AP - CT Types - Chapter 4
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Areolar Connective Tissue Overview
least specialized tissue and universal packing tissue
gel-like matrix with all 3 fibers (elastic, reticular, collagen) and many types of cells
its viscosity absorbs shocks
Areolar CT Function
wraps and cushions organs
phagocytic cells defend against pathogens
provides support and allows movement
Where is areolar CT located?
dermis of the skin
lines the digestive and respiratory tracts
between muscles and around joints
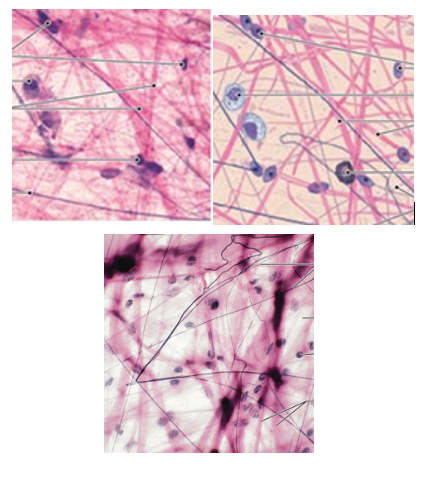
type
areolar tissue image
Adipose Tissue Overview
provides padding/packing around structures, insulator, absorbs shocks
adipocytes are metabolically active and deflate/inflate in response to lipid use
balloon like cell appearance
White Fat vs Brown Fat
white fat = pale, yellow; energy storage, insulation, hormone production
brown fat = deep, rich, brown; vascularized, upper body fat, only in young children
Adipose Tissue Function
insulates, provides packing/cushion, provides reserve energy storage
Where is adipose tissue located?
hypodermis
sides, buttocks
around eyes
breasts
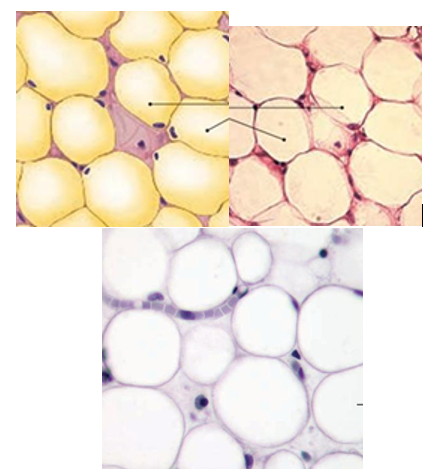
type
adipose tissue image
What type of CT is adipose tissue? (1)
Loose CT (1)
Reticular Tissue Overview
thin reticular fibers in 3-D network
resist forces (interwoven), stabilize positions of structures
cells are present; reticular fibers are darkly stained and look like squiggly lines
Reticular Tissue Function
makes supportive internal framework, supports other cell types (WBC, mast cells, macrophages)
Where is reticular tissue found?
liver
kidney
spleen
bone marrow
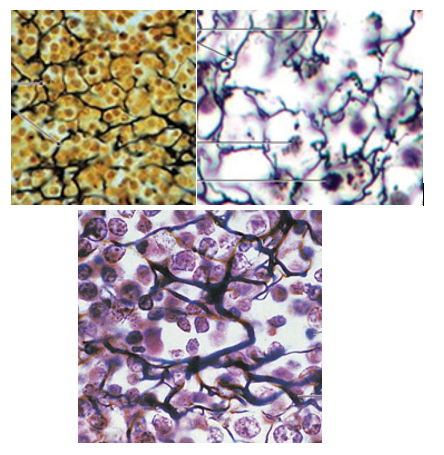
type
reticular tissue image
What type of CT is reticular tissue? (2)
Loose CT (2)
What are the three types of loose CT?
