Section 11: Giant Planets - Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Giant Planets/ Jovian Planets
Make up 0.13% of the solar systems mass
All have large orbits due to their larger gravities
Lower densities
Jovian Planet Core: All have a rock or ice core
Rotation: All rotate quickly on their y axis
Differential rotation: Found in Jovian planets with atmospheric bands
Magnetism: very strong and found in all jovian planets caused by…
HEating
Lower densities
Different densities: Caused by various compression of the gasses by gravity
Bigger planet = greater gravity = more compression
COmpression effects: HYdrogen is in the form of metallic liquid
Rotation in jovian planets
Due to conservation of angular momentum: L=mrv
Larger the radius larger the velocity since its proportional
More gas being collapsed inwards making it speed up
Surface rotates even quicker since they are so large
Axial Tilts: Found in all jovian planets
They all have seasons and changing day lengths
Differential rotation:
Found in Jovian planets with atmospheric bands
Their atmosphere is sectioned and rotate at different rates, and also different at different depths
Most noticeable in the sun: with differences up to 10 days
FUnction of Latitude: Depends on the distance from the equator
Magnetism
very strong and found in all jovian planets caused by…
Convection
Rotation
Conduction → usually their core
Magnetism causes aurorae
Create aurorae →when charged particles from the sun, known as the solar wind, collide with gases in Earth's upper atmosphere
HEating in Jovian Planets:
Heating is suggested to be caused by the compressing gas to a high pressure
Emits more heat themselves than they receive from the sun
Based on Blackbody Law higher temps = more light energy is being emitted
They are therefore hotter than the equilibrium and are are slowly cooling
Convections
Caused by the strong heating at the equator and hot air rises and then it cools at the poles and the cold air falls back down to the equator
Convection cells
Hadley cells: The ones next to the equator
East to west winds
Ferrel Cells: Between the hadley and polar cells
West to east winds
Polar cells: the ones at the poles
Coriolis Forces
Angular momentum wont allow air to flow straight north or south rather it bends in the opposite direction the planet is rotating ALways to the right in the northern hemisphere
Going to the poles that rotate more slowly so it will be ahead
Going to the equator its not caught up so it will be behind
Always to the left in the southern hemisphere
Hurricanes, typhoons and Cyclones
Hurricanes: Northern east hemisphere - Counterclockwise to the right
Typhoon: Northern west hemisphere - Counterclockwise to the right
Cyclone: In the southern hemisphere - clockwise to the left
Fast Rotation
Various conventions and rotation speeds lead to the banding and cells
Jupiter
Visible with a Telescope
Jupiter
It’s four galilean moons
Great red spot
A perpetual storm/hurricane
A lot of rotation keeps it going
Deep atmosphere with minimal friction (no land) forces to stop it
Banded atmosphere
Jupiter Composition
Hydrogen and helium
Internal Volume: Liquid hydrogen
Core: Metallic hydrogen/ liquid hydrogen → conducts
Jupiter's magnetic field is so strong it takes over the sun's field and helps prevent solar winds in that region
Jupiter heating
Heat from initial formation → Primordial Heat
HEat from compressed gas
Jupiter Rotation
Axial Tilt: Very small, minimal seasons (3o)
Differential Rotation:
Poles rotate a lot slower than the equator
Cells Created by Convections: Jupiter banding
Jupiter Banding:
Light zones and dark belts rotate at different rates and in different directions
Different colours: Caused by cooling and heating of different chemicals creating new compounds causing colour changes
White bands: Light zones are areas of strong upwelling, higher altitudes
Dark bands: Dark belts are areas of strong downflow, with lower altitudes
Convection moves gas up and down, but due to the coriolis effect the rotation makes those flows curve sideways
ANgular momentum is channeled to the equator → making it spin faster
Multiple convection cells
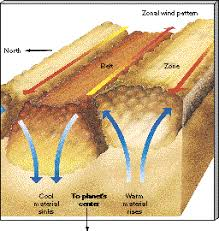
Saturn
Rings and its gaps
Cassini Division: the most notable gap in Saturn's rings
Atmospheric Bands
Haze on top of atmosphere making it seem smoother
Saturn Atmosphere
strong internal heating and strong rotation causing a dynamic atmosphere and banding
Bands: seen in infrared wavelengths
Saturn Composition
Hydrogen and helium
Internal Volume: Liquid hydrogen
HIgh altitude white haze created by crystals
Core: Metallic hydrogen/ liquid hydrogen
Saturn Heating
Primordial heat
Helium rain → gravitational potential energy is released in the form of heat
Saturn Rotation
Axial Tilt: Tilted by 26.7o
Strong rotation
Uranus
Uranus can be seen with the naked eye
Similar to a star in the sky
Discovered by William Herschel
Nearly featureless
Uranus Atmosphere
Mainly composed of methane (CH4) → reflect blue
Very thick high altitude haze with only some visible clouds
Less altitude heating leaving to significantly less banding
Neptune Compositon
Denser and heavier icy/ rocky materials
Small layer of hydrogen on top
Core: Dissolved Ammonia and water as well
Uranus heating…?
TRICK QUESTION NYAH NYAH
Lack of heating → Its primordial heat is gone
Uranus Rotation
Axial Tilit: Heavily tilted by 97.8o
Experiences extreme seasons
Slower rotation than jupiter, neptune and saturn
Neptune discovery
Determined due to Uranus orbit being unexplained by a simple Kepler Ellipse suggesting a separate planets’ gravitational force was effecting it
Neptune
Blue hue → SImilar to uranus just slightly lighter
Atmospheric bands and clouds
Great Dark spot → no longer there
Neptune Atmosphere
Methane rich → also gives a blue
More active than uranus leading to bands and spots
Has a source of internal heating
Neptune Composition
Denser and heavier icy/ rocky materials
Small layer of hydrogen on top
Core: Dissolved Ammonia and water as well
Neptune Heating
Primordial heat still present
Methane possible insulates the planet
Neptune Rotation
Axial Tilt: Tilted by 28.3o
Faster rotation than uranus but still slower than jupiter and saturn
Different Spacecrafts
Pioneer programs
Voyager 1 and 2
Galileo
Dropped a probe into jupiter
Helped analyze structure and atmosphere composition
Cassini
Dropped a probe onto titan (Saturn's largest moon)
Takes pictures
Spacecraft Movement uses 2 things
Gravitational Slingshots: Used to adjust the speed and the direction of spacecrafts to save fuel
Launch dates and times are calculated to use these
Natural Slingshots: Flying objects that are accidentally taken in
Comets coming close and they get ripped apart
Conservation of Angular Momentum: Planets orbit affected a negligible amount, while spacecraft's trajectory get greatly altered