Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression: Operons, Quorum Sensing, and Global Systems
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the common regulatory mechanisms in bacteria?
Regulation of gene expression, alteration of enzyme and protein activity, and sensing environmental changes.
What are constitutive genes?
Housekeeping genes that are continuously expressed by the cell.
What are inducible genes?
Genes that code for enzymes needed only in specific environments, such as β-Galactosidase.
What are repressible genes?
Genes that code for enzymes necessary for synthesizing required molecules, like amino acids.
What is the function of transcriptional activators?
They enhance the transcription of specific genes.
What is the function of transcriptional repressors?
They inhibit the transcription of specific genes.
What is the lac operon?
A gene cluster in bacteria that regulates lactose uptake and metabolism.
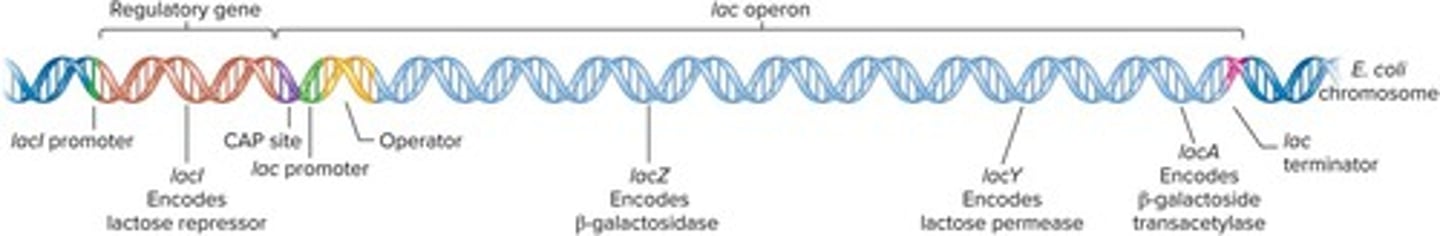
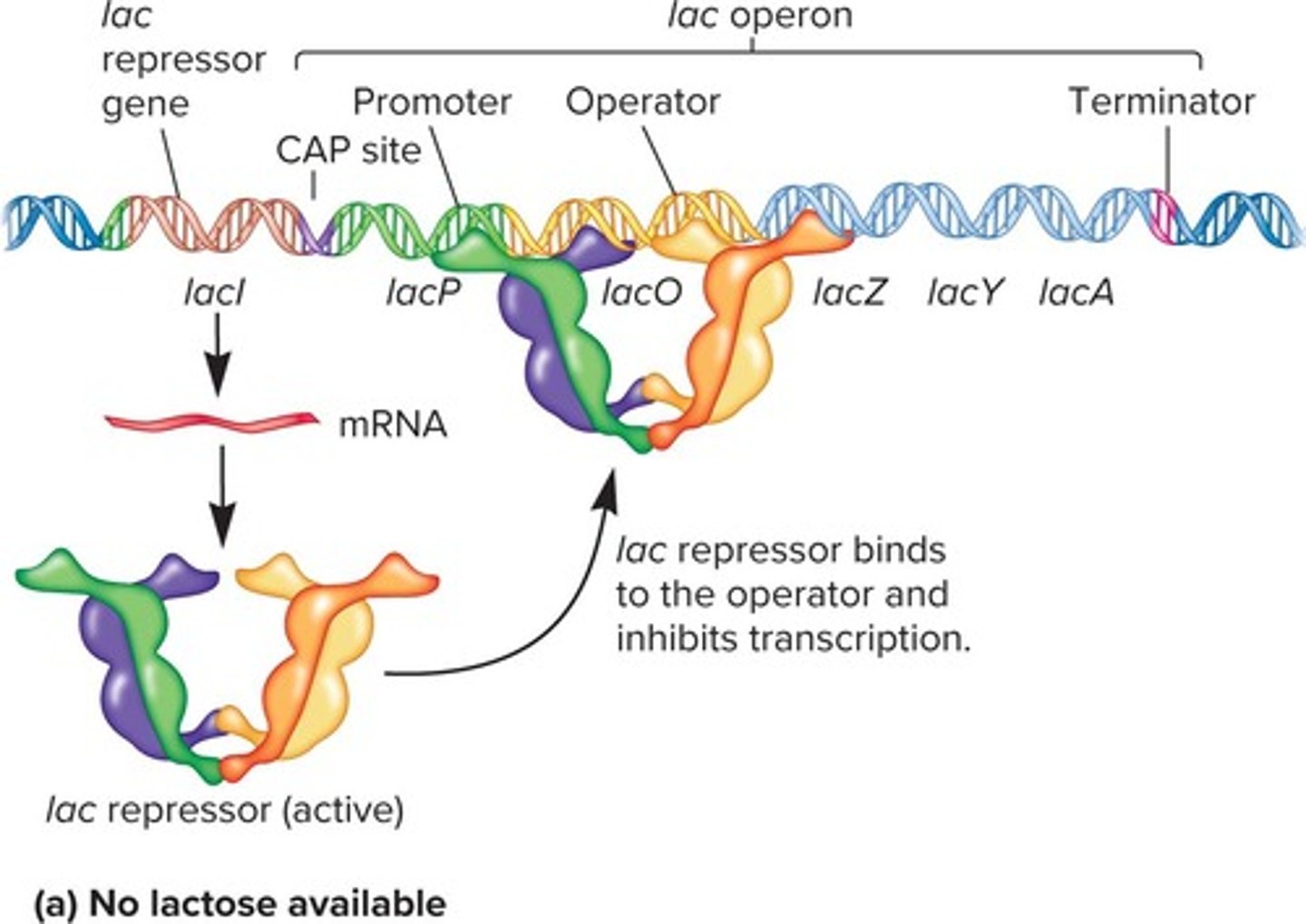
How does the lac repressor function?
It binds to the operator to inhibit transcription of the lac operon.
What is catabolite repression?
A regulatory mechanism where the presence of glucose inhibits the metabolism of alternative sugars.
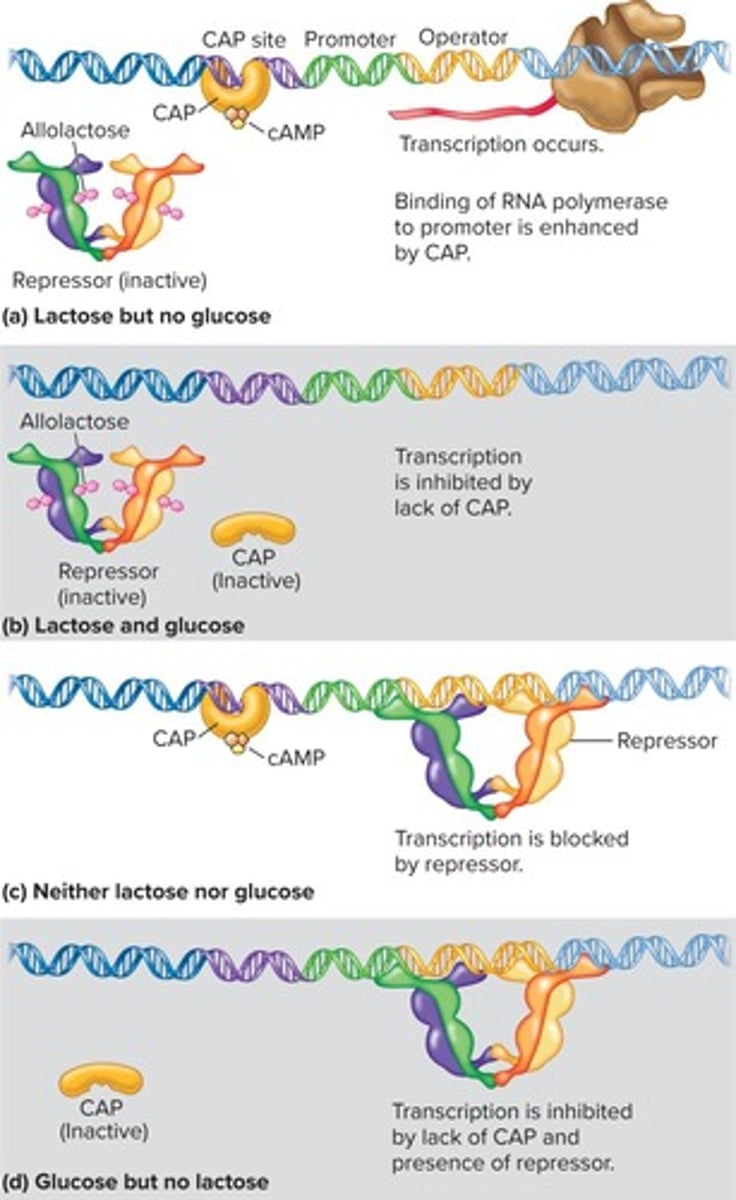
What role does CAP play in the lac operon?
