15.4 Sympathetic Division
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
sympathetic division
function: energy and exercise, “fight or flight division”
thoracolumbar division (T1-L2)
two types of ganglia:
sympathetic trunk ganglia
prevertebral ganglia
sympathetic preganglionic neurons
cell bodies housed within lateral horn of T1-L2
sympathetic trunks
left and right trunks later of cerebral column
pearl necklace
string of axons
pearls of sympathetic trunk ganglia housing bodies
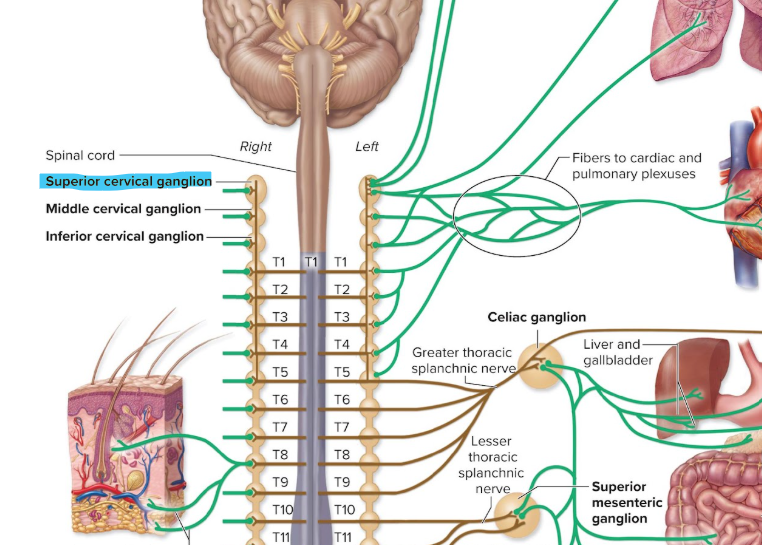
superior cervical ganglion
cells have postganglionic axons going to head, neck, thoracic viscera
targets: sweat glands, blood vessels, dilator pupillae muscle of eye, superior tarsal muscle of eyelid
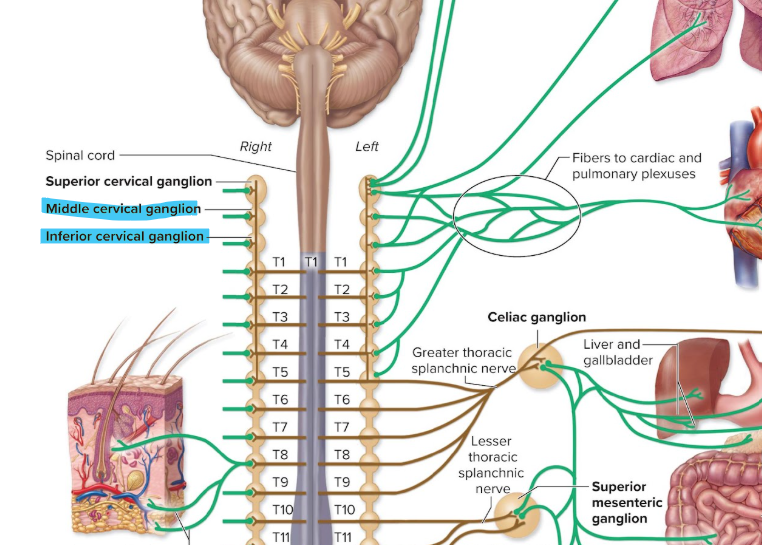
middle and inferior cervical ganglion
cells have postganglionic axons that innervate neck structures and thoracic viscera
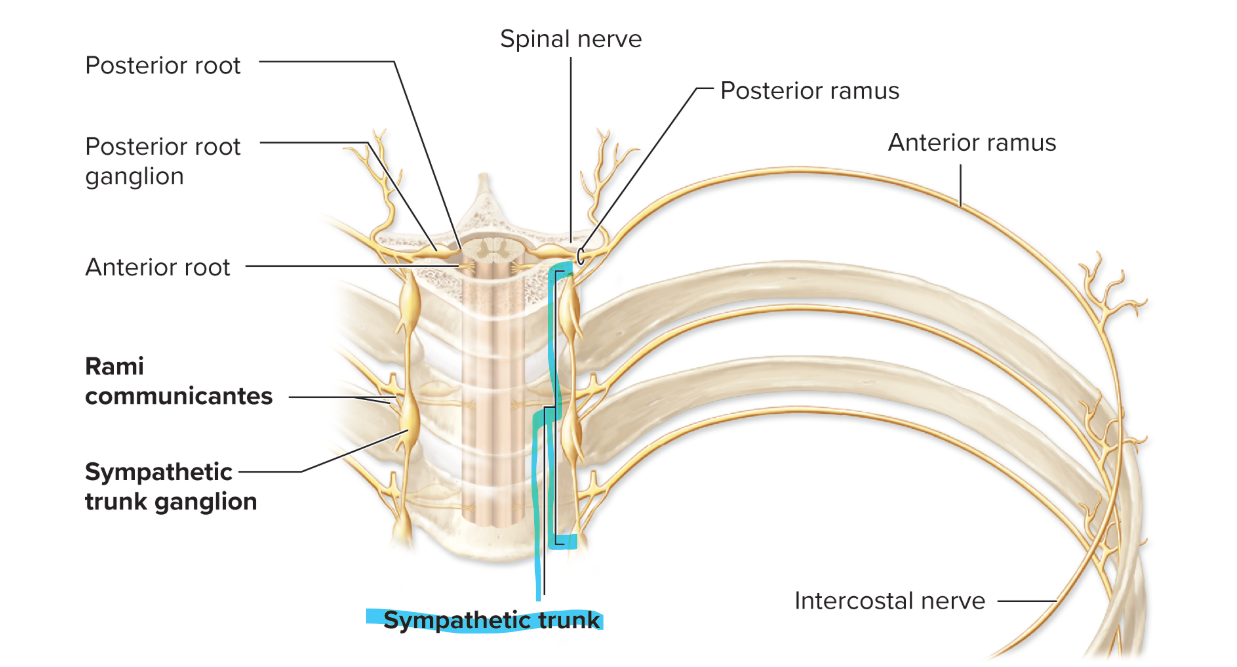
white and gray rami
