JCU Late Antiquity and Medieval (305-1340)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms

1. Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine (aka Basilica Nova), Roman Forum Valley, c. 305-315

2. *Colossal portrait of the emperor Constantine, c. 313-15; found in the Basilica Nova in the Roman Forum Valley; marble fragments of acrolithic statue; head recut from a portrait of Hadrian
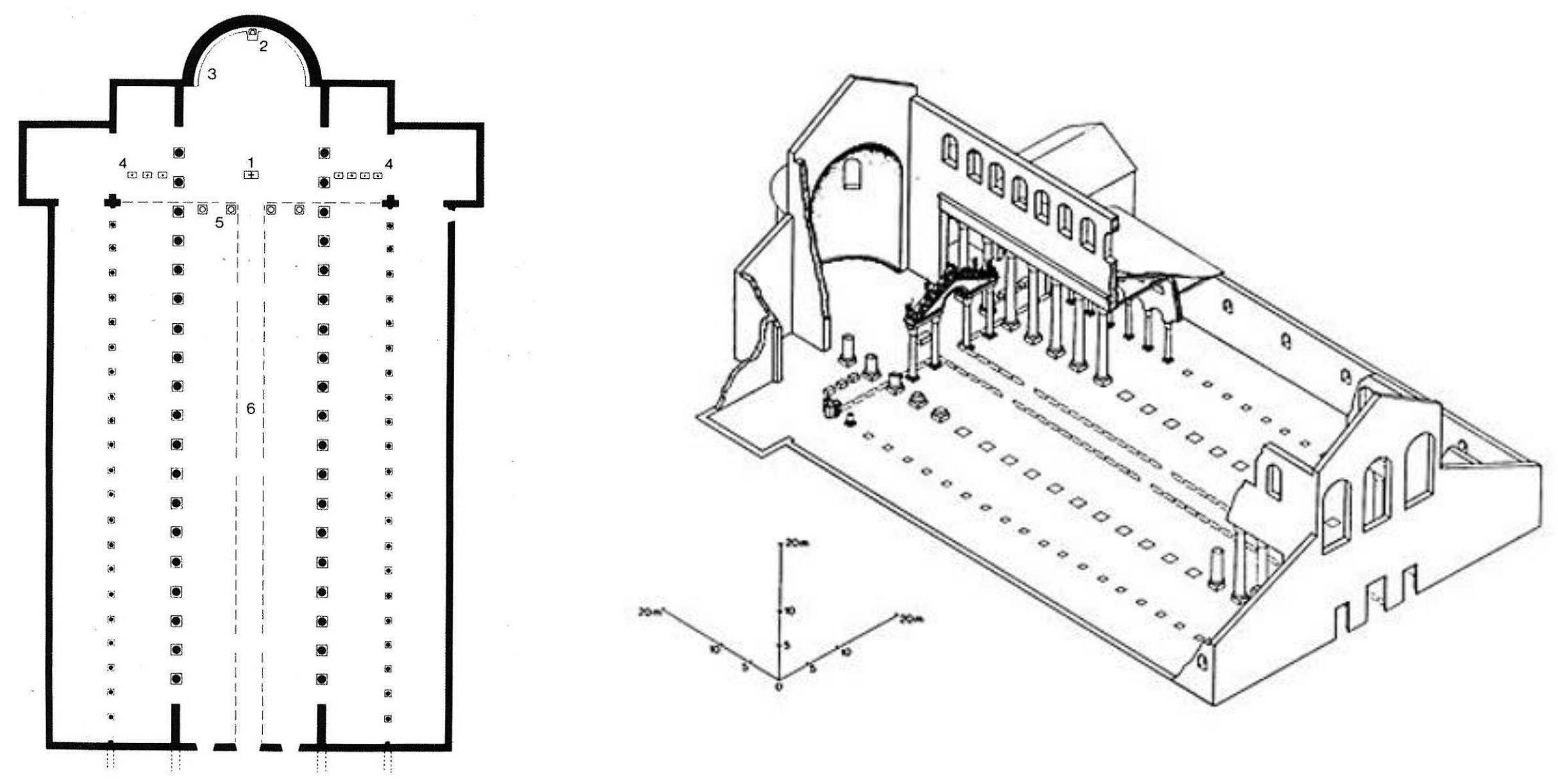
3. *Rome, Lateran Basilica, c. 314 (Constantinian; original no longer extant); first cathedral in city; built on imperial land
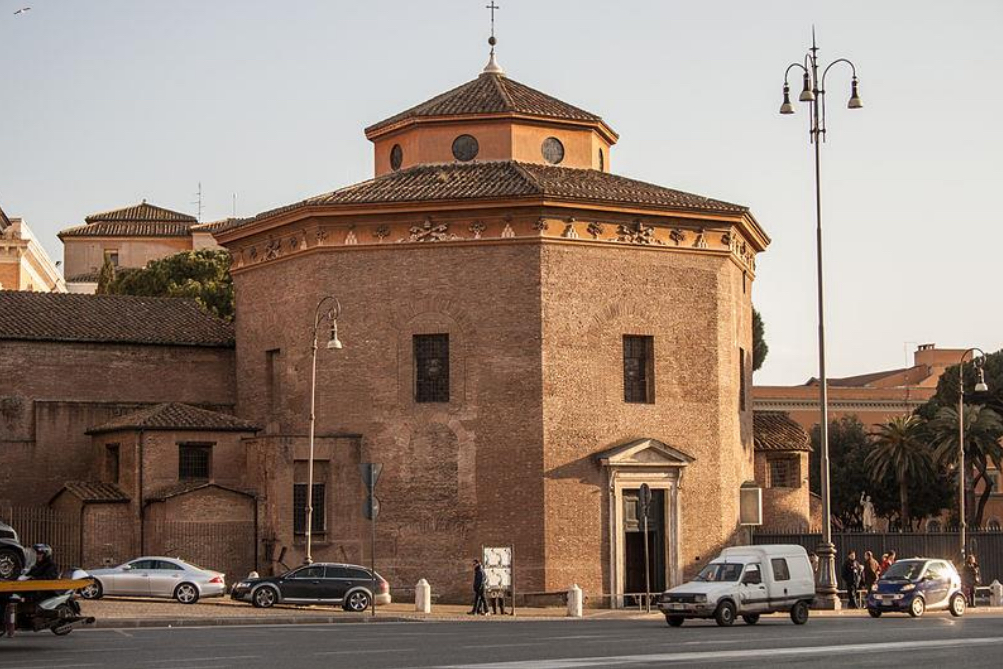

4. Rome, Lateran Baptistery, originally c. 314 (Constantinian); first free-standing baptistery in city; built on imperial land
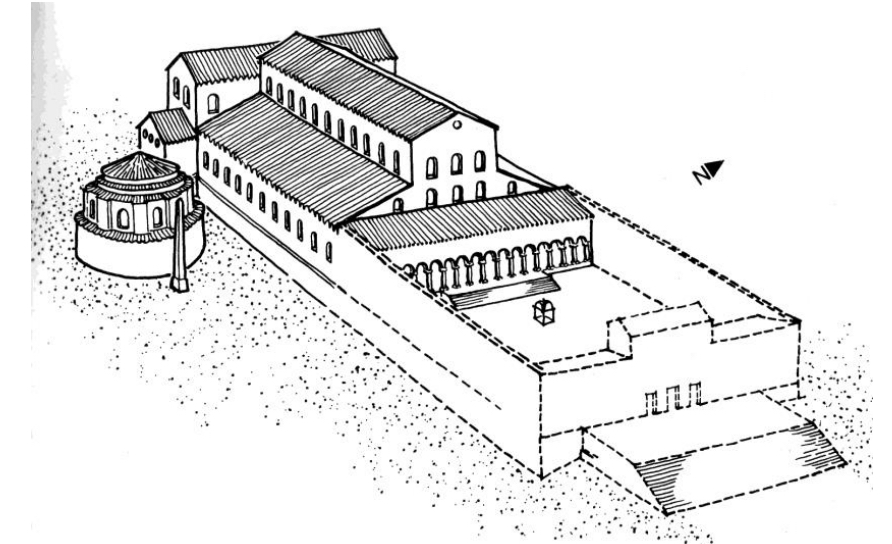
5.*Rome, Old St. Peter’s, c. 319-330 (Constantinian; original no longer extant); funerary basilica / martyrium built over tomb of St. Peter (latter referred to as the tropaeum)
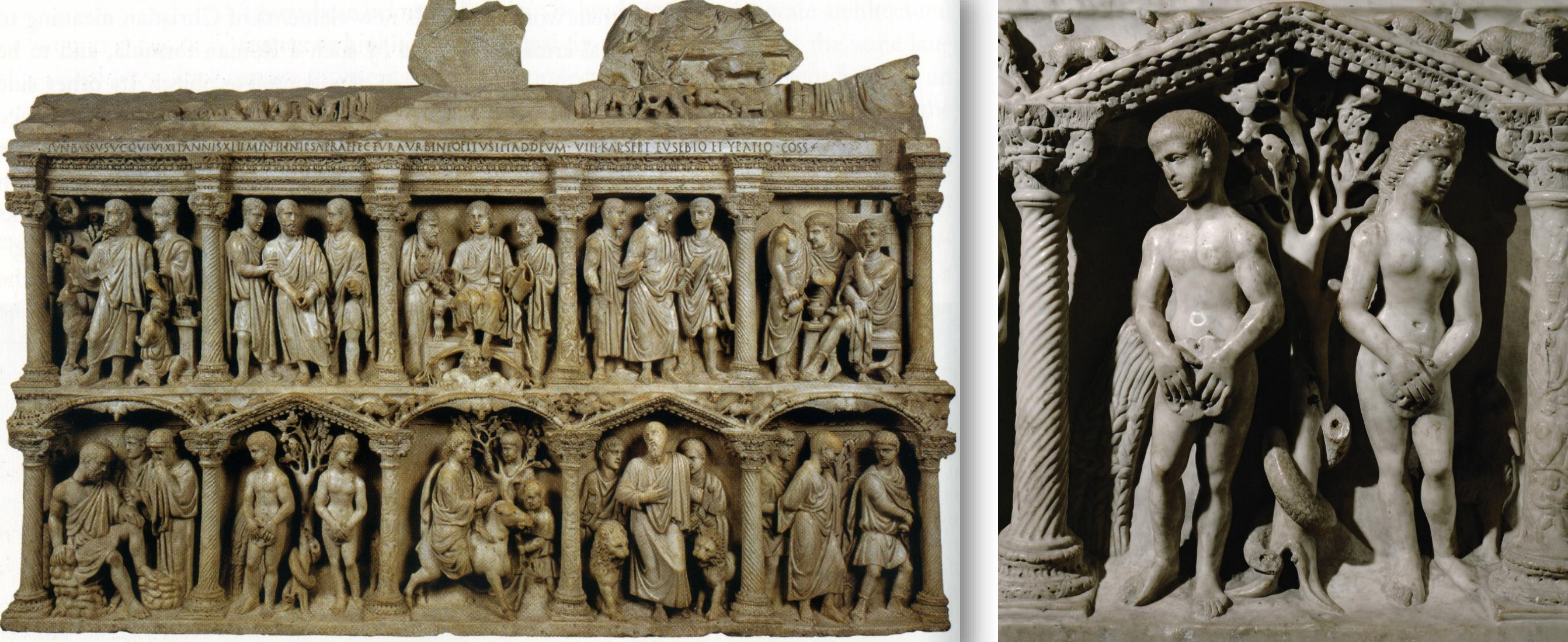

6. *Marble sarcophagus of the Roman prefect Junius Bassus; 359; originally buried in front of St. Peter's tropaeum in the Vatican necropolis; reliefs combine Old and New Testament scenes; detail shows the Fall
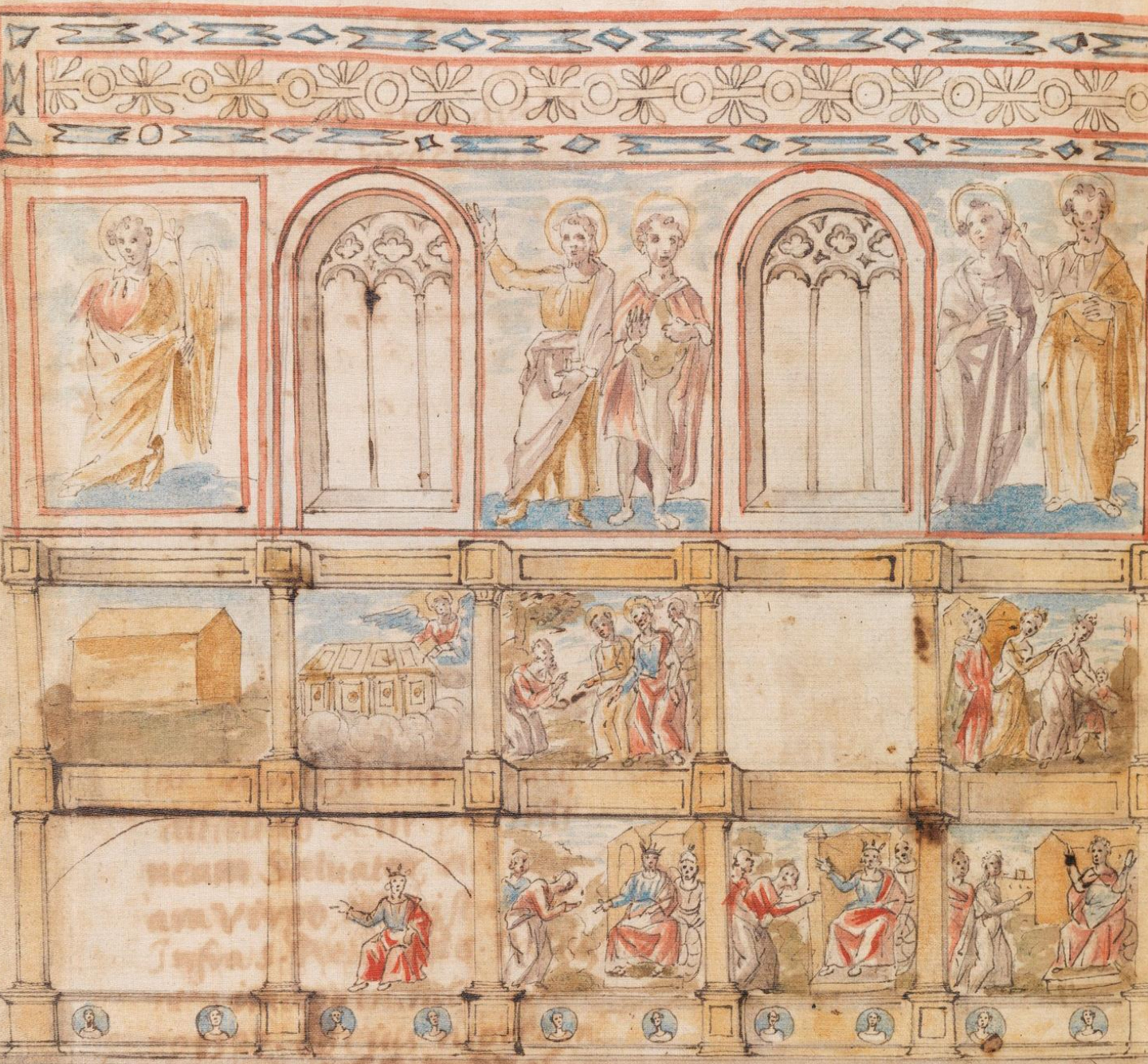

7. Rome, frescoes from the nave of Old St. Peter’s, 4th or 5th cent. (no longer extant; image is rendition)
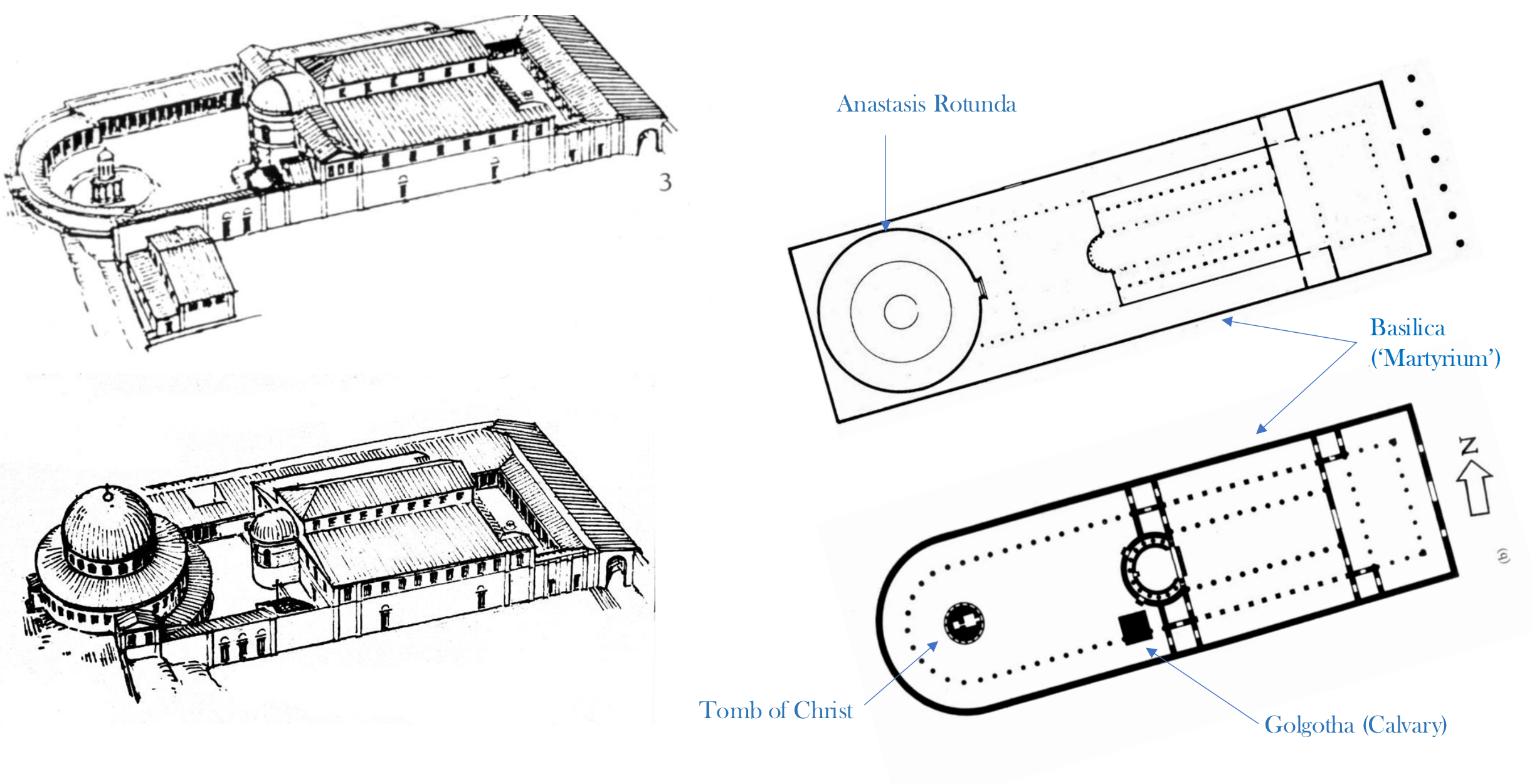
8.*Jerusalem, complex of the Church of the Holy Sepulcher; begun in 326 under Constantinian patronage: basilica and monumentalized sites of the Crucifixion (Golgotha) and the tomb of Christ (known as the Anastasis rotunda)
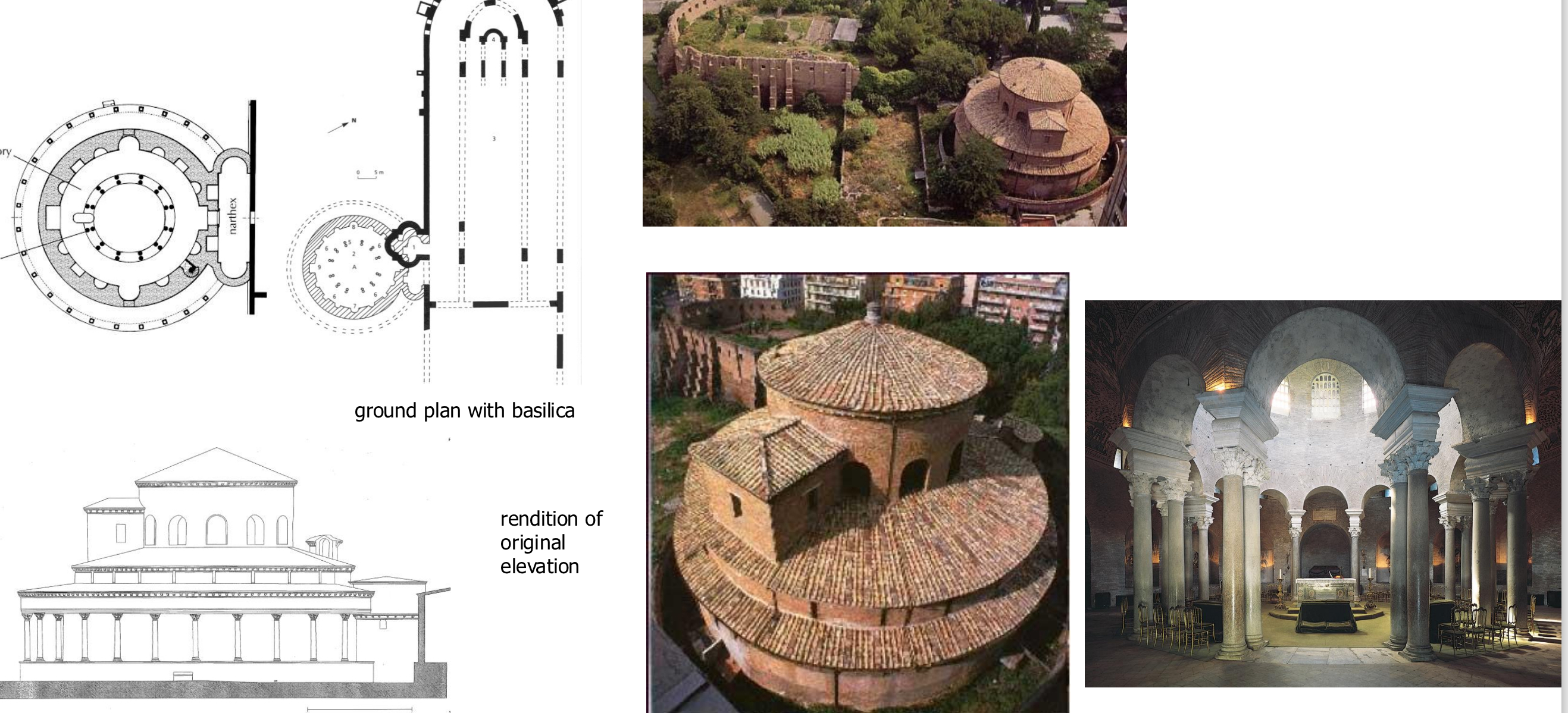

9. Rome, Mausoleum of Constantina, c. 355 or 360/70; attached to 4th century funerary basilica of St. Agnes; (c. 318-330); built on imperial estate in vicinity of pre existing catacomb
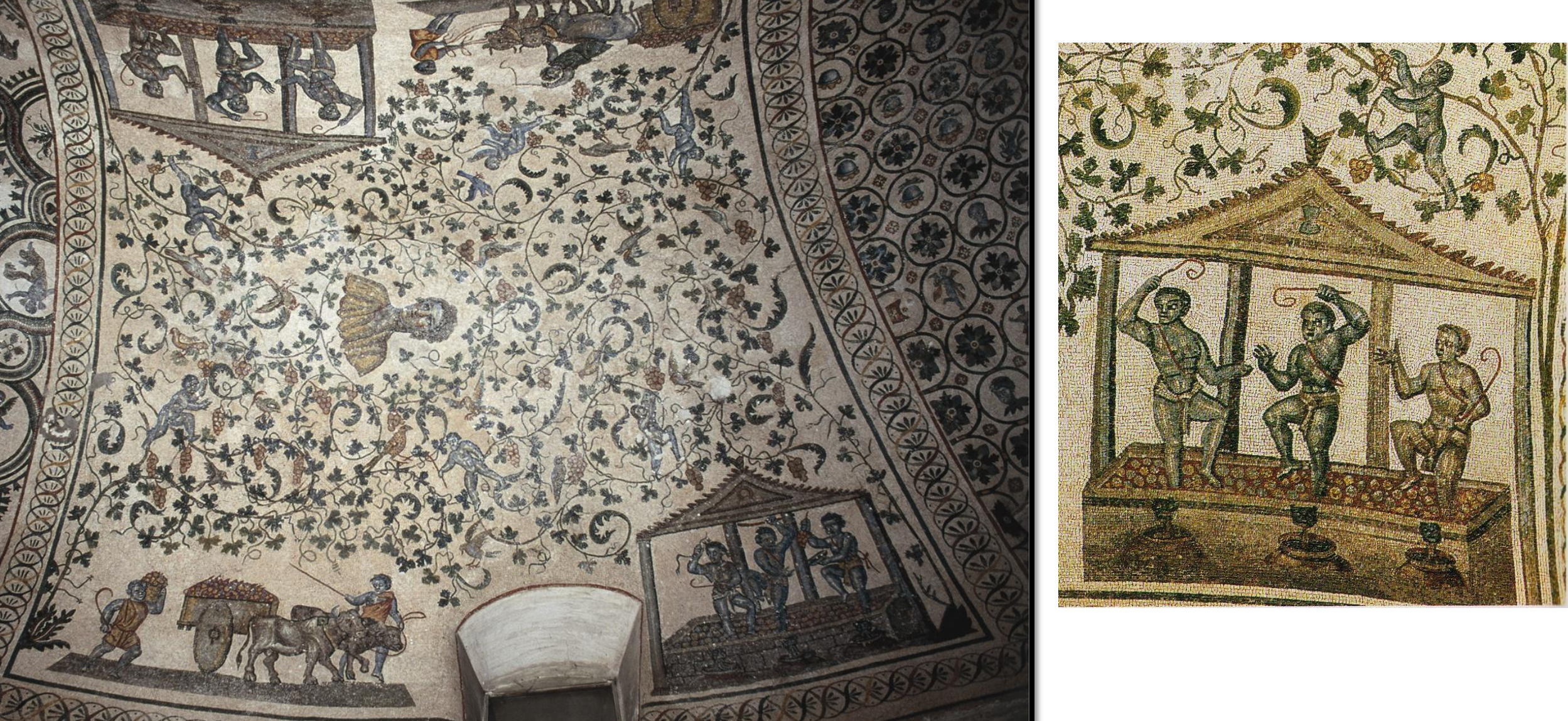

10.*Rome, Mausoleum of Constantina, c. 355 or 360/70: mosaic panel depicting putti harvesting and making wine with portrait bust of the deceased (?), panel from the
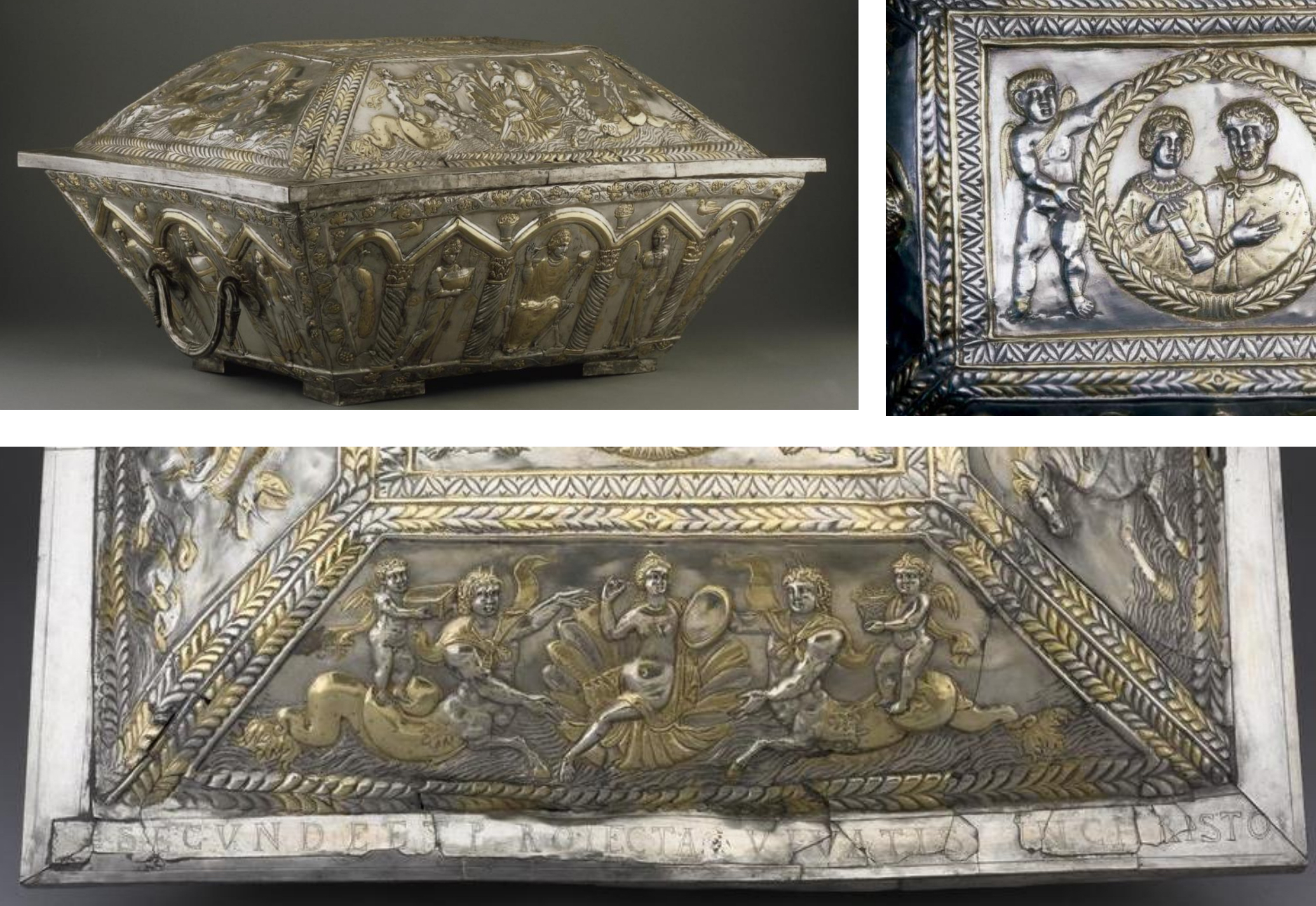

11.*The Projecta Casket, silver and silver gilt, c.350-390; made Rome (?); found on Esquiline Hill; decoration includes pagan imagery and a Christian inscription

12. Opus sectile floor from the hall at Porta Marina at Ostia, c. 388-394; cut and inlaid marble and porphyry; geometric, vegetal designs, as well as panels depicting animals and a human figure
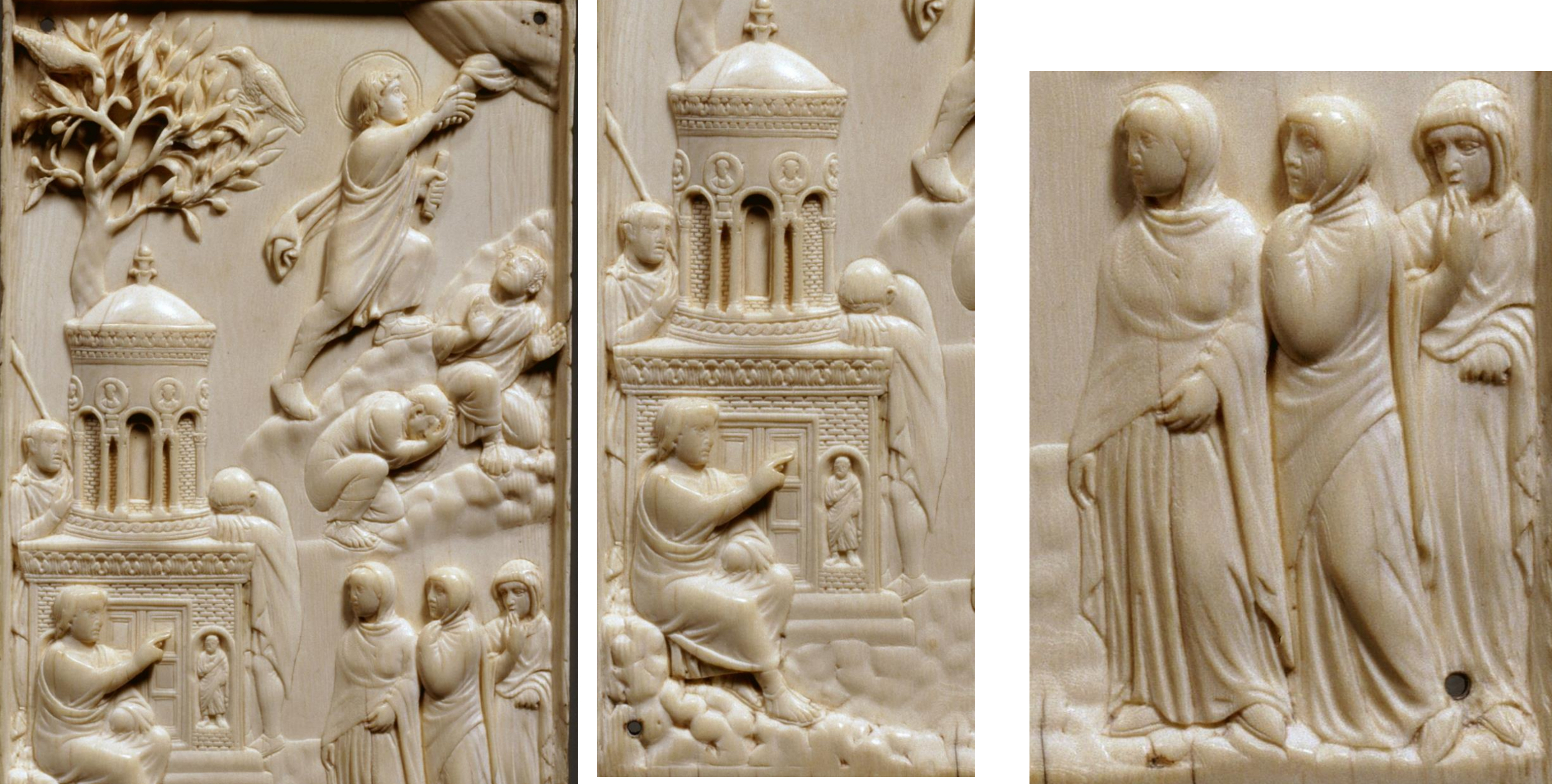

13.*Diptych ivory leaf of the Resurrection and Ascension of Christ (known as “Reider-Panel” or "Munich Ivory"), c. 400; made Rome or Milan (?)

