yr9 body systems-coordination systems
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
endocrine and nervous systems like that
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what is the nervous system composed of?
central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
what is the CNS composed of?
the brain and the spinal cord
what is the PNS composed of?
all the nerves that are not in the central nervous system (CNS)
what is the role of the CNS
to decide what to do with incoming sensory information and to coordinate responses through muscles or glands
what is the role of the PNS
to connect the CNS to limbs and organs, and facilitate communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
this note is meant for an image of nervous system for labelling
what are the difference between sensory neurons, interneurons and motor neurons?
Sensory neurons (or receptors) transmit sensory information to the CNS, interneurons transmits this information within the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands)
define synapse and neurotransmitter
what are some examples of neurotransmitters (this is for the syllabus pls memorise)
the synapse is the gap between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite of other. neurotransmitter is the chemical signal that crosses the gap.
serotonin and dopamine
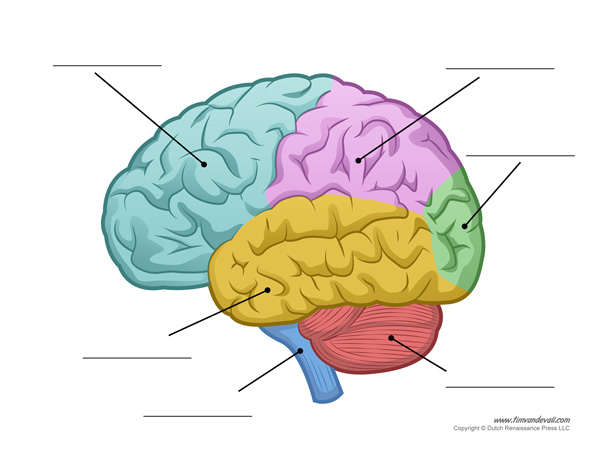
label
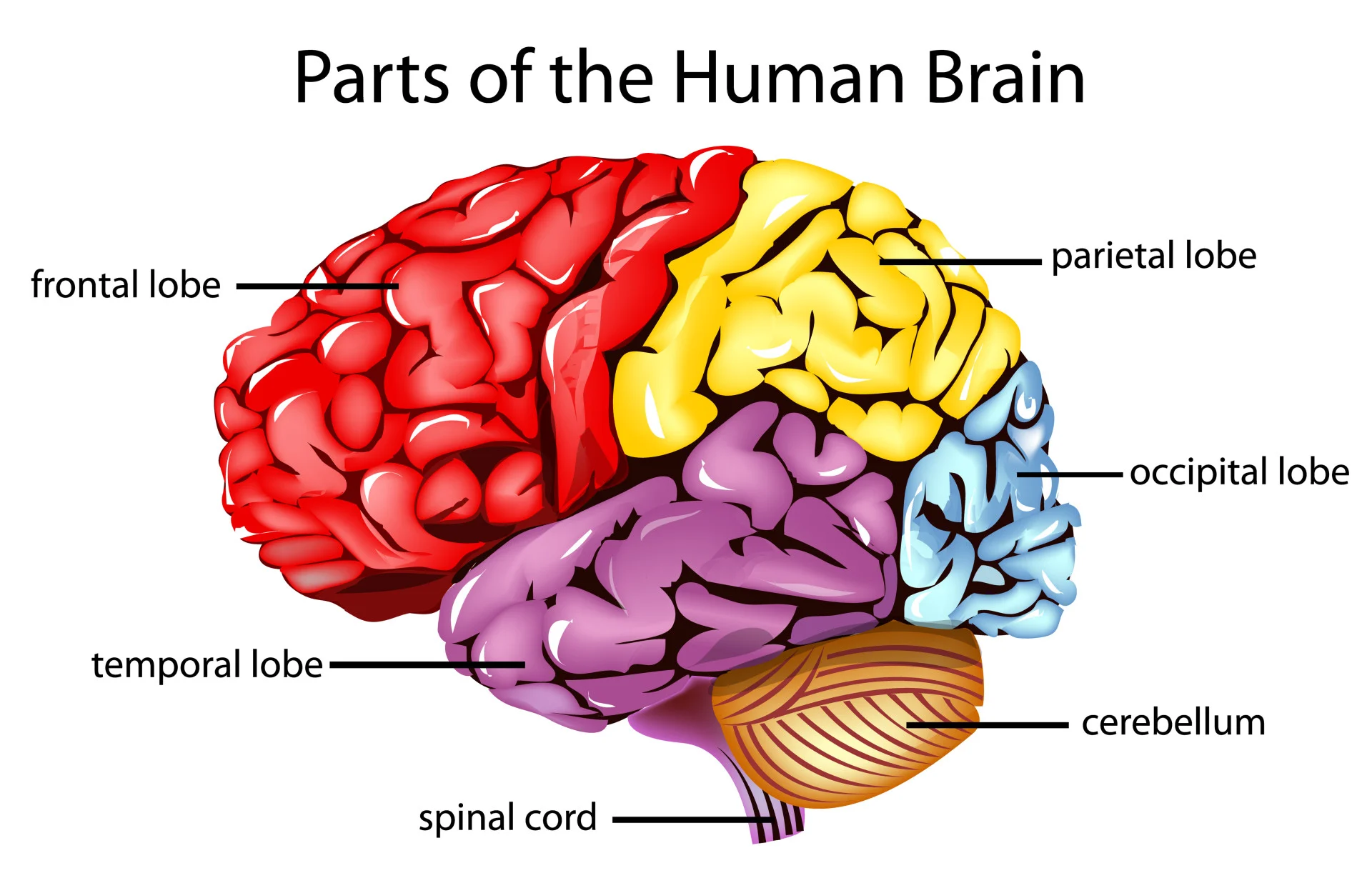
limbic system please refer to book for diagram
why does a reflex action work so quickly?