connect spinal nerves to sympathetic trunk
white rami communicantes
carry myelinated preganglionic sympathetic axons from T1–L2 nerves to trunk
“Entrance ramps” to trunk
gray rami communicantes
Carry unmyelinated postganglionic sympathetic axons from trunk to all spinal nerves
“Exit ramps” from trunk
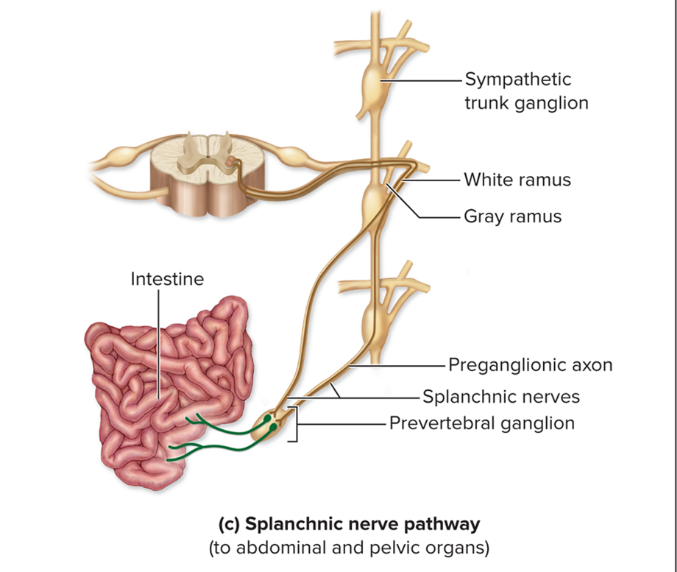
Sympathetic splanchnic nerves
not synapsing in sympathetic trunk
typically terminate in prevertebral ganglia
prevertebral ganglia
celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric ganglia
celiac ganglia
greater thoracic splanchnic nerves enter
axons innervate stomach, duodenum, spleen, liver, gallbladder, pancreas (digestive organs)
T5-T9
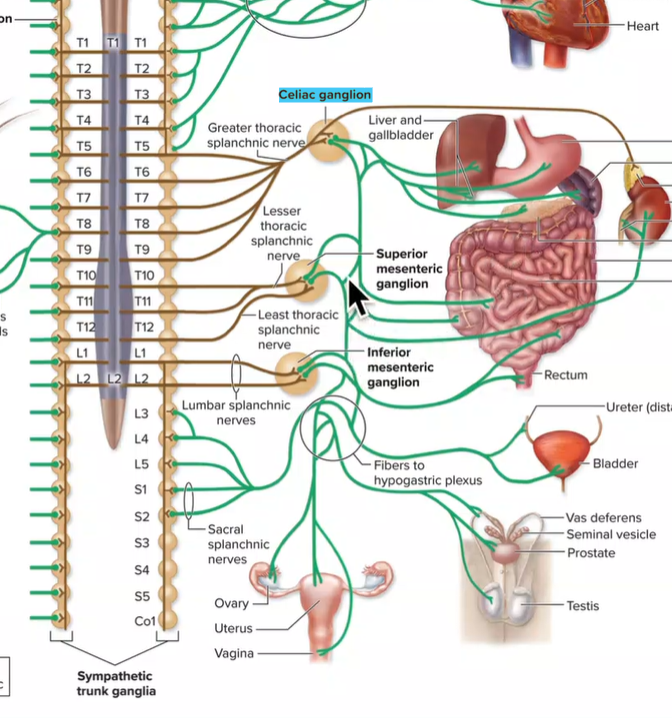
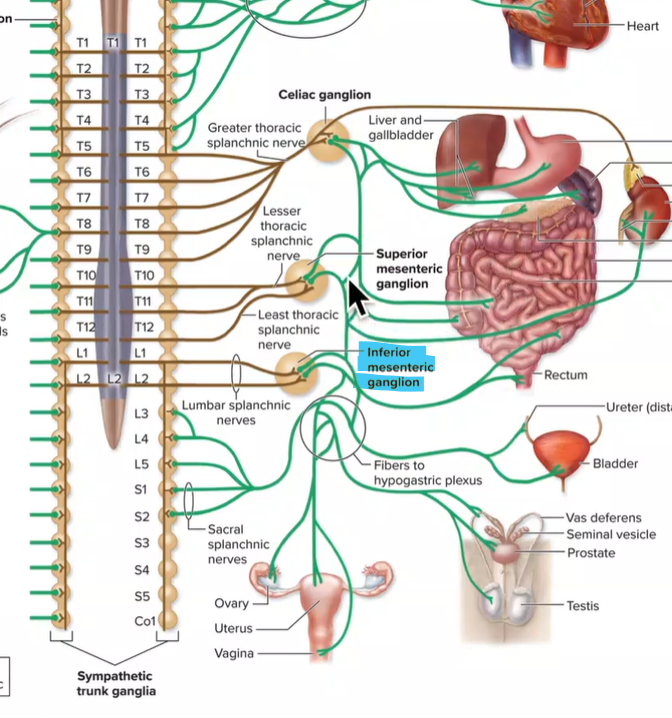
Superior mesenteric ganglia
Lesser and least thoracic splanchnic nerves enter
Postganglionic axons innervate small intestine, large intestine, pancreas, kidneys, ureters (digestive, kidneys)