14.*Manuscript bifolium from the "Vatican Virgil;" illustrated manuscript of Virgil’s Georgics and Aeneid, c. 400; made Rome(?); miniatures depict the death of Laocoon and his sons (left); and the Sack of Troy (right)
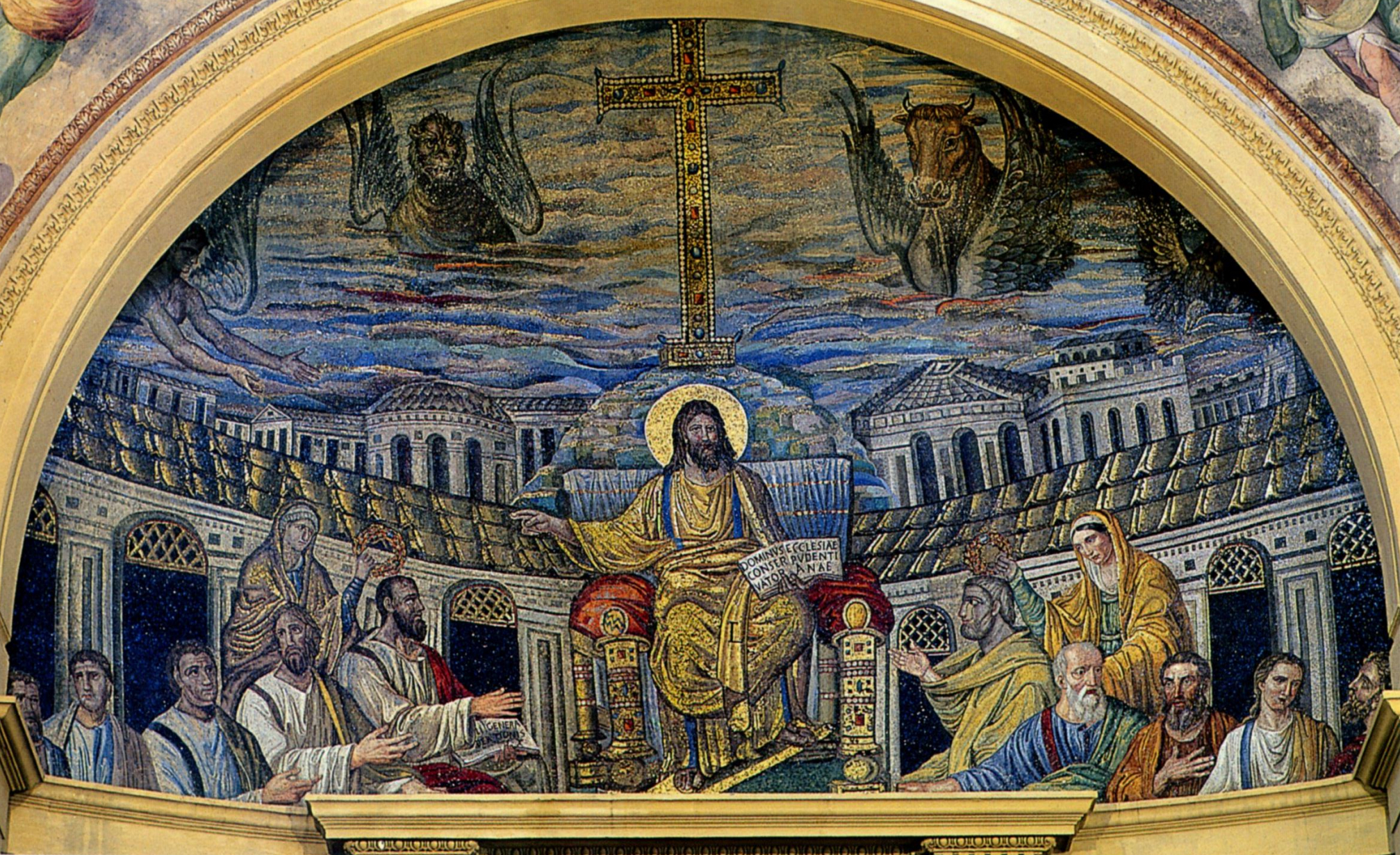
15. Rome, Santa Pudenziana apse mosaic, c. 401-417. Christ enthroned with Apostles, female personifications of the Church, the Four Living Creatures, and hill (Golgotha?) with gem-studded cross
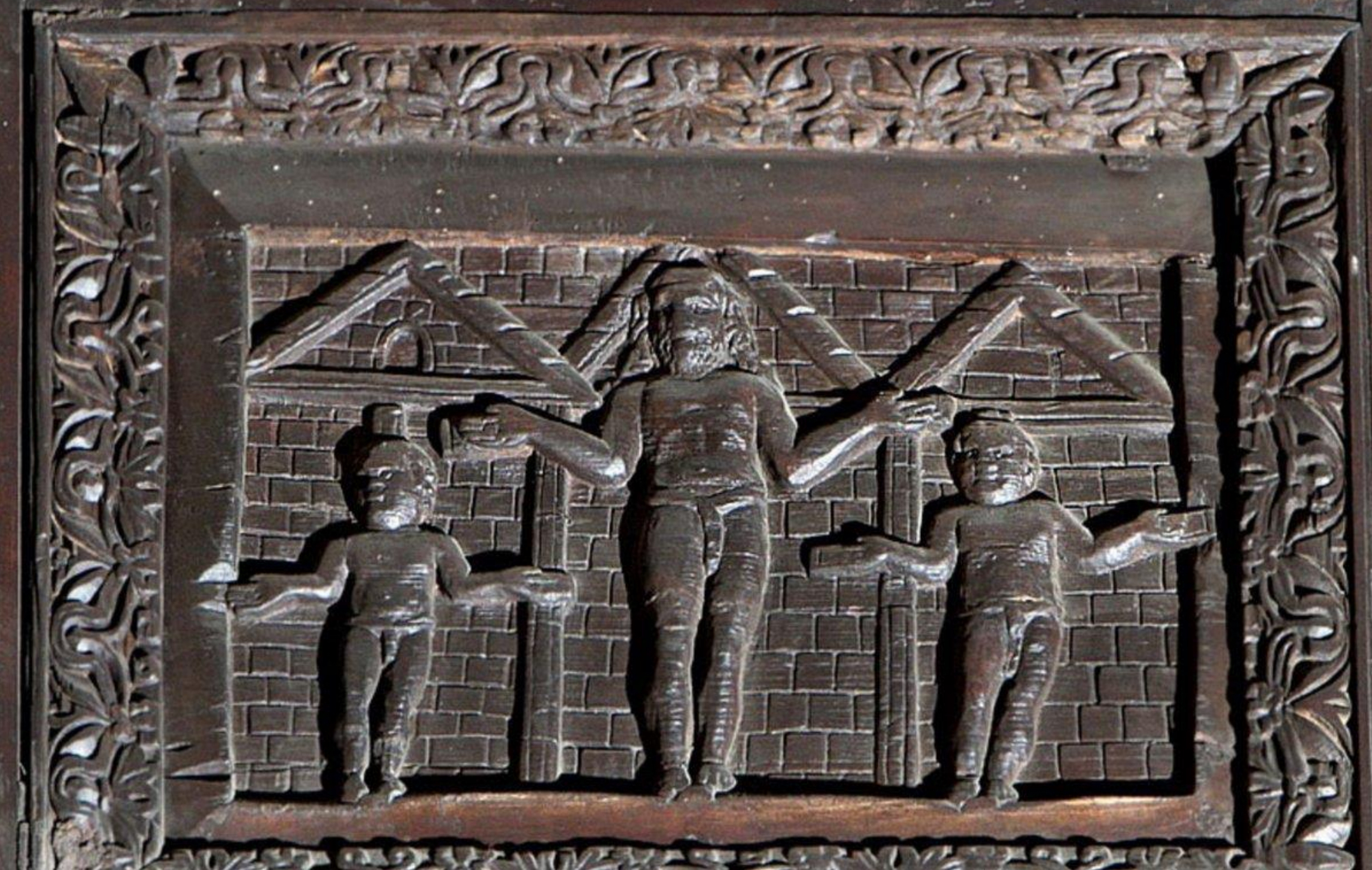

16.*Rome, Santa Sabina, c. 422-430: Crucifixion panel from the carved cypress wood doors
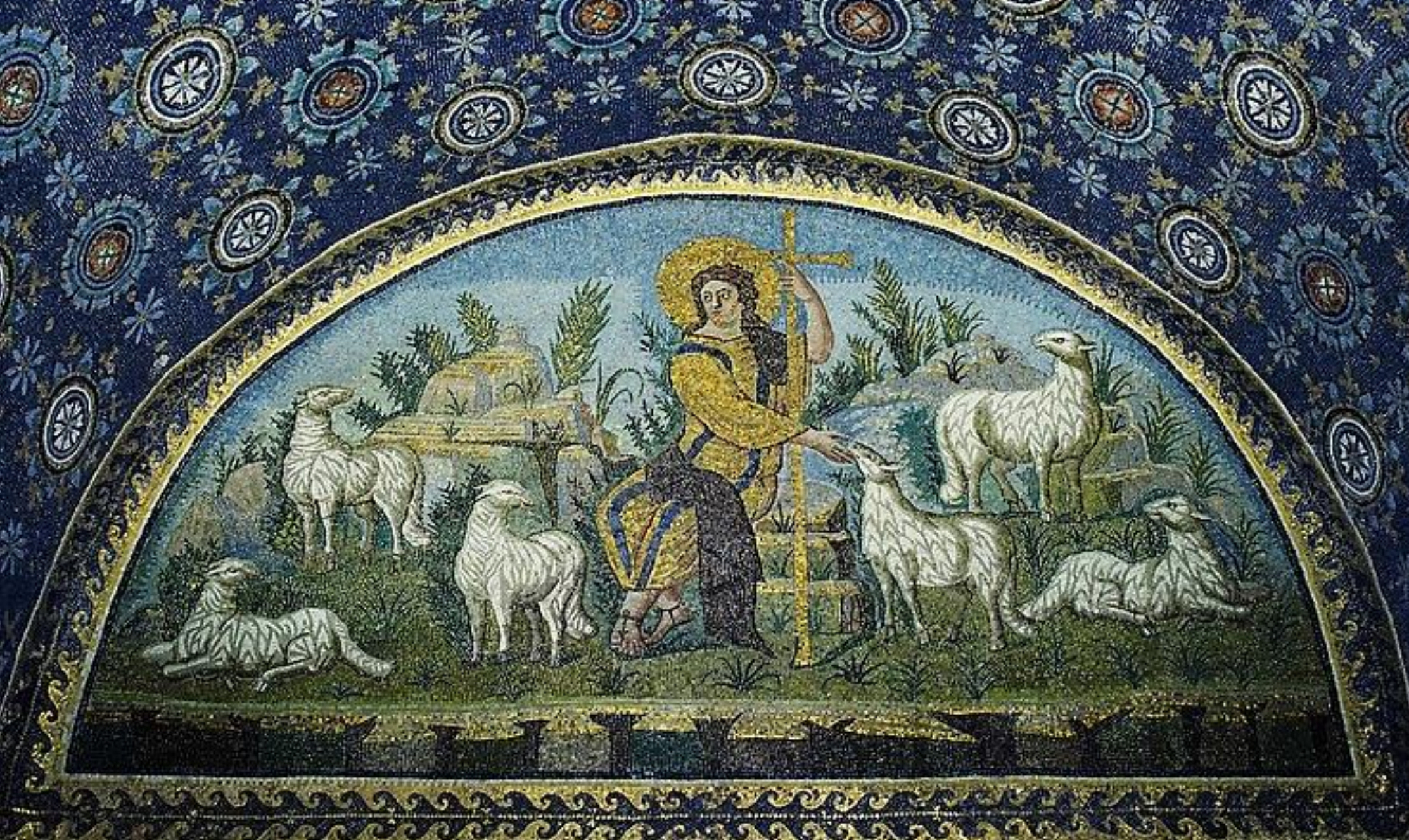

17. *Ravenna, Mausoleum of the empress Galla Placidia, 425-450: mosaic panel of the Good Shepherd
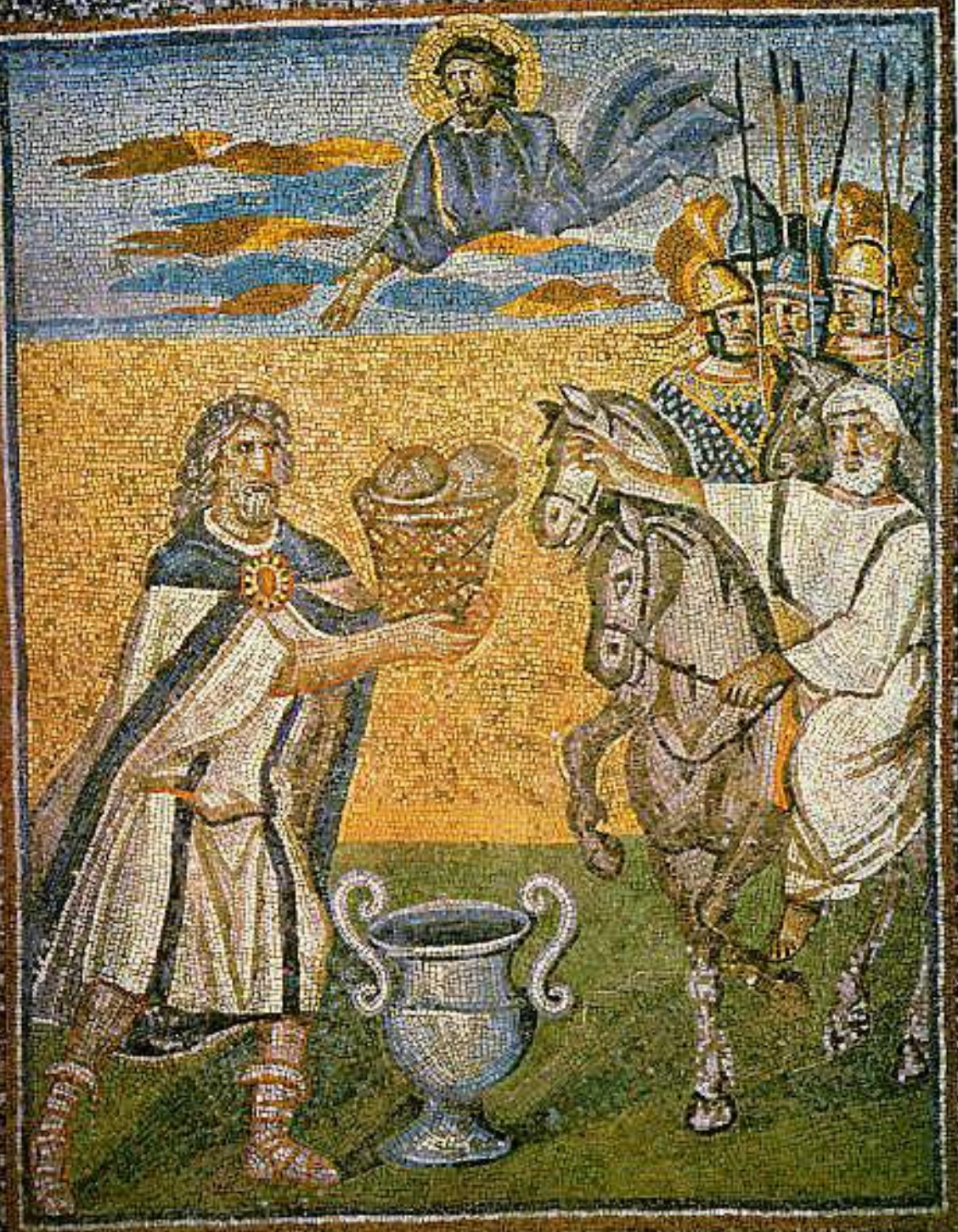

18. *Rome, Santa Maria Maggiore, mosaic panel from the nave, c. 432-440: Melchisidech offering bread and wine to Abraham; commissioned by Pope Sixtus III
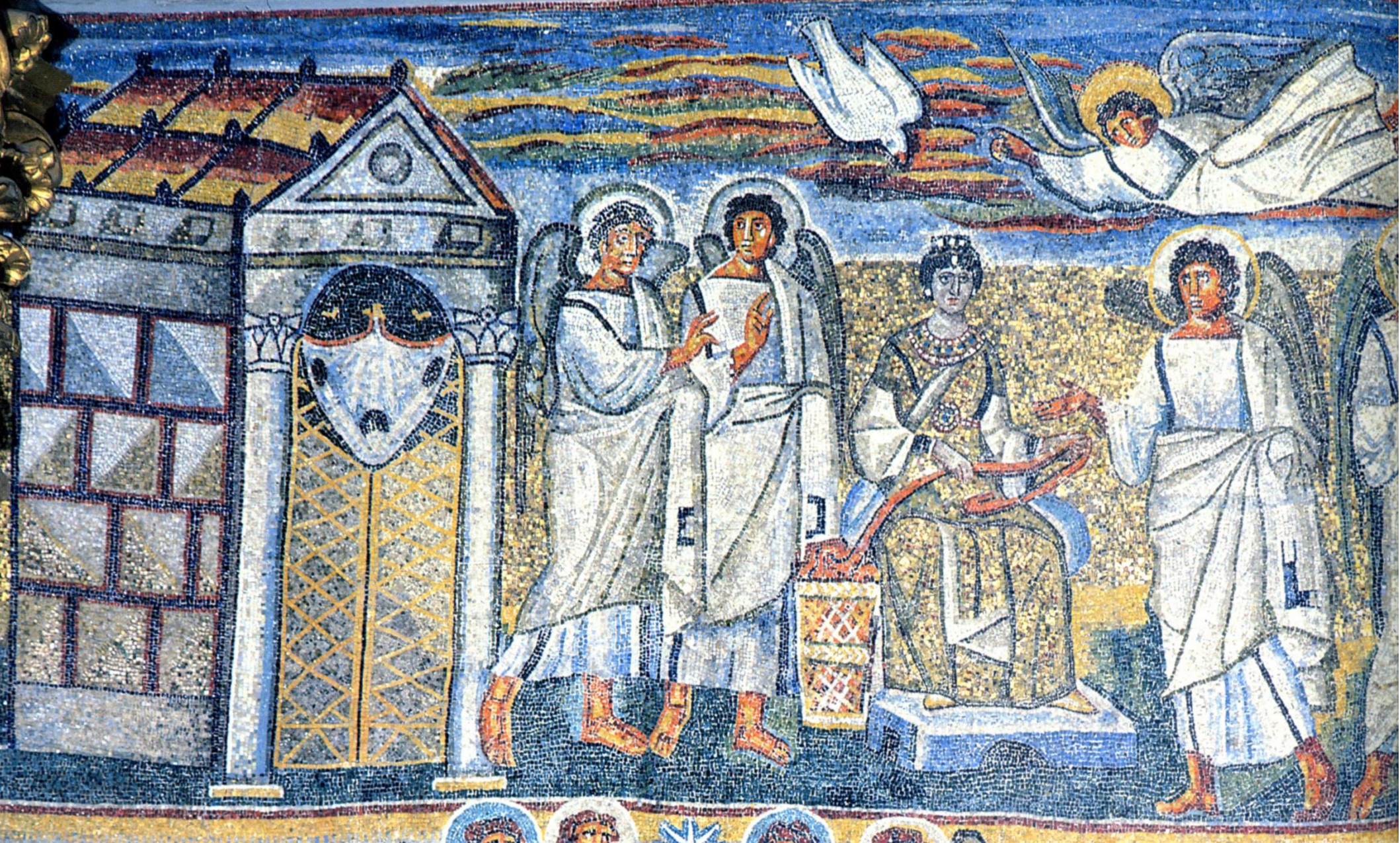

19. *Rome, Santa Maria Maggiore, mosaic panel from the "triumphal arch," c. 432- 440: the Annunciation; commissioned by Pope Sixtus III
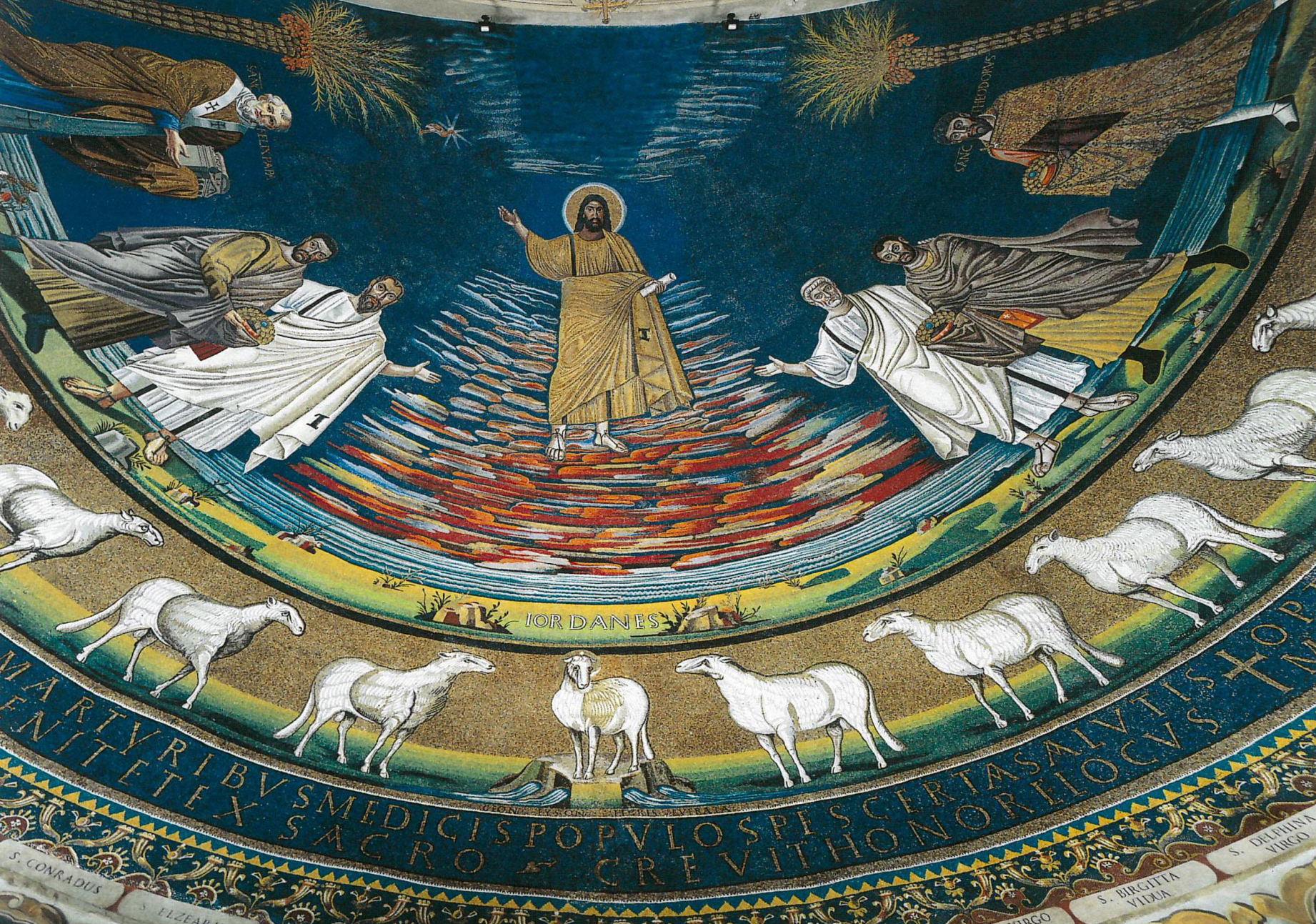