areolar
adipose
reticular
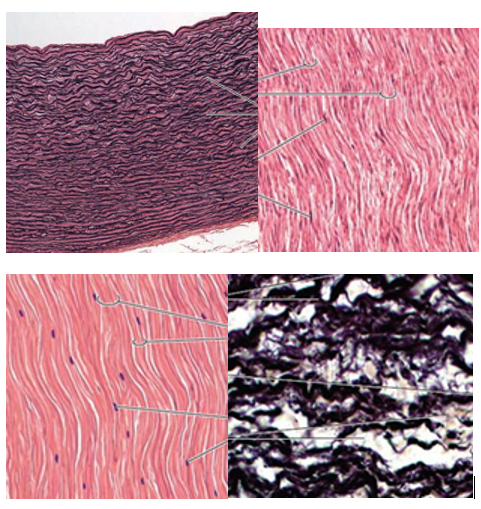
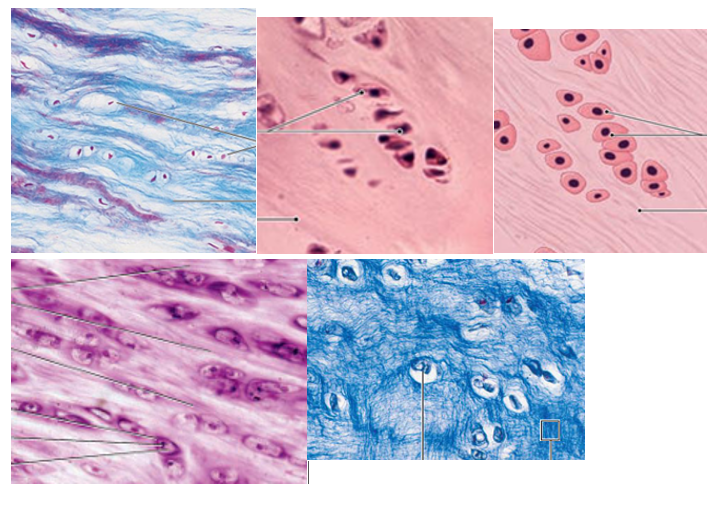
Dense Regular CT Overview
wavy bundles of collagen running in the same direction(great resistance to tension)
fibroblasts are present, but no other cells
poorly vascularized
Dense Regular CT Function
attaches muscles to bones, bone to bone, etc.
withstands great pulling force (parallel collagen fibers)
Where is dense regular CT located?
tendons
ligaments
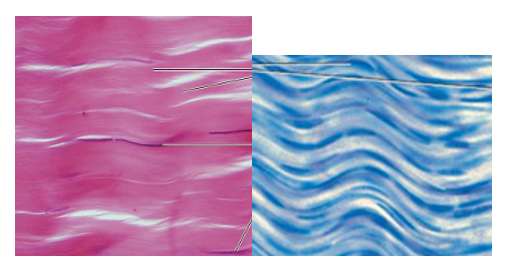
type
dense regular CT image
Dense Irregular CT Overview
same structure as regular CT (fibroblasts & collagen fibers) but collagen fibers are thicker and are arranged without pattern
helps withstand force from different directions
Dense Irregular CT Function
gives strength to resist tension in many directions
helps prevent over expansion of organs/structural strength
Where is dense irregular CT located?
fibrous capsules of joints/organs
dermis of skin
type
dense irregular CT image
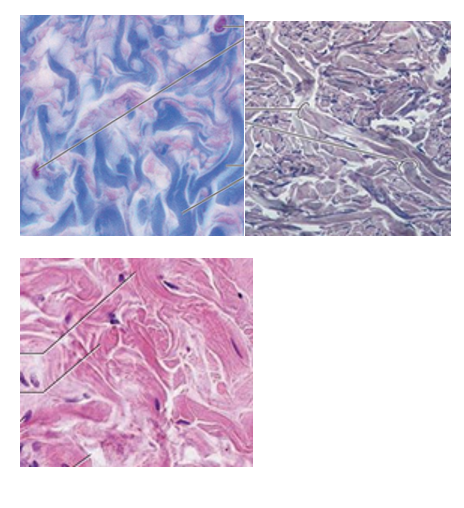
Elastic CT Overview
elastic fibers present (in abundance over collagen fibers)
allow extension and recoil
composed of fibroblasts and elastic fibers
Elastic CT Function
gives tissue ability to extend and recoil (organs pulsating)
stabilizes vertebrae and penis positions
Where is elastic CT located?
