Personal Development || 1st Semester || Midterms
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Jean Piaget
proponent of the cognitive development theory
education
key element in the growth of an individual
object permanence
object continues to exist even if its no longer seen
egocentrism
child's way of thinking is toward onseself
equilibrium
state of balance
maturation
factor affecting development involving biological changes
sensorimotor
child explores the world through interaction of his mouth and hands with the environment
concrete operational
thinking logically about concrete events; grasping concrete analogies and performing arithmetical operations
pre-operational
language and pretend play take off, still cannot conserve, egocentric
formal operational
abstract reasoning
Lawrence Kohlberg
proposed that moral reasoning guides moral actions
morality
ability to distinguish right from wrong
cognitive development
other development theory that Kohlberg recognized as essential to his theory
pre-conventional stage
reward and punishment
conventional stage
following the rules
post conventional stage
set of general principles that reflect core values
punishment and obedience orientation
the child obeys to avoid punishment
reward orientation
the child obeys to get rewarded
good boy-good girl orientation
approval of other people
authority orientation
right and wrong is determined by society's rules and laws
social contract orientation
following the rules but also deiciding what is good for the majority
universal ethical principles
believes in their own principles
Sigmund Freud
proponent of psychosexual theory
erogenous zones
also known as pleasure areas which are sensitive to stimulation
fixation
attachment to a particular object or activity that may affect development
instinct
most important factor in psychosexual theory
oral
(0-1 year) pleasure centers on the mouth- sucking, biting, chewing
anal
(1-3 years) toilet training; obsessive-compulsive and being too generous
phallic
(3-6 years) pleasure zone is the genitals; coping with incestuous sexual feelings
latency
(7-13 years) resolving fixations; develops closeness to parents
genital
(puberty on) maturation of sexual interests
Erik Erikson
expanded Freud's theory that recognizes early childhood experiences' importance