T10-T12
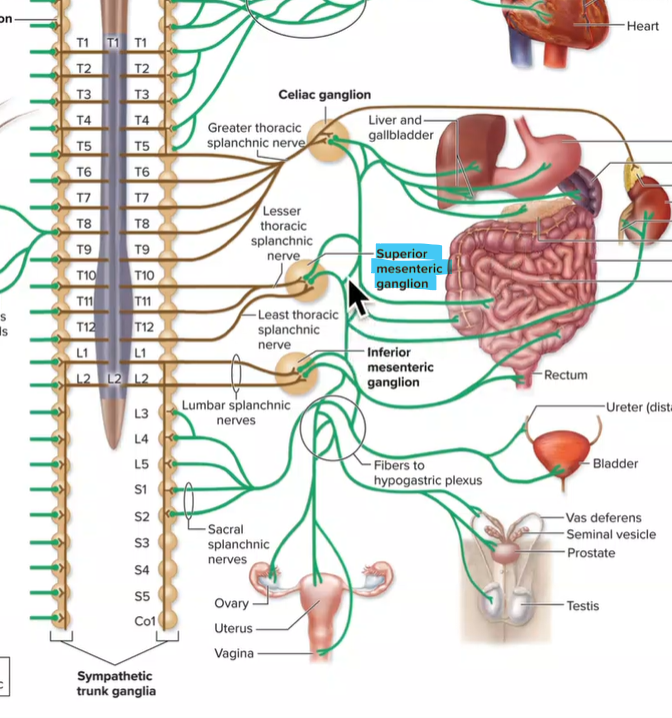
Inferior mesenteric ganglia
Lumbar splanchnic nerves enter
Postganglionic axons innervate large intestine, rectum, bladder, ureters, reproductive organs (digestive and urinary)
L1-L2
Sympathetic Pathways
Axons exit the sympathetic trunk by one of these four pathways
spinal nerve pathway
postganglionic symp. nerve pathway
splanchnic nerve pathway
adrenal medulla pathway
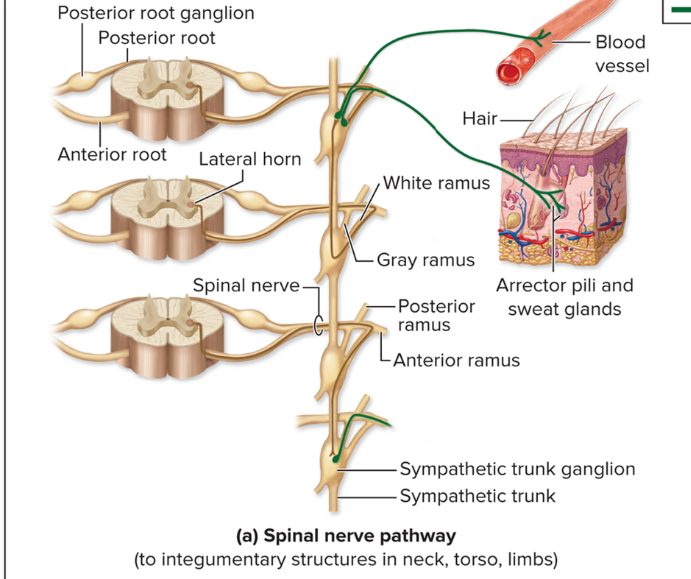
spinal nerve pathway
For skin effectors (For example, sweat glands) of neck, torso and limbs
Pre neuron enters sympathetic trunk ganglion and synapses with ganglionic neuron
Postganglionic axon travels through gray ramus at same spinal level as ganglion, joins that level’s spinal nerve and extends to effector
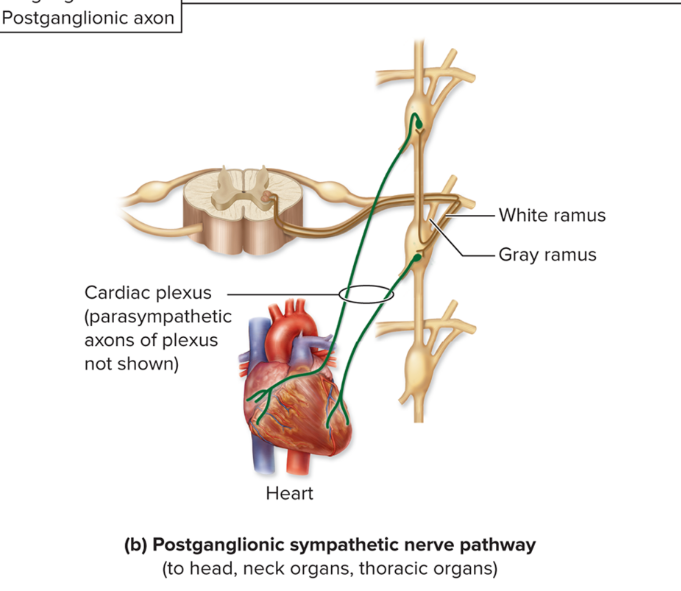
postganglionic sympathetic nerve pathway
For effectors that are internal organs of thorax and neck (for example, heart and esophagus); skin effectors of head and neck; eyelid and dilator pupillae muscles
