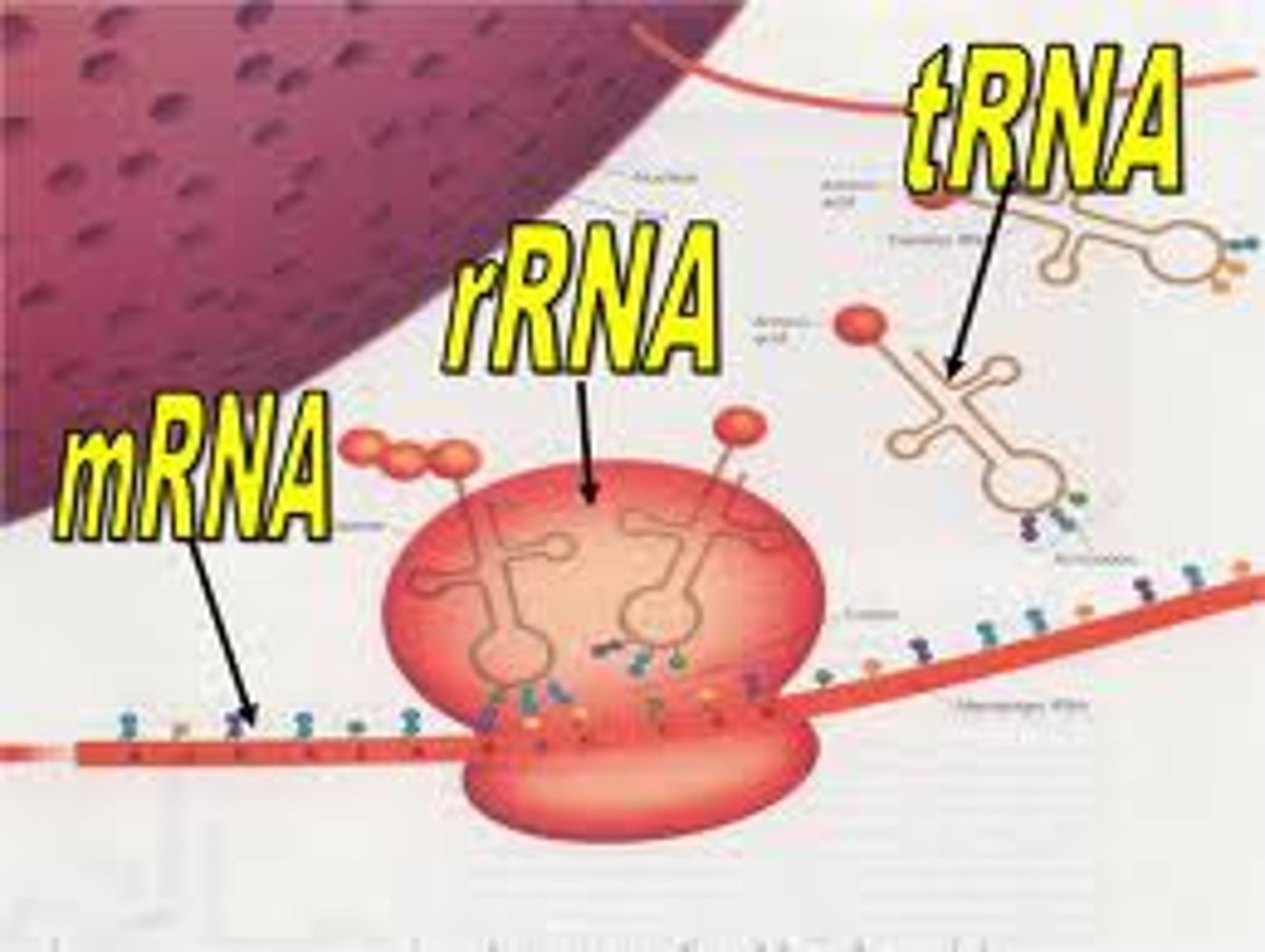
Which type of RNA copies & carries the message from the nucleus/DNA to the ribosome
messenger RNA (mRNA)
