Alkenes as Electrophiles
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
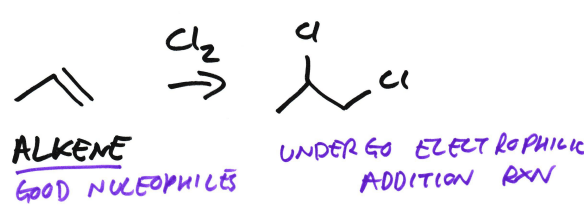
Are alkenes good nucleophiles?
Yes
Alkenes undergo…
electrophilic addition reactions
Are aromatics good nucleophiles?
Generally no.
Aromatic rings are resonance-stabilised, and nucleophilic attack would disrupt aromaticity, which is energetically unfavourable.
They only behave as nucleophiles toward very strong electrophiles, and electron-donating substituents increase nucleophilicity.
Can aromatics be electrophiles?
Yes.
Aromatic rings can act as electrophiles in nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) reactions, if the ring is electron-poor (e.g. contains strong electron-withdrawing groups like –NO₂) and has a good leaving group (e.g. Cl, F).
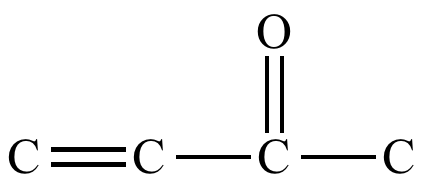
Is enone a type of α, β - unsaturated carbonyl?
An enone is a type of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl, but not all α,β-unsaturated carbonyls are enones.
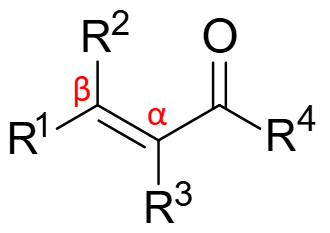
Why are α, β - unsaturated carbonyls toxic?