Psychosocial
considers the role of social factors in influencing development
Identity Confusion
in which the individual feels confused about his or her purpose
Socialization
Essential process in psychosocial
Trust vs. Mistrust (1-2 years)
1. provision of basic needs; support
2. becomes hopeful or optimistic; trust someone now, we can trust others in the future
1. deprivation, lack of support, inconsistency
2. becomes fearful, we develop doubt and mistrust
Autonomy Vs. Shame and Doubt (2-4 years)
1. support; patience
2. develops self confidence
1. lack of confidence/ support; overprotective
2. becomes independent
Initiative vs. Guilt (4-5 years)
1. opportunity; encouragement
2. develops sense of purpose
1. lack of opportunity; negative feelings
2. feels guilty
Industry Vs. Inferiority (5-12 years)
1. good education/training and models
2. becomes industrious
1. lack of training/ support
2. develops sense of inferiority
Identity Vs. Identity Diffusion (13-19 years)
1. Clear sex models; good sense of stability; positive feedback
2. develops identity
1. Confusing purpose; vague expectations; unclear feedback
2. identity crisis role confusion
Intimacy vs. Isolation (20-40 years)
1. Understanding, trust, acceptance
2. Is able to love and commit
1. Loneliness; exclusion
2. Loneliness; depression; isolated
Generativity vs. Stagnation (40-63 years)
1. Productivity; purposefulness
2. Feels productive
1. Lack of opportunity; enrichment
2. Feeling unproductive; stagnant
Integrity vs. Despair (65-death)
1. Sense of closure; clear attainment of direction
2. Feels complete; has sense of achievement
1. Lack of completeness; dissatisfaction
2. Feels dissatisfied with Life; in despair
Four Identity Statuses
- diffusion, foreclosure, moratorium, achievement
- by James Marcia
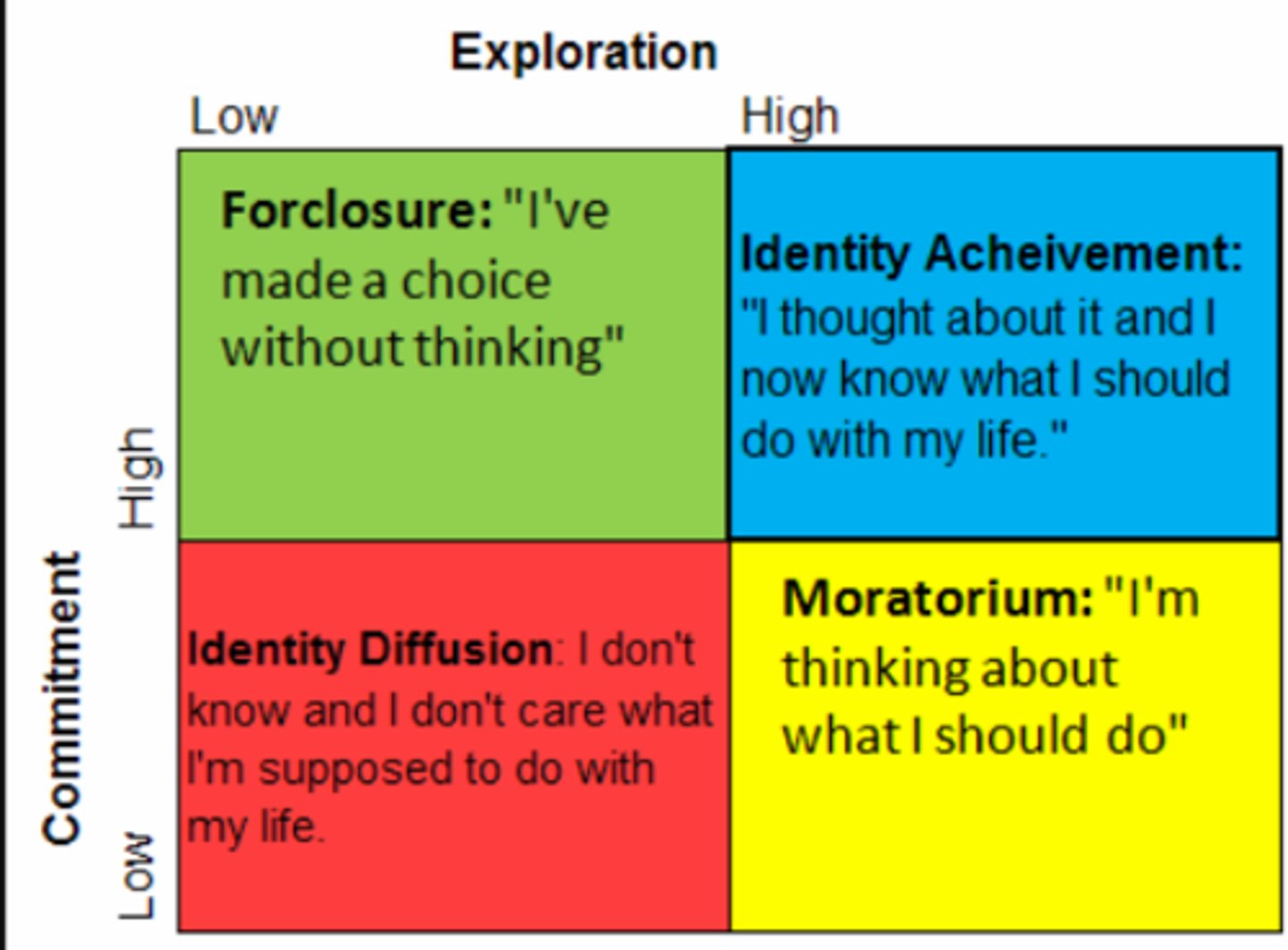
Identity Diffused
- Low exploration
- Low commitment
- Has no plans in life and doesn't know
Foreclosed
- Low exploration
- High commitment
- Parents decided on their actions
Moratorium
- High exploration
- Low commitment
- Joins many things but never commits
- Only trying several things to know what they want
Identity Achieved
- High exploration
- High commitment
- Has explored and has committed to one goal for their life