large artery walls (aorta)
bronchial tubes (breathing)
penis
between vertebrae
type
elastic CT image
Cartilage Overview
differs bc chondrocyte is the only cell present
avascular so cells use diffusion through perichondrium
injuries heal slowly
Chondrocytes are found in small openings called ______.
lacunae
What is the CT membrane that surrounds the cartilage mass?
the perichondrium
What are the 3 main elements of cartilage?
special cells
ECM
collagen fibers
Chondroblasts are ________ cells that grow into __________.
immature
chondrocytes
Chondroblasts Characteristics
found under perichondrium near outer surface
secrete ECM
become entrapped and mature into chondrocytes
Chondrocytes Characteristics
mature chondroblasts
divide and cluster to make lacunae
ECM Characteristics
Made up of
aggrecans = proteoglycan
water = 75% of ECM
collagen + more
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrous
Hyaline Cartilage Overview
most prevalent type
lower collagen amount gives translucent appearance
Hyaline Cartilage Function
gives stiff, somewhat flexible support and reinforcement
reduces friction between bony surfaces
resilient cushion/resists compression
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
embryonic skeleton
tips of ribs
sternum
trachea
nose/nasal septum
ends of bones at joints
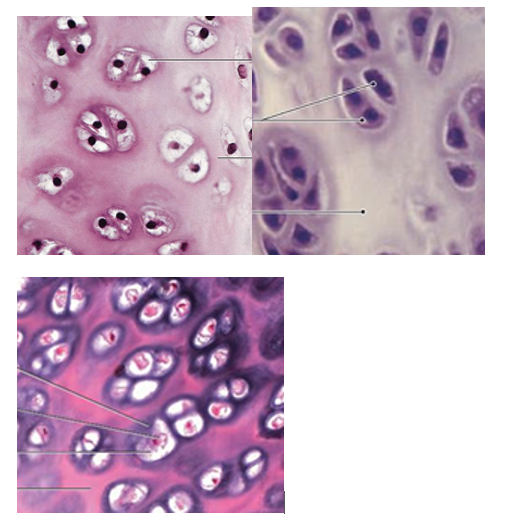
type
hyaline cartilage image
Elastic Cartilage Overview
few collagen fibers but abundance of fine elastic fibers
high degree of flexibility
Elastic Cartilage Function
maintains shape of structure but gives lots of flexibility
provides support
Where is elastic cartilage found?
external ear (pinna)
epiglottis
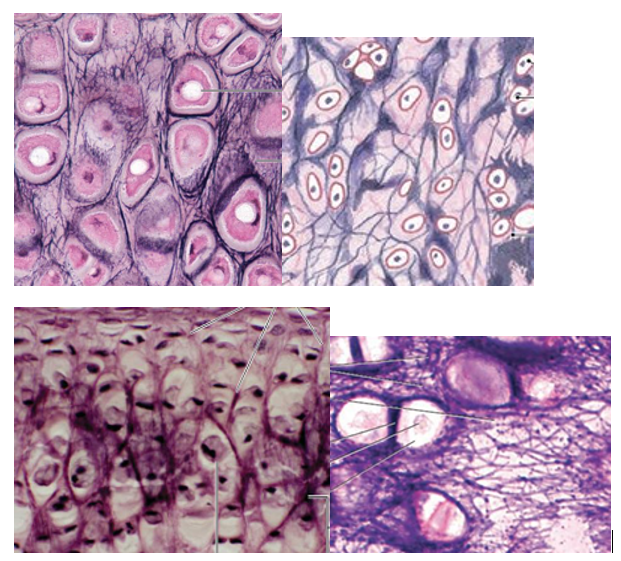
type
elastic cartilage image
Fibrocartilage Overview
little ground substance, high abundance of interwoven collagen fibers (very durable and tough)
resists compression
Fibrocartilage Function
tensile strength absorbs compression
prevents bone-to-bone contact
Where is fibrocartilage located?