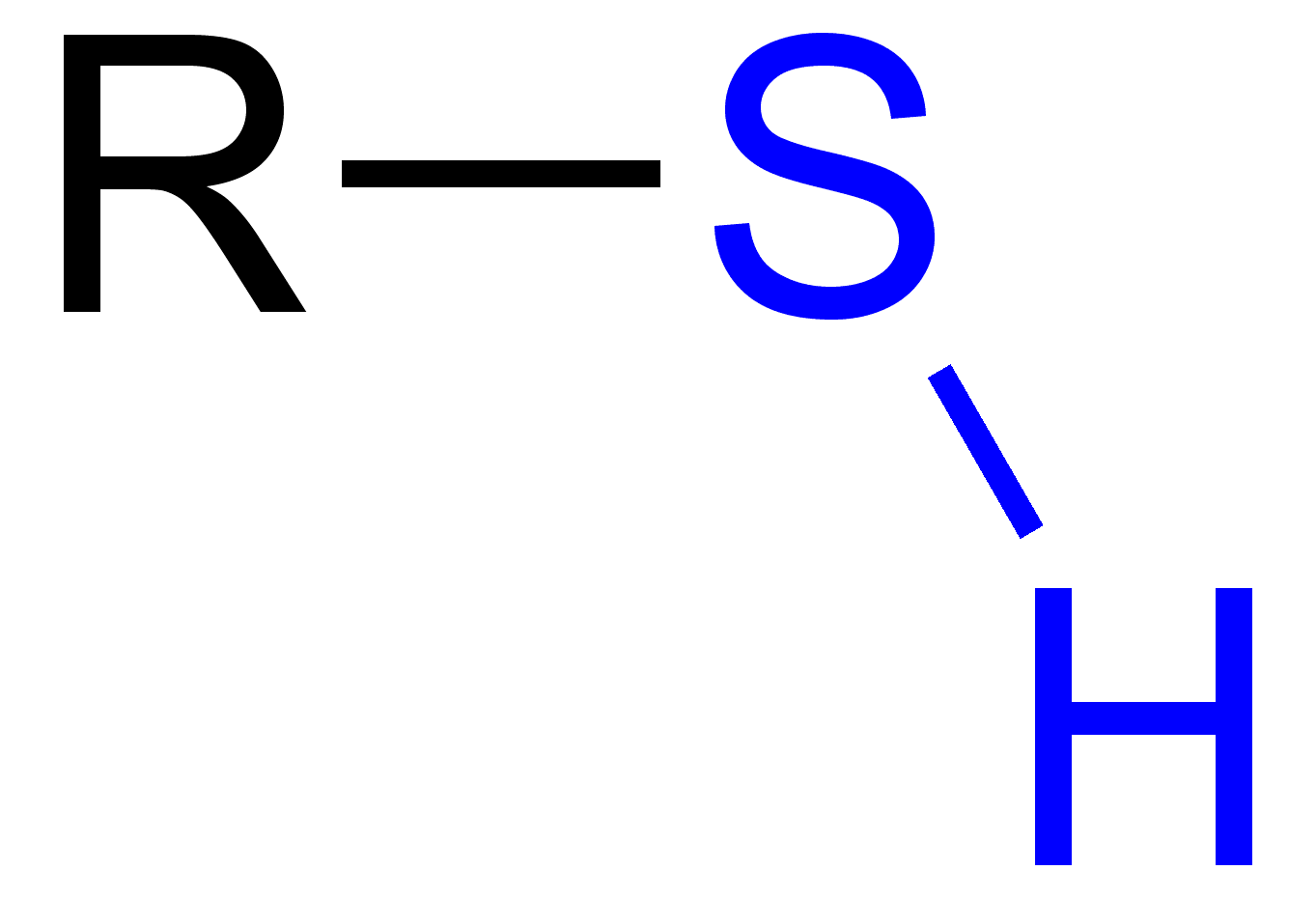
Since α, β - unsaturated carbonyls are electrophilic, they are readily reactive to nucleophiles e.g. R-OH, R-SH, R-NH2
This allows them to covalently bind to DNA, amino acids, proteins (which have these nucleophiles) and stop their function
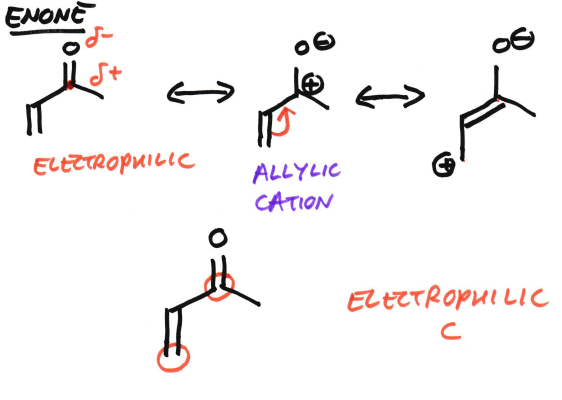
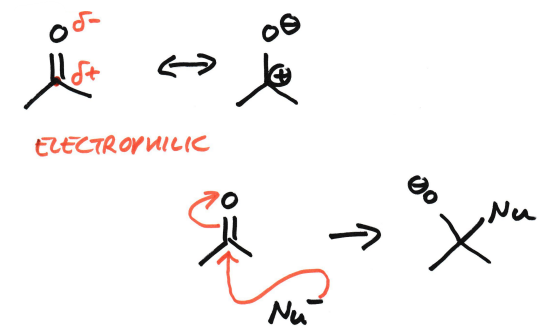
Why are enones electrophilic?
Which carbons can nucleophiles attack?
The C=O bond is polar (so the carbonyl carbon is already electrophilic)
The C=C-C=O system is conjugated, allowing for π-electron delocalisation
Resonance places partial positive charge on both the carbonyl carbon and the β-carbon.
Therefore nucleophiles can attack at:
• the carbonyl carbon (1,2-addition)
• the β-carbon (1,4-/Michael addition)
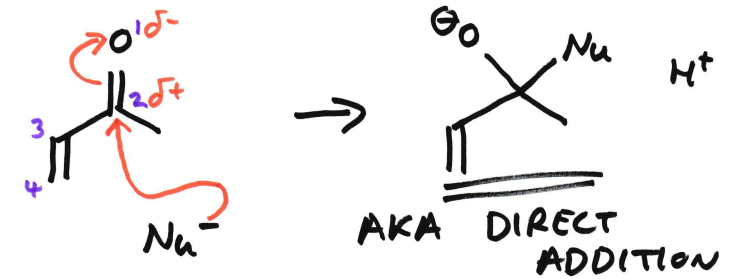
1,2-Addition in enone
The numbering is 1 to 4, with 1 being oxygen.
The nucleophile attacks the 2 C which then attacks the 1 O. Therefore it is called 1,2-addition.
Also known as direct addition
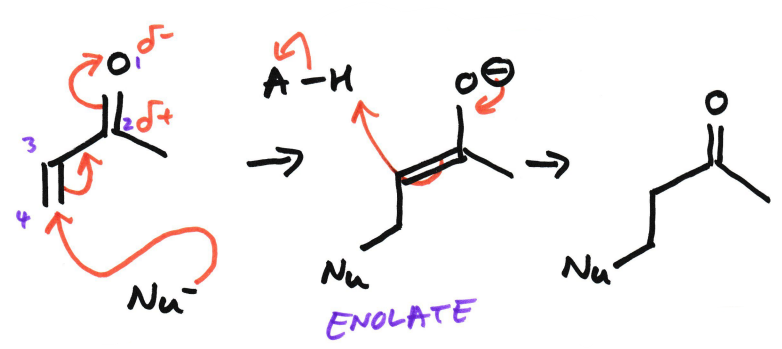
1,4-Addition in Enone
The numbering is 1 to 4, with 1 being oxygen.