20. *Rome, Santi Cosma e Damiano apse mosaic, c. 520-527; commissioned by Pope Felix IV; detail shows central image of Christ
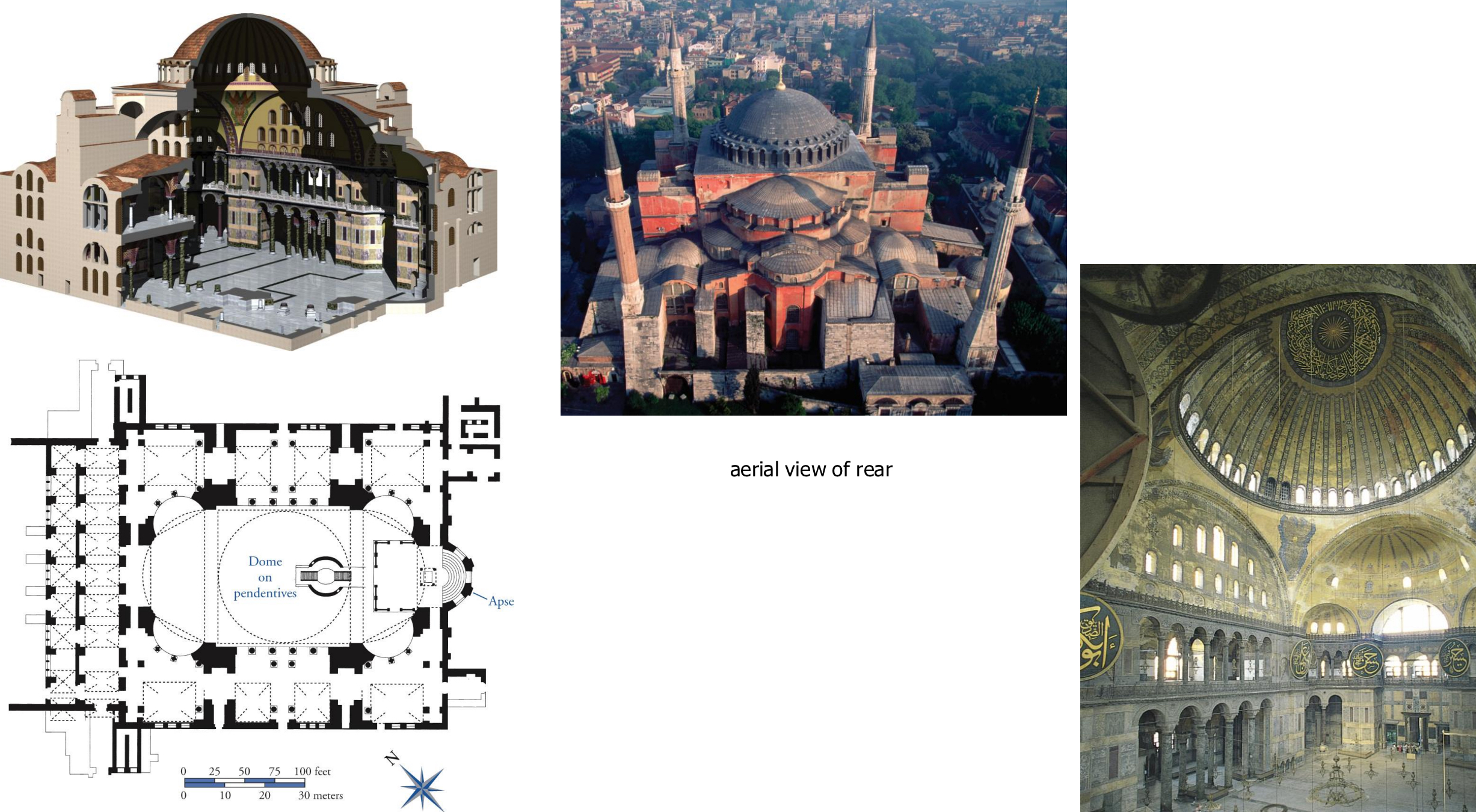
21. Istanbul (Constantinople), Hagia Sophia, 532-537: centrally planned domed structure, with narthex and apse; commissioned by the Byzantine emperor Justinian
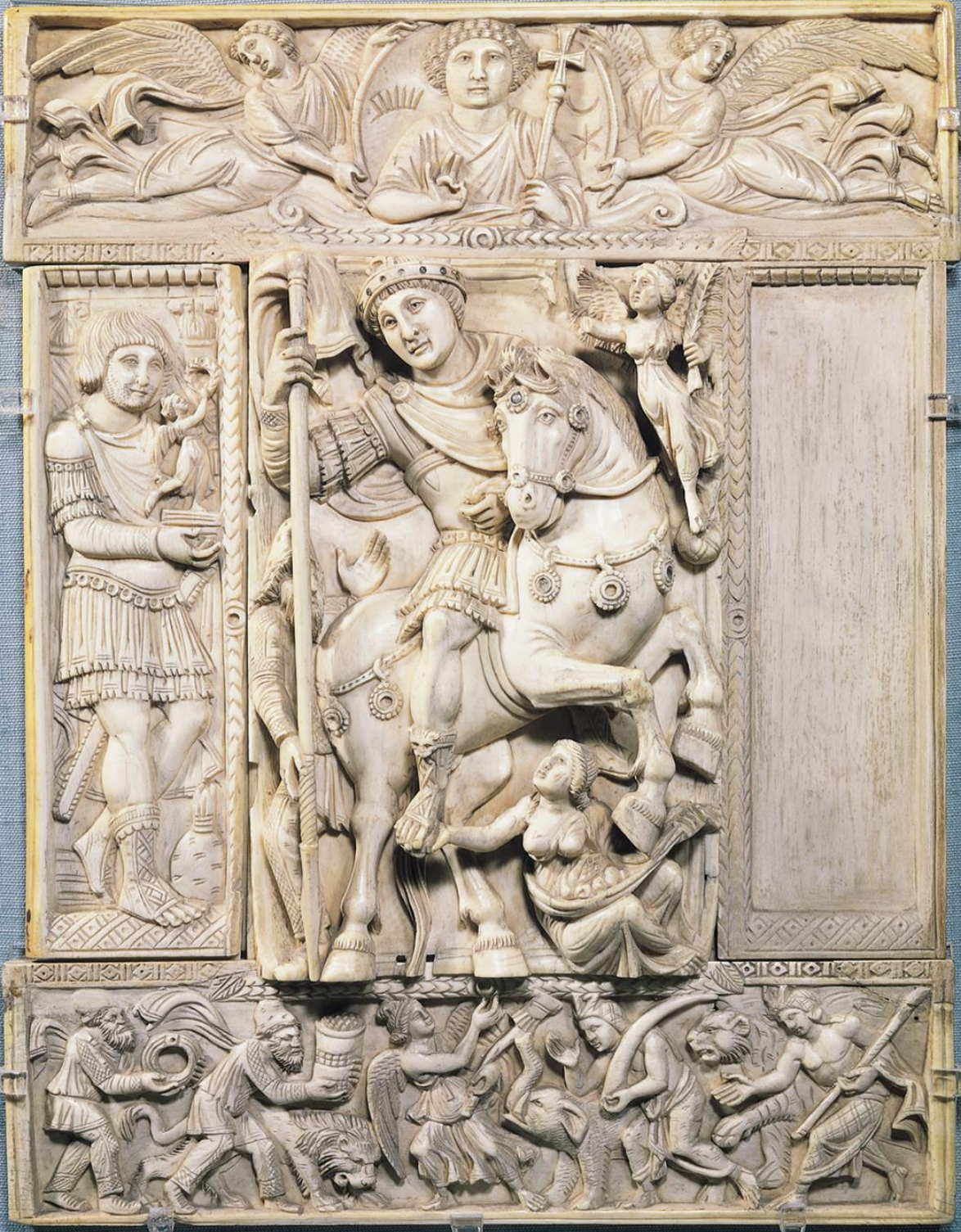

22.*The Barberini Ivory, 6th century. Early Byzantine diptych leaf: general/ emperor (Justinian?) on horseback, bust of Christ and angels (above), and tribute bearers from conquered territories (below)
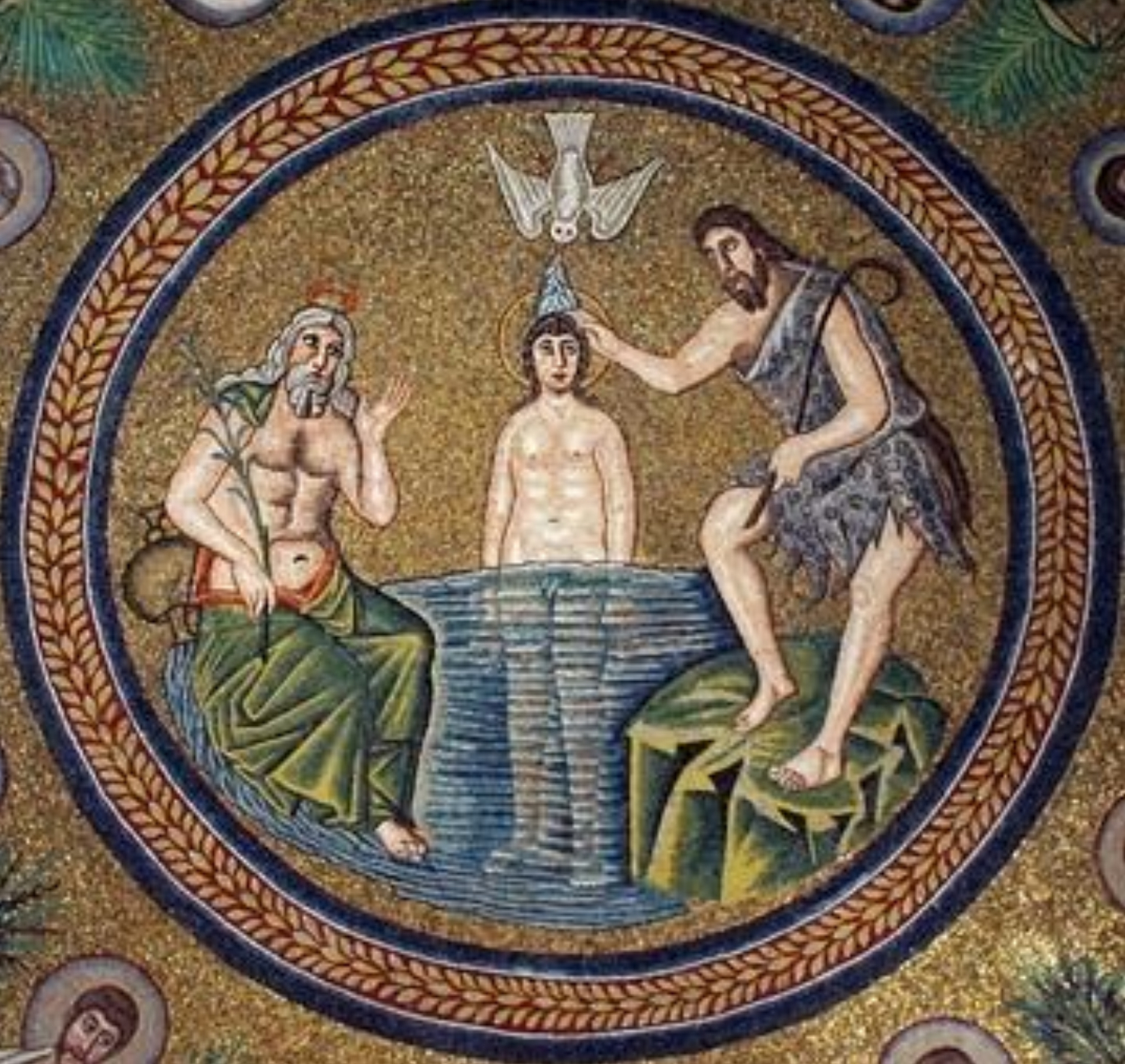

23.*Ravenna, Arian Baptistery detail of vault mosaic, c. 500: Baptism of Christ; commissioned during reign of the Ostrogothic king Theodoric.
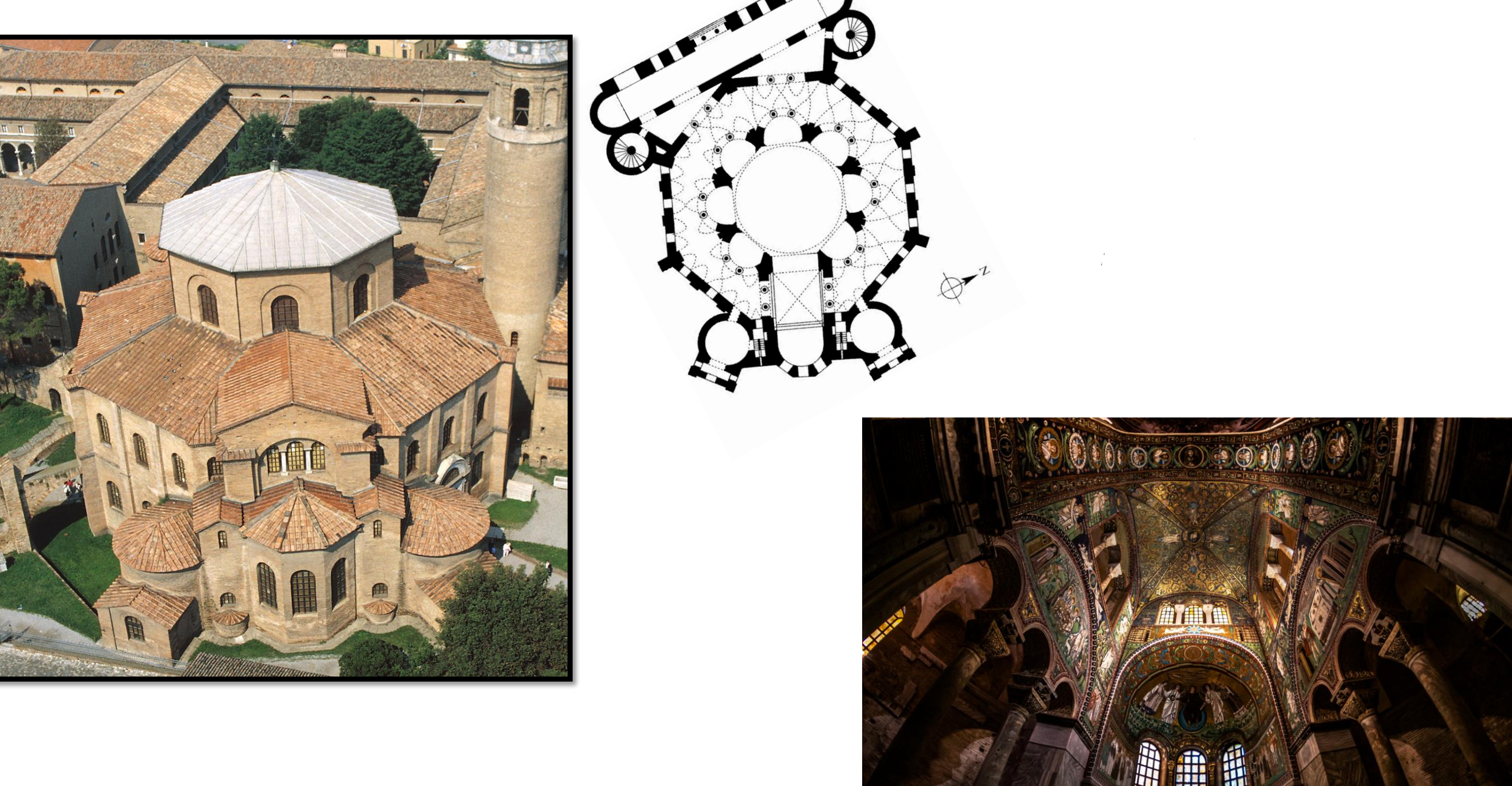

24. Ravenna, San Vitale, completed 547: centrally planned basilica with narthex and projecting apse; built during tenure of bishop Maximian; patron Julius Argentarius, banker and architect
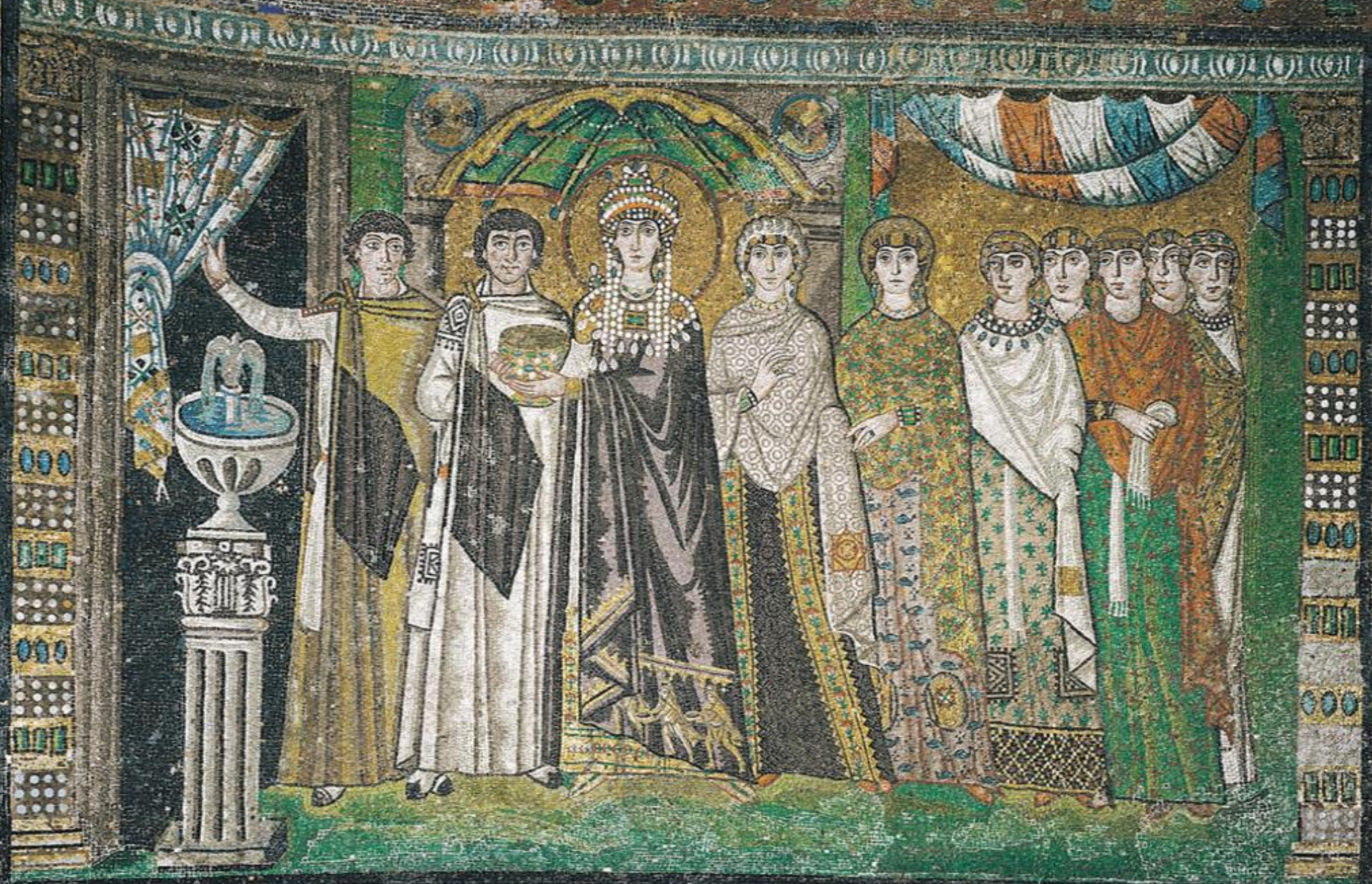

25. *Ravenna, San Vitale mosaic panel from sanctuary, c. 547: the empress Theodora offering chalice to church, with accompanying courtiers
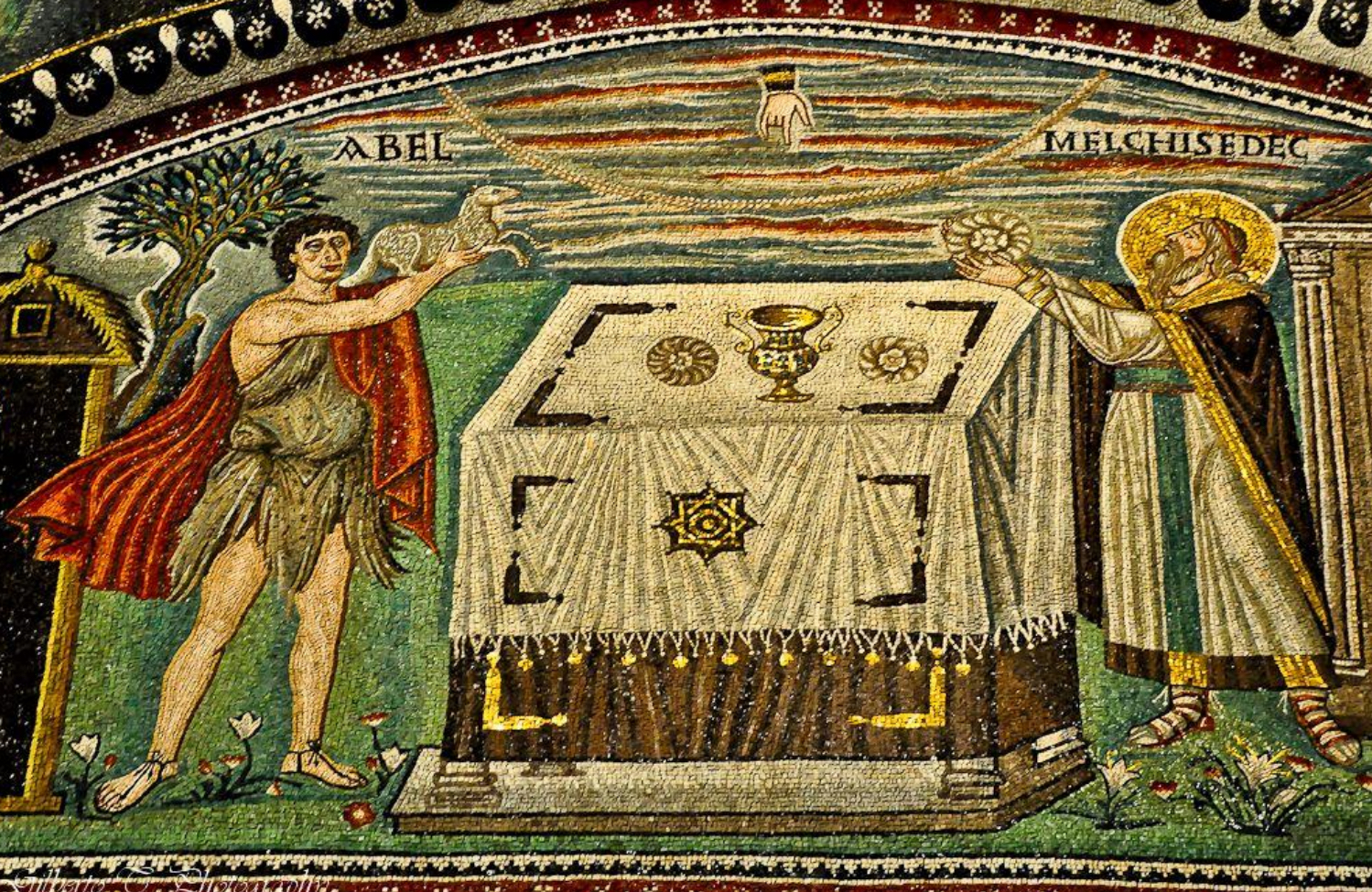

26. *Ravenna, San Vitale mosaic panel, from sanctuary c. 547: Abel and Melchisidech making offering at altar
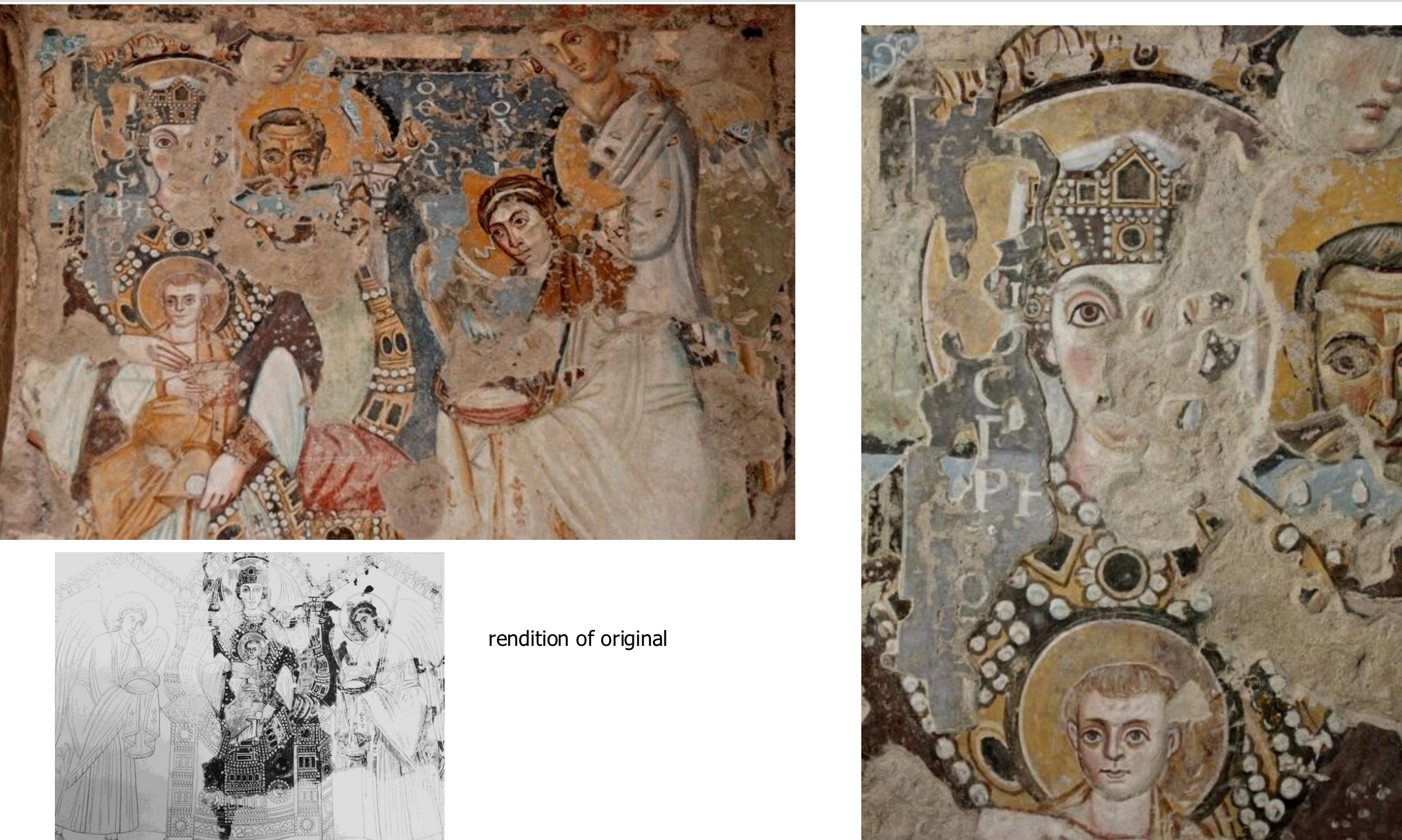

27. *Rome, Santa Maria Antiqua "Maria Regina" fresco, c. 550; earliest layer from from the "palimpsest" wall in the sanctuary
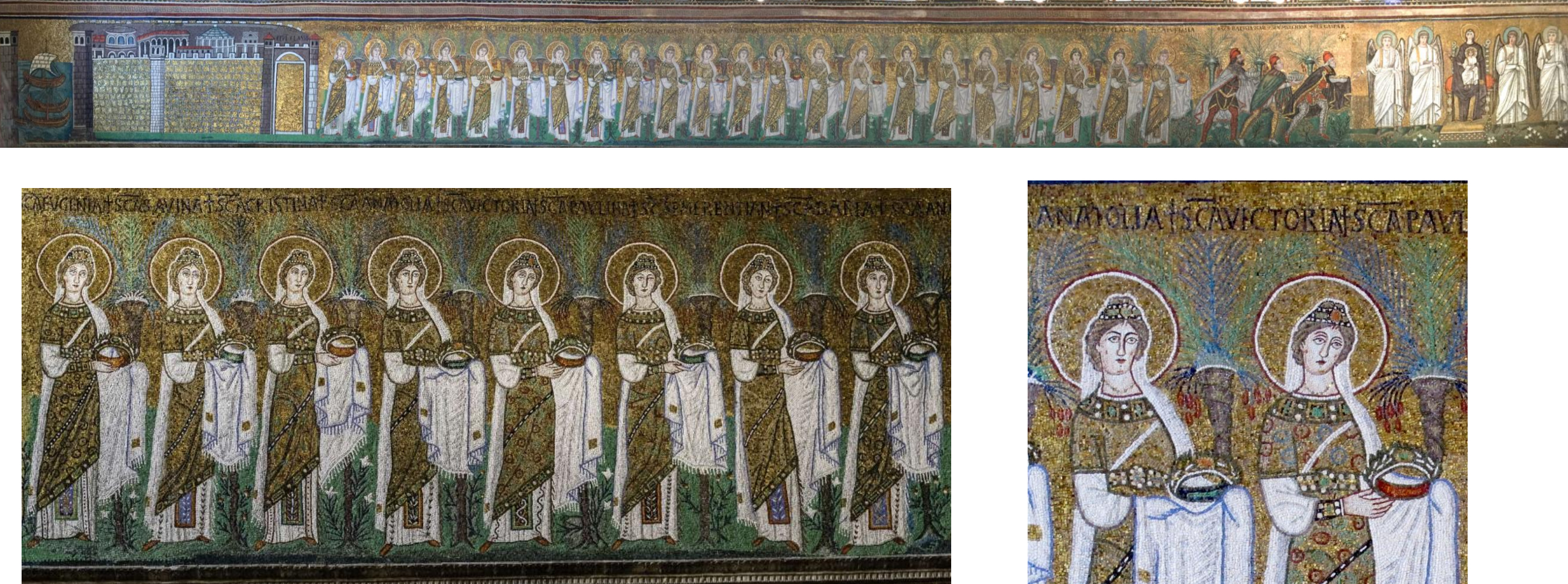

28. *Ravenna, Sant’Apollinare Nuovo nave mosaic, c. 560-570: female martyrs in procession towards the Virgin and Child; commissioned by the Catholic Bishop Agnello to replace the earlier mosaics (c. 500) commissioned by Arian authorities during the reign of the Ostrogothic king Theodoric
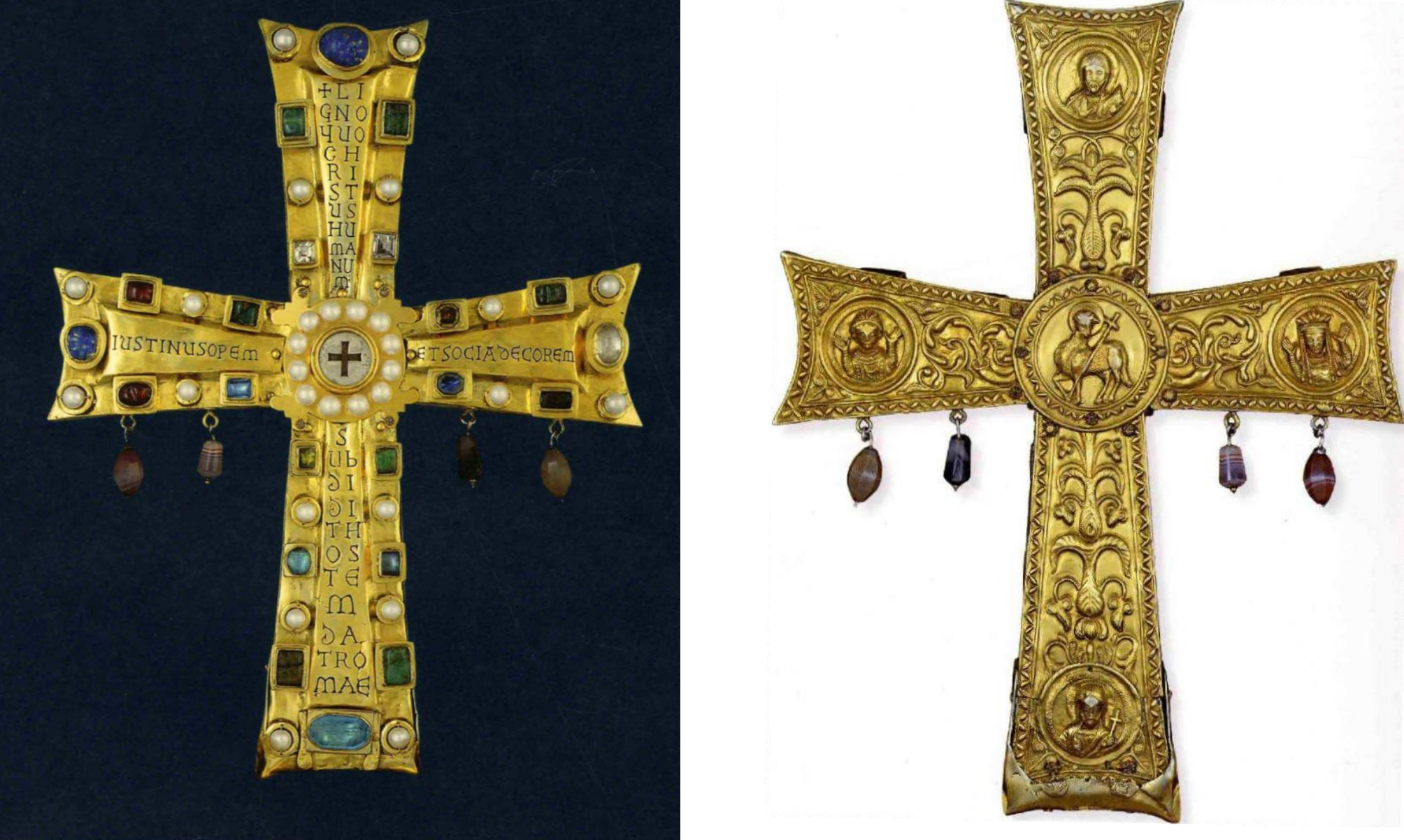