intervertebral discs
pubic bones
disc of knee joint
type
fibrocartilage image
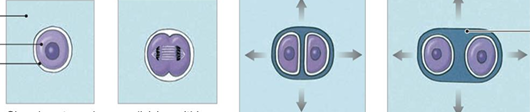
Interstitial growth grows cartilage from ________. Chondrocytes divide and daughter cells make ________. Its important in __________.
within
ECM
development
type
interstitial growth image
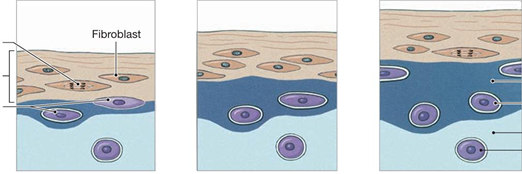
Appositional growth adds new layers to the _________. Cells differentiate into chondroblasts and secrete new _______. As new ECM enlarges, more chondroblasts are encased and mature into __________. This grows the amount of cartilage.
surface
ECM
chondrocytes
What are the 3 main functions of cartilage?
supportive framework for airways
forms articular surfaces of bone
is a template for the skeleton
type
appositional growth image
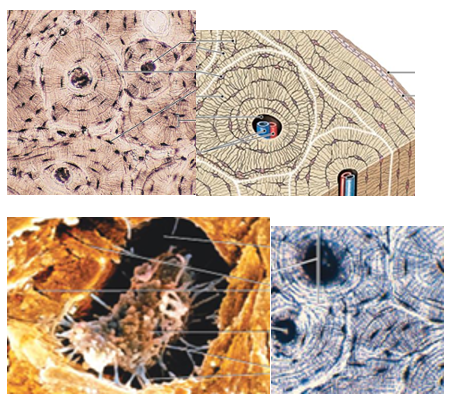
Osseus Tissue Overview
supports and protects body structures
matrix is similar to cartilage but is more rigid/harder bc of calcium salts and more collagen fibers
vascularized
__________ make organic part of matrix.
Osteoblasts
__________ reside in the lacunae.
Osteocytes
Bone units that are concentric rings with the central canal containing blood vessels.
Osteons
Osseus Tissue Function
hematopoiesis
lipid/mineral storage
support
protection
Hematopoiesis
formation of blood cells from stem cells in bone marrow
Lipid/mineral storage
bone holds adipose tissue and calcium in its crystals
type
osseus tissue image
Fluid CT Function
transport respiratory gases, nutrients, waste, etc.
Where is fluid CT located?
contained in blood vessels
What are elements in the blood?
RBCs = transport O2
WBCs = monocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, etc.
Platelets = blood clotting
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Overview
long, cylindrical, multinucleated cells with striations die to actin and myosin fibers
produce voluntary movement
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Function
moves/stabilizes skeleton
generates heat
facial expression
Where is skeletal muscle tissue located?
