Functional Anatomy Quiz 1 Part 2
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Wear to Articular Cartilage
Interfacial Wear
Adhesion: fragments stick to each other
Abrasion: soft material is scraped by a harder one
Fatigue Wear
Tensile failure of collagen fibres
PG washout: degradation of these fibres due to excessive loads
Impact Loading: high stress too quickly does not allow fluid distribution to take place
Skeletal Muscle
Striated and Voluntary
Cardiac Muscle
Striated and Autonomous
Smooth Muscle
Smooth and Autonomous
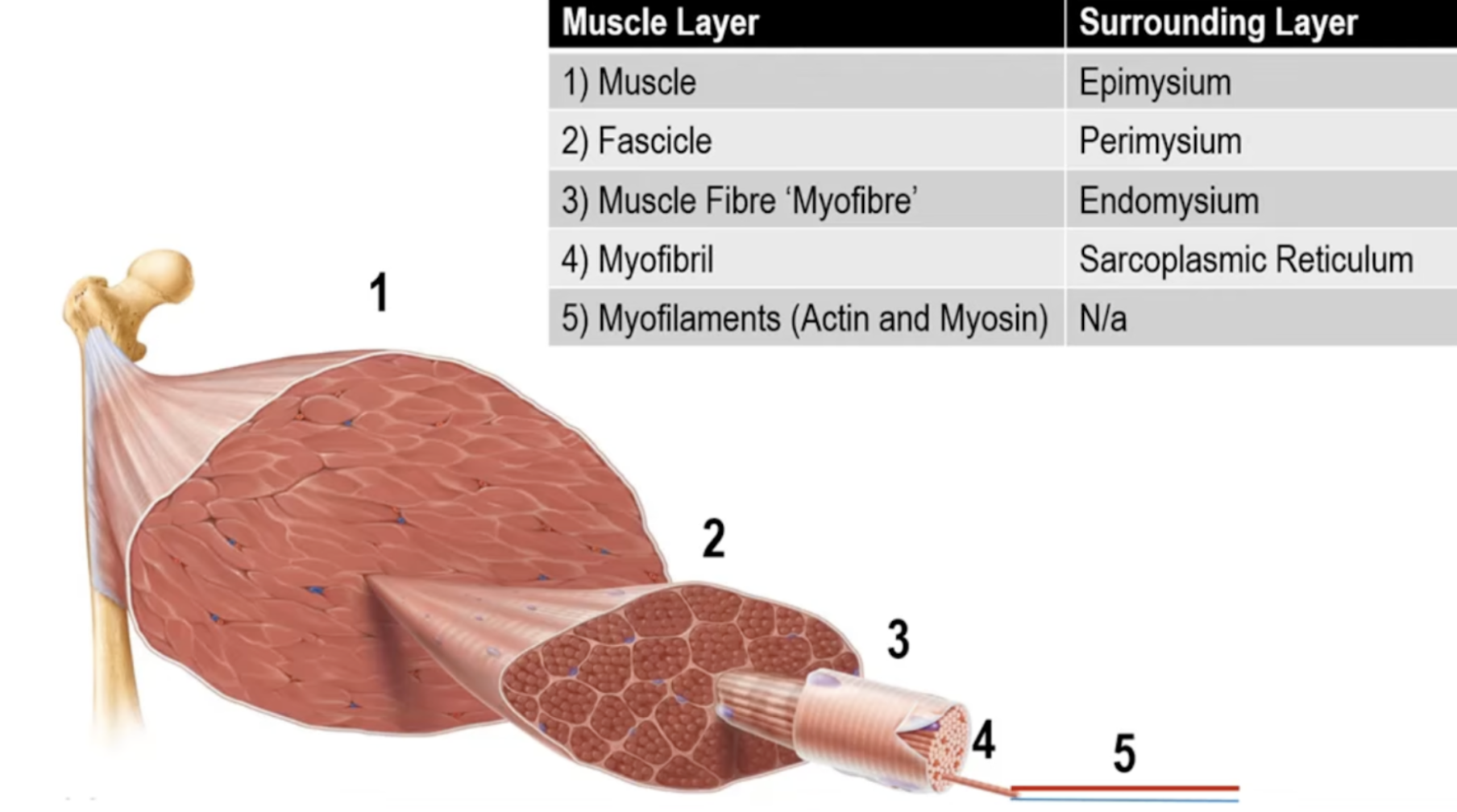
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
SR surrounds each myofibril
responsible for storing and regulating calcium
Muscle Layers
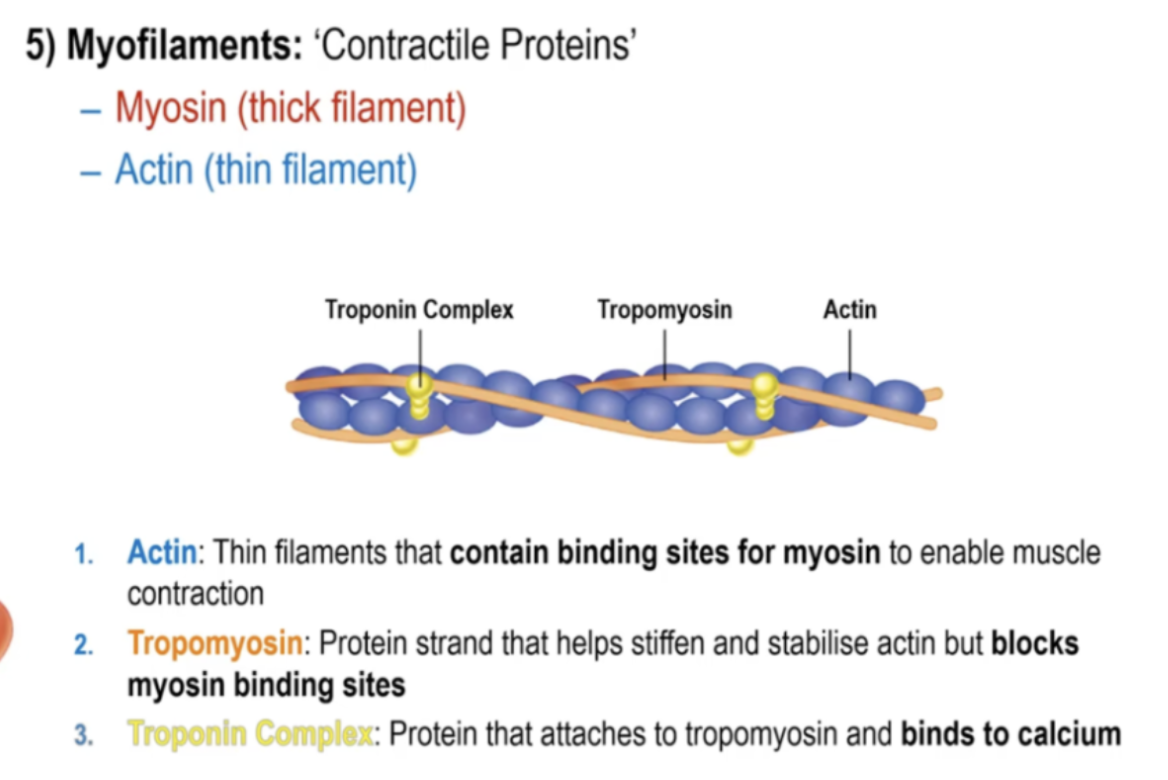
Myofilaments
Excitation - Contraction Coupling
Excitation
Step 1: Action Potential