29. *Crux Vaticana/ Cross of Justin II, c. 570: processional cross reliquary donated by the emperor Justin II and his co-ruler and wife Sophia to Rome (by way of pope John III); silver guilt with precious and semi-precious stones set in gold
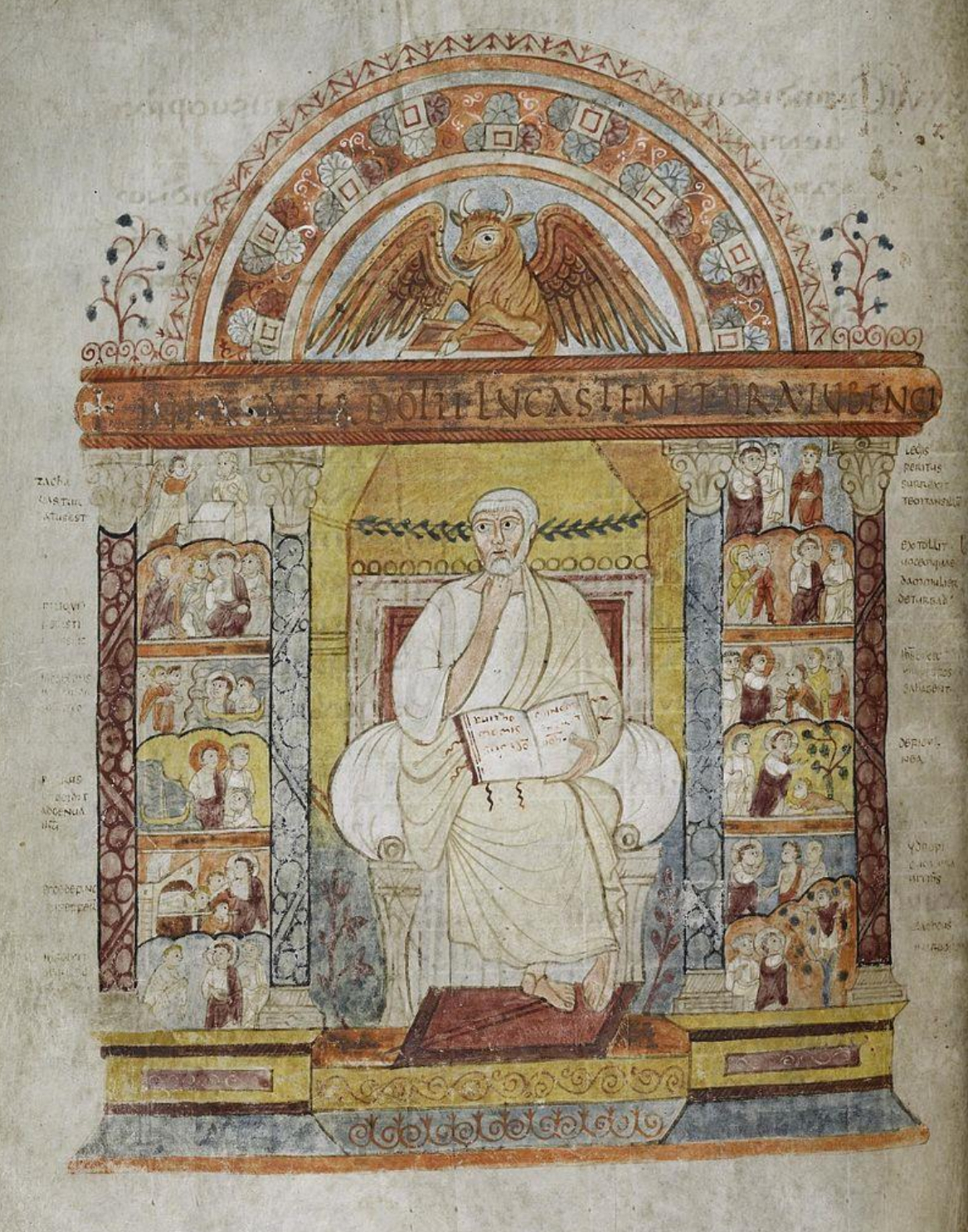

30. *The "Gospels of St. Augustine," late 6th cent.: full page miniature of the Evangelist Luke; made in Italy (Rome?); manuscript thought to be "missionizing gift” to Britain
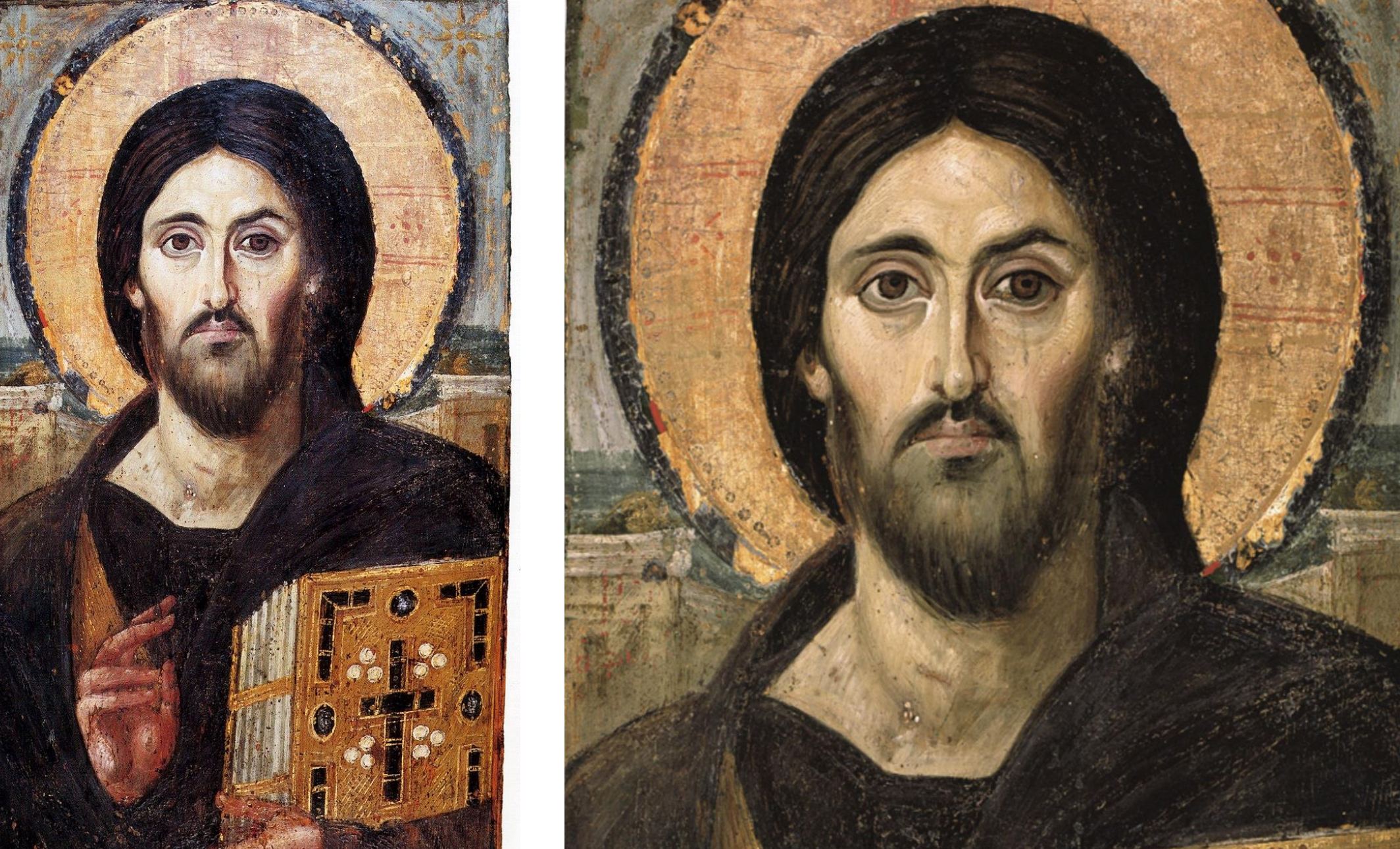

31. Icon of Christ, late 6th-early 7th century; encaustic, made Egypt (?); from the monastery of St. Catherine on Mt. Sinai in Egypt
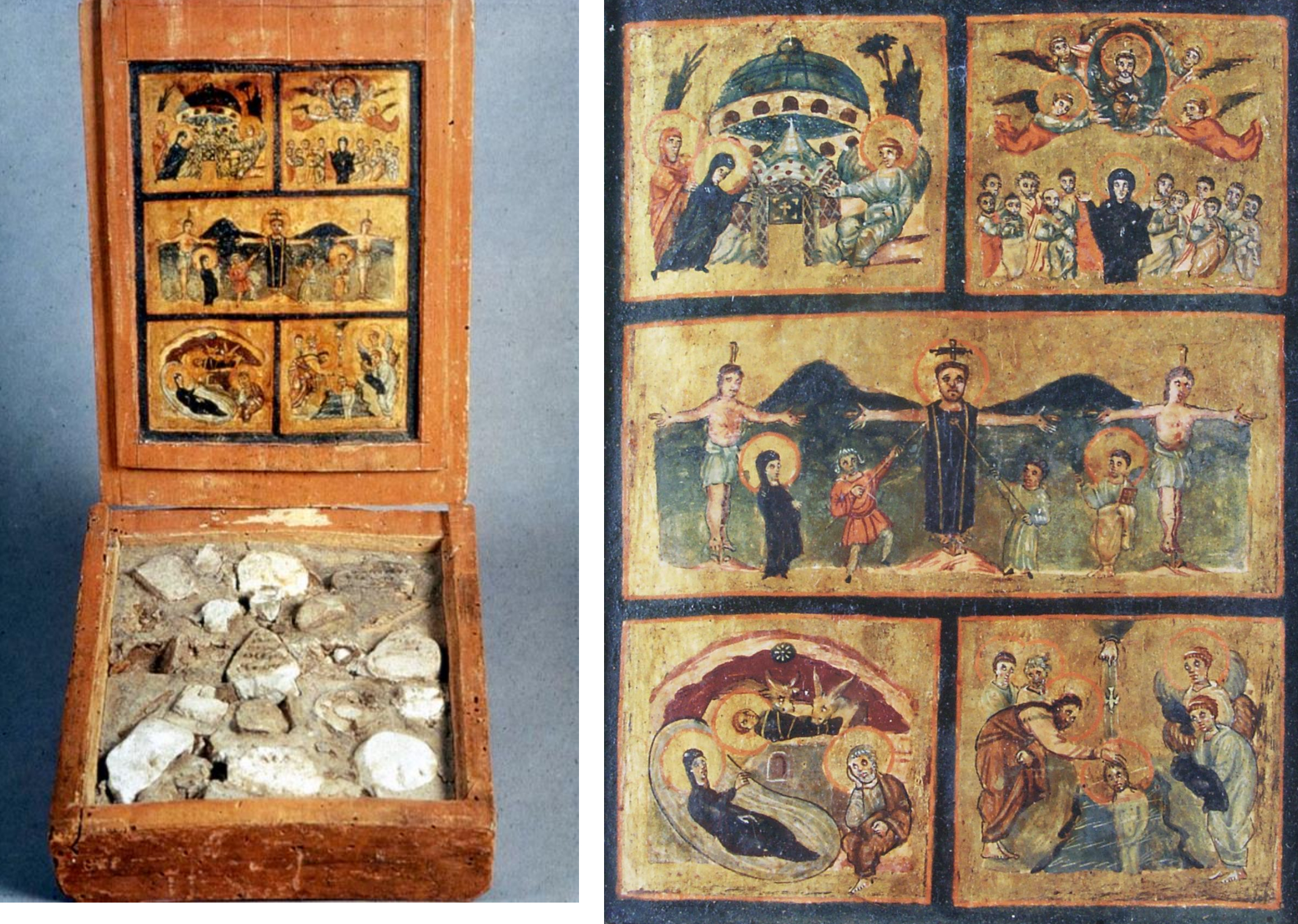

32. *Painted wooden reliquary box containing stones from the Holy Land, late sixth early seventh century; made Syria-Palestine (?); originally part of the collection of the Sancta Sanctorum in the Lateran Palace.
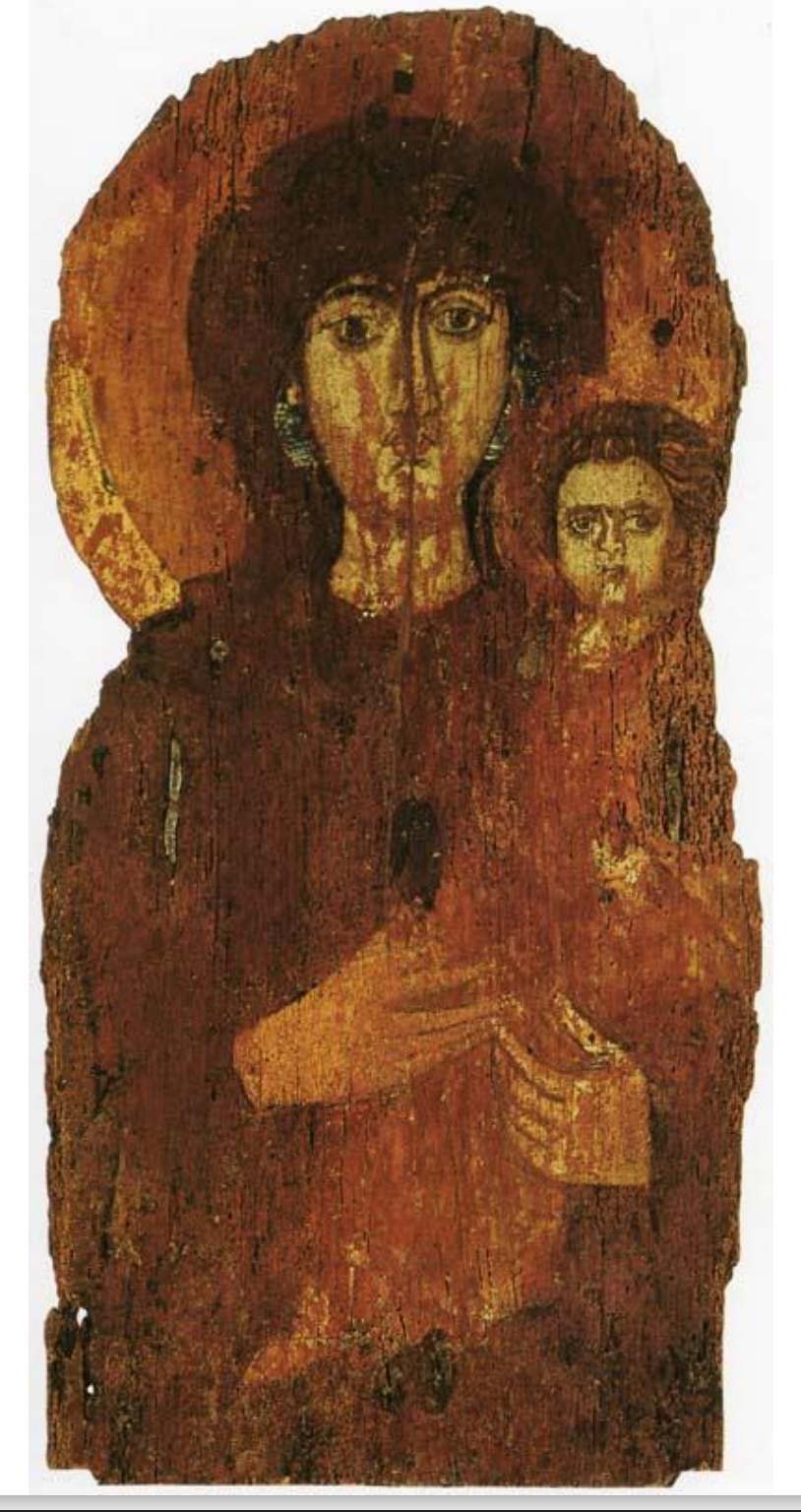

33. *Rome, icon of the Madonna and Child icon in Santa Maria ad Martyres (Pantheon), early 7th cent., tempera on wood
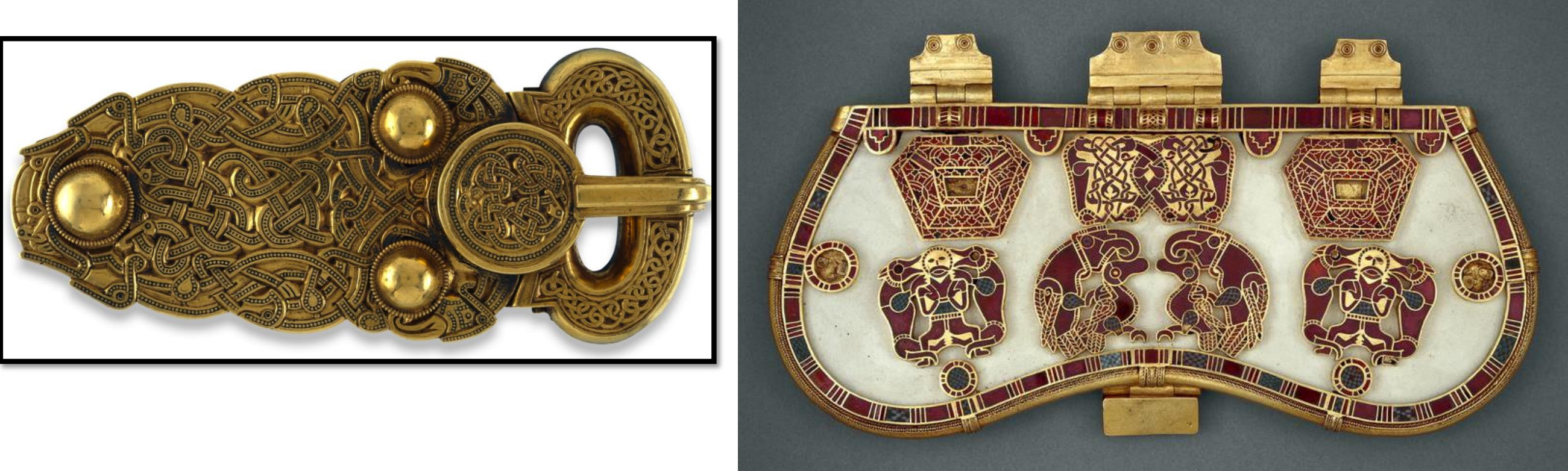

34.*Gold belt buckle and purse lid in gold and cloisonné enamels from the Anglo Saxon Sutton Hoo (England) ship burial, early 7th century
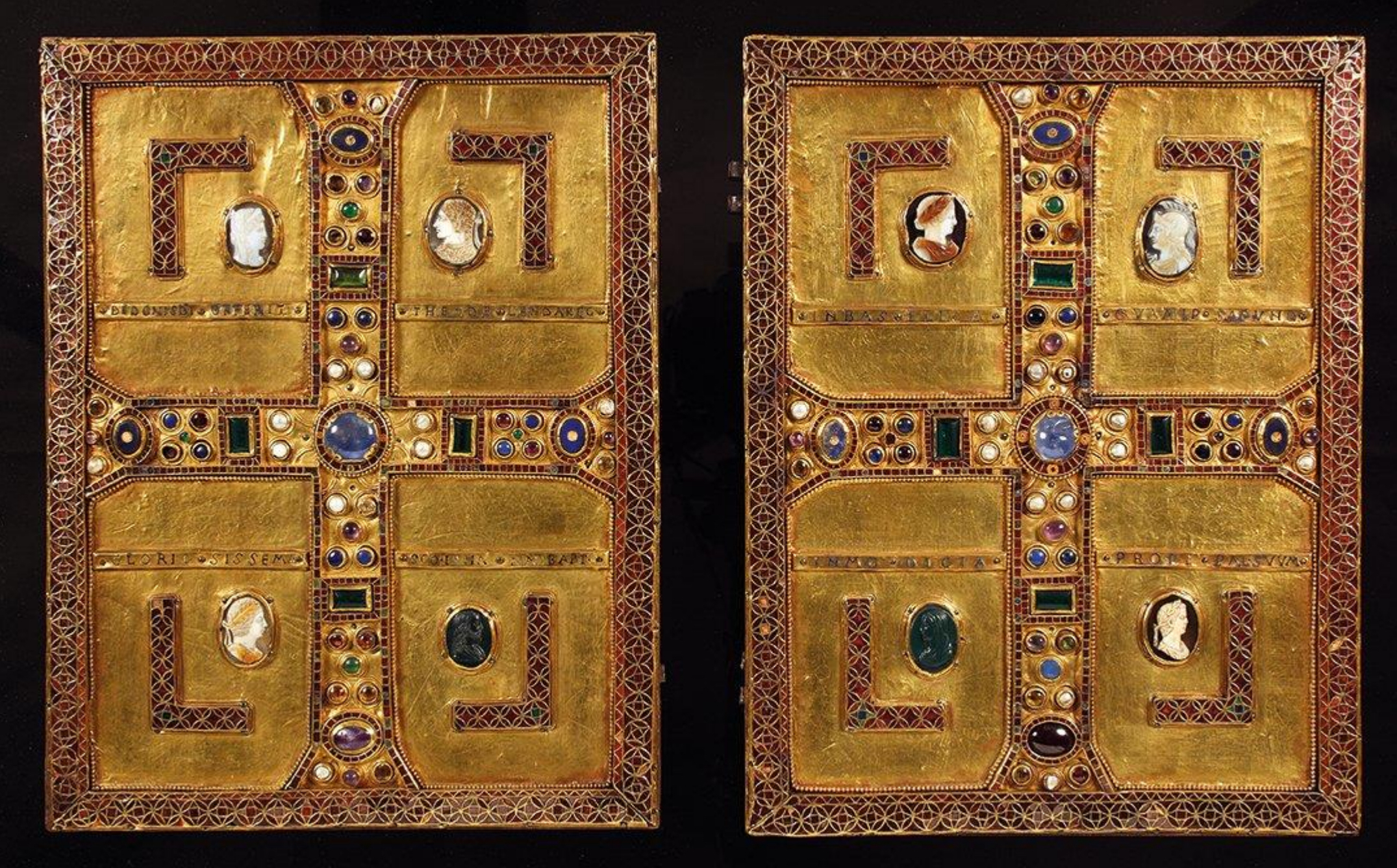

35. *Gospel Book Cover, gold with gems, enamels, and ancient Roman cameos. early 7th cent.; commissioned by the Longobard Queen Theodelinda
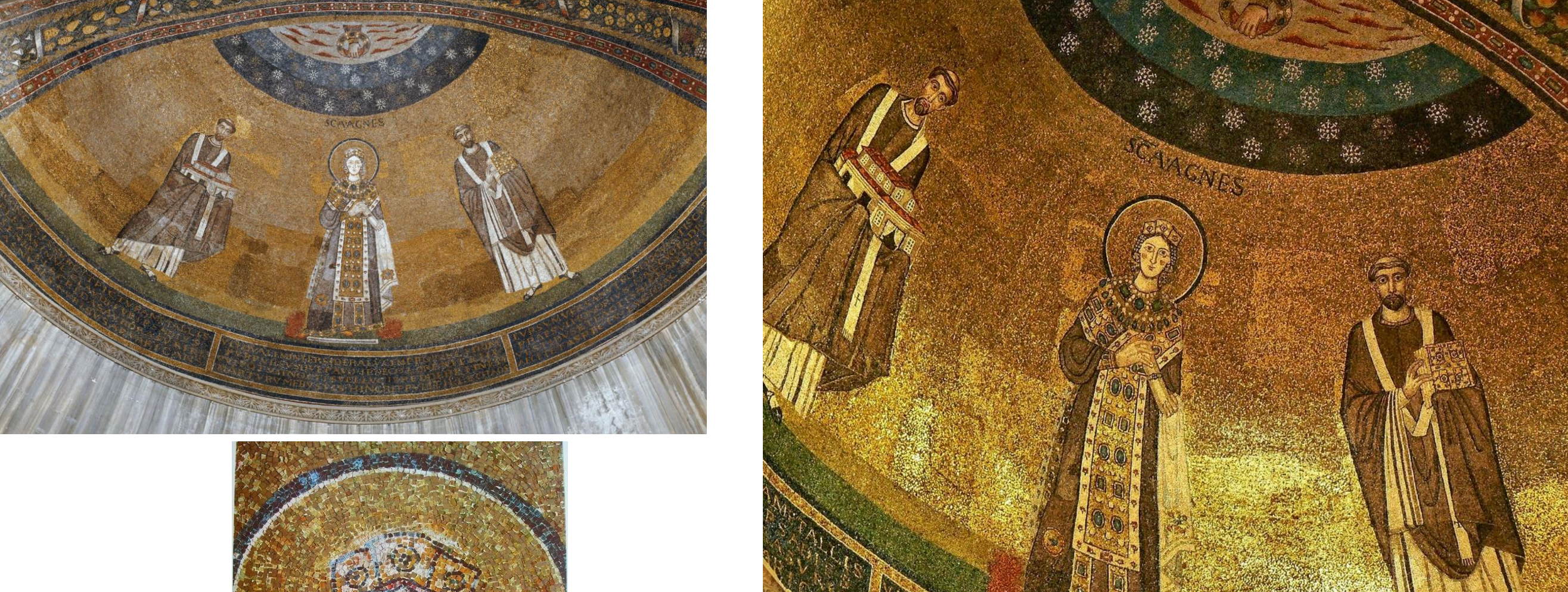

36. *Rome, Basilica of Santa Agnese, flm, apse mosaic, c. 630: St. Agnes between Pope Honorius I and pope Symmachus (?); commissioned by Pope Honorius I
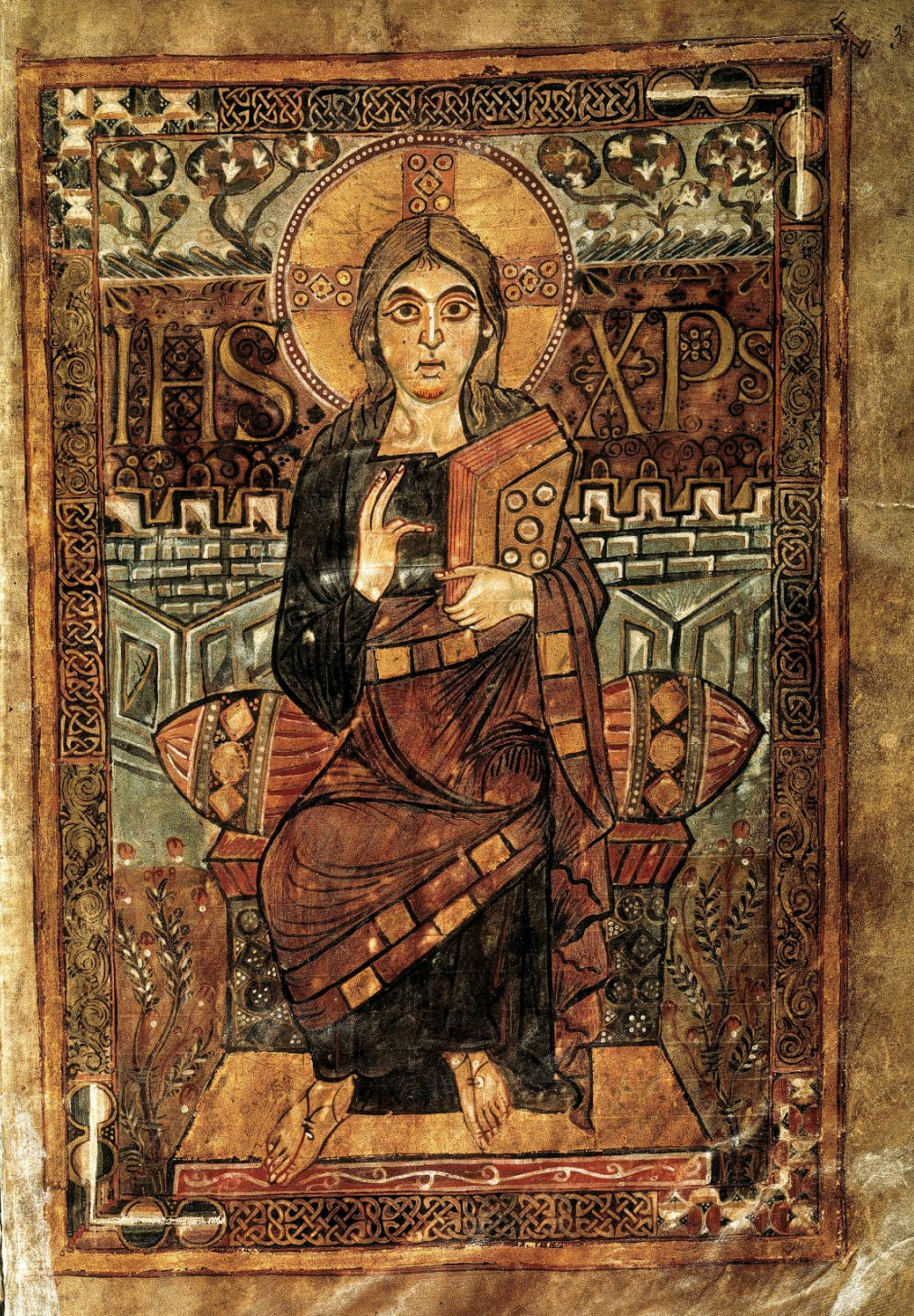

