Physics I- Exam #2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
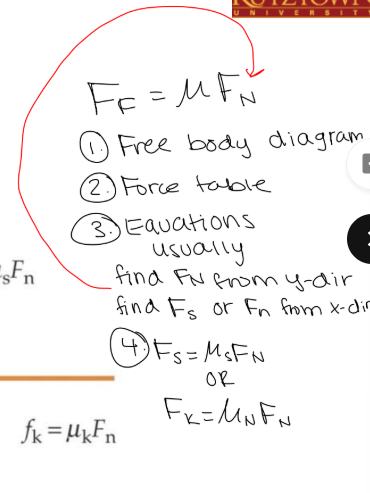
When an object is still at rest, f =
f = fs = -Fext
What is fs?
force of static friction
when an object is at rest
has a maximum:
fs,max = μsFn where μs is the coefficient of static friction.
When Fext > fs, max, f becomes the __
force of kinetic friction: fk = μkFn
In general, is the coefficent of kinetic friction or static friction larger?
μk < μs.
IN general, how do you solve for frictional force?
An object in circular motion must undergo a change in __
velocity → acceleration
Which way does centripetal acceleration point?
toward the center
What is required for centripetal acceleration?
object at constant speed (but acceleration changing)
circular path
Work is done when, and only when, an object __
when an object is moved
What are the units for work?
N.m = J
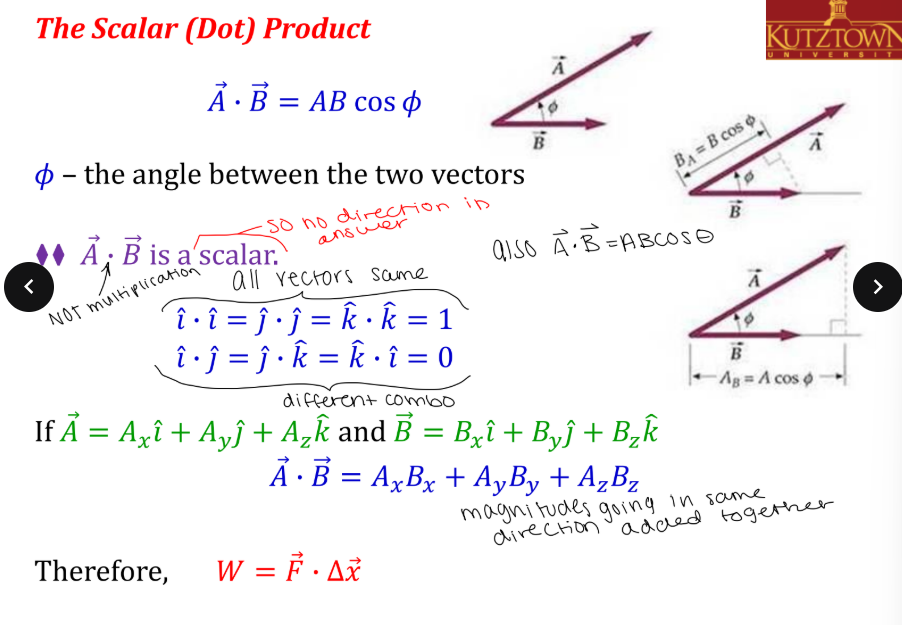
Is work a scalar or vector?
scalar; this means there is only magnitude, no direction and can be +, -, or 0
How do you solve for the scalar (dot) product?
Is kinetic energy a scalar or vector?
scalar
How do you solve for work from a graph?
work = area under the curve
What are the units of power (p) ?