Step 2: Diffusion
Step 3: Depolarisation
Step 4: Opening of Binding Sites
Excitation - Contraction Coupling
Contraction
Step 5: Cross Bridge
Step 6: Movement
Step 7: Release
Step 8: Preparation
Excitation - Contraction Coupling Notes
Notes
Step 9: The Action Potential
Step 10: Importance of Calcium
Muscle Length-Tension Relationship
If the length is too long, there is minimal overlap between myosin and actin
If the length is too short, actin becomes overlapped and functionally polarised in opposite directions
Muscle Load-Velocity Relationship
- velocity of a concentrically shortening muscle is inversely related to the external load applied
When the load is less than the force, a concentric contraction will occur
When the load is equal to the force, an isometric contraction will occur
When the load is greater than the force, an eccentric contraction will occur
Muscle Force-Time Relationship
The longer the contraction time, the greater the force
Muscle tension is influenced by the time for the tension to transmit through parallel elastic components to the tendon
Muscle Architecture
Muscle fibre arrangements
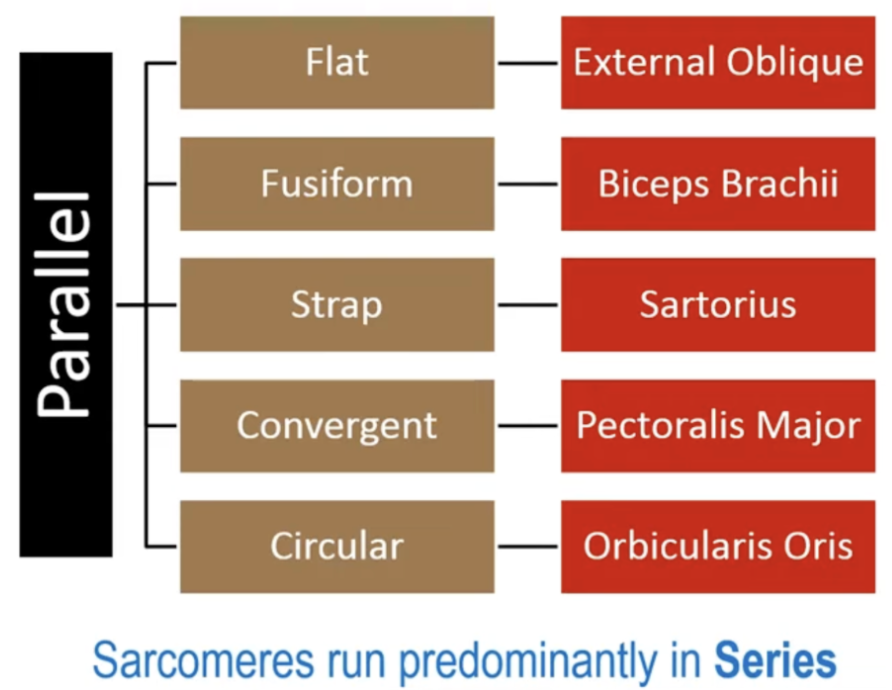
Fascicles attach obliquely to a central tendon called the aponeuroses
Muscles with long fibres and small cross-sectional areas are designed to produce movement and velocity (parallel)
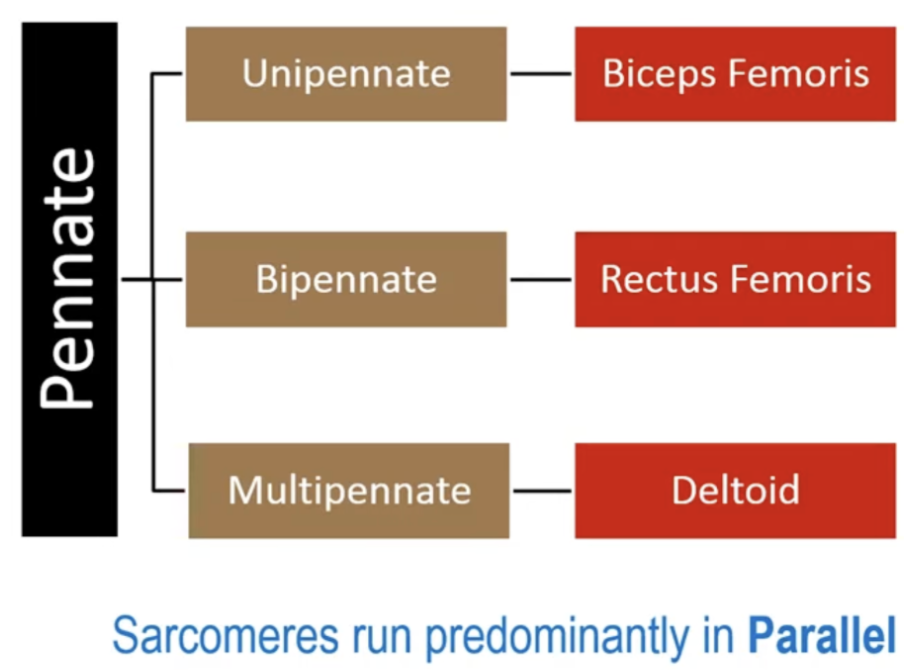
Muscles with short fibres and large cross-sectional areas are designed to produce force (pennnate)
Pararel Muscle Fibre Arrangement
Pennate Muscle Fibre Arrangement
Lifting Phase
harder
CONCENTRIC
SAME AS ACTION
Lowering Phase
easier
ECCENTRIC
OPPOSITE TO ACTION