ekg
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
purpose of an EKG
records the electrical activity of the heart
Normal electrical conduction pathway
SA node
Atrial pathway
AV node
Bundle of HIs
Right & left bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Where is the SA node located
Right atrium
What is the SA node
The heart’s natural pacemaker
What does the AV node do
delays impulses briefly, allowing time for atria to contract and ventricles to fill with blood
What is the Bundle of His
Electrical connection between atria and ventricles
What do the left and right bundle branches do
carries impulses to ventricles
What do the purkinje fibers do
Rapidly spread impulses from Bundle of His to the ventricles
ECG paper speed
25 mm/sec
A small box is how many seconds?
0.04
One large box is how many small boxes?
5
One large box is how many seconds?
1
There should be one ____ wave before every _______
P; QRS complex
The P wave represents…
atrial depolarization (contracting)
An absent P wave suggests…
Atrial rhythm problems
The PR interval is normally how long?
0.12-0.20 seconds
A prolonged PR interval represents…
AV block
The PR interval represents…
The time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria through the AV node, and into the ventricles
What does the PR segment represent
The delay in electrical impulse conduction through the AV node
The PR segment is usually…
flat
What is the PR segment
The flat line between the end of the P wave and beginning of QRS complex
The QRS complex represents…
ventricular depolarization (leading to ventricular contraction)
Ventricular contraction occurs just after the _______ and during the _______
QRS complex; ST segment
Normal duration of the QRS complex
less than 0.12 sec
The J point represents
It marks where the QRS complex ends and the ST segment begins
The ST segment is normally…
flat
The ST segment represents…
The period when the ventricles are fully depolarized and actively contracting
The T wave represents…
Ventricular repolarization (beginning of relaxation)
The U wave represents….
repolarization of the purkinje fibers
The U wave follows the …..
T wave
The T wave follows…
Each QRS complex
The QT interval represents…
One complete ventricular cycle (depolarization & repolarization)
The QT interval starts at the _____ and ends with the _____
QRS; T
Qualities of a normal sinus rhythm
Rate: 60-100 bpm
P wave before every QRS
QRS is less than 0.12 sec
PR interval: 0.12 - 0.20 sec
Regular rhythm
Sinus bradycardia rate
Less than 60 bpm
True or false: sinus bradycardia has normal P waves
True
Sinus tachycardia rate
greater than 100 bpm
Causes of sinus tachycardia
Fever
Pain
Anxiety
Dehydration
Hypoxia
Atrial fibrillation
Chaotic, disorganized heart rhythm where the atria quiver instead of contract
Characteristics of atrial fibrillation
Chaotic
No identifiable P wave
Narrow QRS complexes
Irregular RR intervals
Blood can pool in atria (↑ risk of clot formation)
Atrial flutter
Rapid but organized atrial rhythm, where the atria contracts but too fast to fill effectively
Characteristics of atrial flutter
Organized
Regular RR intervals
Ventricular tachycardia characteristics
Rate: 100+ bpm
Wide QRS complexes (greater than 0.12 sec)
No P waves
Ventricular fibrillation characteristics
Ventricles quiver instead of contract
No cardiac output
No P waves
No QRS complexes
Chaotic/irregular
Why should you not defibrillate during asystole
defibrillators work by resetting electrical activity- but in asystole, there is no electrical activity to reset- CPR and epinephrine instead
First degree atrioventricular block
delay in conduction from SA node to the AV node
PR interval in first degree atrioventricular block is typically….
Greater than 0.20 seconds
Second degree atrioventricular block, type 1 is also known as…
Wenckebach
Second degree atrioventricular block, type 1 characteristics
Blocked impulses from AV node to ventricles
PR interval gets progressively longer, then one QRS is dropped
Second degree atrioventricular block, type 2 characteristics
Classic heart block
AV node selectively blocks specific impulses
PR interval stays consistent, then sudden QRS complex
No warning or slowing
Third degree atrioventricular block characteristics
Complete heart block
Atria and ventricles beat independently
No pattern
Random PR intervals
No relationship between P and QRS
All electrical impulses that original above the ventricles are blocked
Right bundle branch block
The left ventricle contracts first, then the right ventricle contracts late
Left bundle branch block
The right ventricle contracts first, then the left ventricle contracts late
What is more serious, right bundle branch block or left bundle branch block?