CAP (catabolite activator protein) enhances the transcription of the lac operon in the absence of glucose.

What happens to the lac operon in the presence of high glucose and high lactose?
The lac operon is off due to low cAMP concentrations.
What is the trp operon?
A repressible operon that functions in the absence of tryptophan.
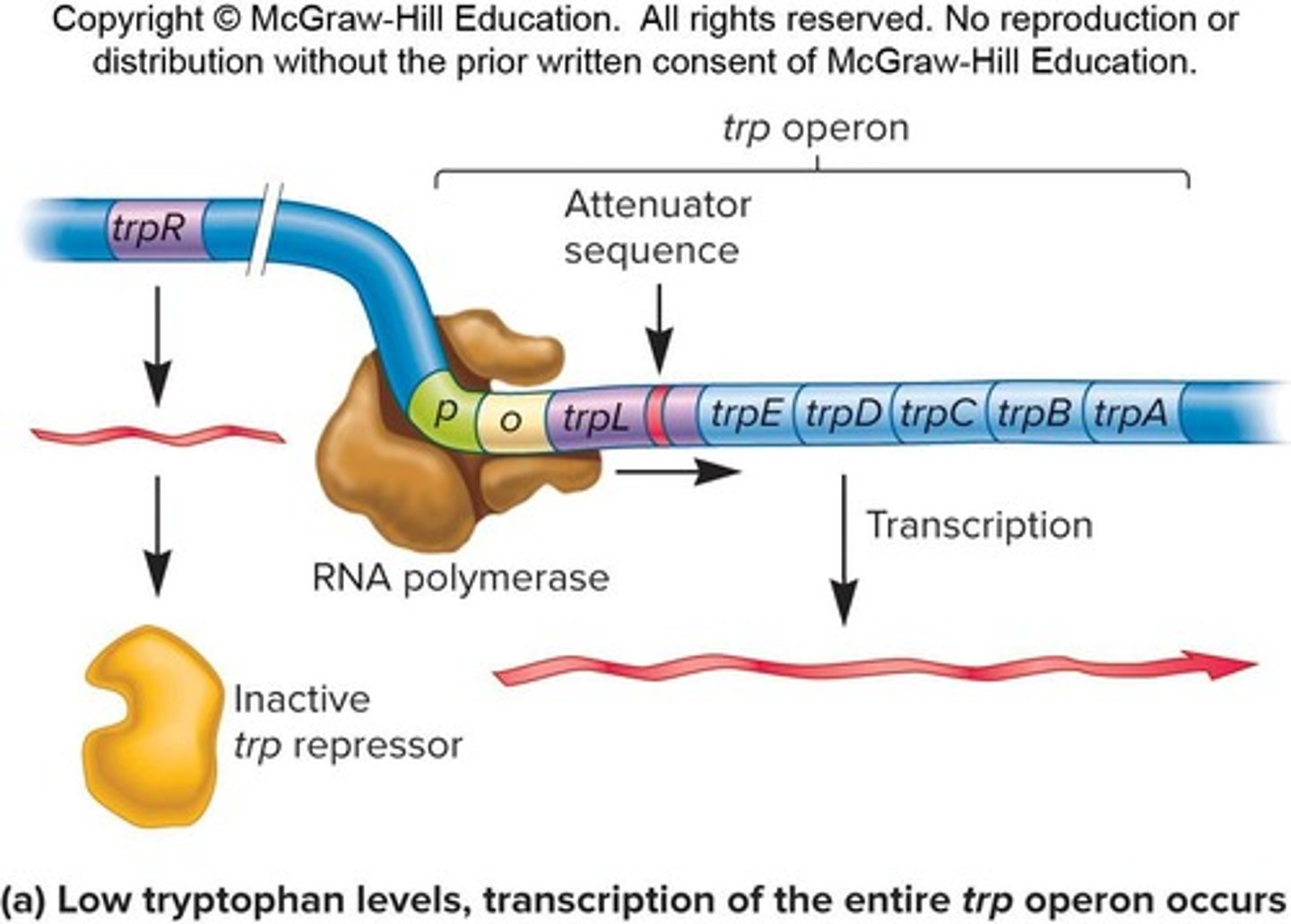
What occurs when tryptophan is present in the environment of a cell?