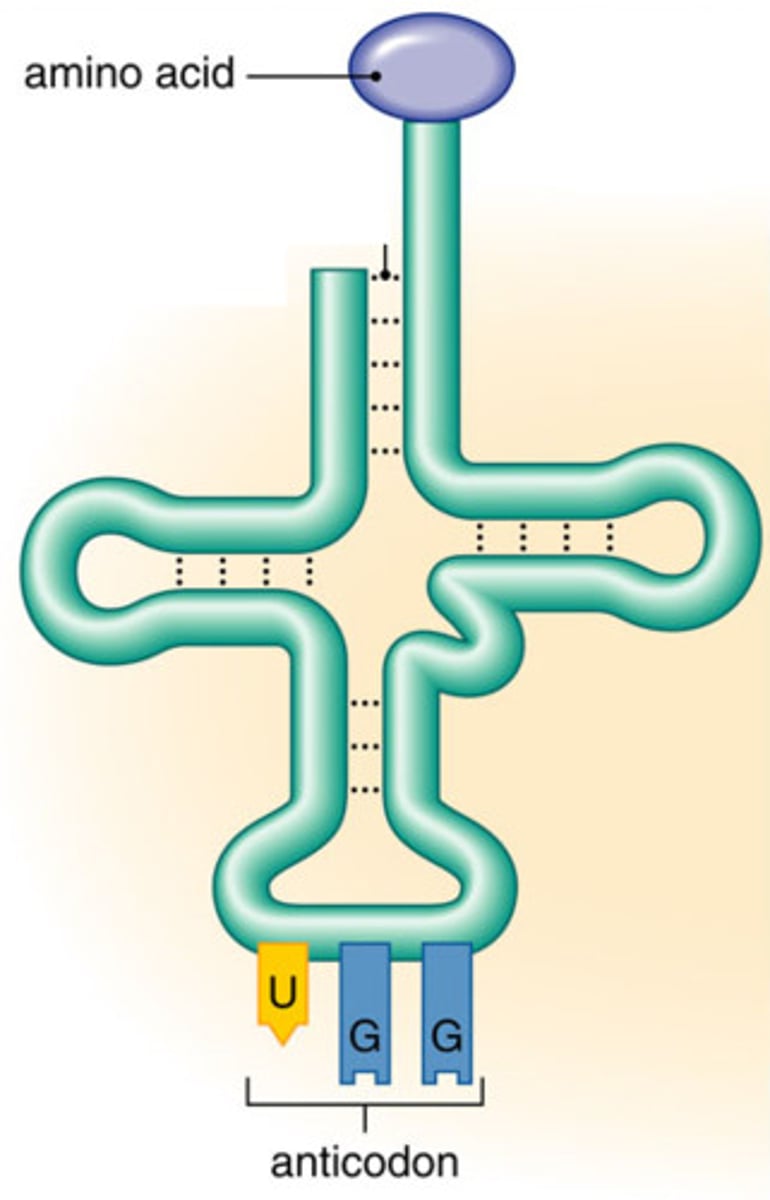
Which type of RNA transfers Amino acids from the cytoplasm into the ribosomes.
transfer RNA (tRNA)
Which type of RNA are what