US CONSTITUTION TEST (updated 2024) (copy)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
system of government in which power is divided between a central and state government
Federalism
laws will be fair and rules will be applied without exception; life, liberty, and property cannot be denied without this
Due Process

each branch of government can limit the power of the other two examples include presidential veto, Congressional override, and the court ruling a law unconstitutional
Checks and Balances
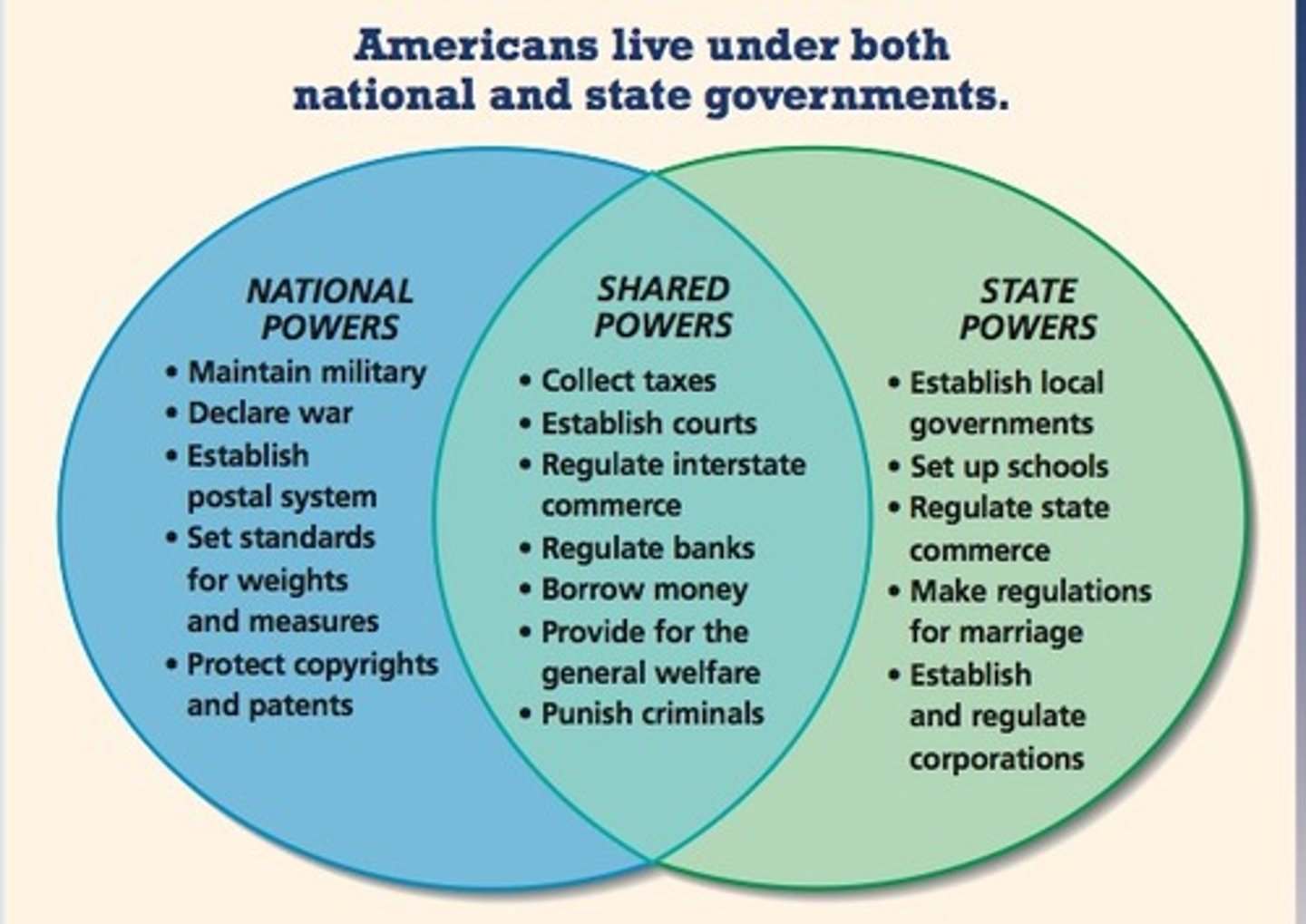
powers shared by the national and state government like making laws, collecting taxes, and establishing courts
Concurrent Powers
Montesquieu's idea that powers of government should be divided between separate branches
Separation of powers
comes from the people
Governmental power
Constitution
Supreme Law of the Land
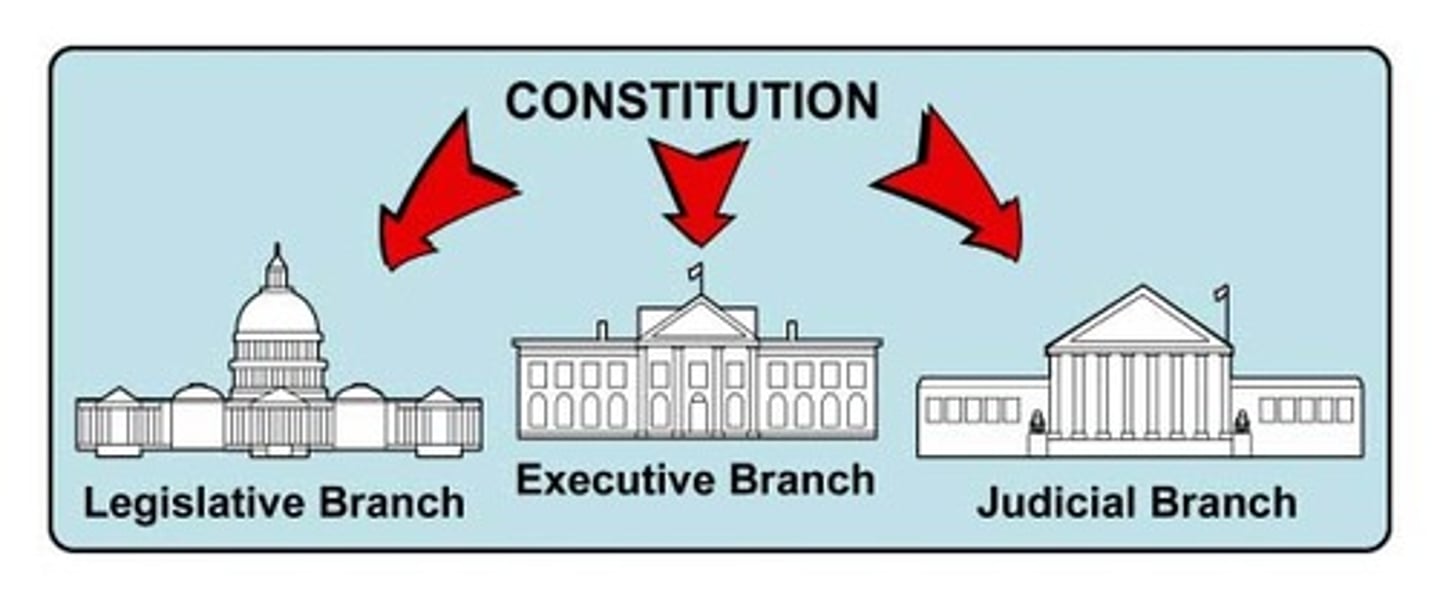
legislative, executive, judicial
Branches of Government