Tryptophan binds to the trp repressor, turning off transcription.
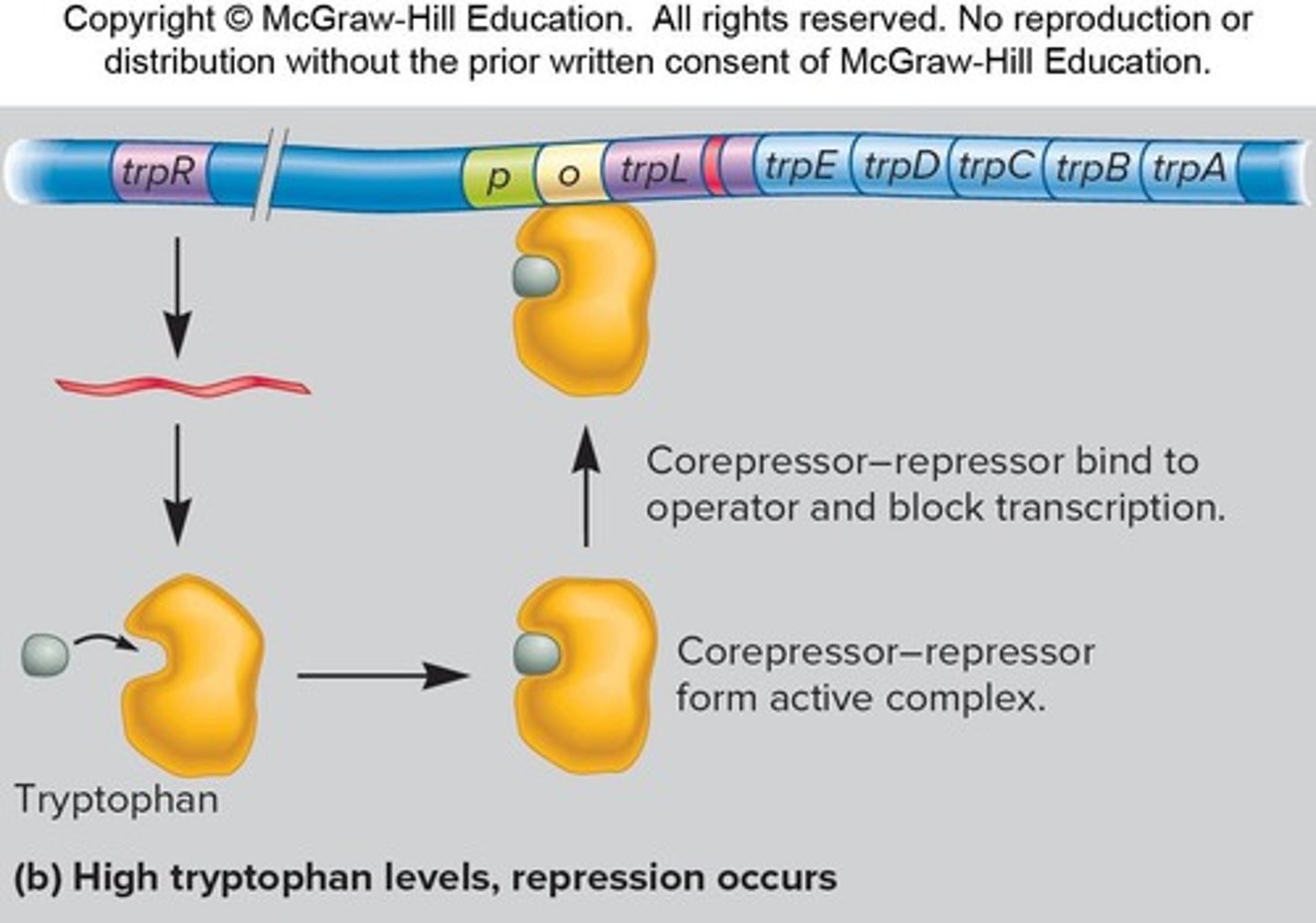
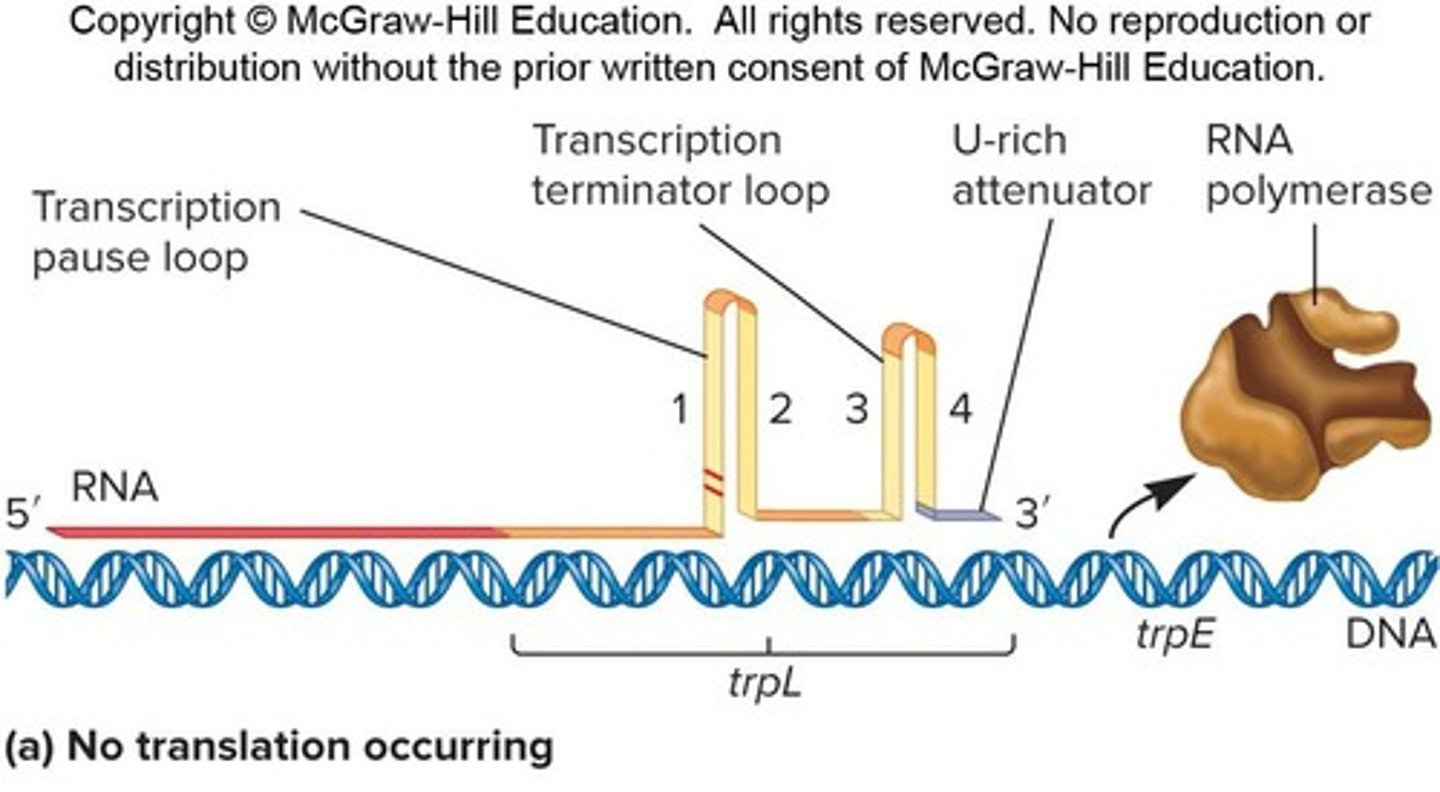
What is attenuation in the context of the trp operon?
Termination of transcription within the leader region depending on tryptophan levels.
What is the primary reason glucose metabolism genes are not controlled like the lac operon?
Glucose is the preferred carbon source and is utilized first when available.
What is the significance of operons in bacteria?
They allow for coordinated gene expression of related genes controlled by one promoter.
What is the fastest level at which enzyme activity can be changed?
Posttranslational modification of the enzyme.
What is the role of inducers in metabolic pathways controlled by repressors?
Inducers bind to repressors and inactivate them, allowing transcription to occur.
What is a common feature of all control mechanisms in bacteria?
The ability to sense changes inside or around the cell.
What is the effect of high glucose on cAMP levels?
High glucose results in low cAMP concentrations.