ribosomes are made of and responsible for making new ribosomes.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Translation is the __________ stage of protein synthesis.
final
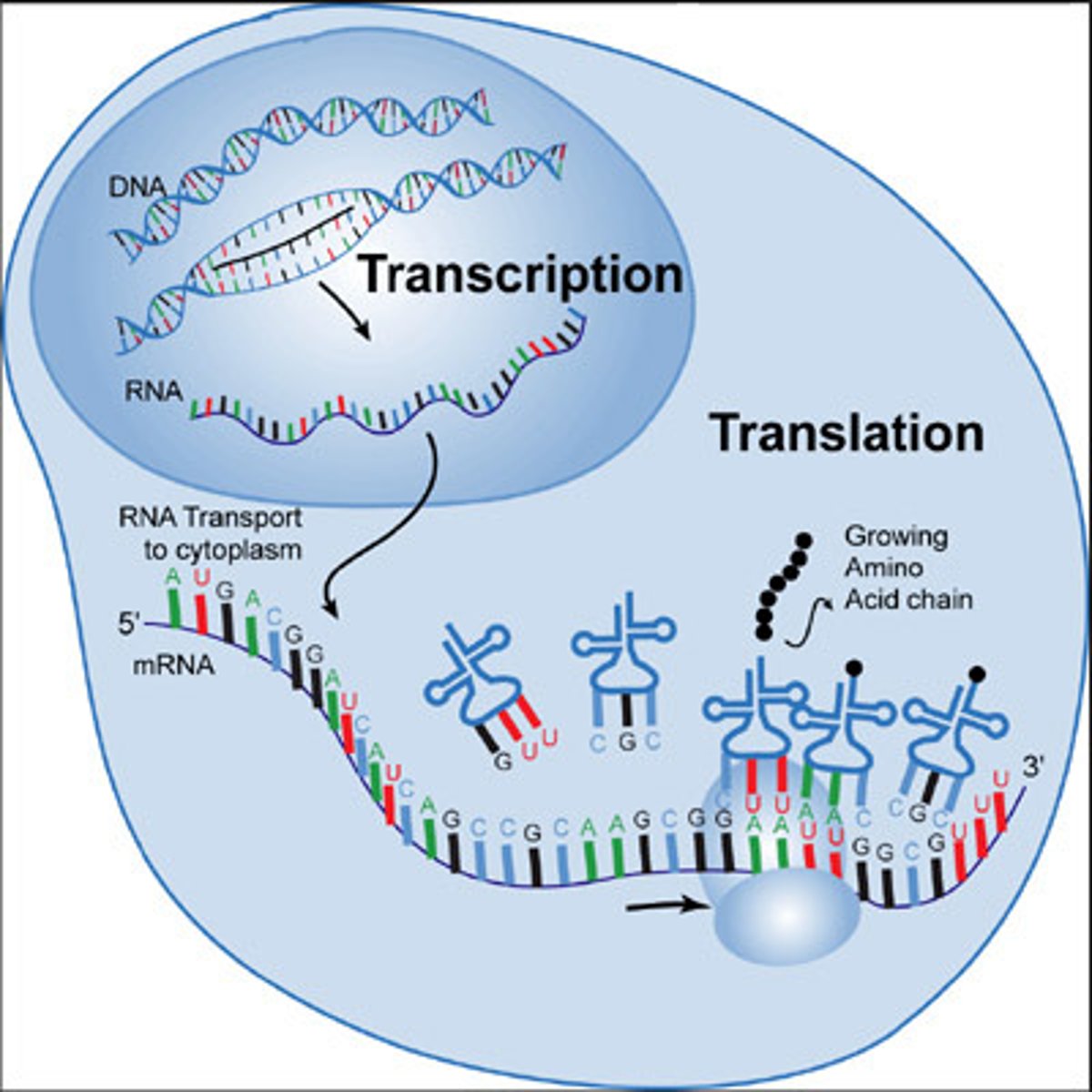
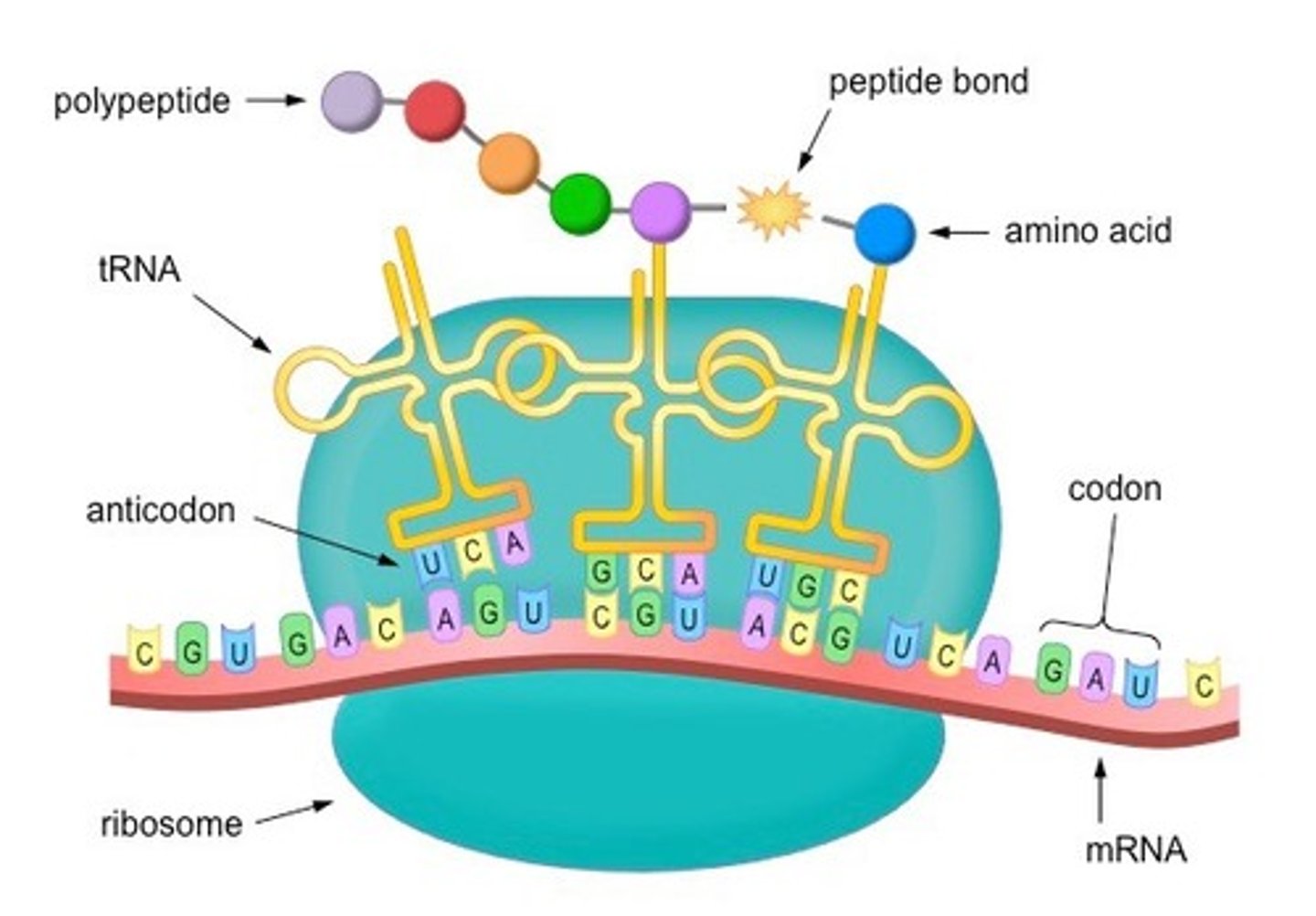
Describe the process of translation