37. *Godescalc Gospels full-page miniature, 783: Christ Enthroned; made at the Carolingian court school of Aachen; commissioned by Charlemagne and his wife
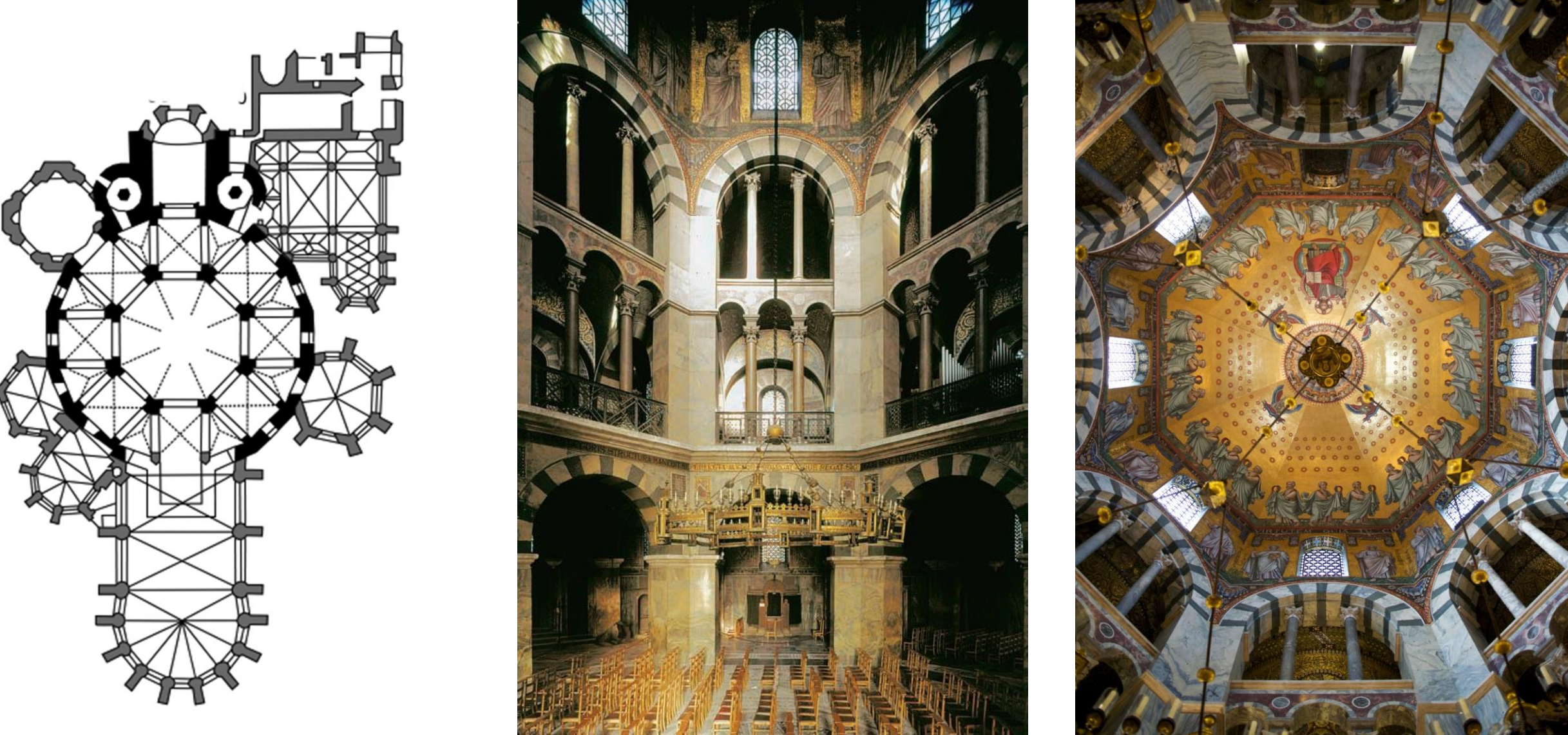

38. *Aachen, Palatine Chapel, 792/3-813: centrally planned domed chapel with apse and ambulatory; patron: Charlemagne; architect Odo of Metz; chapel consecrated by Pope Leo III in 805
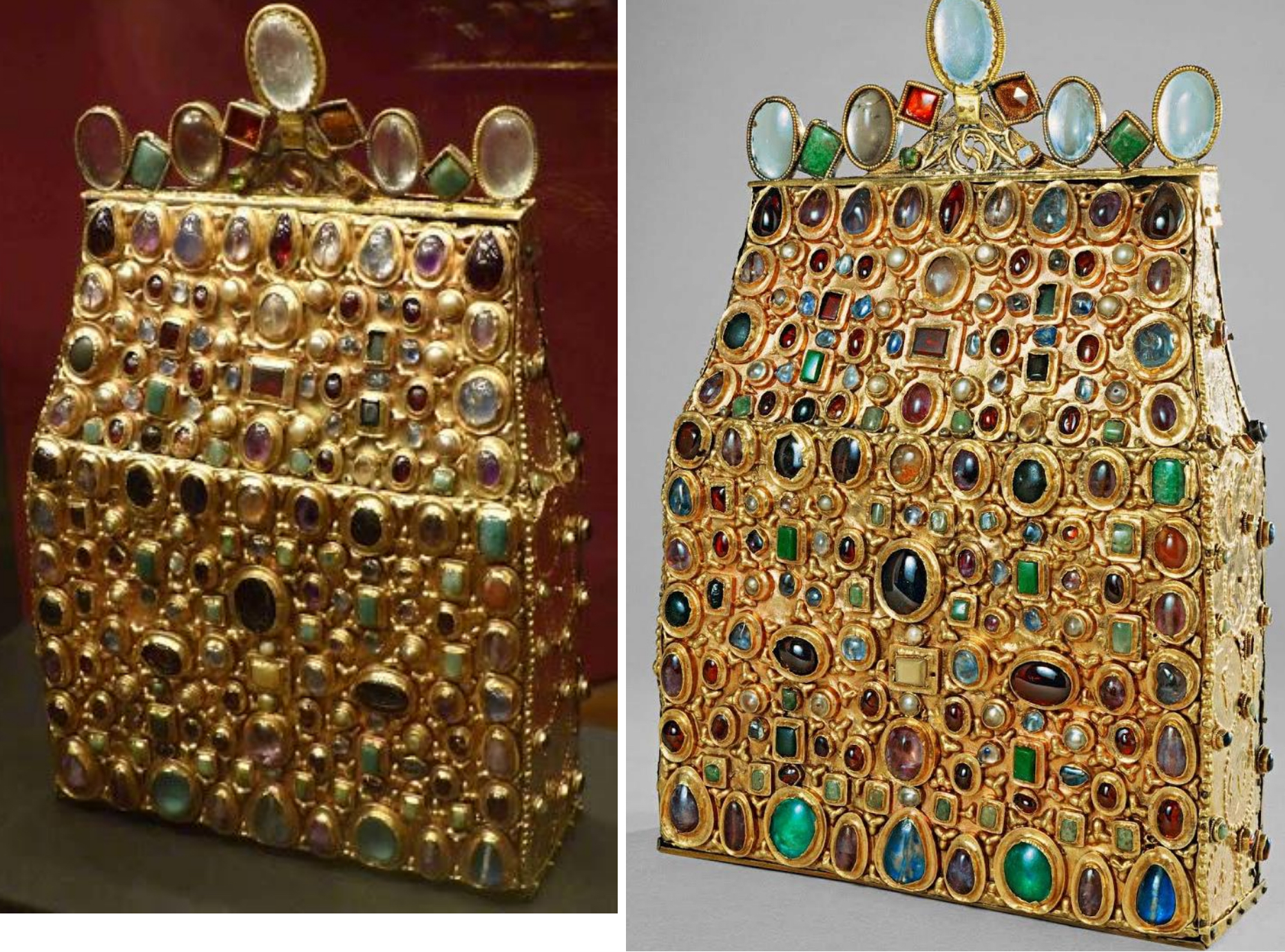

39. *"Purse reliquary" of St. Stephen (aka Stephansbursa); made Reims, c. 830 (Carolingian): gold, rock crystal, gems and jewels (contains soil soaked with blood of St. Stephen)
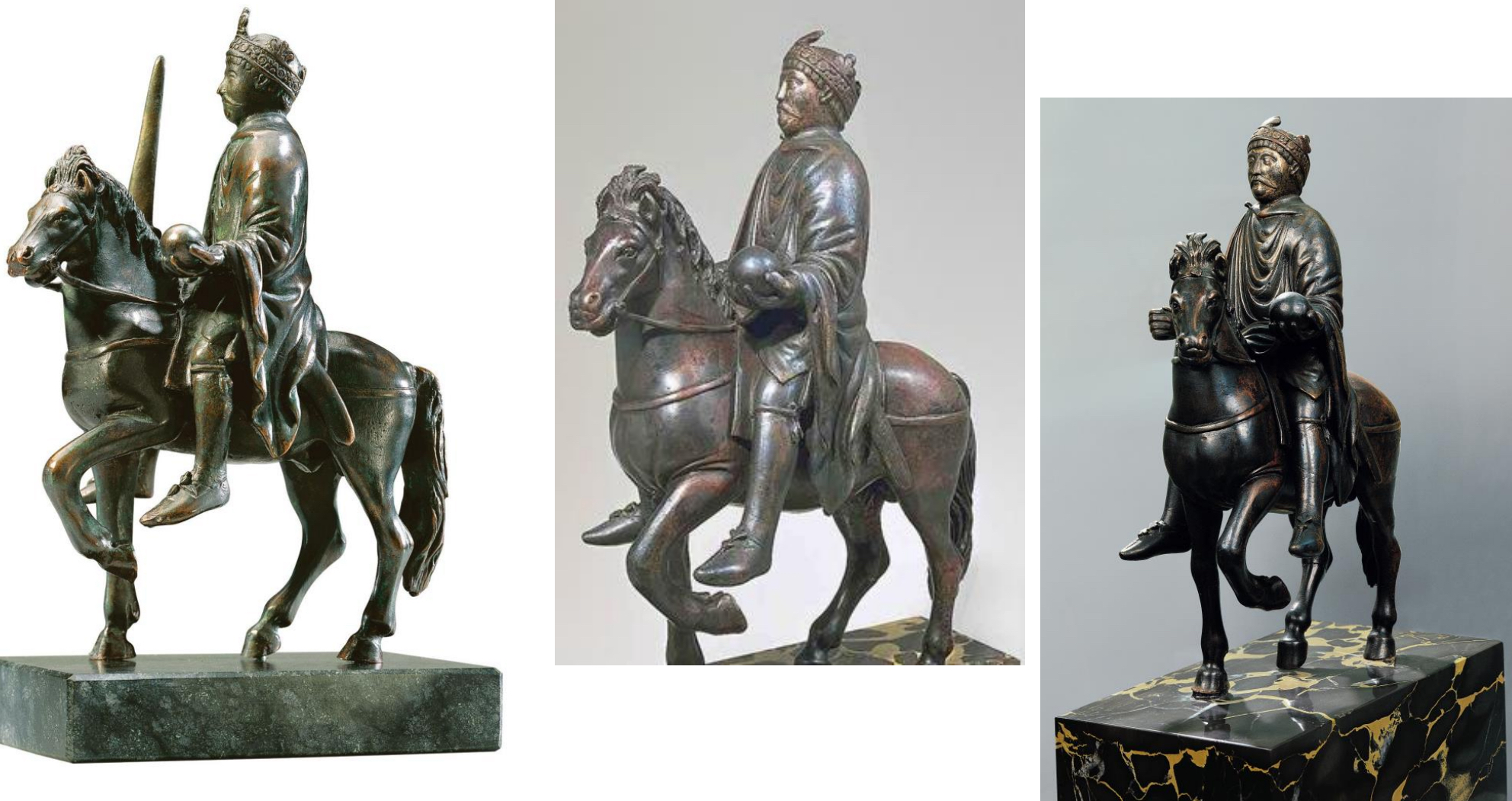

40. *Bronze equestrian portrait-statuette of Holy Roman Emperor (Charlemagne or Charles the Bald); horse dates to late Antiquity; rider is c. 870; presumably made for the Archbishop Drogo of Metz
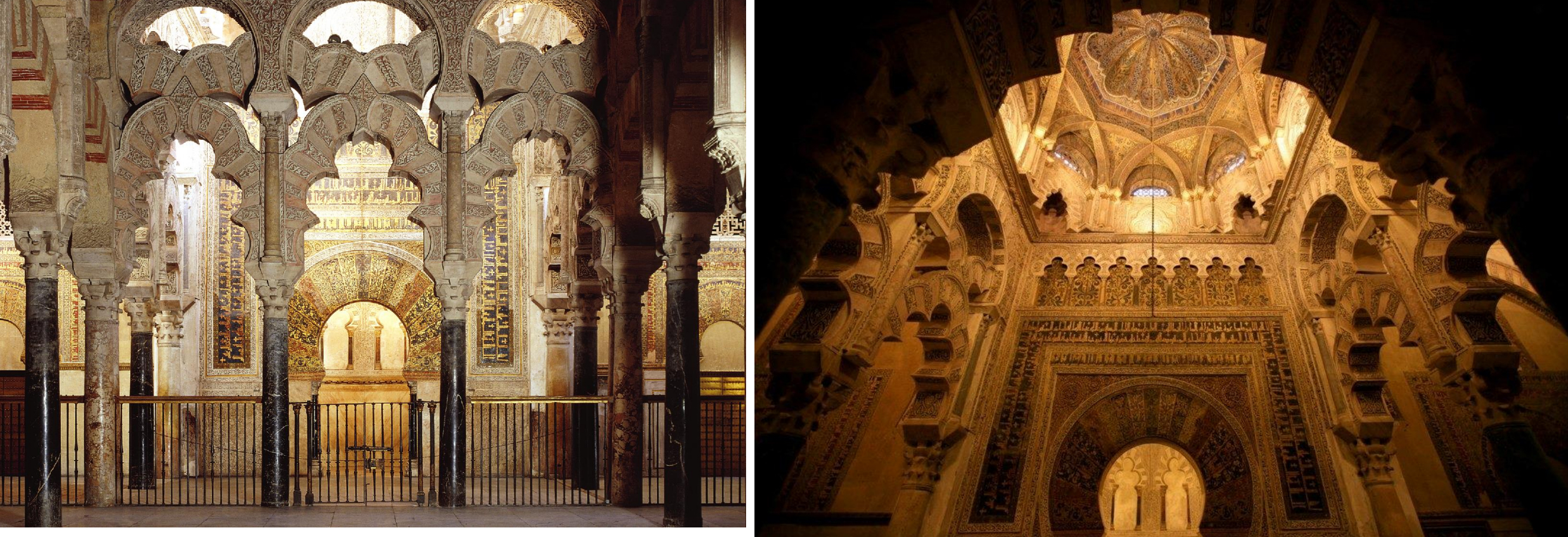

41. *Cordoba (Spain), masqura of the Great Mosque of Cordoba, 961-967; carved marble, stucco and mosaics.
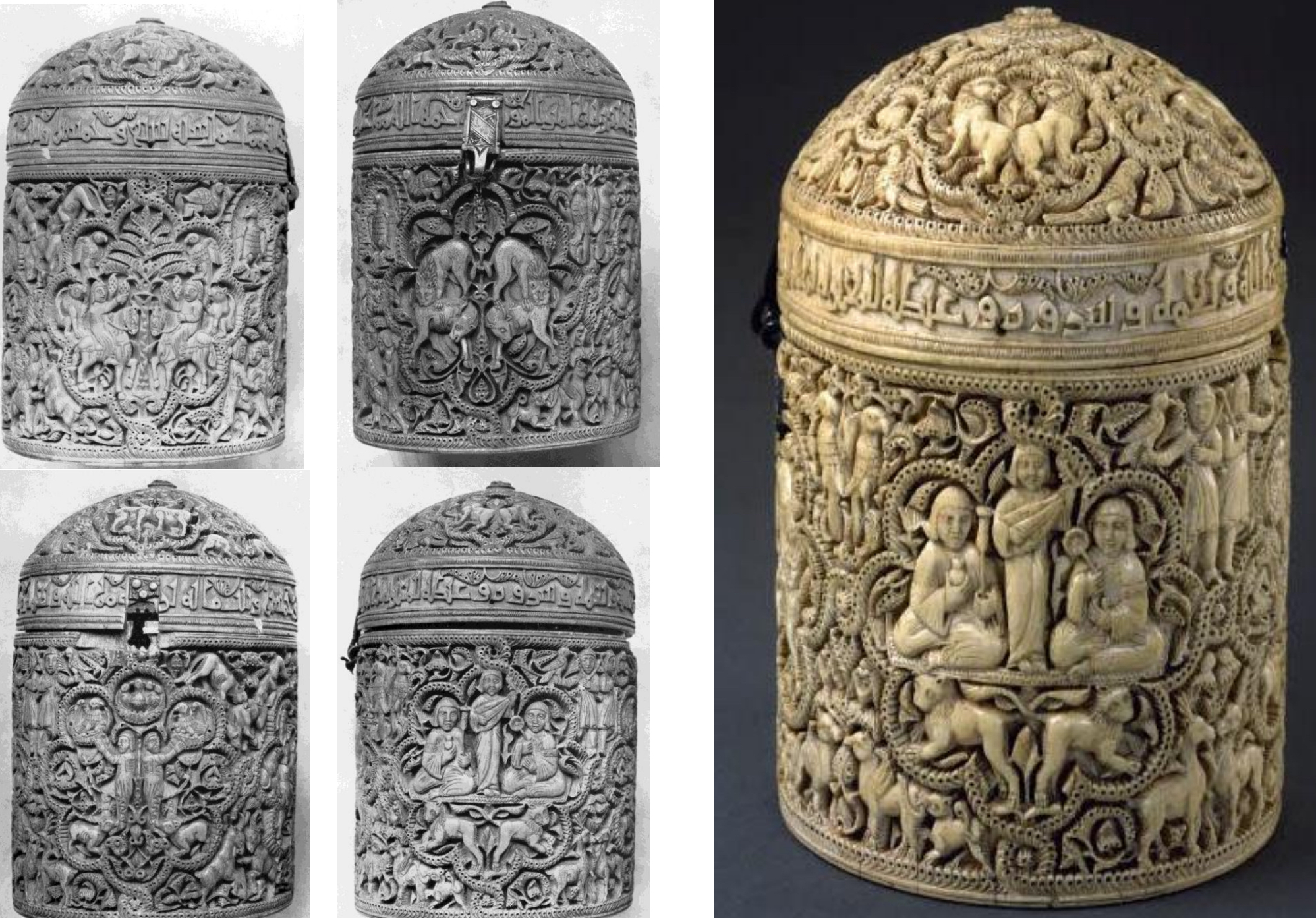

42. *Ivory pyxis of al-Mughira, 968: carved relief of an Islamic ruler or prince; made in the caliphal workshop of Madinat al-Zahra in Ummayad Spain
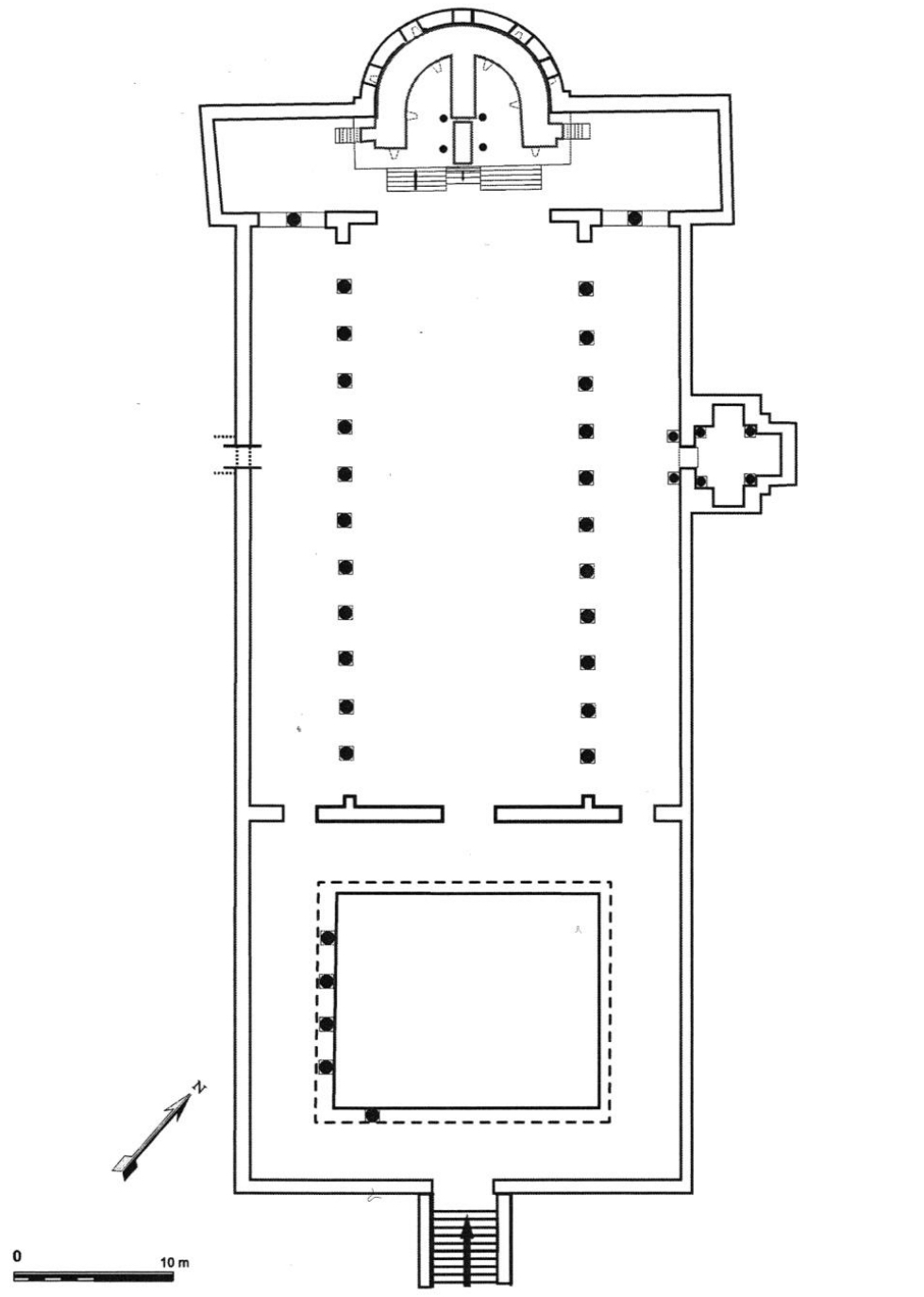
43. *Rome, Santa Prassede: ground plan as in c. 820; commissioned by Pope Paschal I.
44. *Rome, Santa Prassede: mosaic of the triumphal arch, 820: detail depicting martyrs entering the heavenly Jerusalem; commissioned by Pope Paschal I
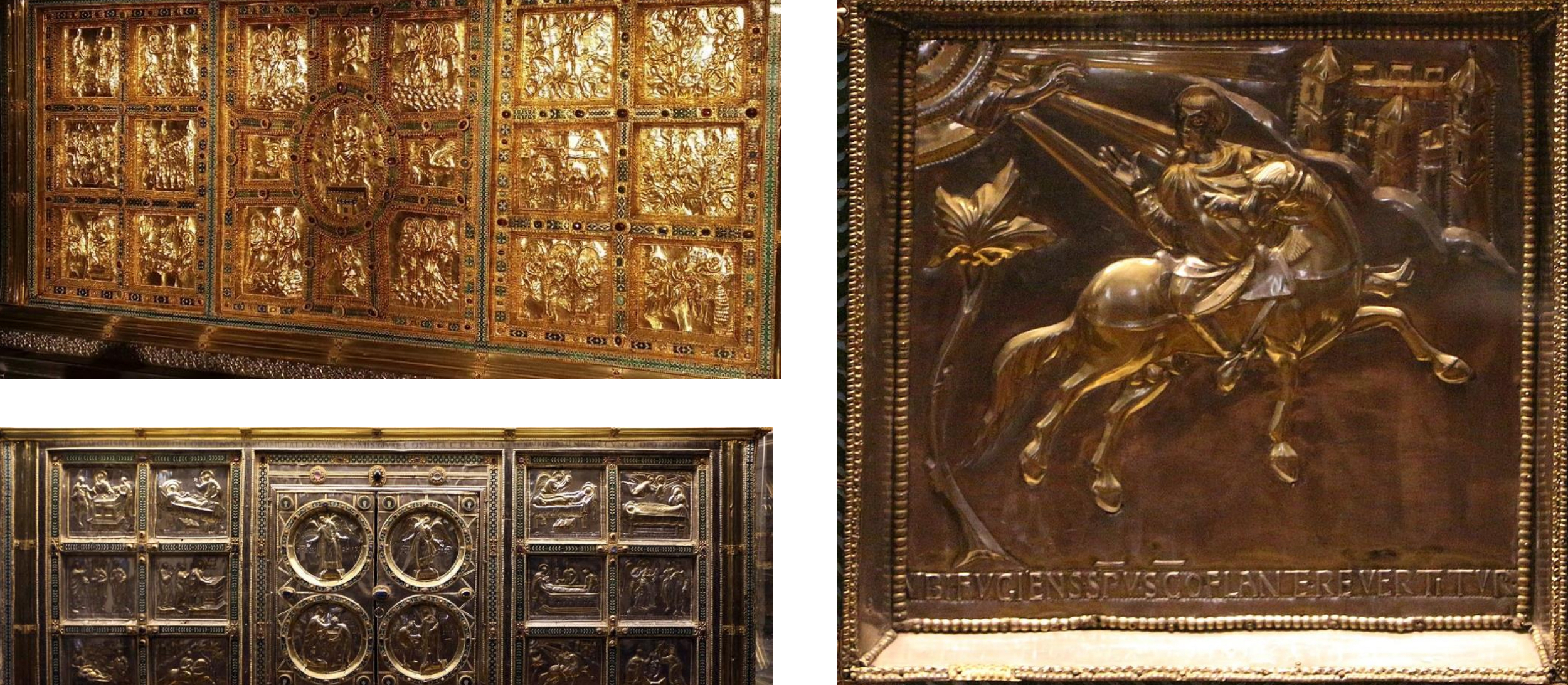


45. Milan, Altar of St. Ambrose or Altar of Volvinius, 824-859 in situ in the Basilica of St. Ambrogio; gold, silver, silver gilt, enamel, gems and precious stones; signed by the master craftsman Volvinius and commissioned by the bishop of Milan Angilbertus II; detail shows the "conversion" of St. Ambrose
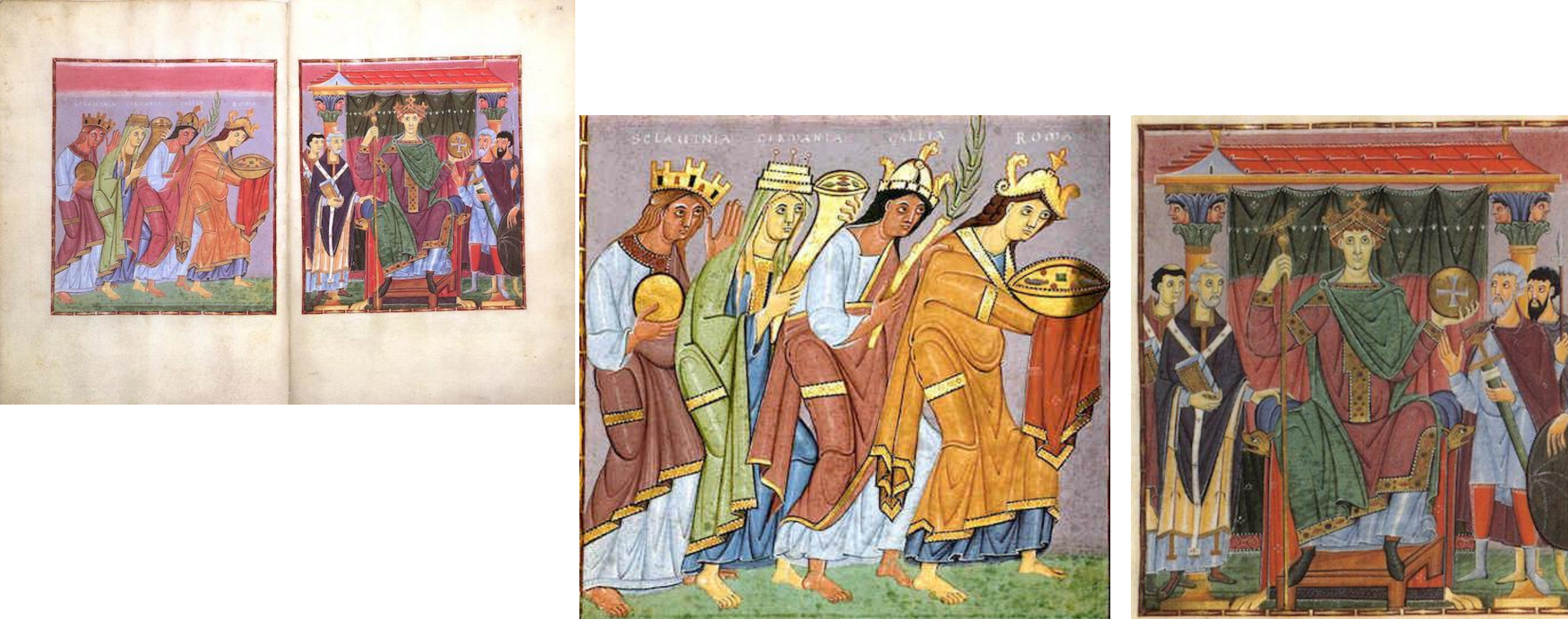