What is the relationship between lactose and the lac operon?
Lactose acts as an inducer for the lac operon, enabling the expression of genes for lactose metabolism.
What happens to the lac operon when lactose is absent?
The lac repressor binds to the operator, inhibiting transcription.
What is attenuation in the context of transcription?
Termination of transcription within the leader region, influenced by the level of tryptophan.
What is the role of riboswitches in bacteria?
They are specialized forms of transcription attenuation that alter mRNA folding in response to effector molecules.

How do riboswitches function in Gram-positive bacteria?
They regulate transcriptional termination.
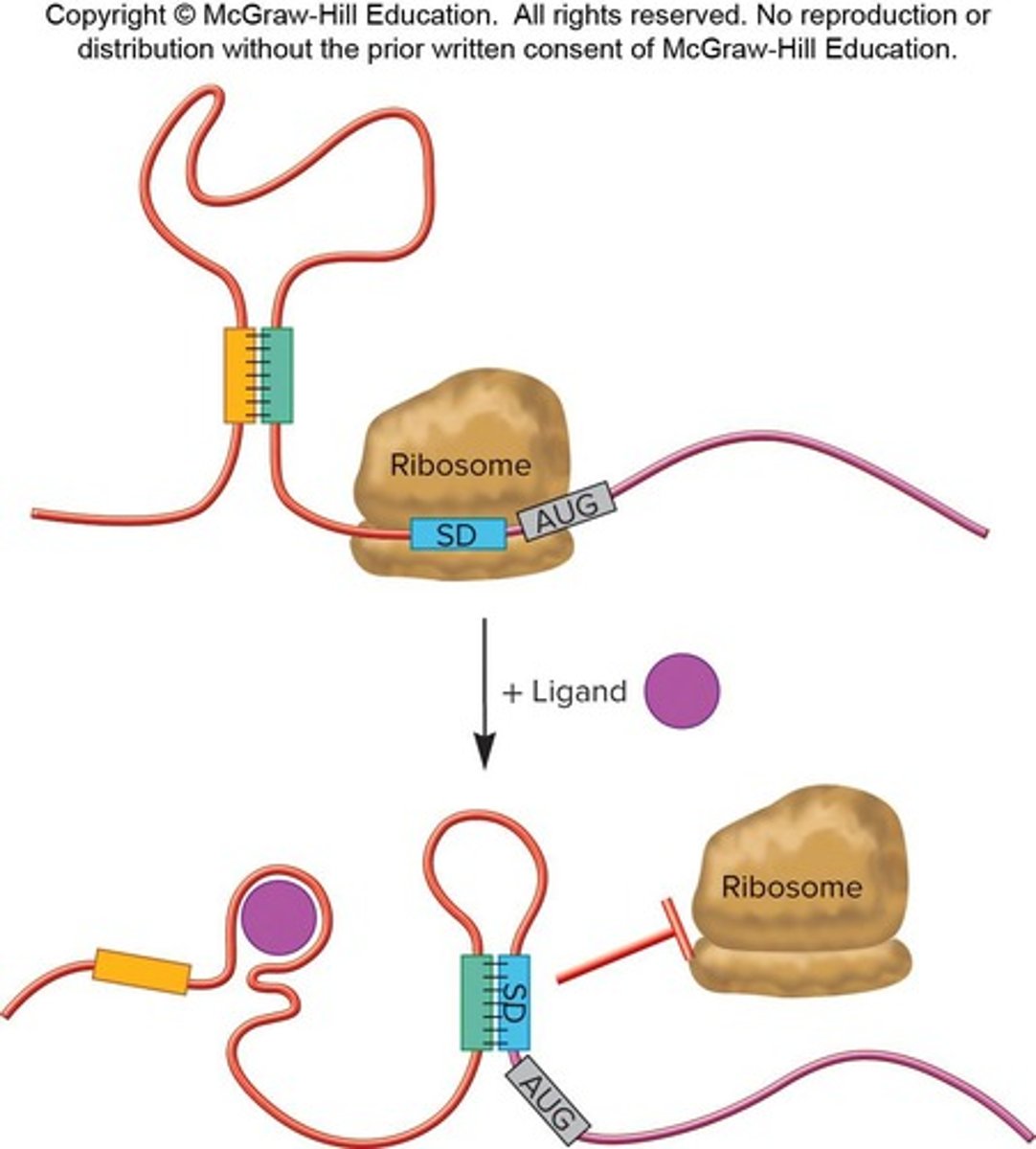
What is the function of riboswitches in Gram-negative bacteria?