Process of translating a sequence of mRNA to a sequence of amino acids.
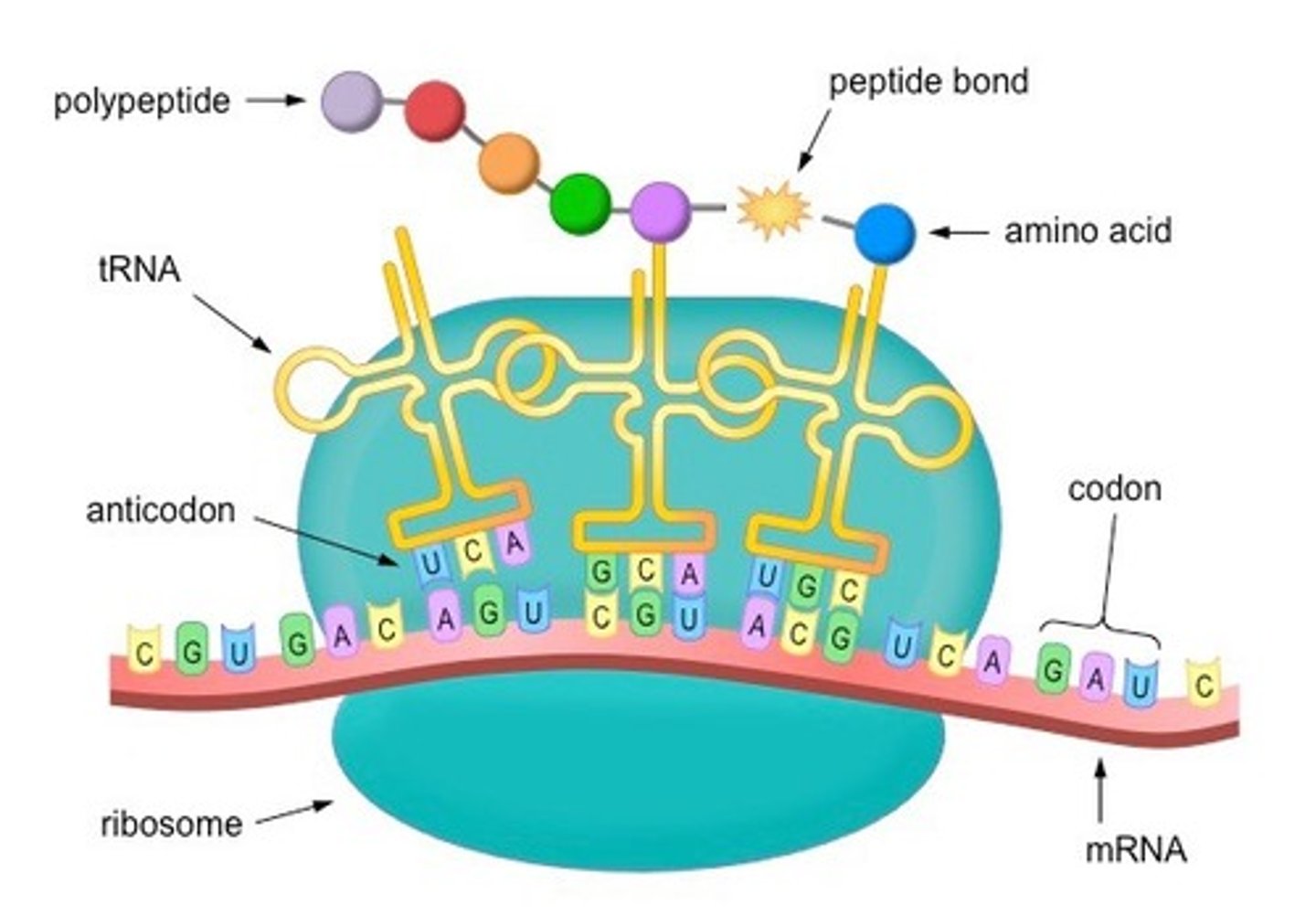
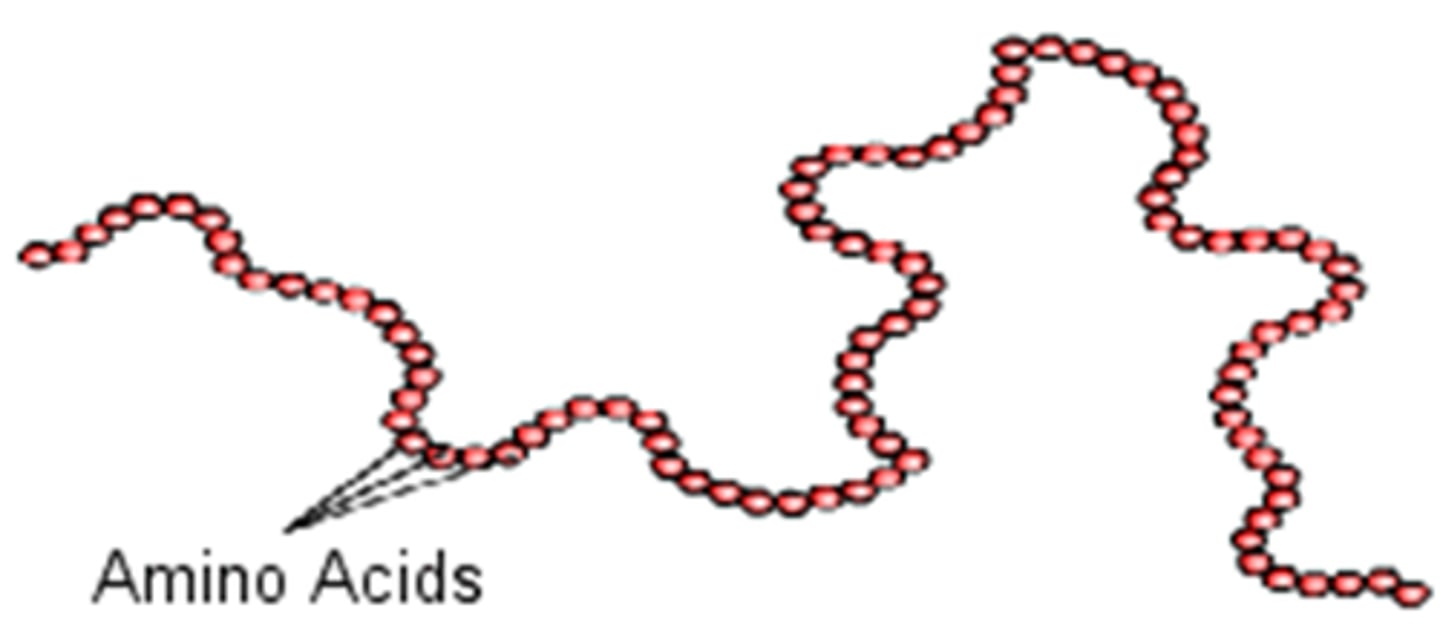
What are amino acids?