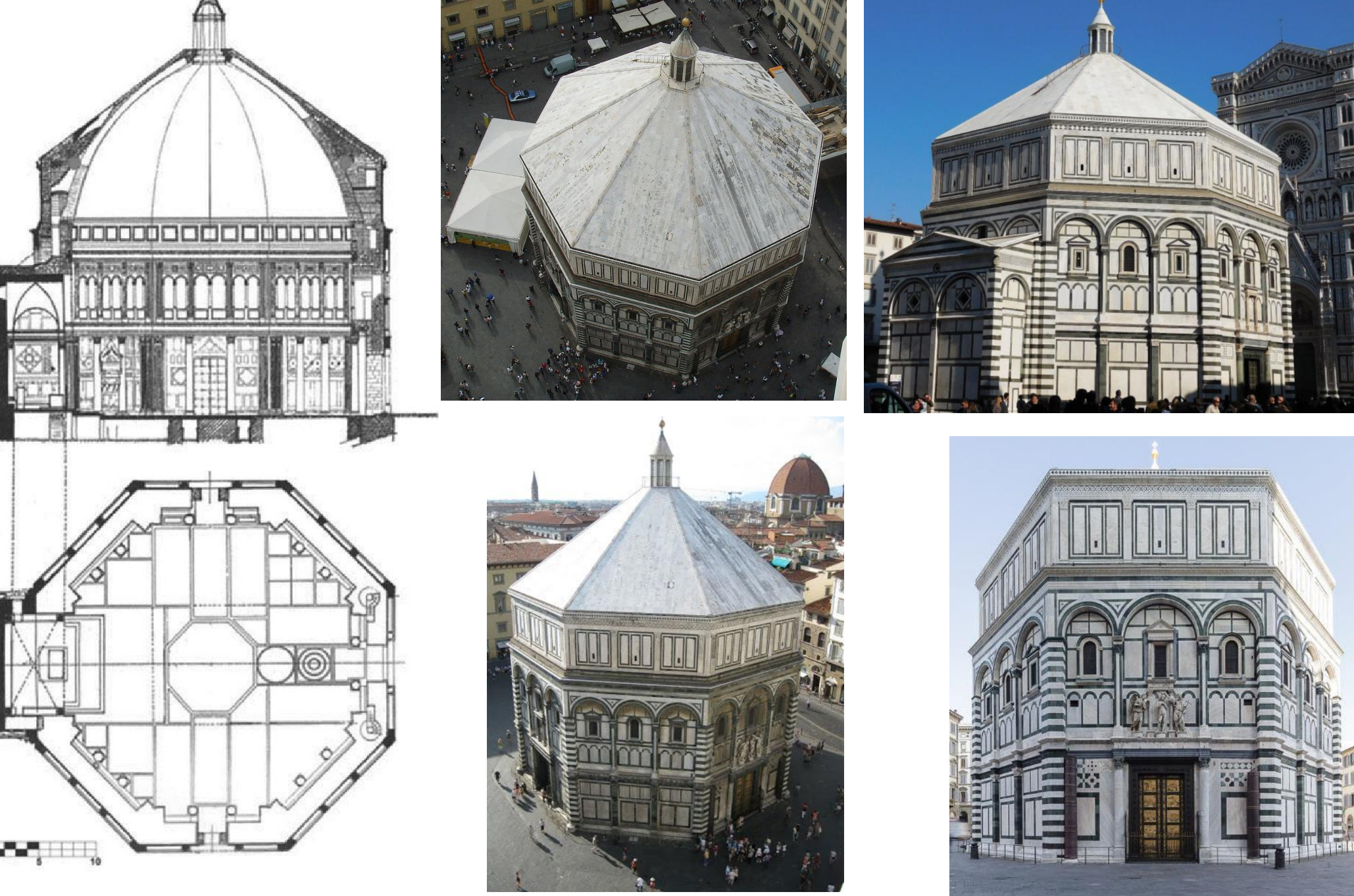
46. *Gospels of Otto III, c. 1000 (Ottonian): double folio opening depicting female personifications of the Provinces of the Holy Roman Empire bearing gifts to Otto III
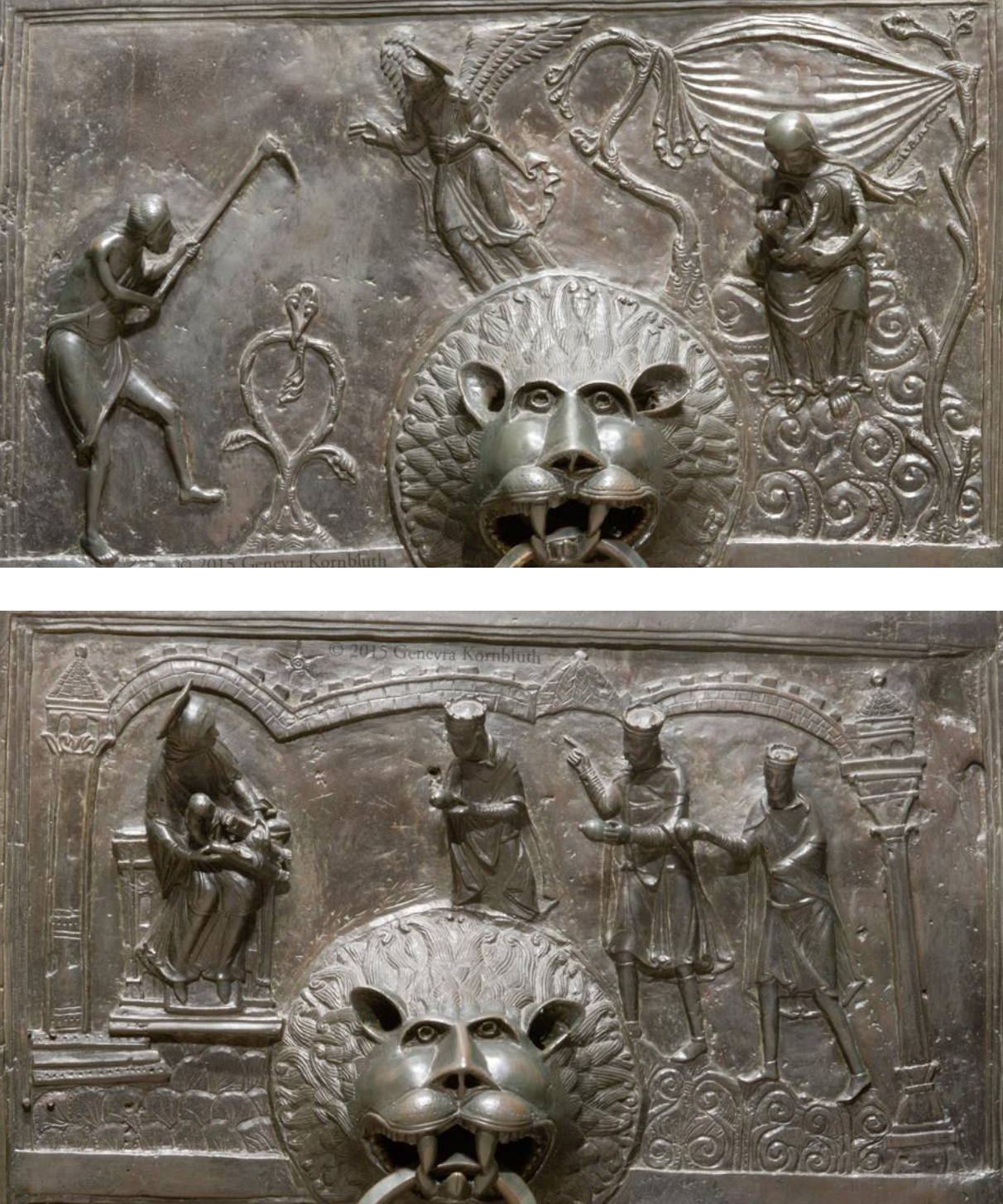

47. *Hildesheim (Germany), Bernward Doors," c. 1012-5 (Ottonian): detail depicting the labours of Adam and Eve and the Adoration of the Magi; commissioned by bishop Bernward of Hildesheim
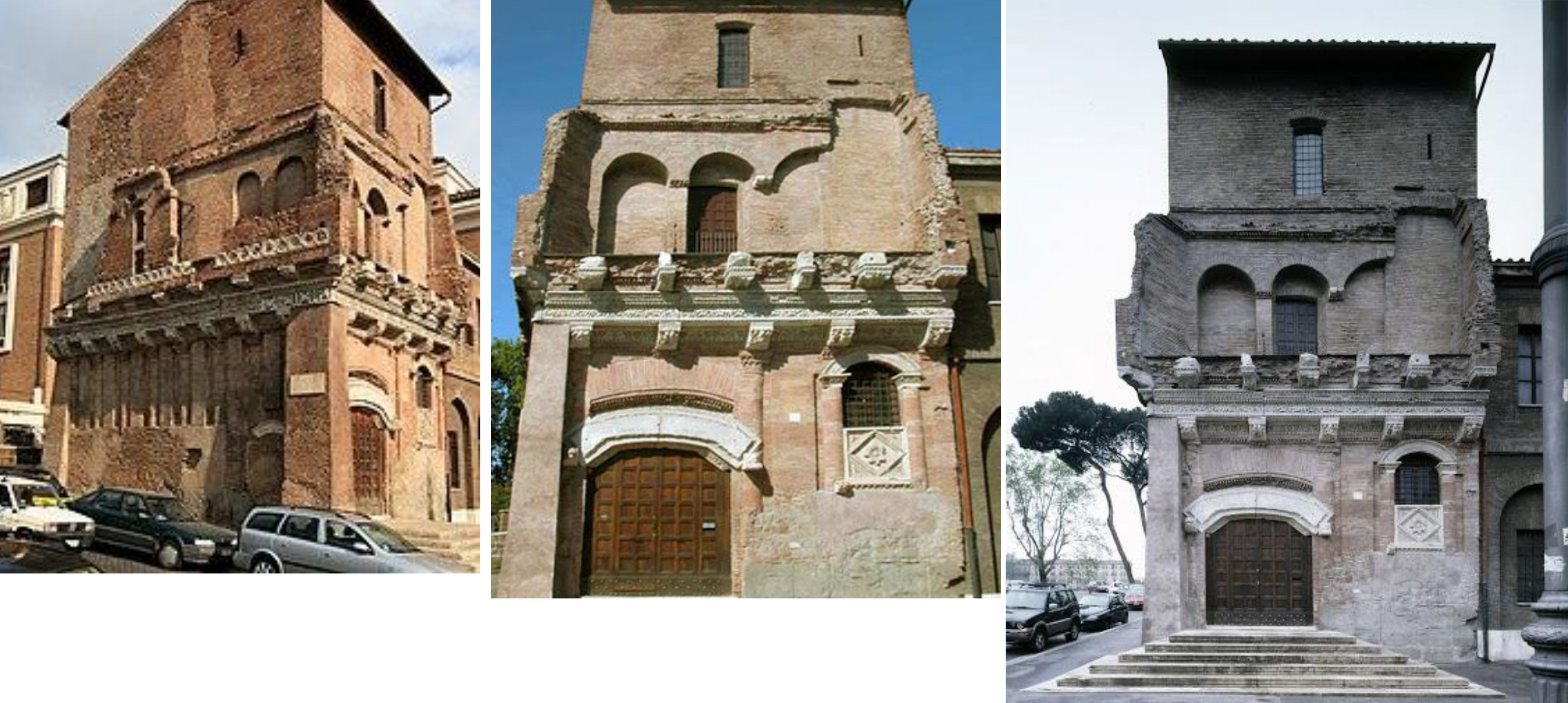

48. Rome, Casa dei Crescenzi, 1040-1065; built near Ancient Forum Boarium (by Tiber) by Niccolò di Crescenzio to oversee the surrounding territory and- by extant inscription- to renew the ancient glory of Rome.
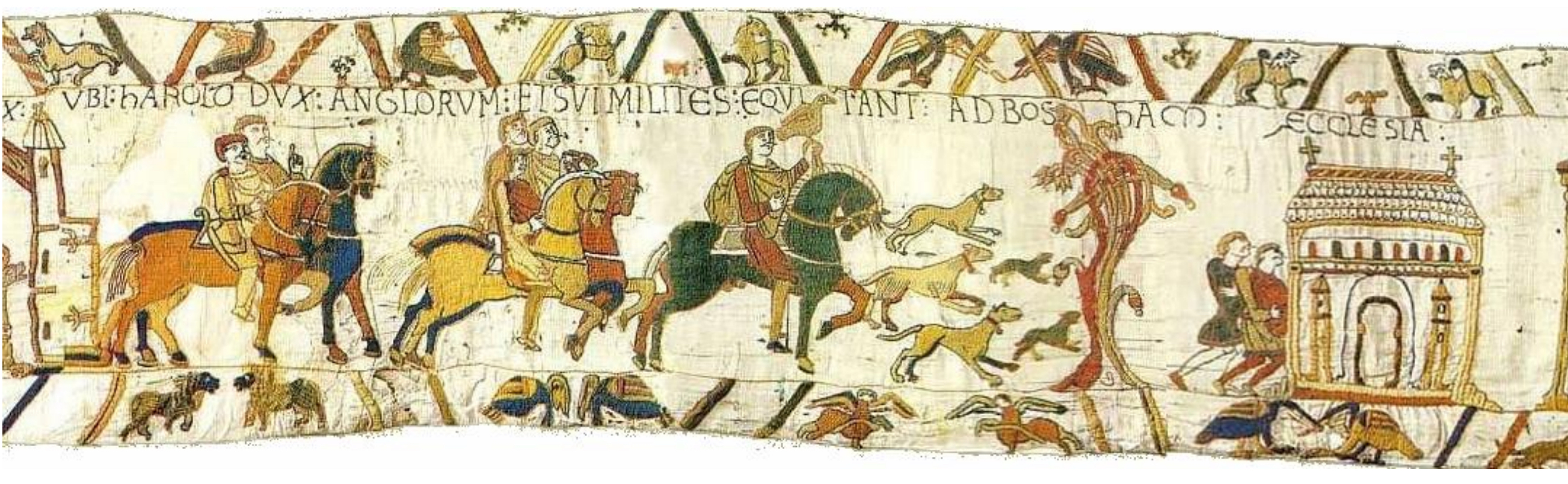

49. Bayeux embroidery, 1077 (Anglo-Norman). Embroidered linen cloth; depicts narrative of the events leading to the Norman conquest of England

50. Barberini Exultet Roll, c. 1080-1100. Illuminated rotulus with illustrated musical texts for easter Vigil Easter; intended to be unrolled from a pulpit; made in Benedictine Abbey of Montecassino
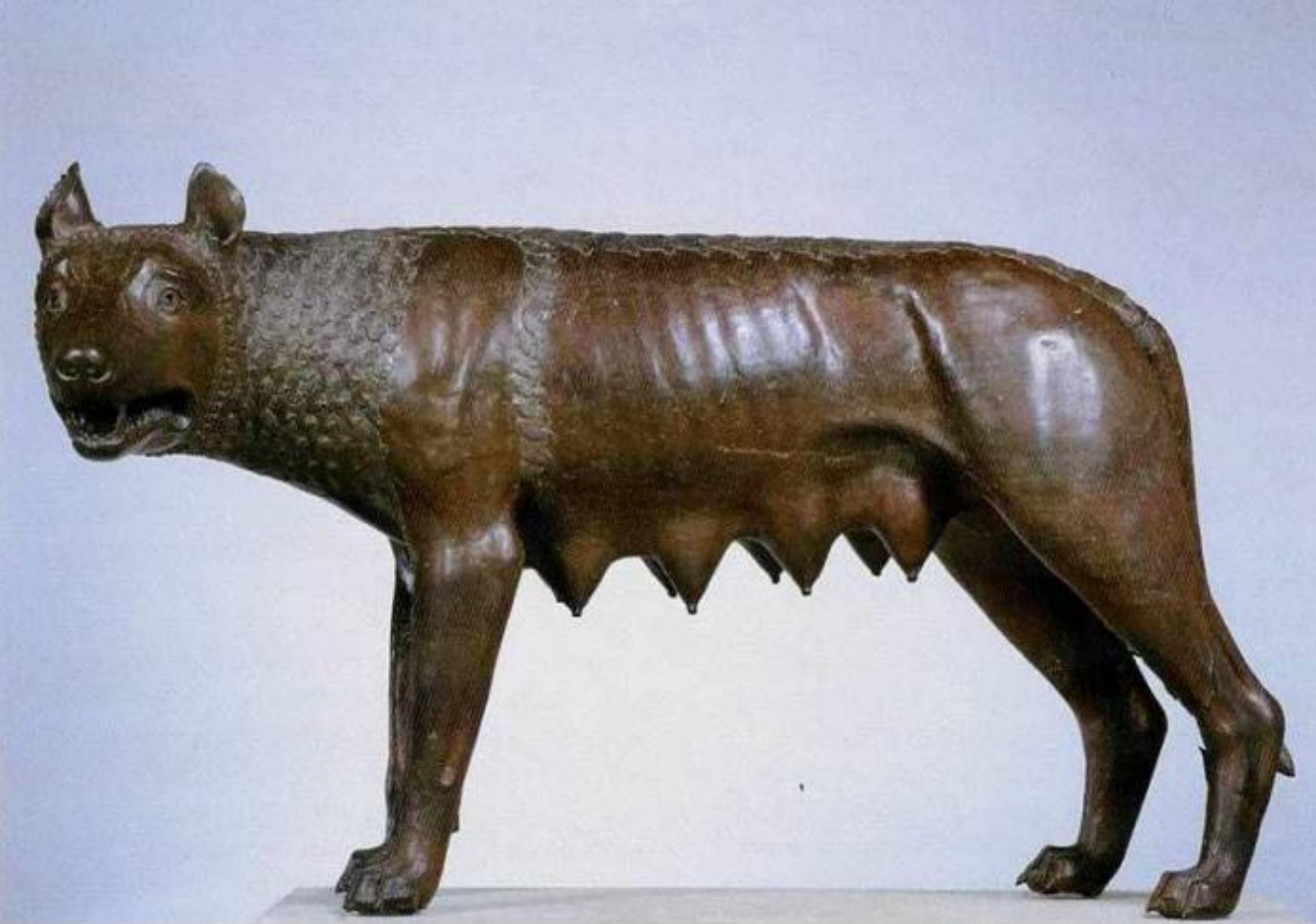

51. Rome, Capitoline She-Wolf (aka Lupa Capitolina), now dated 11th-12th century (but still disputed: some scholars date it to the 5th cent. BC); refers to foundational myth of Rome
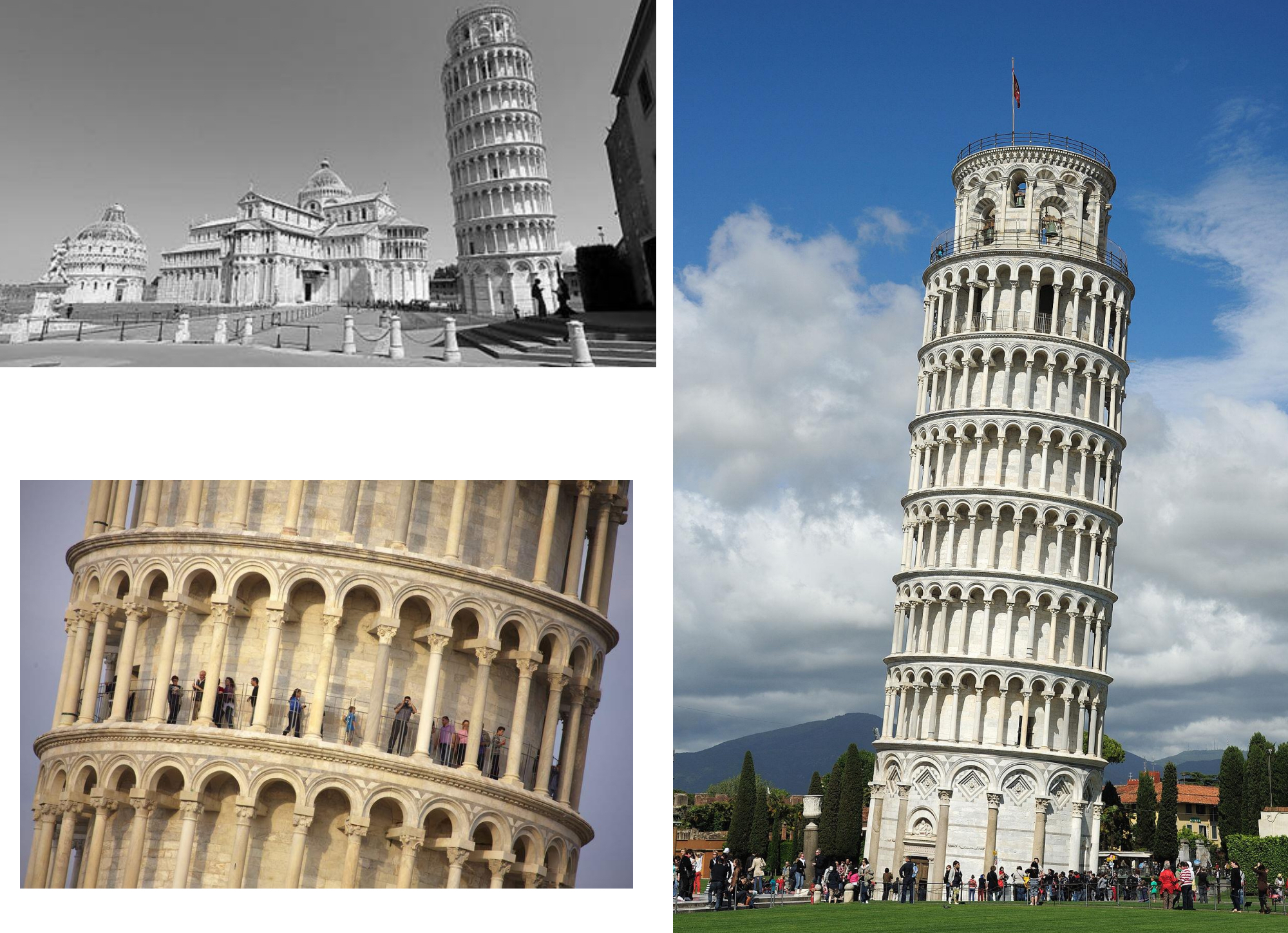

52. Pisa, Bell tower (campanile) from the Cathedral Complex ("Campo dei Miracoli"), begun 1173/ 1174; architect Bonano da Pisa
53. *Florence, Baptistery, 1059-1128 (exterior revetment 13th century); part of Florence Cathedral Complex
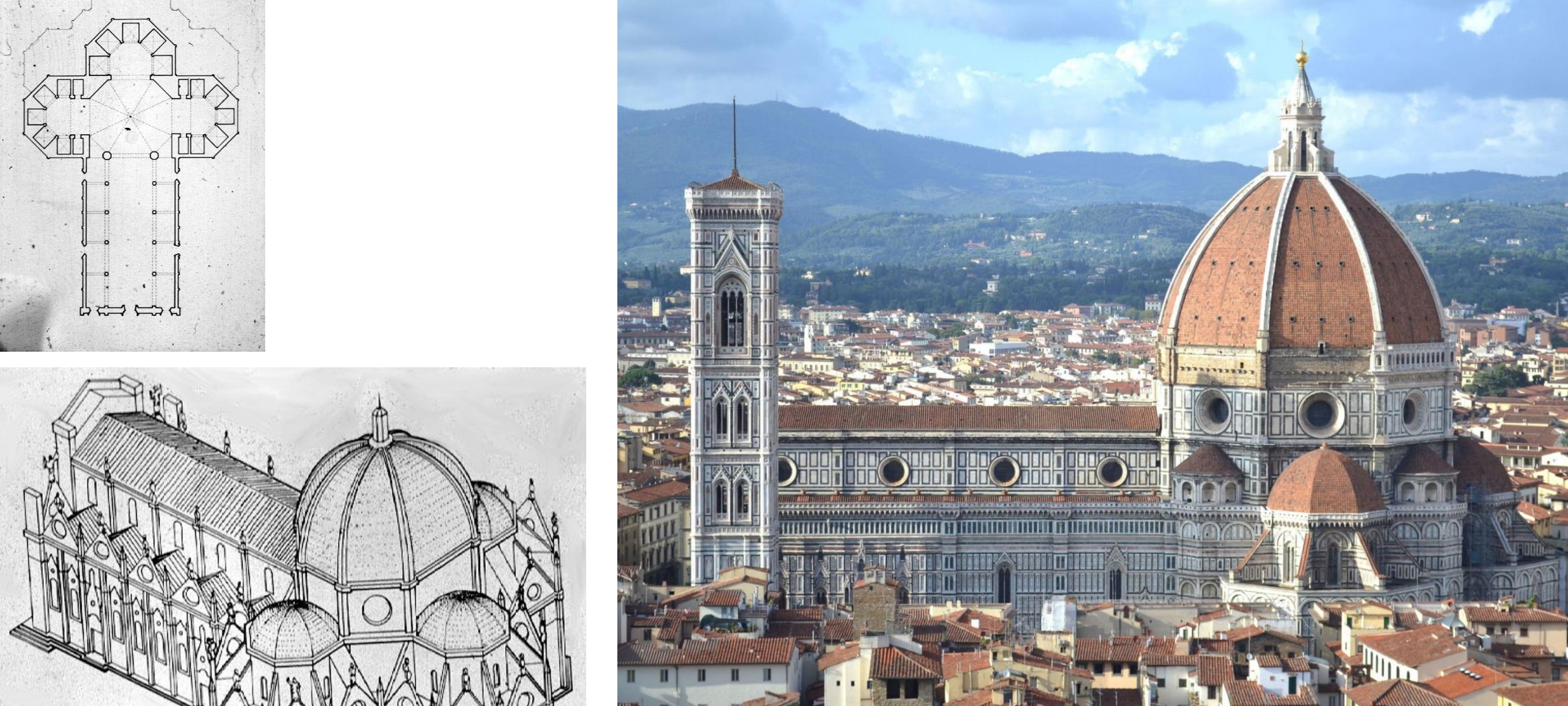

54. Florence, Santa Maria del Fiore, 1296-2436 (minus facade and dome), Italian Gothic style; design by Arnolfio di Cambio
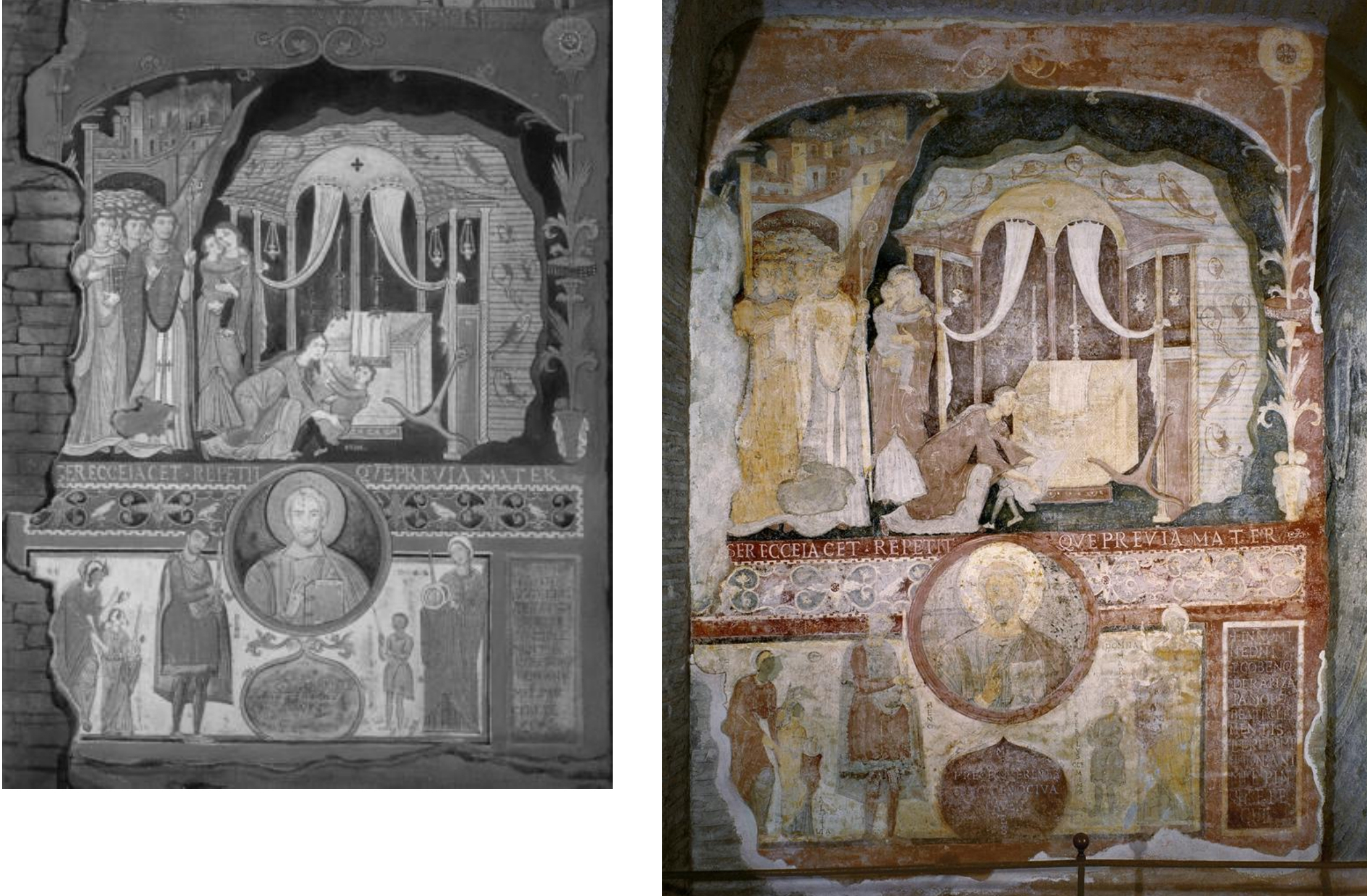

55. Rome, San Clemente Lower Church: narthex fresco of the miracle of St. Clement's underwater tomb at Chersona, c. 1080-1100

56. *Rome, San Clemente, Upper Church apse mosaics, c. 1100-118: detail of the Crucifixion in apse conch
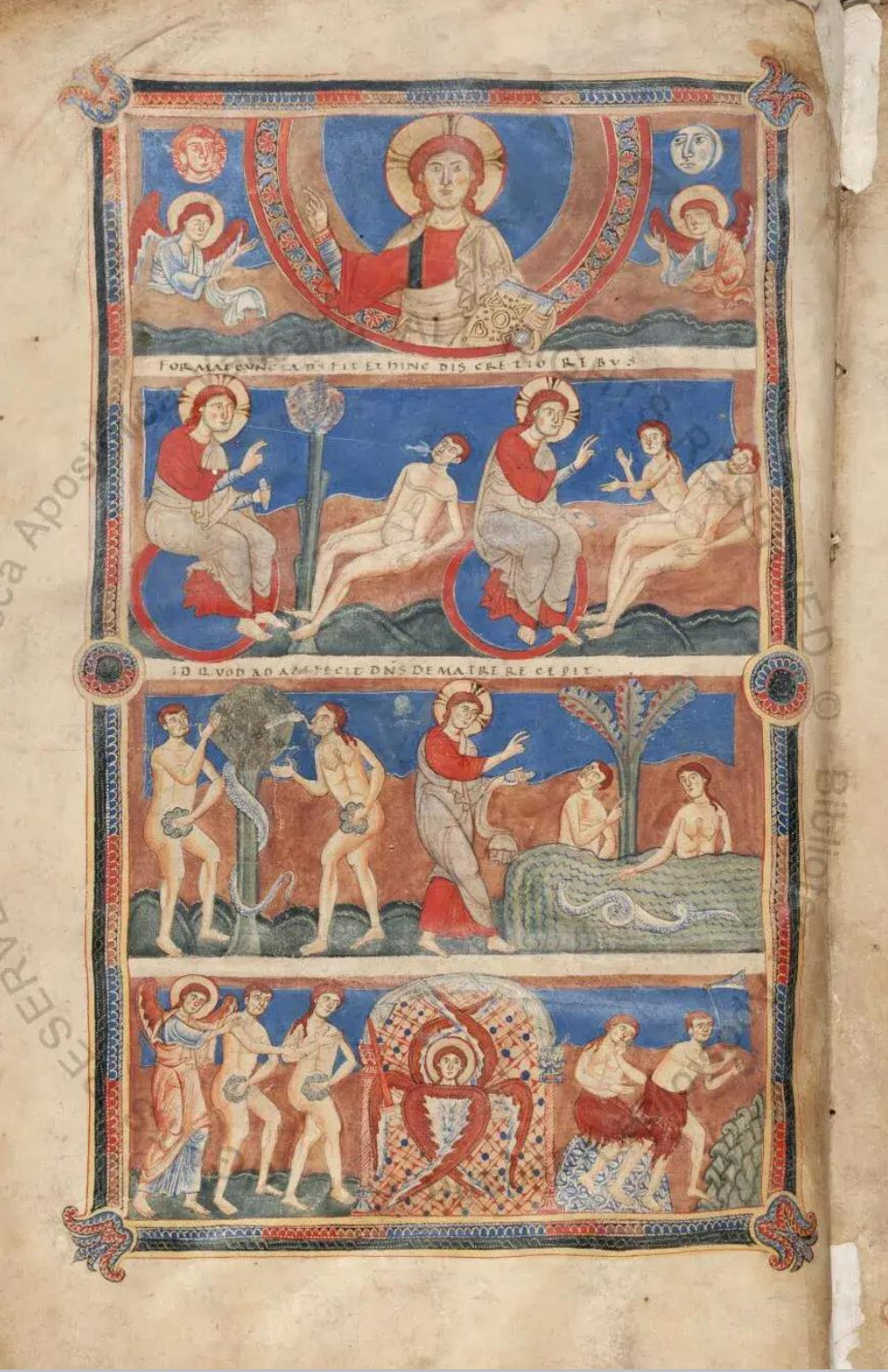