They regulate translation of mRNA by altering the folding pattern of the mRNA leader.
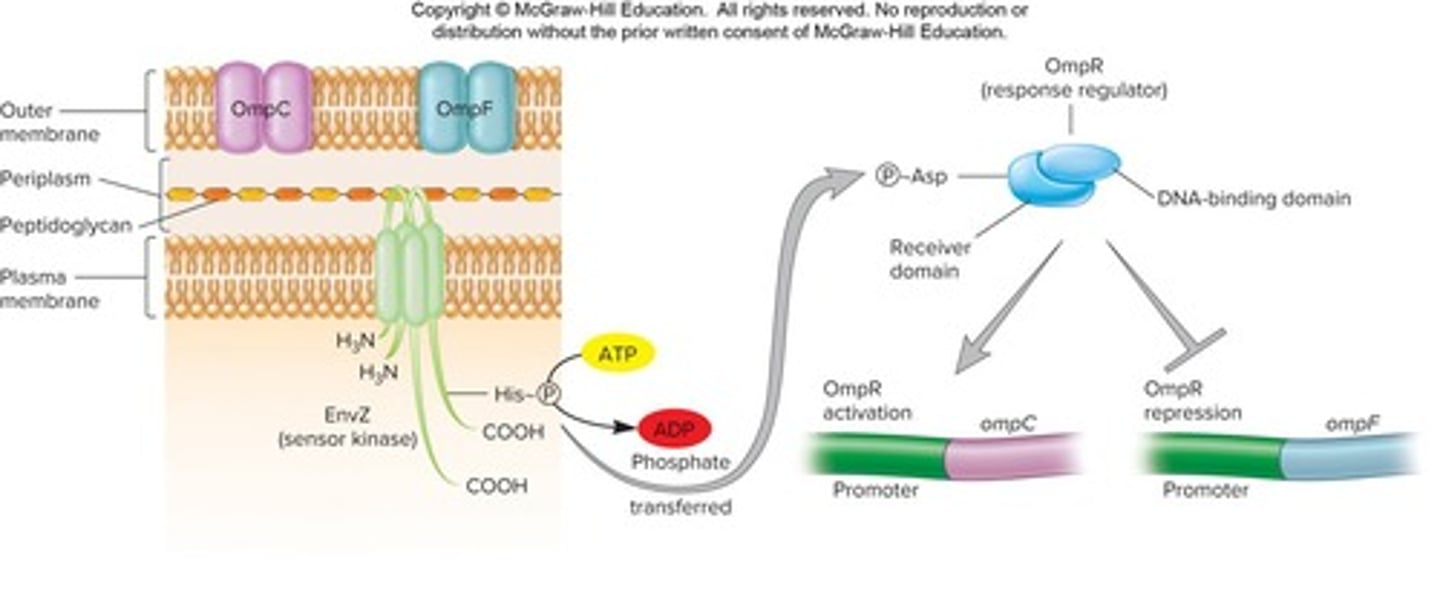
What are two-component signal transduction systems?
Regulatory systems consisting of a sensor kinase and a response regulator that govern cellular responses.
What is a regulon?
A collection of genes or operons controlled by a common regulatory protein.
What is the role of alternate sigma factors in bacterial transcription?
They help RNA polymerase recognize different promoter sequences, altering gene expression patterns.
What is quorum sensing?
Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria mediated by signaling molecules that regulate gene expression based on cell density.