building blocks of proteins
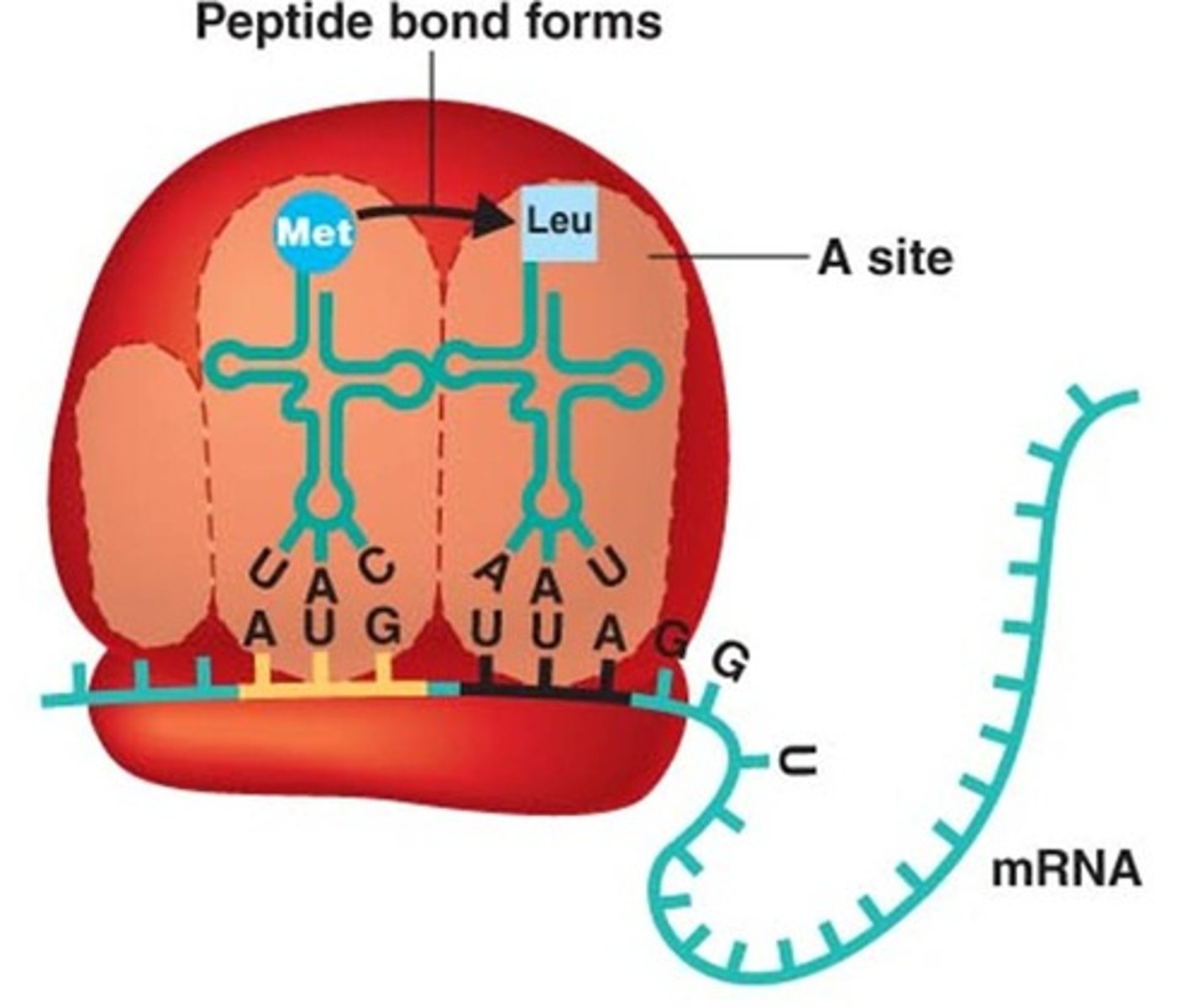
1st step of translation
The mRNA brings the message to the ribosome.
2nd step of translation