Pre neuron enters and synapses in sympathetic trunk ganglion
Postganglionic axon goes directly from trunk ganglion to effector
Does not leave trunk via grey ramus
splanchnic nerve pathway
For effectors in abdominal and pelvic viscera
Pre axons pass sympathetic trunk without synapsing
Axons travel in splanchnic nerves to prevertebral ganglia where they synapse
Post axons innervate effectors
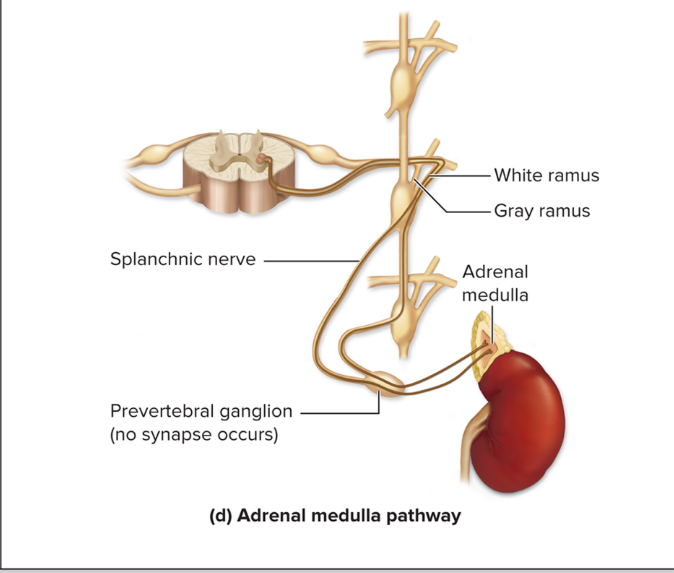
adrenal medulla pathway
For central region of adrenal gland (its medulla)
Pre sympathetic axons extend through sympathetic trunk and pre ganglia without synapsing in either
Pre cells stimulate adrenal medulla cells to release epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood
These hormones enhance and prolong the fight-or-flight response
Effector Stimulation: cardiovascular system
heart: increases heart rate and force of contraction
coronary arteries: vasodilation
Effector Stimulation: digestive system
salivary glands: viscous saliva
GI tract wall: decrease motility
pancreas: inhibit insulin, stimulate glucagon
liver: glycogenolysis
Effector Stimulation: respiratory system
bronchi/bronchioles: dilation to increase airflow
Effector Stimulation: urinary system
urinary bladder: retention of urine
kidney: release of renin, helps increase blood flow
Effector Stimulation: reproductive system
reproductive glands: stimulate release of secretions in male during ejac.
uterus and vagina: contraction of walls during orgasm
Effector Stimulation: integumentary system
arrector pili: contraction, goosebumps
sweat glands: release sweat
blood vessels: vasocontriction
Effector Stimulation: nervous system
iris: dilation
Effector Stimulation: other structures
Release of epinephrine/norepinephrine from adrenal medulla
lipolysis in adipose tissue
vasodilation of vessels in skeletal muscle