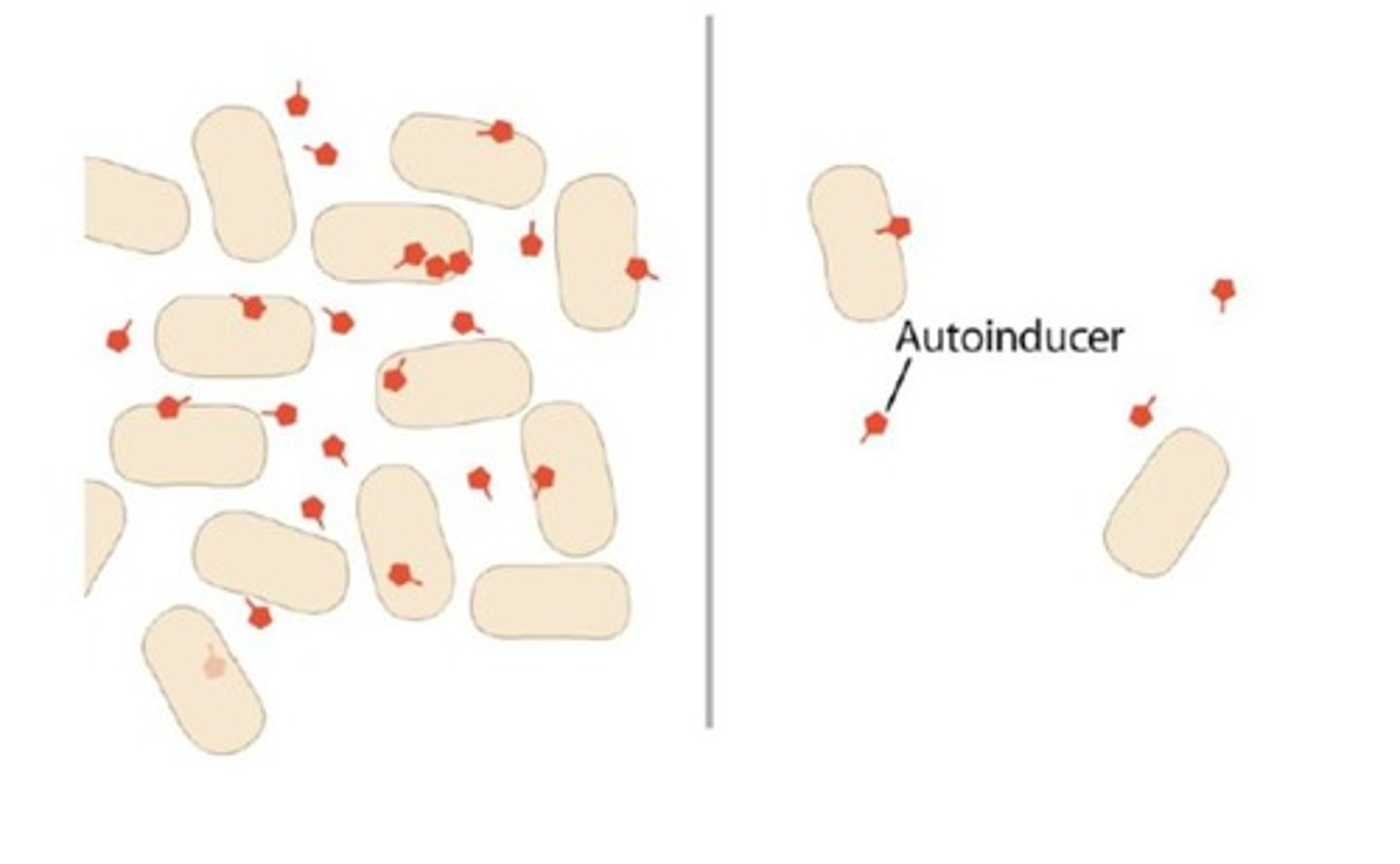
How does quorum sensing affect gene regulation in V. fischeri?
High concentrations of AHL activate transcription of genes necessary for light production when a critical cell density is reached.
What is the significance of reaching a critical population density before gene expression?
It ensures synchronized activity for processes that require group cooperation.
What are autoinducers in the context of quorum sensing?
Signaling molecules that regulate gene expression by interacting with regulatory proteins affecting transcription.
What types of genes are regulated by quorum sensing?
Genes involved in virulence, biofilm production, and other cooperative behaviors.
What happens when the effector binds to a riboswitch?
It may either terminate or continue transcription of the target mRNA.
What is the function of the sensor kinase in a two-component signal transduction system?
It detects signals and phosphorylates the response regulator.
Which sigma factor is involved in genes needed during exponential growth?
σ70
Which sigma factor is associated with the general stress response?
σ38
What is the role of σ32 sigma factor?
It is needed to protect against heat shock and other stresses.
What type of regulation would be affected if transcription and translation were not coupled in bacteria?
Attenuation
What is the outcome of riboswitch binding to an effector molecule?
It alters the mRNA folding pattern, affecting transcription or translation.
What is the role of response regulators in two-component systems?
They can act as activators or repressors that bind to DNA.