J/s = W (watts)
Work done against a conservative force can be __
recovered (ex: gravitational force)
Non-conservative forces are __
dissipative (ex: friction)
Work done by a conservative force is __ and can be expressed as
is conservative force, can be expressed as potential energy
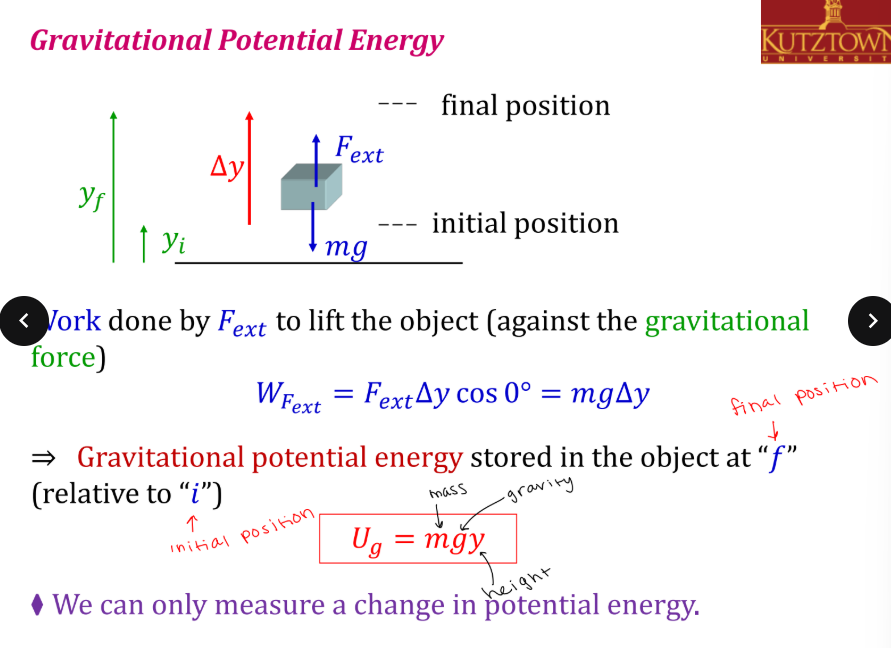
How do you solve for gravitational potential energy?
What is Hooke’s law?
force exerted on the mass by a spring
spring force is a conservative force
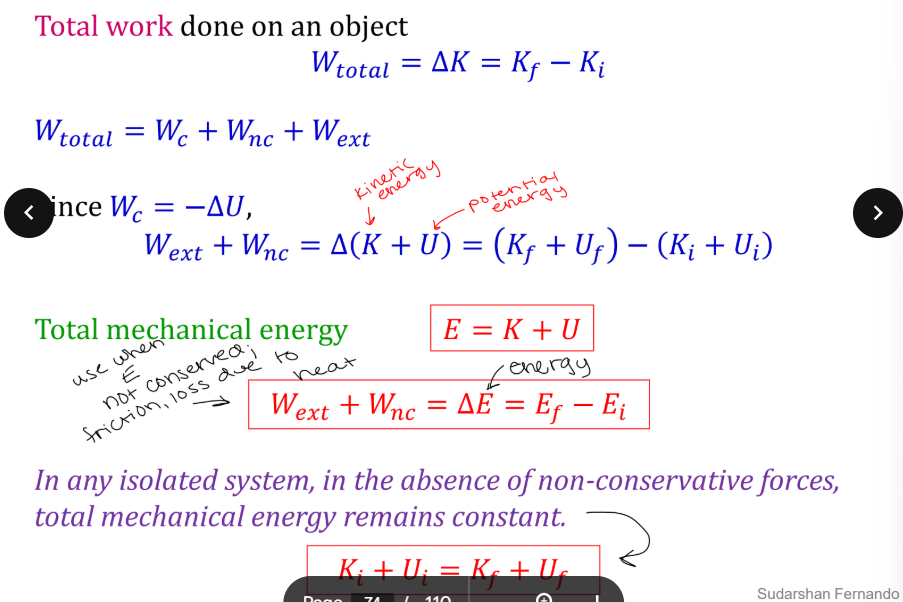
What is conservation of mechanical energy?
Is momentum a scalar or vector?
vector
What is the law of conservation of linear momentum?
if the sum of the external forces on a system remains zero, the total linear momentum of the system remains constant
During the collision, net force on the system is __
zero. total momentum must be conserved
In elastic collisions, __ is/are conserved.
both momentum (p) and k (kinetic energy)
speed of separation = speed of approach
In elastic collisions, __ is conserved
p is conserved, k is not
Wa=hat is the coefficient of restitution?
measure of elasticity of a collision closer to 0 = more perfectly inelastic
between 0 and 1
In perfectly inelastic collisions, __
objects stick together
What is the e value for elastic and perfectly inelastic collisions?
elastic: e=1
perfectly inelastic: e=0
What is center of mass?
“mean location” of all the mass in the system/object