57. Pantheon Bible, central Italy, circa 1100 (?): full page miniature with scenes from Genesis from an Italian Giant Bible (Bibbia atlantica); imagery probably recalls Early-Christian frescoes in the nave of Old St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome
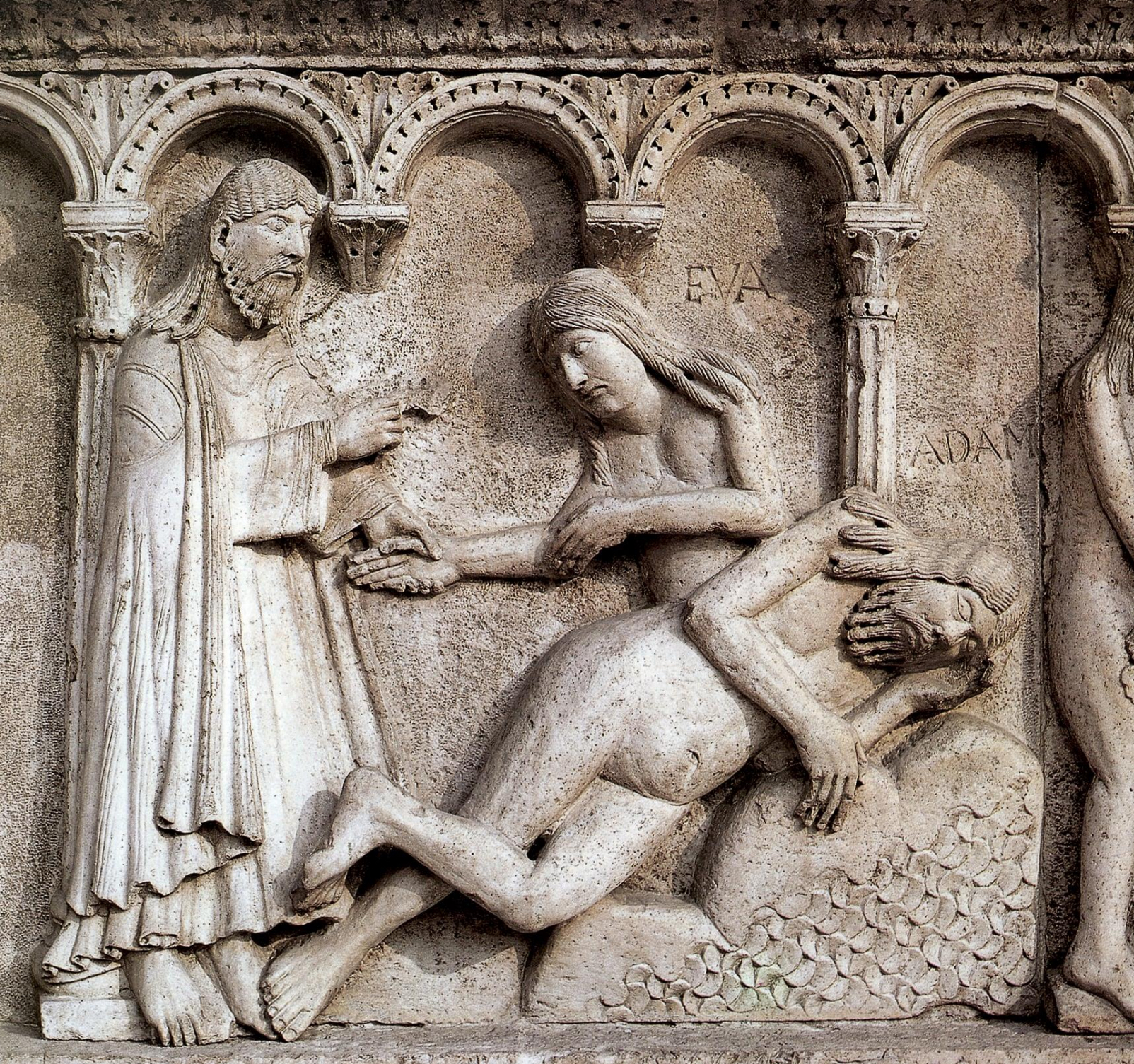

58. *Modena, cathedral: creation of Eve, early 12th century: limestone relief from the facade of the cathedral by the sculptor Willigelmo and / or his workshop
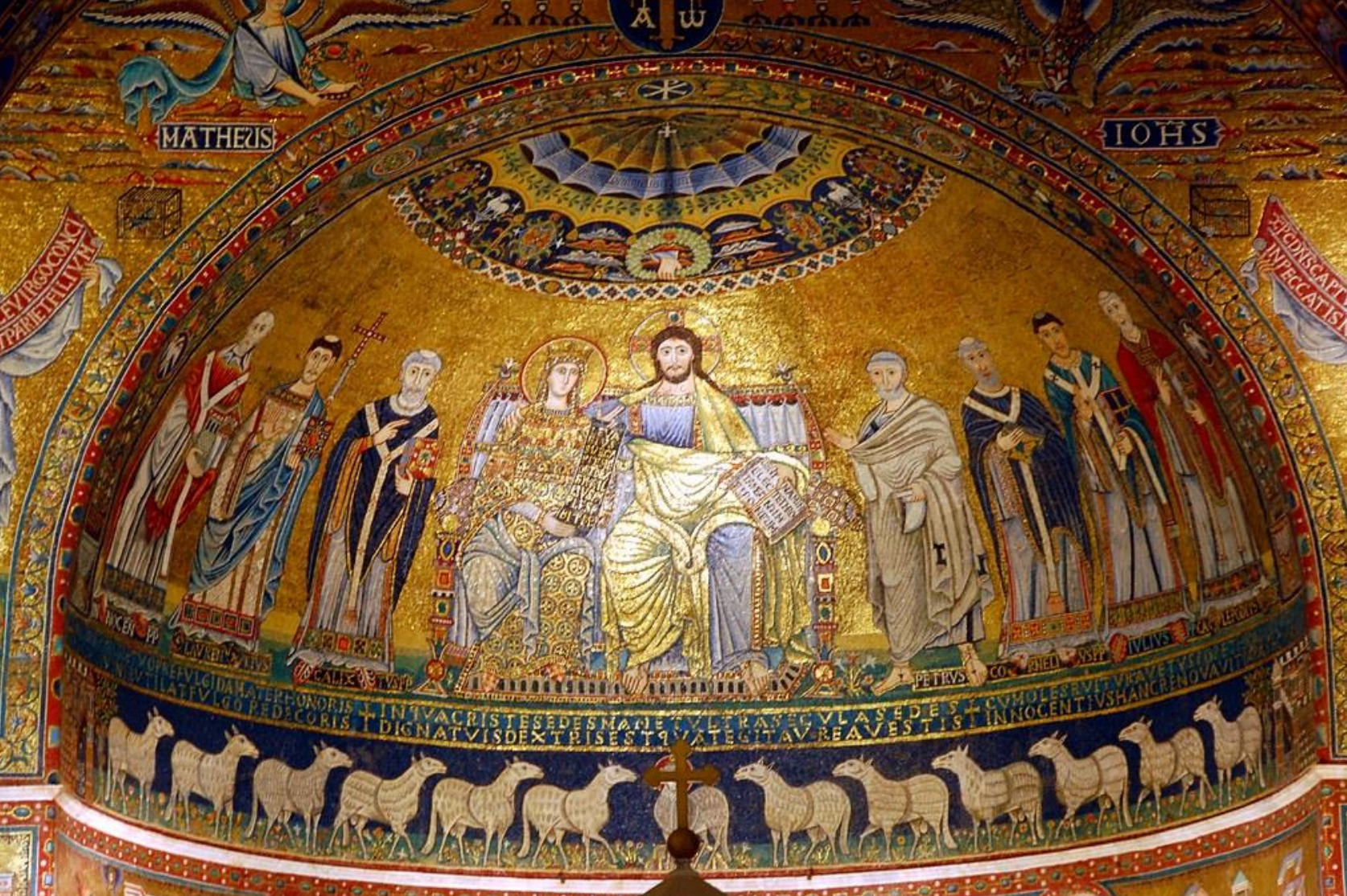

59. *Rome, Santa Maria in Trastevere: apse mosaic of Christ and Mary enthroned in heaven with saints; c. 1130-1143; commissioned by Pope Innocent II
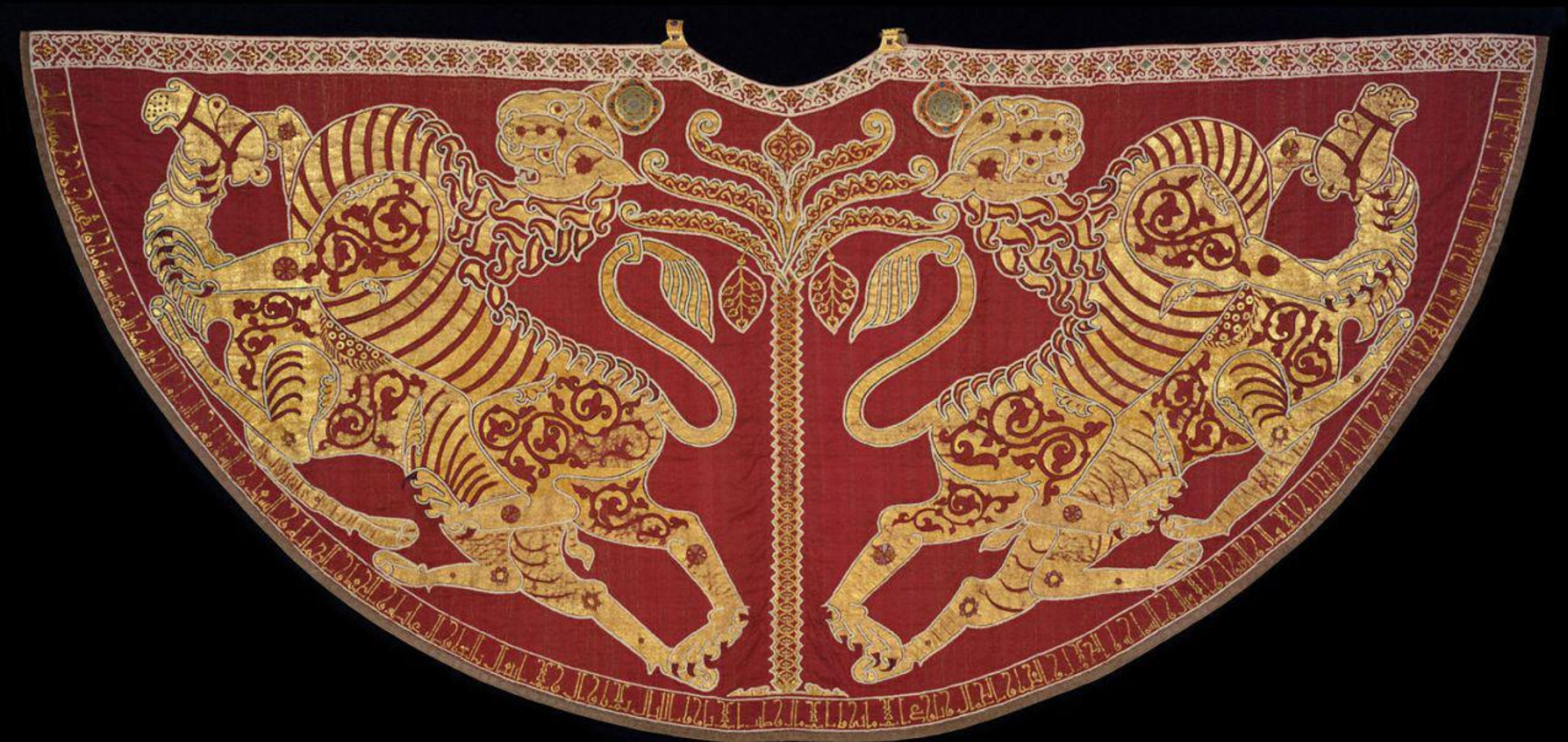

60.*Coronation Mantle of King Roger II, 1133/34: silk, gold, pearls, enamel, filigree, precious stones, woven fabric; made in royal workshop in Palermo (?)
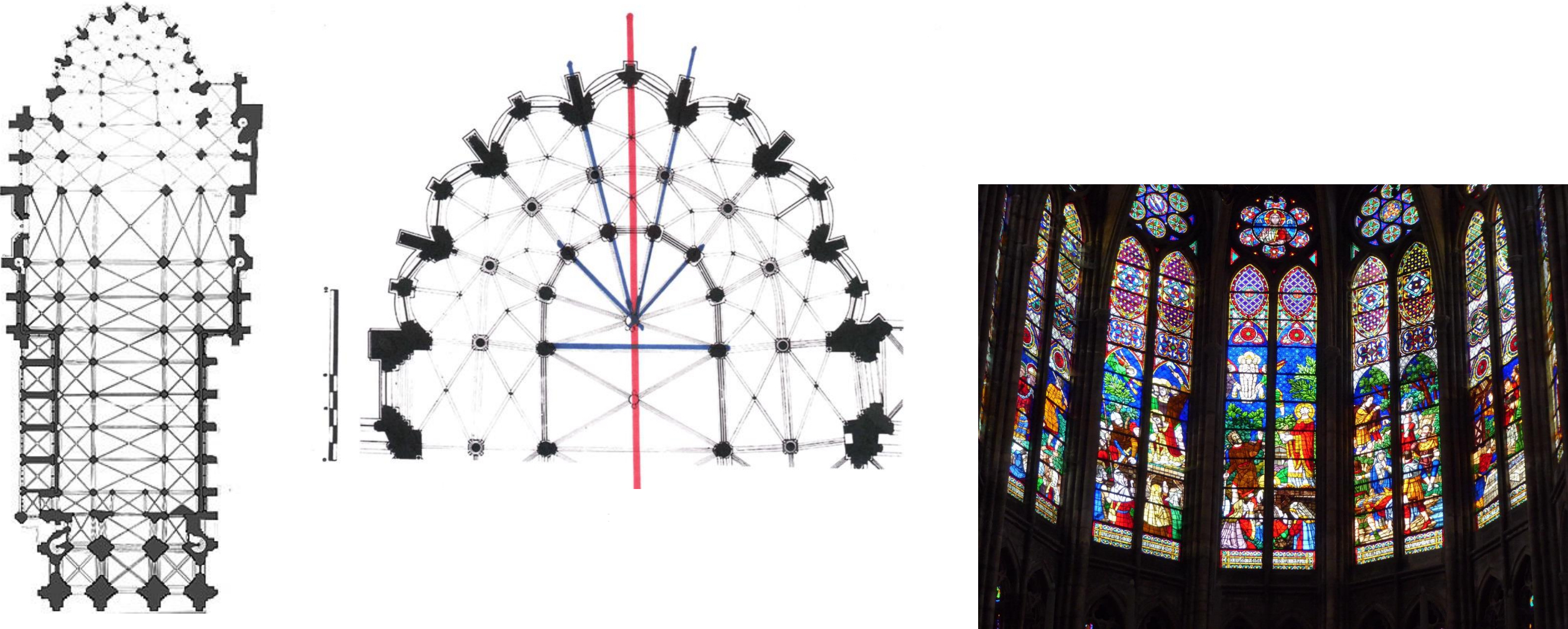
61. Paris, Chevet of the Church of the Royal Abbey of St. Denis, 1135-1144. Patron Abbot Suger. Considered first truly French Gothic structure.
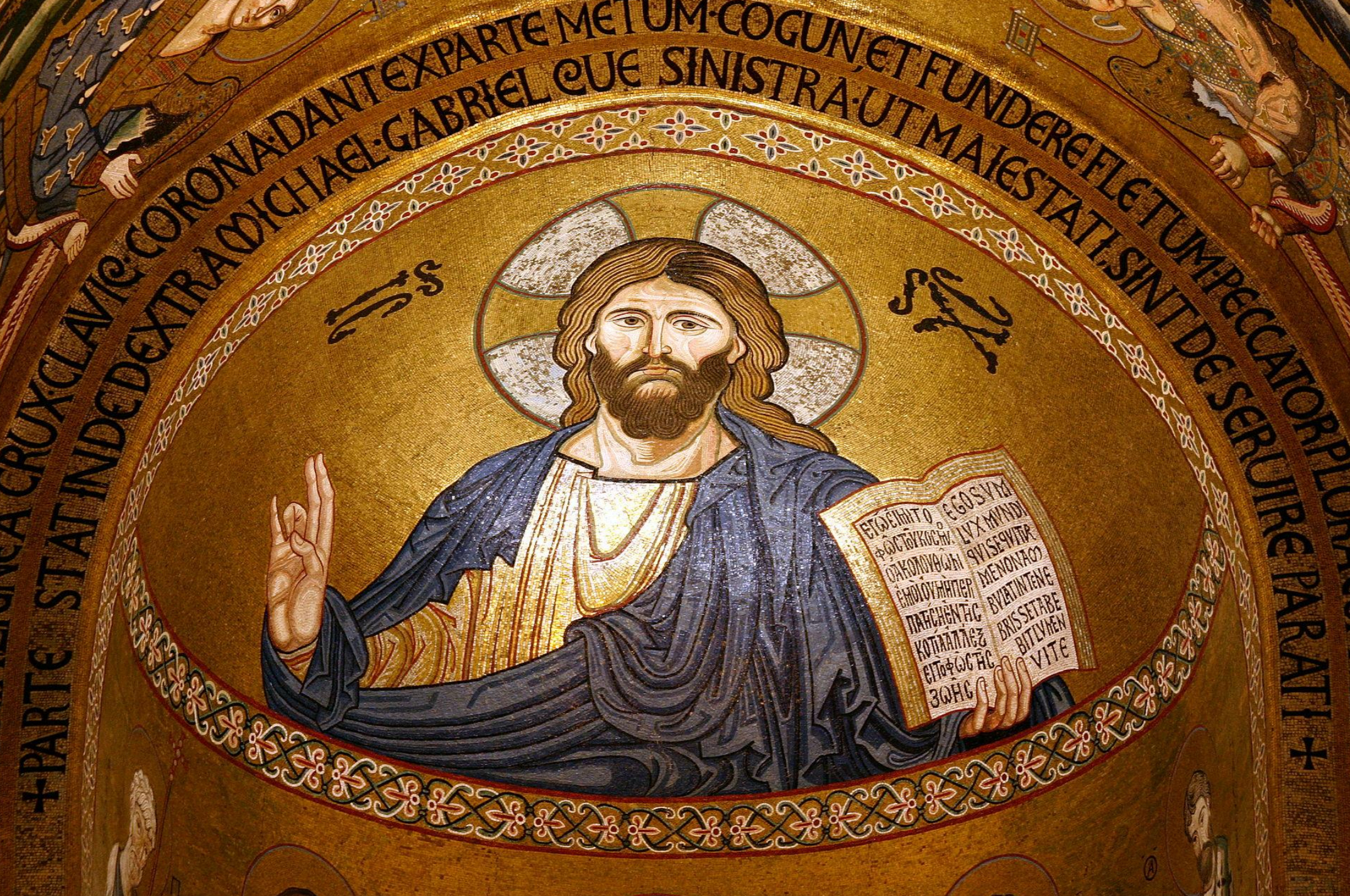

62.*Palermo, Cappella Palatina: apse mosaic of Christ Pantocrator, c. 1140-1150 ("Middle Byzantine" style); commissioned by King Roger II
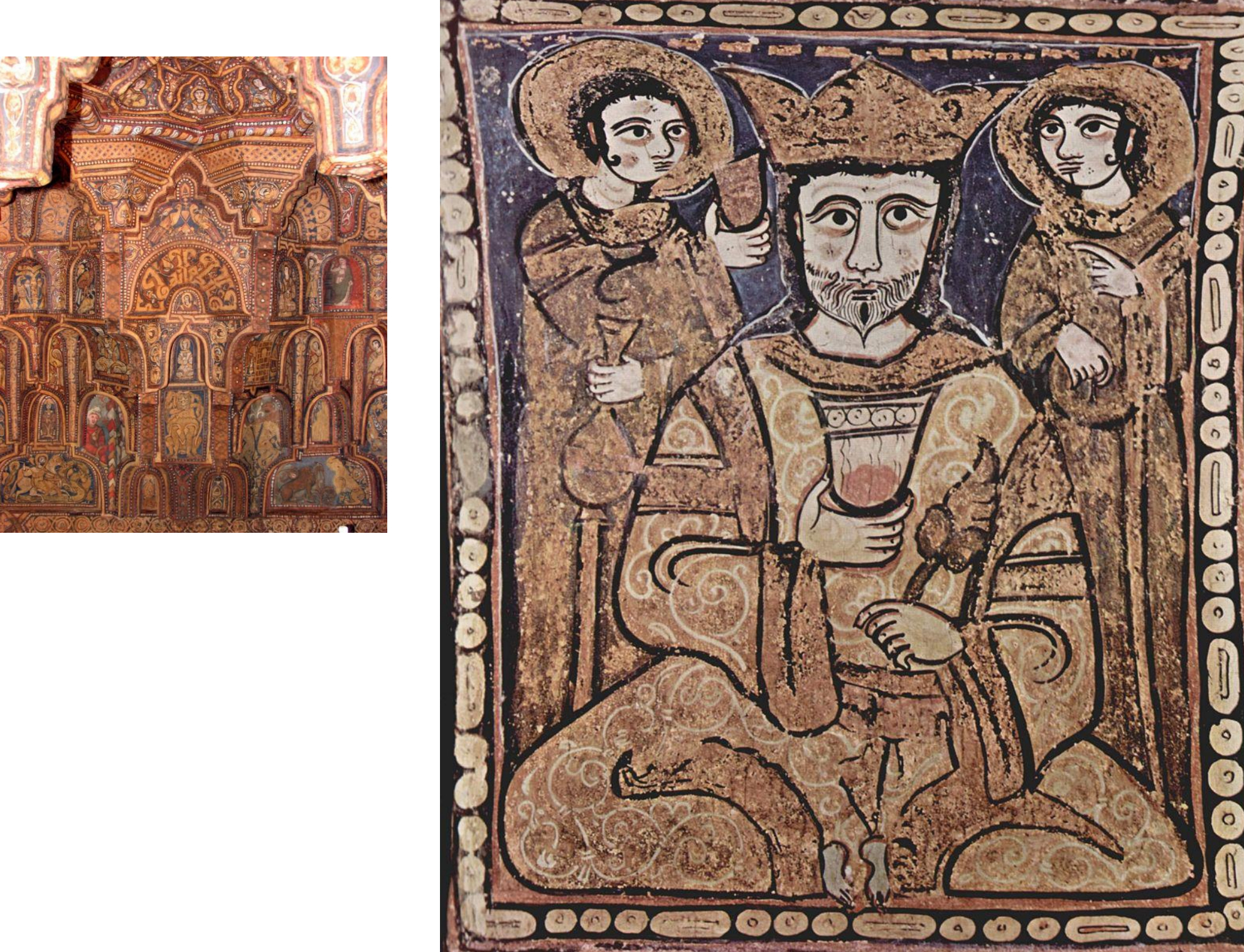

63.*Palermo, Cappella Palatina: section of painted wooden muqarnas ceiling depicting ruler with attendants (Islamic style/ courtly subject matter), c. 1140-1150
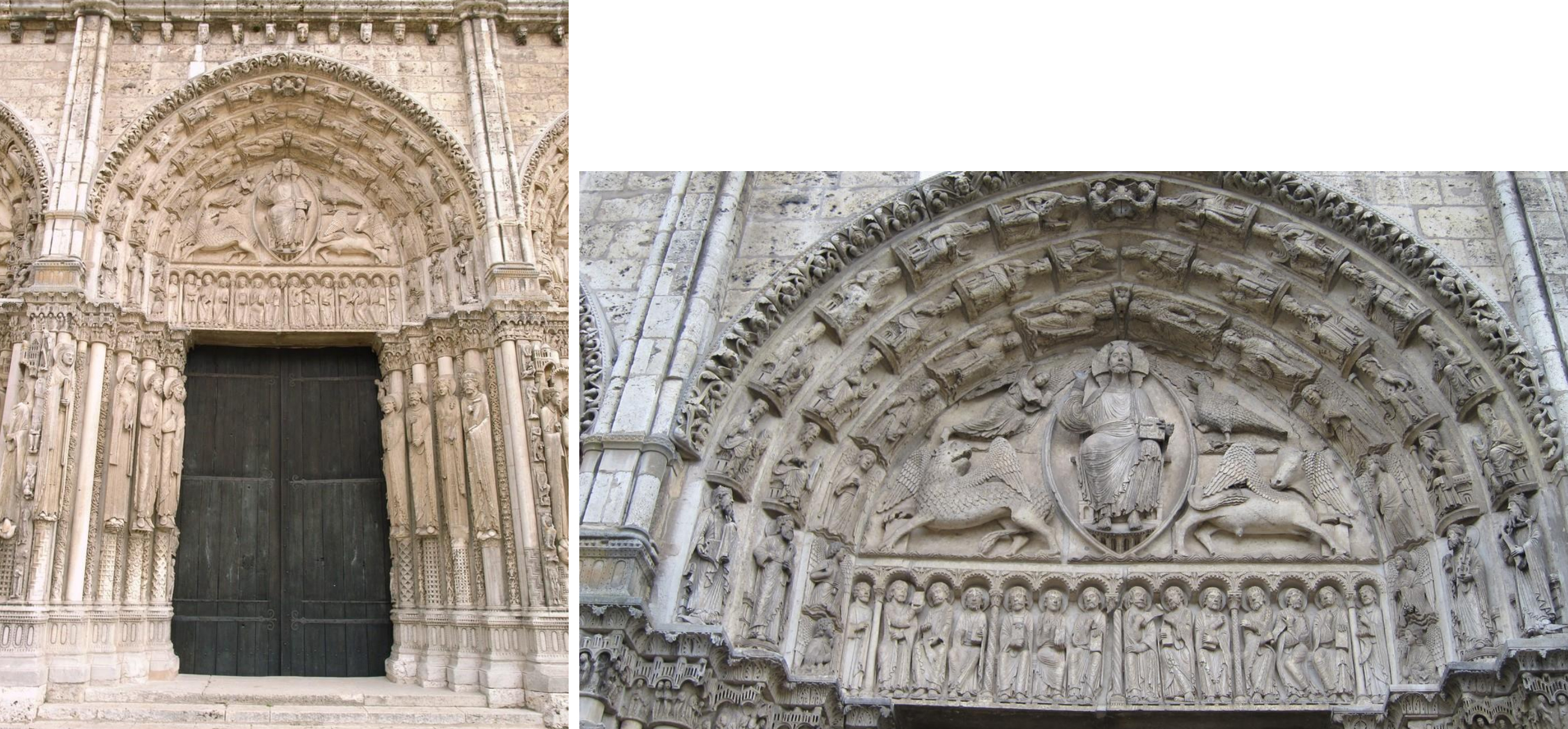

64. Chartres Cathedral: central door of West portal (aka the Royal portal), 1145-55

65. *Venice, St. Mark’s Basilica, begun 1063: combination of central plan and basilican plan with multiple domes and deep narthex
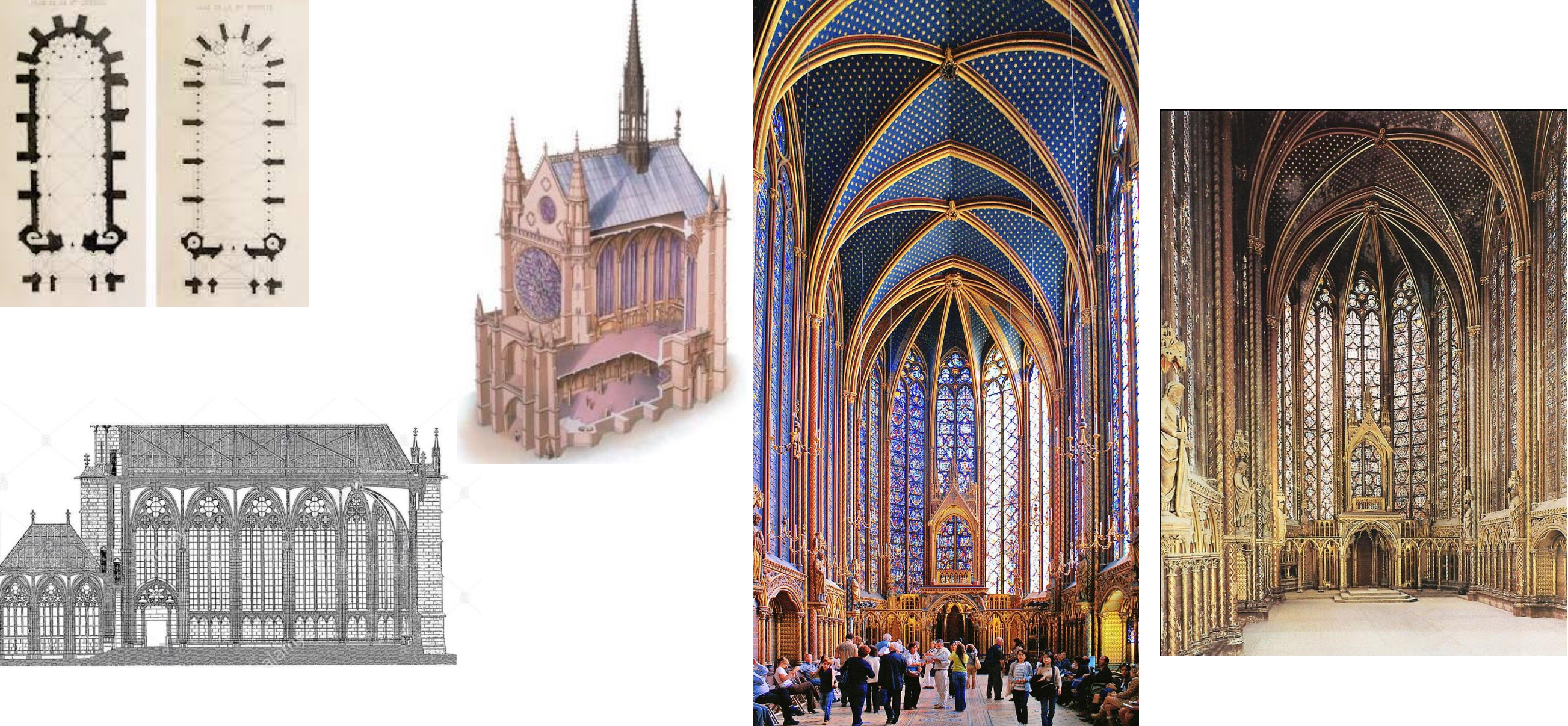