reflex actions work quickly as they bypass the brain, and instead go to the spinal cord for a faster response, as spinal cord also has relay/inter neurons, which can directly send signals to effectors
identify two parts of peripheral nervous system and their role
the somatic which controls voluntary movement of muscles (not effectors in general) and autonomic which controls involuntary functions such as the heartbeat, digestion
which part of the peripheral nervous system is further split into two branches?
autonomic system is split into sympathetic, which controls body in times of stress (eg flight or fight) while parasympathetic controls the body in relaxation (rest and digest)
Define endocrine system
glands located through the body which secrete hormones into bloodstream, regulating bodily functions (eg metabolism, digestion, growth, blood pressure)
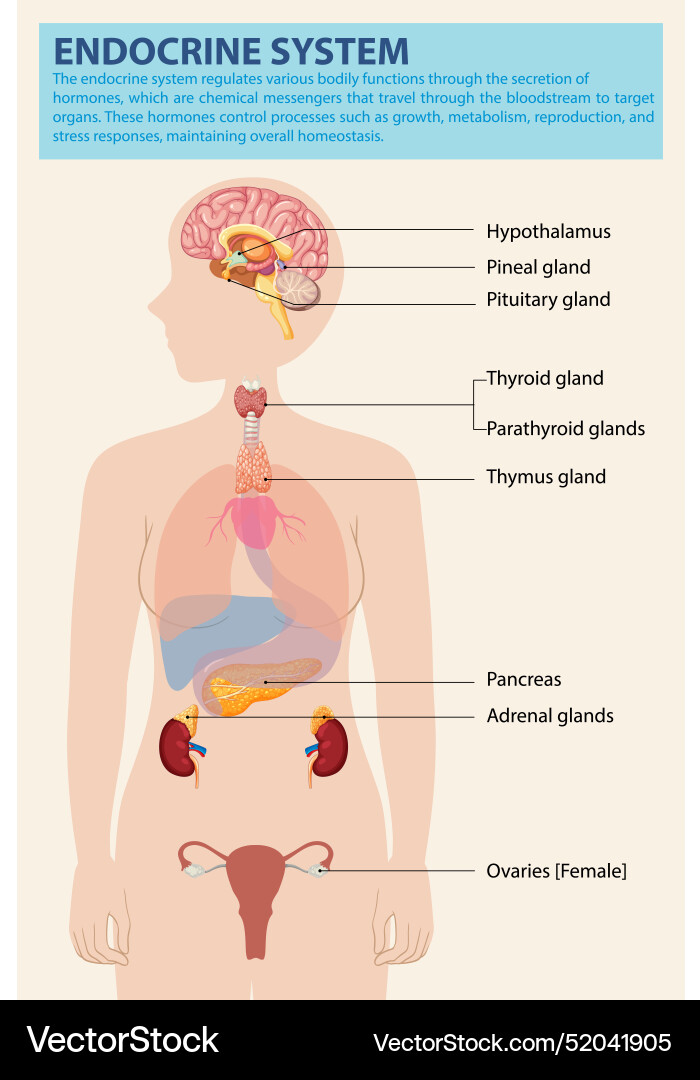
memorise
yeah
Describe how the endocrine system uses hormones to carry chemical messages around the body and the mechanism of negative feedback.
the hypothalamus do later
Name at least three hormones in the body, which organ they originate from, their target and their effects
insulin, by pancreas, decreasing blood sugar lvl by increasing glucose uptake and converting into glycogen which stores glucose for later use of energy.
human growth hormone, by pituitary gland, stimulates cell divison, leading to growth and repair of body.
adrenaline, by adrenal gland, prepares for fight/flight situations, increasing increases heart rate and blood pressure by increasing blood sugar, constricting blood vessels close to skin and dilating blood vessel to muscles.
identify the ‘master gland’
pituitary gland (it monitors and controls other glands/hormones)
define homeostasis
ability to maintain stable internal body environment despite changes in external environment through positive and negative feedback loops
define negative feedback loops
a body’s response to changes in internal environment, by working against initial stimuli (eg too much glucose results in insulin release to lower blood sugar levels).
define positive feedback loops
body works with a stimuli to regulate internal balance (e.g, open wound platelets that clot release chemicals signalling more platelets to arrive until wound clots and bleeding prevented)