The nucleophile attacks 4 C. The pi bond breaks because the pi bond is weaker. A bond is formed between the nucleophile and 4 C. A double bond is formed between 2 and 3 and then the carbonyl double bond is broken. An enolate is formed.
Also known as conjugate addition and Michael addition
What factors influence where the addition is 1,2 or 1,4 in enone?
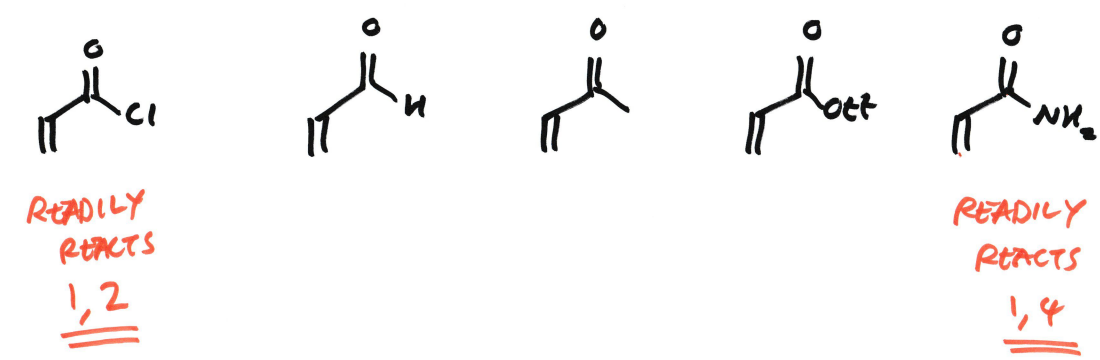
Are ketones electrophilic?
Yes
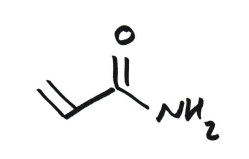
Acrylamide
Toxic

Thiol group
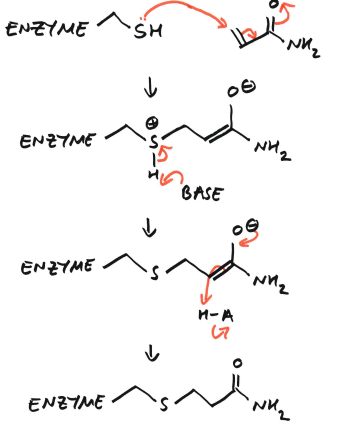
Q) Show how acrylamide is toxic:
The enzyme cysteine (-SH) side chain acts as a nucleophile
The nucleophile attacks the β-carbon of acrylamide, forming an enolate intermediate (1,4-addition)
The sulfur becomes positively charged
Because it is positively charged, it is electron poor. This weakens the S-H bond and sulfur can no longer “hold on to” the hydrogen’s electrons well, making hydrogen behave like a H+.
The S-H group becomes much more acidic so a base removes the H+ to neutralise the molecule and form a stable S-C bond
The enolate oxygen is protonated
The enzyme is covalently alkylated and the bond is therefore irreversible, altering the active site, causing loss of enzyme function.
What is the glutathione (GSH) molecule?
Made up of glutamate, cysteine, glycine
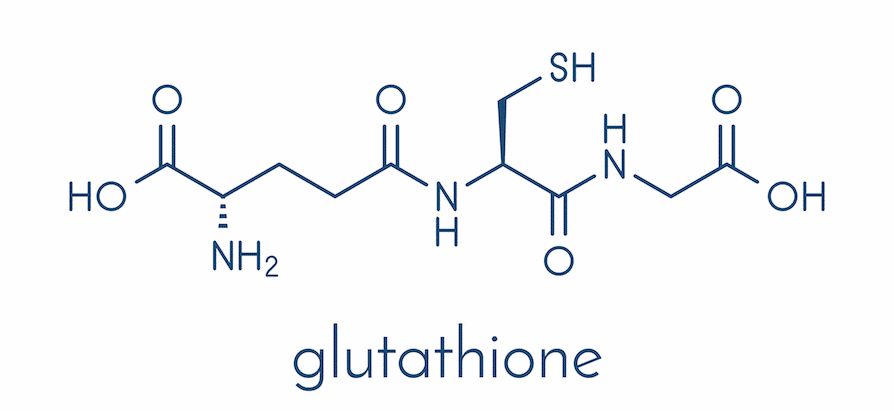
Why is glutathione important in detoxifying α, β - unsaturated carbonyls?
Because α,β-unsaturated carbonyls are electrophilic Michael acceptors, they readily react with cellular nucleophiles like DNA and proteins.
Glutathione detoxifies them by donating its thiol group (–SH) to perform a Michael addition, forming a stable, non-toxic GSH-conjugate that can be safely excreted