66. Paris, Sainte-Chapelle, 1238-1248; palace chapel commissioned by King Louis IX to house his collection of relics, including the Crown of Thorns; prime example of the “Rayonnant” Gothic style
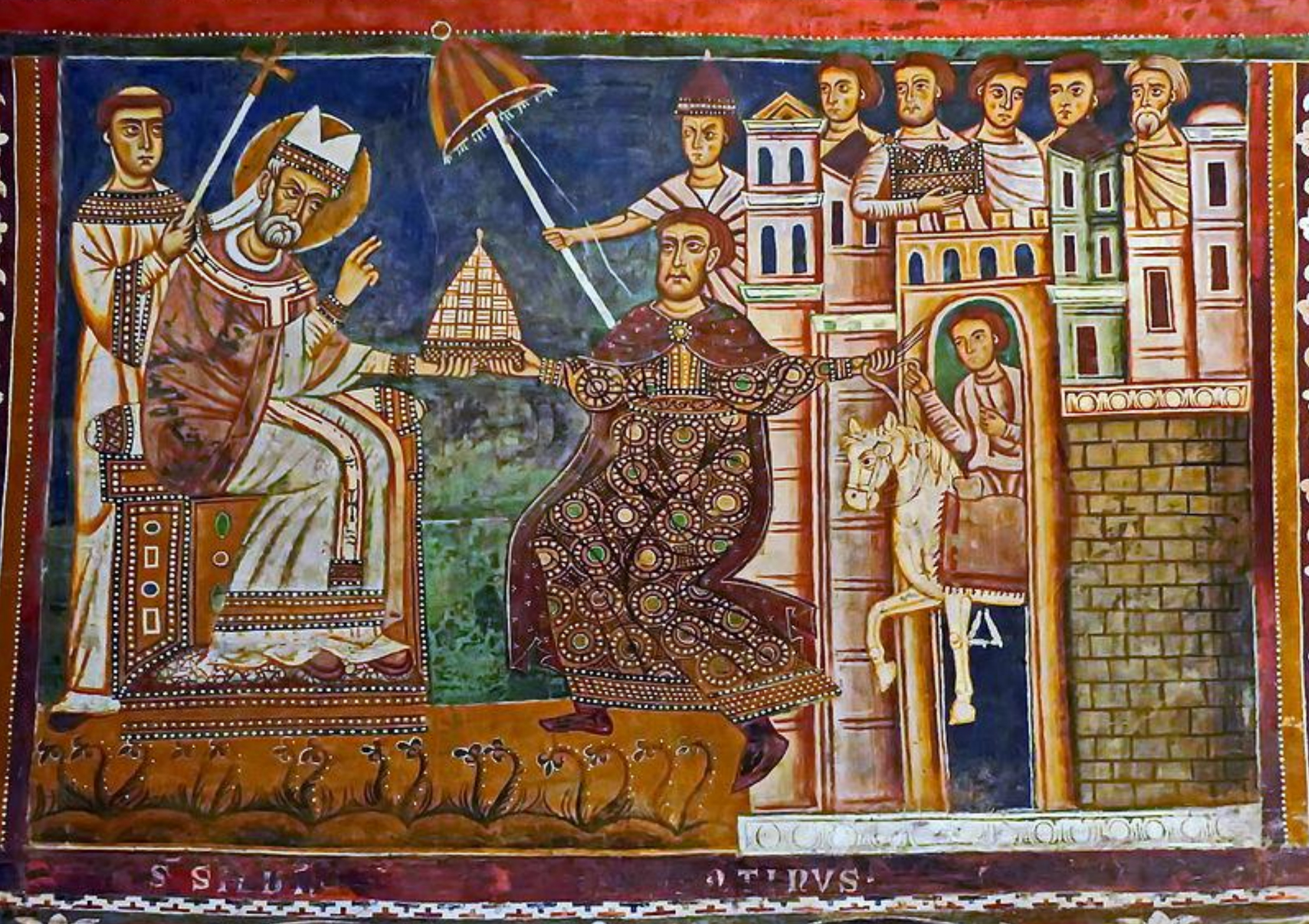

67. *Rome, Chapel of San Silvestro in Santi Quattro Coronati: fresco with the Donation of Constantine, 1246/1247; patron Stefano Conti, nephew of Pope Innocent III
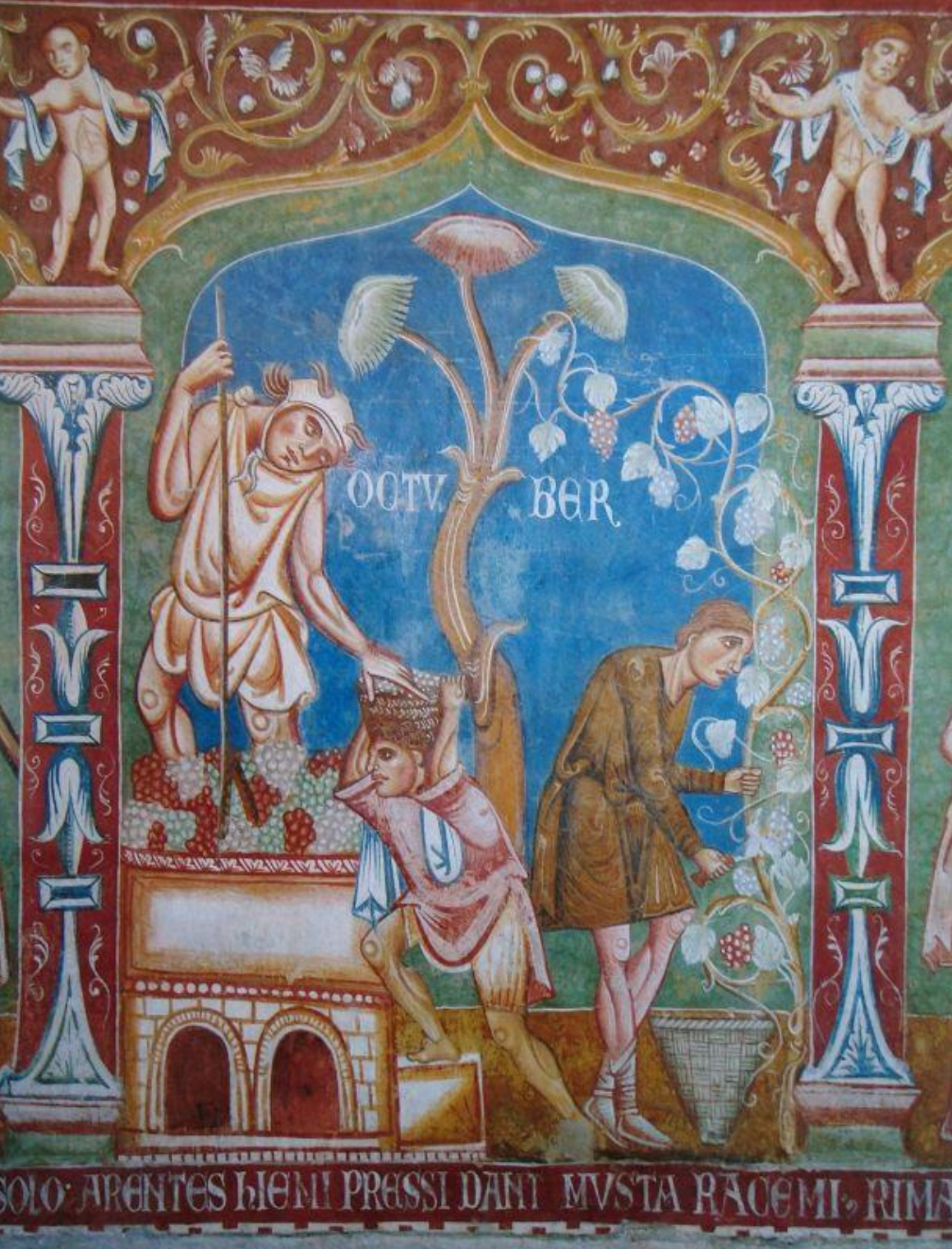

68. "Aula Gotica" in Santi Quattro Coronati SS. Quattro Coronati: fresco with the labors of the months (October), 1240s; patron Stefano Conti, nephew of Pope Innocent III
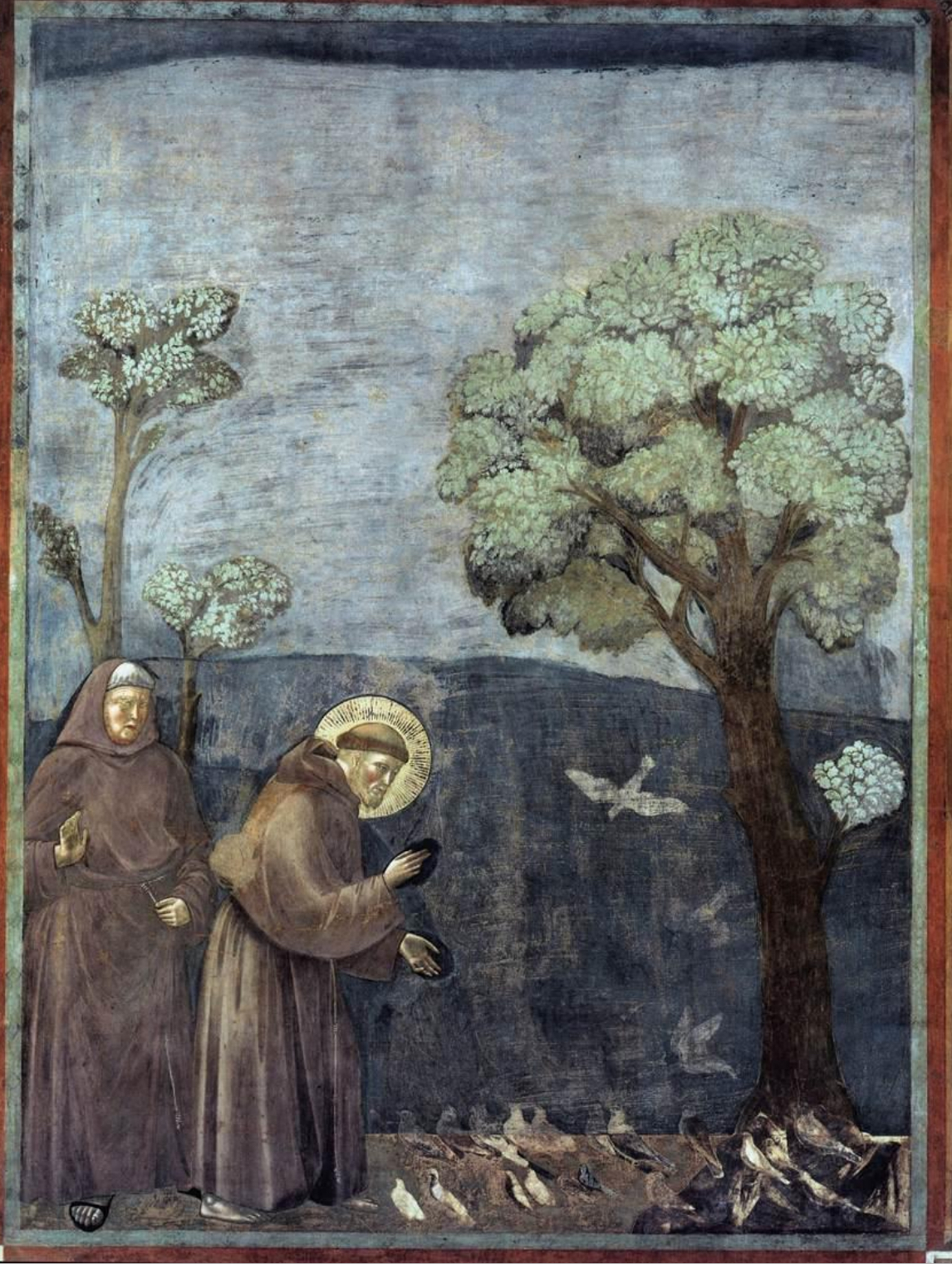

69. Assisi, Basilica of St. Francis, Upper Church, Life of St. Francis of Assisi: St. Francis Preaching to the Birds, c. 1291; possibly painted by Pietro Cavallini and workshop
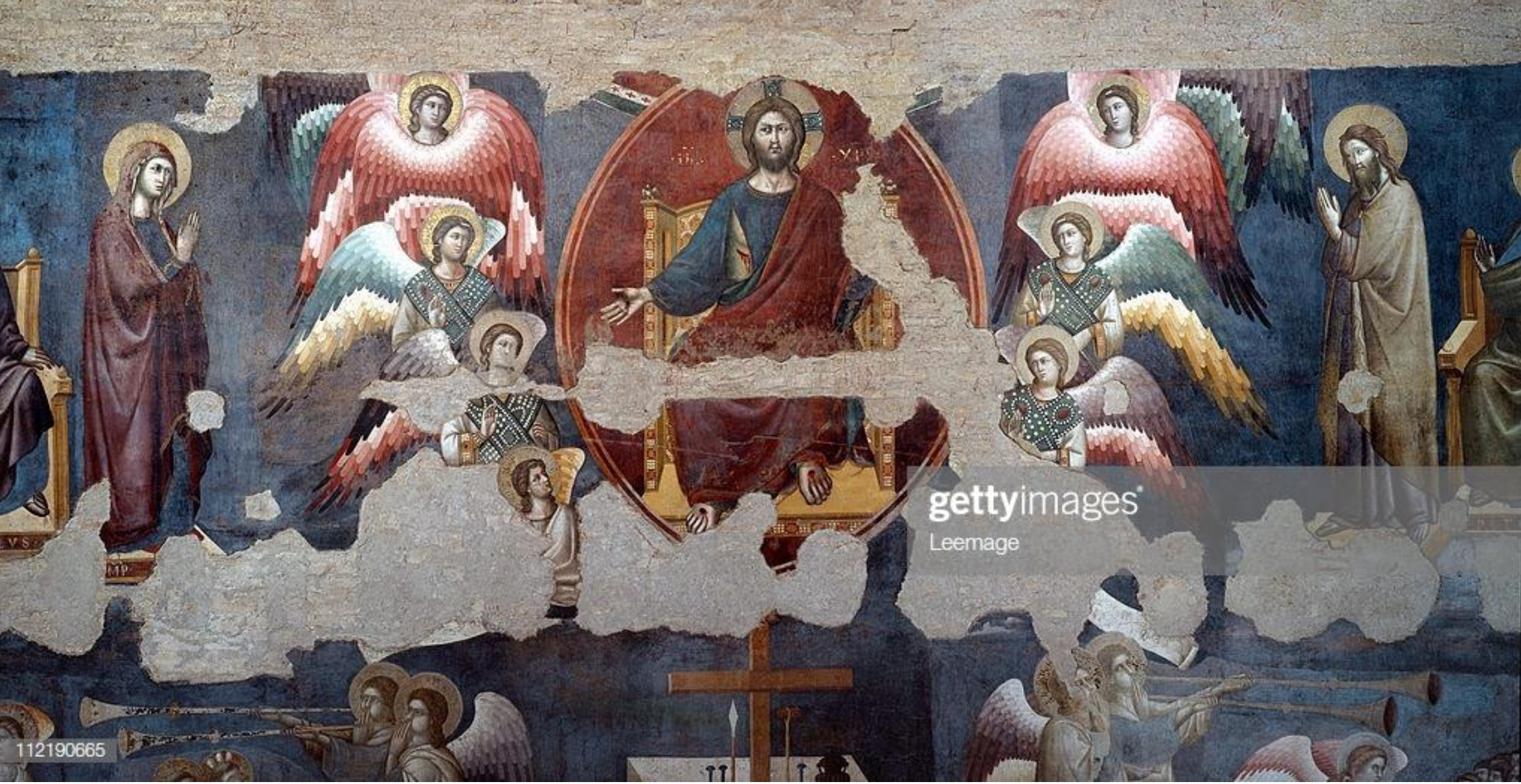

70. *Rome, Santa Cecilia: detail of the Last Judgement fresco by Pietro Cavallini, c. 1293
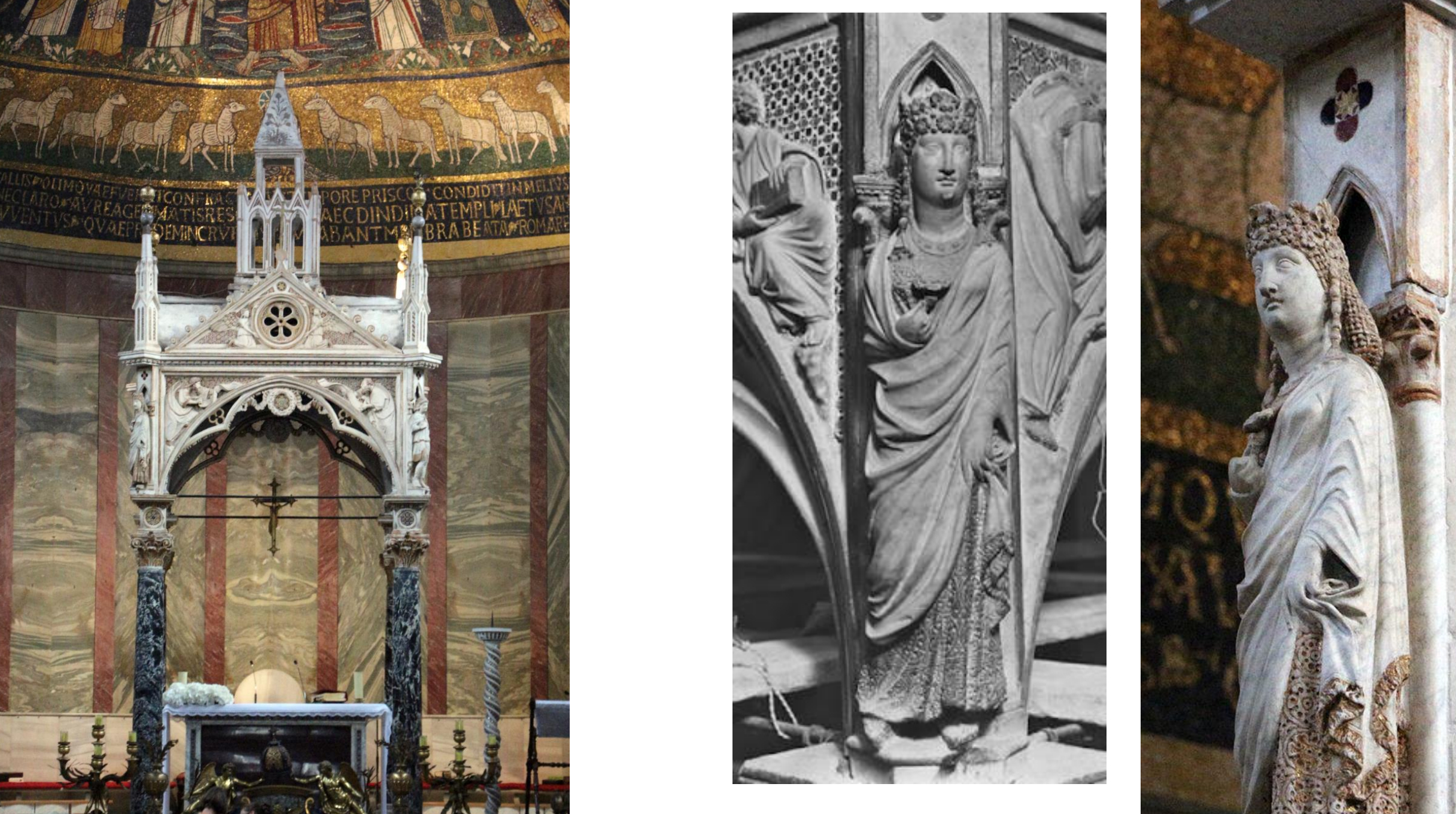

71. Arnolfo di Cambio, Ciborium of Santa Cecilia in Trastevere, c. 1293; detail shows Santa Cecilia
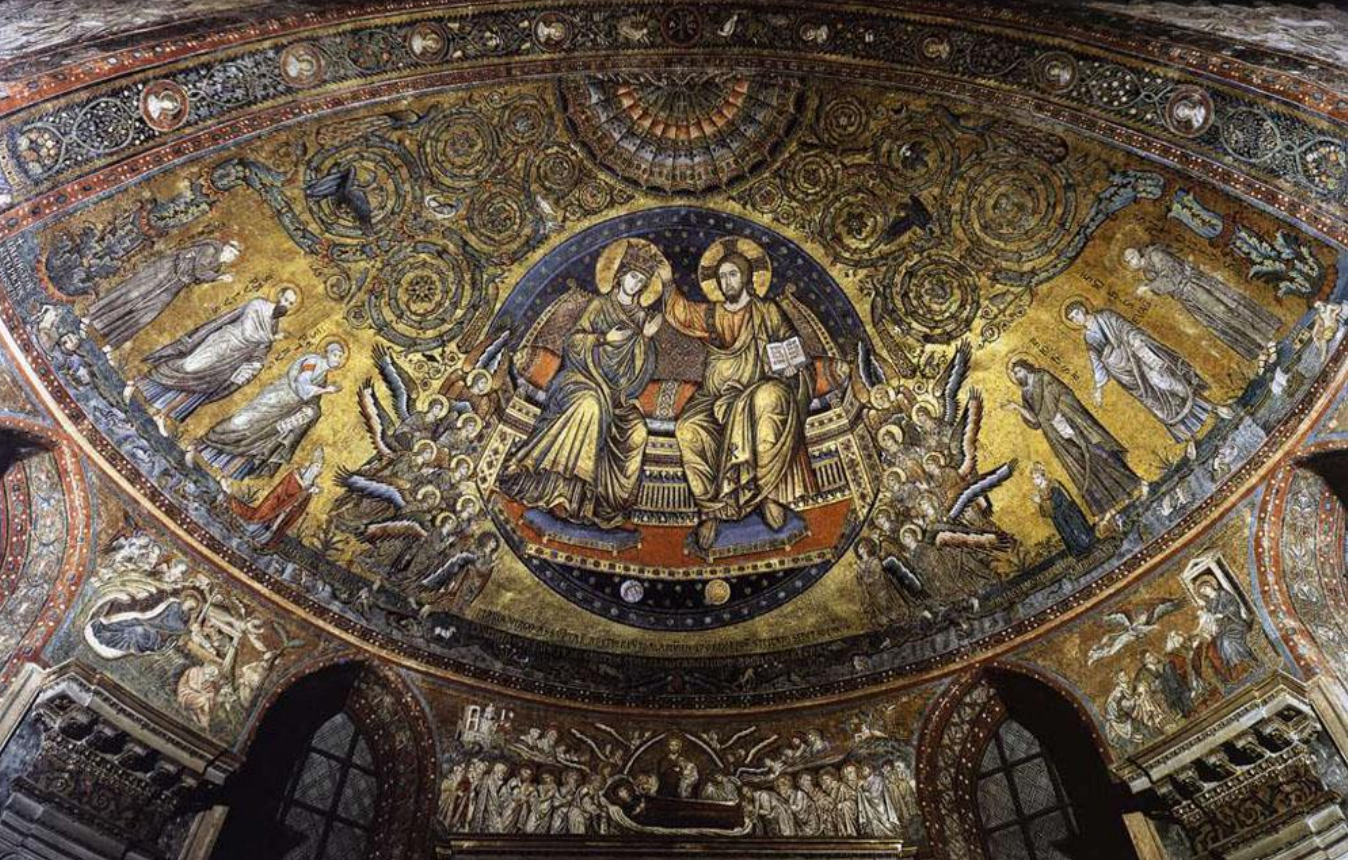

72. *Rome, Santa Maria Maggiore apse mosaic: Coronation of the Virgin; Jacopo Torriti and Jacopo da Camerino, c. 1296

73. Cimabue, Virgin and Child Enthroned, and Prophets (Santa Trinita Maestà), c. 1290-1300; tempera on wood with gold leaf gold background
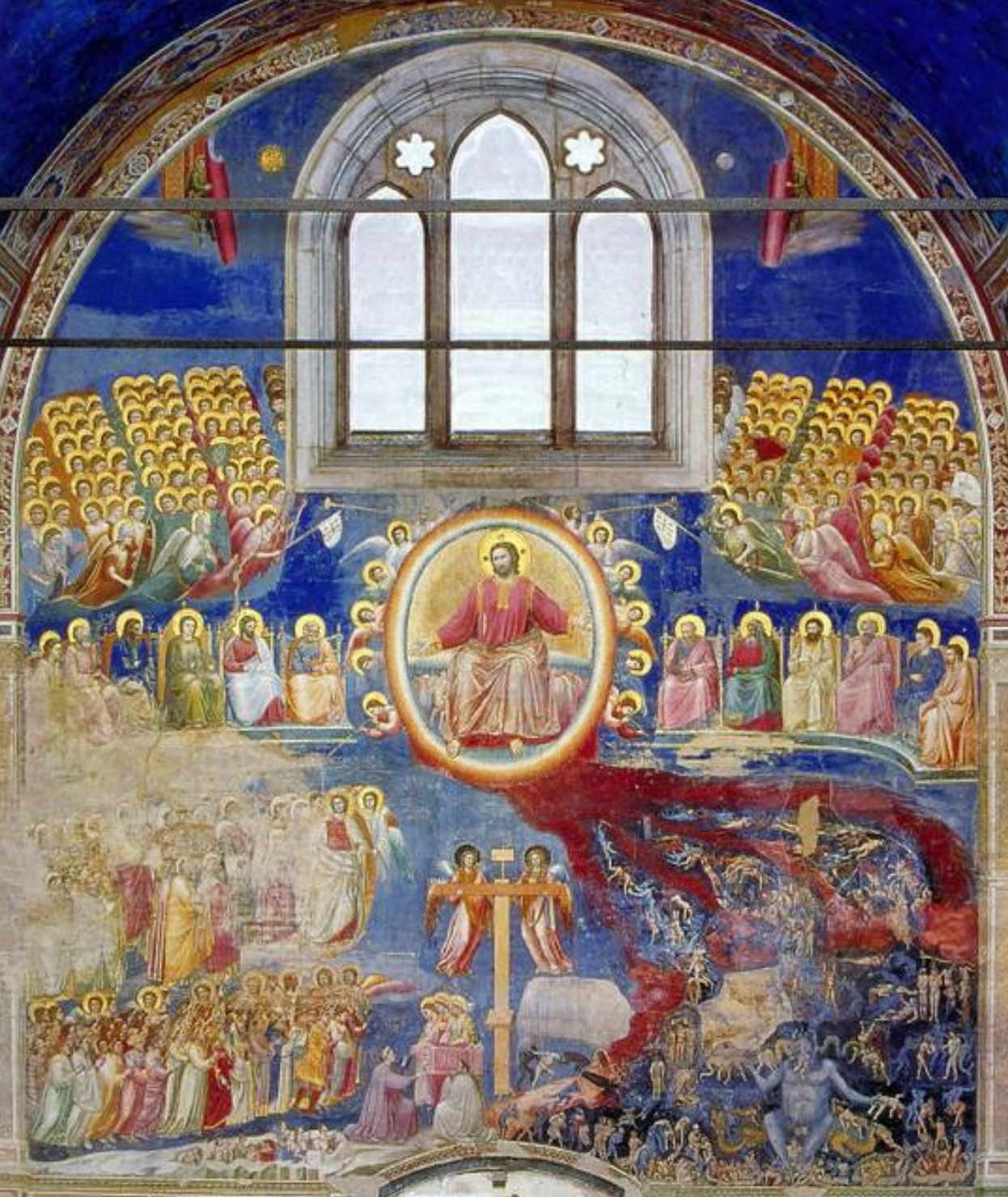

74. *Padua, Arena/ Scrovegni Chapel: Giotto, Last Judgment, completed, 1305.
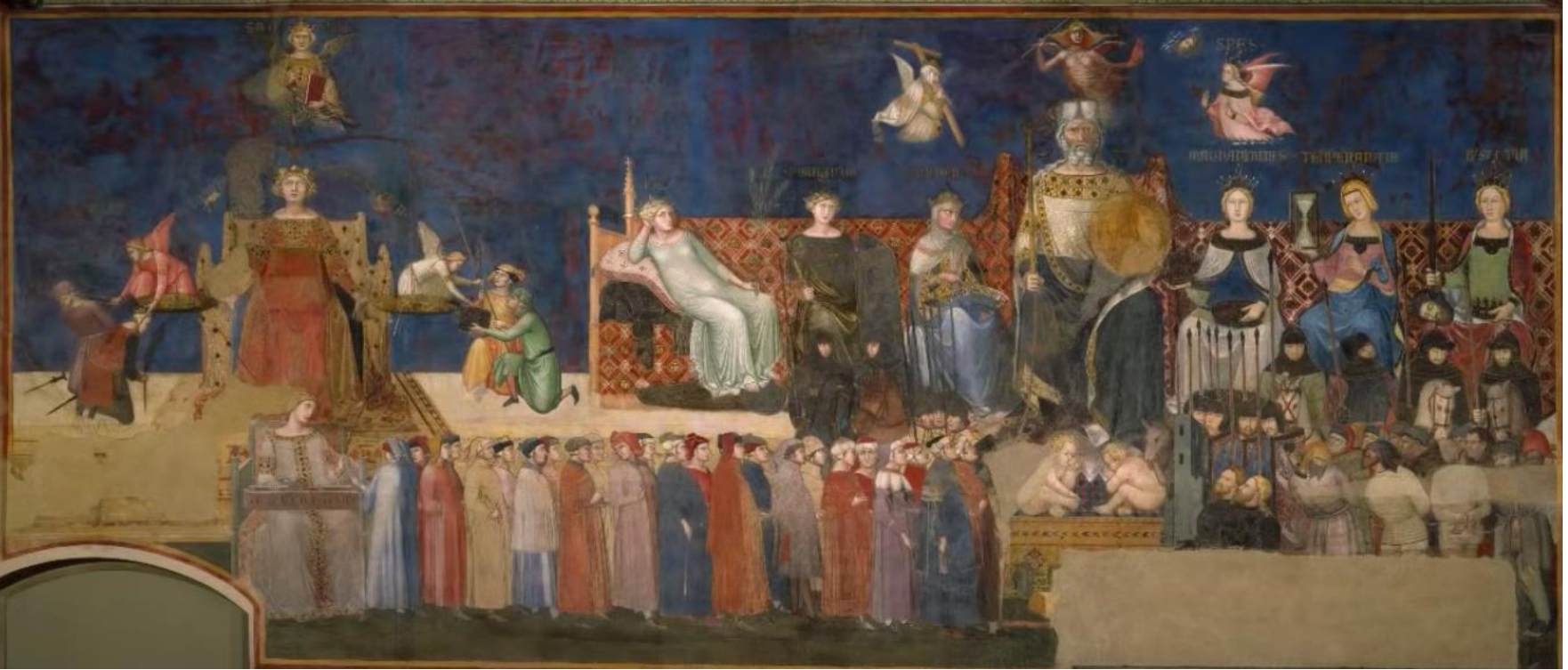

75. *Siena, Palazzo Pubblico fresco by Ambrogio Lorenzetti: Allegory of Good Government, 1338-1339; council hall fresco commissioned by the Council of Nine (the city council); detail shows Pax