tRNA anticodon binds to the codon of mRNA.
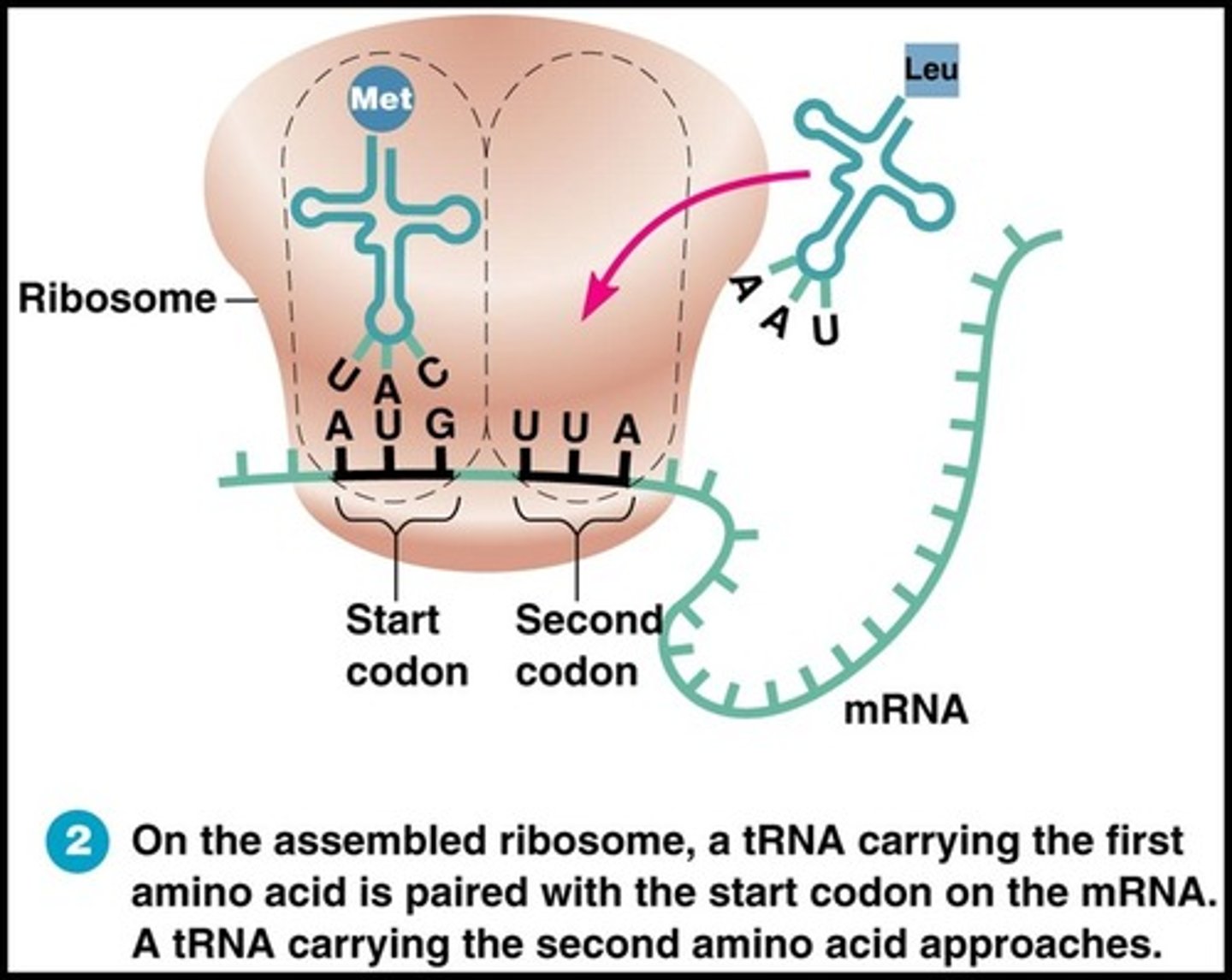
3rd step of translation
tRNA donates its amino acid to the chain.
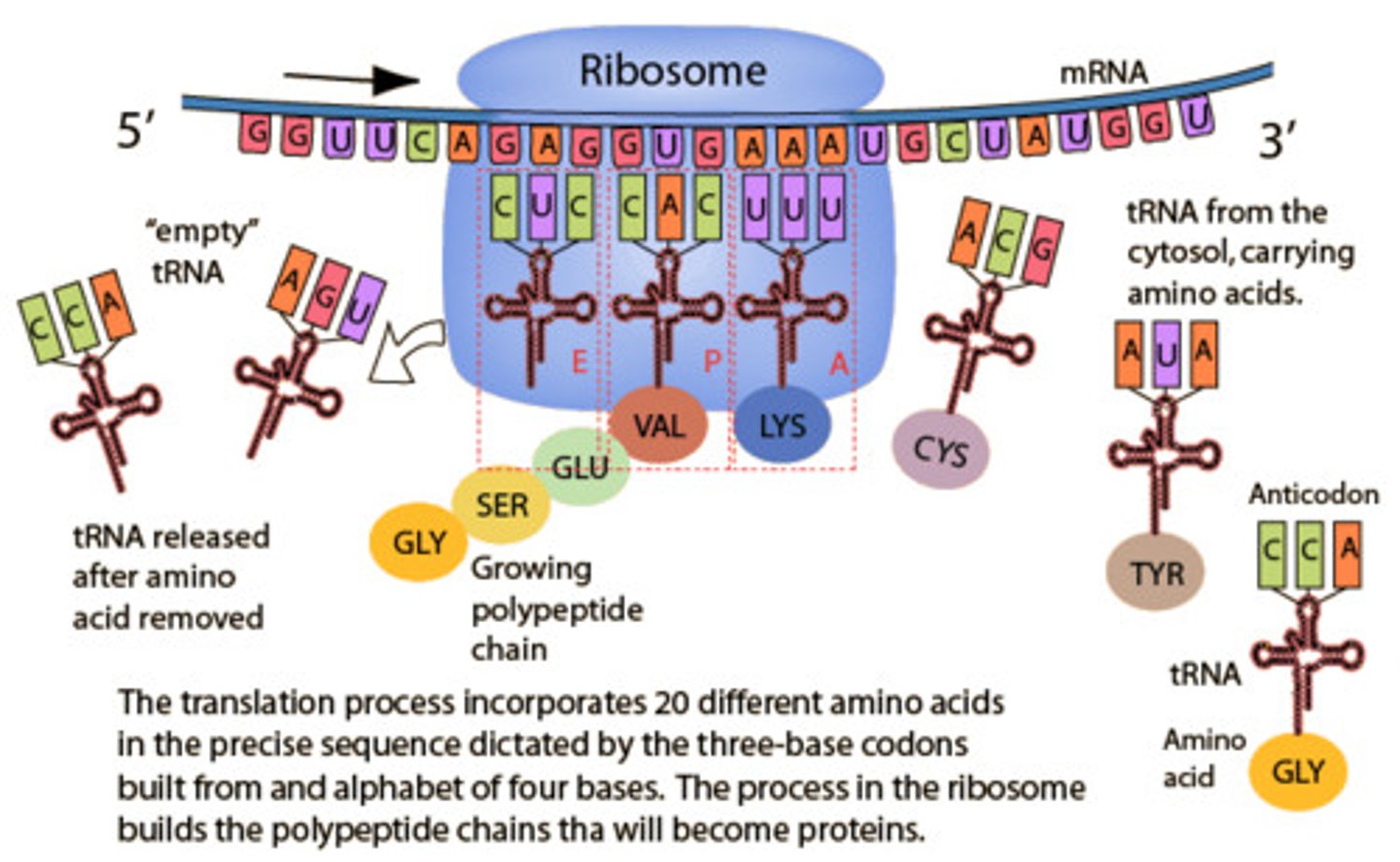