in skeletal muscles attached to bones
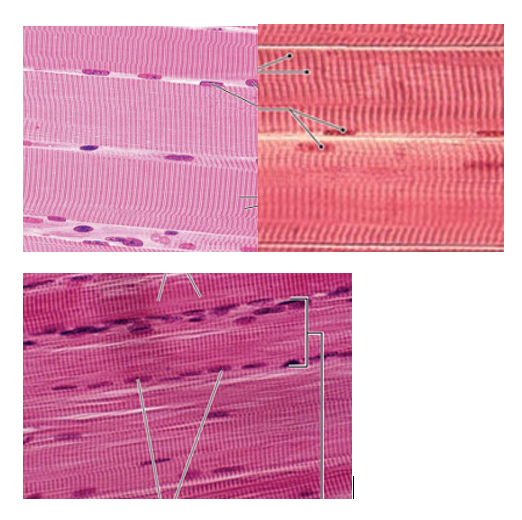
type
skeletal muscle tissue image
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Overview
centrally positioned nucleus, branching, striation, intercalated discs join cells together
connected via desmosomes and gap junctions which aid ion movement and synchronization between cells
limited repair ability
pacemaker cells set their own rate (striated involuntary muscle)
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Function + Location
contraction propels blood for circulation
walls of heart
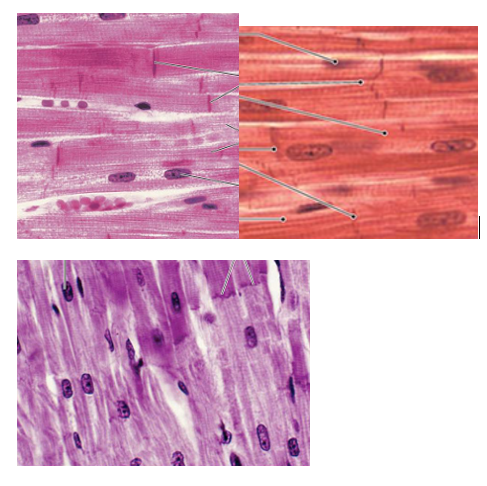
type
cardiac muscle tissue image
Smooth Muscle Tissue Overview
short, spindle-shaped, tapering ends, single nucleus
can regenerate after injury
actin/myosin have different arrangement = NO STRIATIONS
contract on their own (involuntary control) through gap junction coordination
Smooth Muscle Tissue Function
propels substances/objects through internal passages
Where is smooth tissue located?
walls of hollow internal organs (bladder, intestines, reproductive tract)
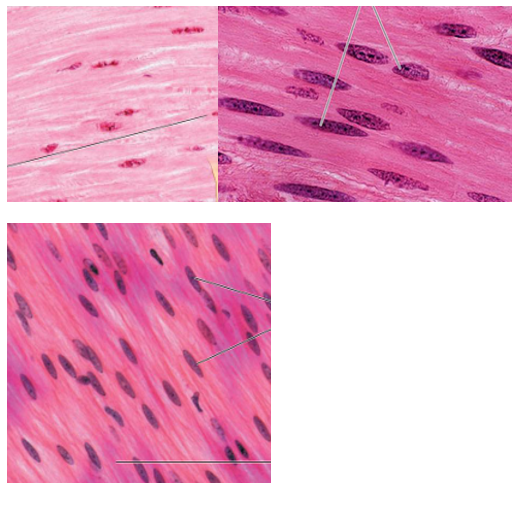
type
smooth muscle tissue image
Nervous Tissue Overview
specialized for propagating electrical impulses for communication
mostly found in brain and spinal cord
2 cells (neurons and neuroglia)
limited ability to repair
Neurons are the ________ cells in the body.
longest
Neurons have ________ : branching ends that receive info, and ______: tails that communicate to other cells. This part is also called a nerve fiber
dendrites
axons
Nervous Tissue Function
transmit electrical impulses to/from sensory receptors
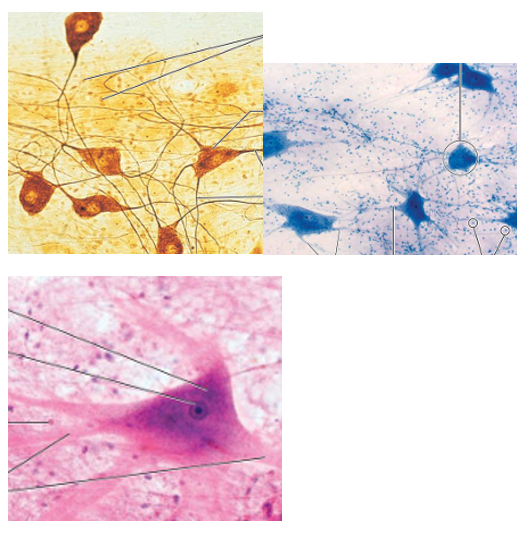
type
nervous tissue image