powers given just to states such as establishing schools, speed limits, and driving age
Reserved Powers

each state receives a number equal to members in Congress
Electoral Votes

national laws take precedence over state laws in a conflict
Supremacy clause

process by which a person of another country can become a US citizen
Naturalization

a person must be charged with a crime to be held more than 48 hours
Writ of Habeas Corpus

taken every 10 years
census

January 20th
Inauguration Day

appointed by the President to represent the US in foreign policy
Secretary of State
presides over the Senate
Vice President
officially elects the President
Electoral College
cabinet member appointed by the President to lead the Justice Department and act as the chief lawyer for the US government
Attorney General
VP, Speaker of the House, President Pro Tempore
Presidential Succession

appointed to oversee and coordinate counter-terrorism intelligence
Secretary of Homeland Security
appointment by President and confirmed by Senate
Federal Judges receive their positions
required to remove a federal judge from office, House accuses(impeaches) and Senate convicts
Impeachment process

Article 1, makes laws, made up of House and Senate
Legislative Branch

article 2 of the Constitution, made up of President and cabinet, enforces laws
Executive Branch

article 3 of the Constitution, made up of Supreme Court and lower courts, interprets laws
Judicial Branch

makes laws, approves cabinet choices and treaties, serves unlimited 6 year terms, 2 per state/100 total members
Senate

435 total, serve unlimited 2 year terms, selects the President if no candidate receives a majority of electoral votes
House of Representatives

25, citizen for 7 years, live in state you represent
US House of Representatives qualifications
30 years old, citizen for 9 years, live in state you represent
Senate qualifications
35 years old, resident of US for 14 years, natural born citizen
Presidential qualifications
4 years. Can serve 2 terms or 10 years total after 22nd amendment
Presidential Term
presides over the Senate in the absence of the Vice President
President Pro Tempore

leader of the House of Representatives
Speaker of the House
interpret laws
Role of Supreme Court
make laws
Role of Congress
enforce laws
Role of President
9 members who serve life terms, only qualification is good behavior
Supreme Court

approved by House and Senate, signed by President
Bill to become a law
the ability of the Supreme Court to declare a law or action unconstitutional
judicial review
voting age 18 , 18 year olds are the most recent group to earn the right to vote
26th amendment