4th step of translation
Translation stops when a stop codon is reached.
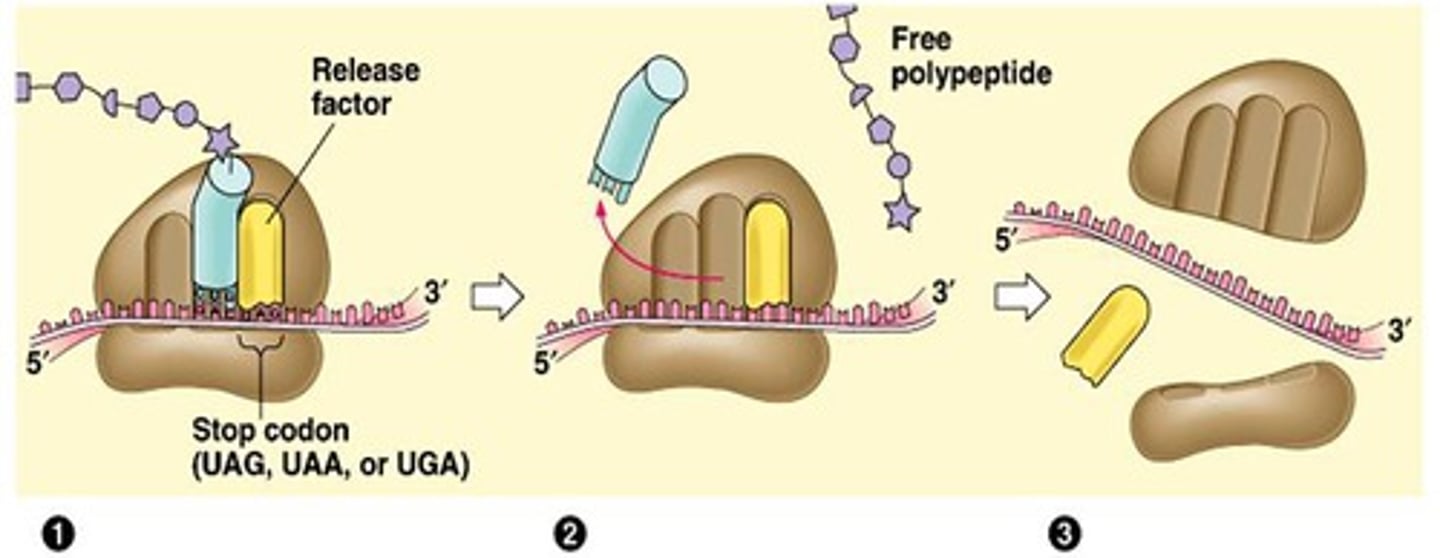
Last step of translation
Amino acid chain released by the ribosome.