abolished poll tax to prevent discrimination against certain voters
24th amendment

right to vote for residents of D.C.
23rd amendment

limited President to two terms or 10 years
22nd amendment

inauguration day
20th amendment
womens suffrage (right to vote)
19th amendment

right to vote regardless of race
15th amendment

defines citizenship; states cannot deny anyone equal protection of the law
14th amendment

powers not given to the national government or prohibited from the states belong to the states or the people
10th amendment

abolished slavery
13th amendment

added to the Constitution to make clear that basic rights were guareenteed even if they were not stated specifically
9th amendment
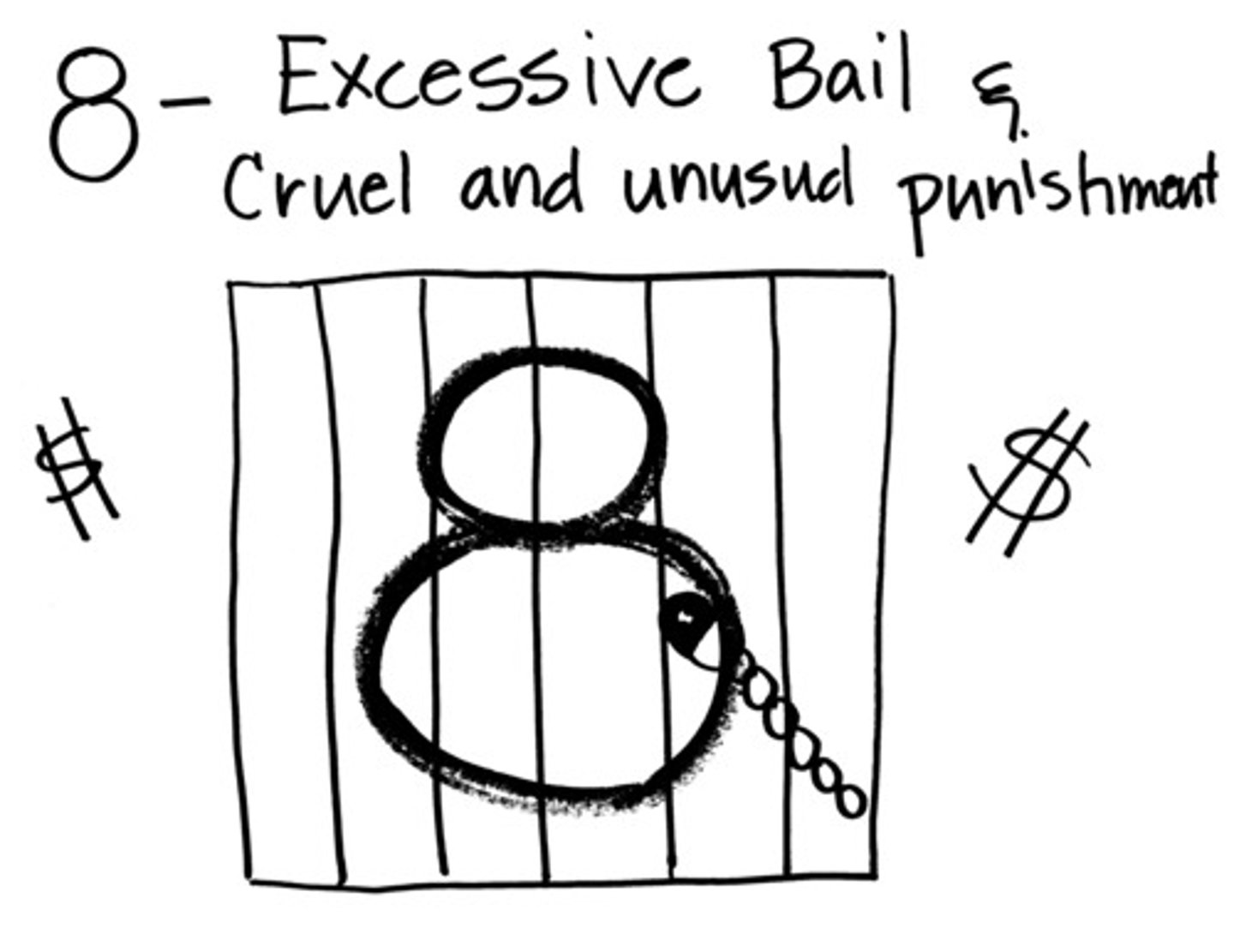
cruel and unusual punishment is not allowed
8th amendment
criminal proceedings (cannot be forced to testify against yourself), due process, double jeopardy and eminent domain
5th amendment

the government has the right to take your property given just compensation
eminent domain

protects citizens against unlawful search and seizure, a judge issued search warrant is required for searches
4th amendment

right to bear keep and bear arms
2nd amendment

freedom of speech, press, religion, assembly, and petition
1st amendment