Left bundle branch block
Chain of infection order
Infectious agent (germ)
Reservoir (where it livers)
Portal of exit (how it leaves)
Mode of transmission (how it travels)
Portal of entry (how it gets in)
Susceptible host (person at risk to getting sick)
Normal BP range
100-140 / 60-90
Normal HR range
60-100
Holter monitor
Portable, wearable device that continuously records heart’s electrical activity for 24 hours
How many leads are used for holter monitor
3-5
Event recorder
Wearable, portable device that monitors and records heart’s electrical activity over days, weeks, or longer
How to calculate max HR
220 - patient’s age
How to calculate target HR
Max HR x 0.7
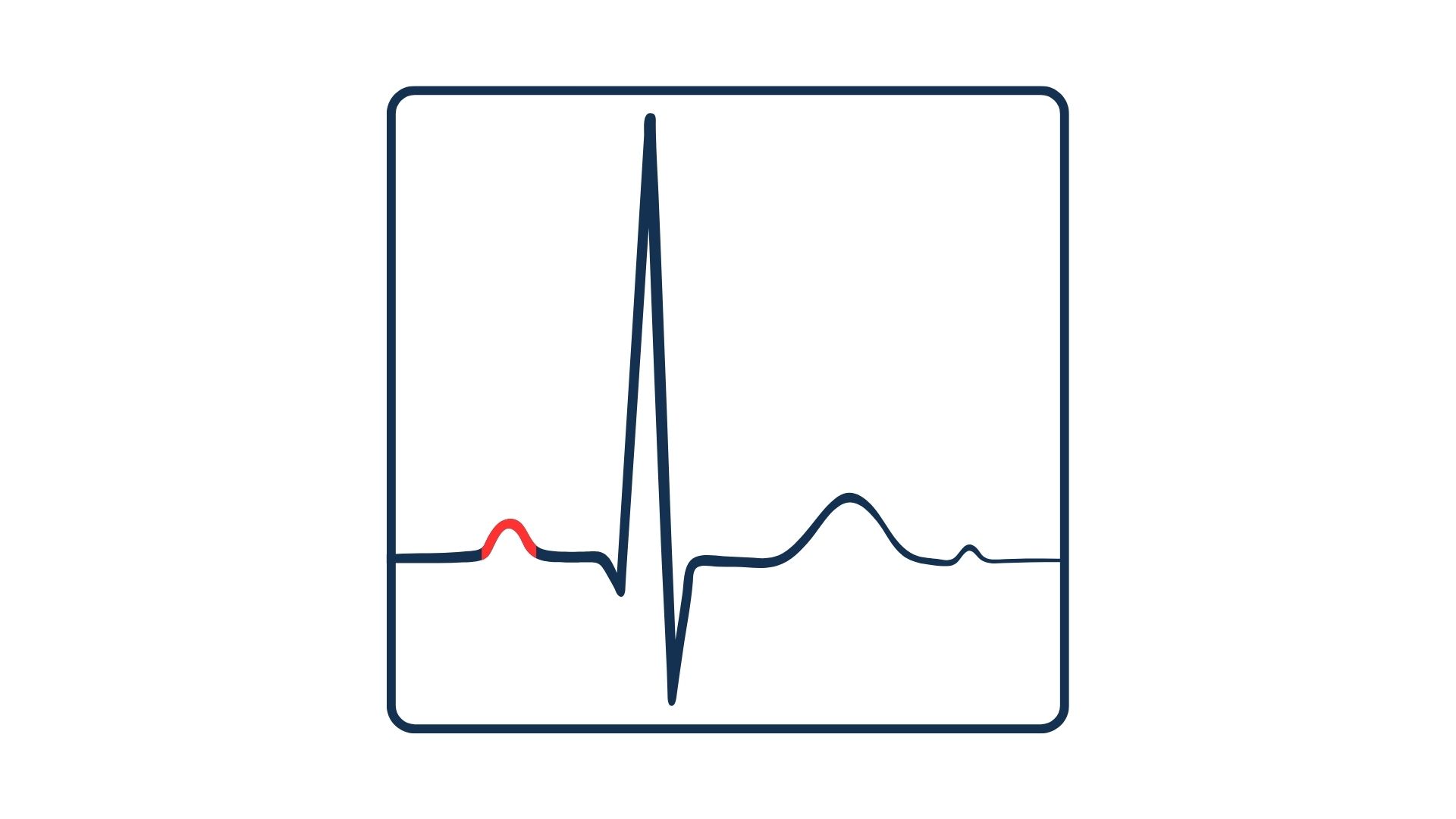
What is the segment highlighted in red
P wave
A tall P wave indicates
Right atrial enlargement
A wide P wave indicates
left atrial enlargement
A prolonged PR interval indicates
Delayed conduction from atria to ventricles (1st degree AV block)
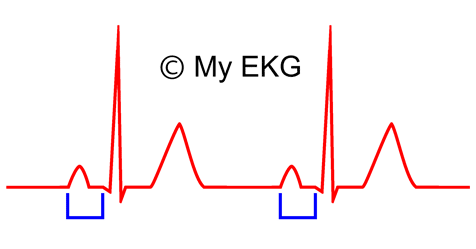
What segment is this (the blue bracket)
PR interval
PR segment depression indicates
pericarditis
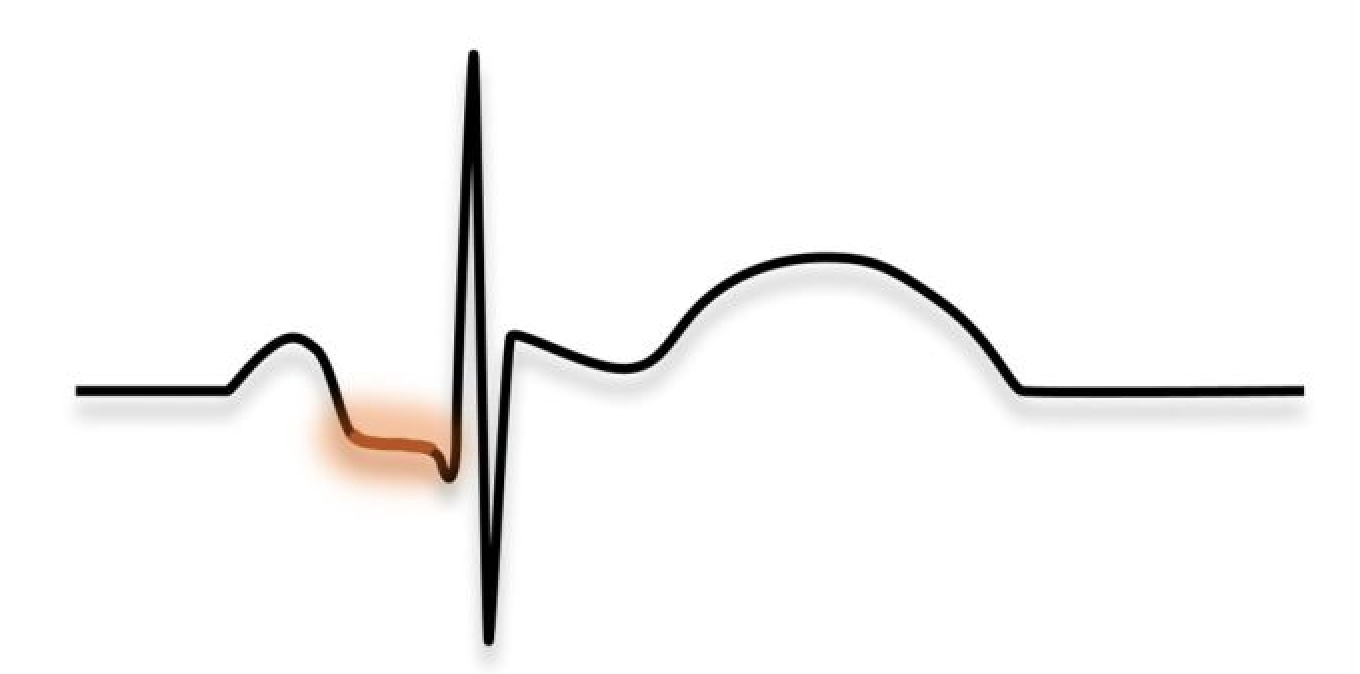
What segment is this
PR segment
What does a wide QRS complex indicate
bundle branch block or ventricular dysfunction
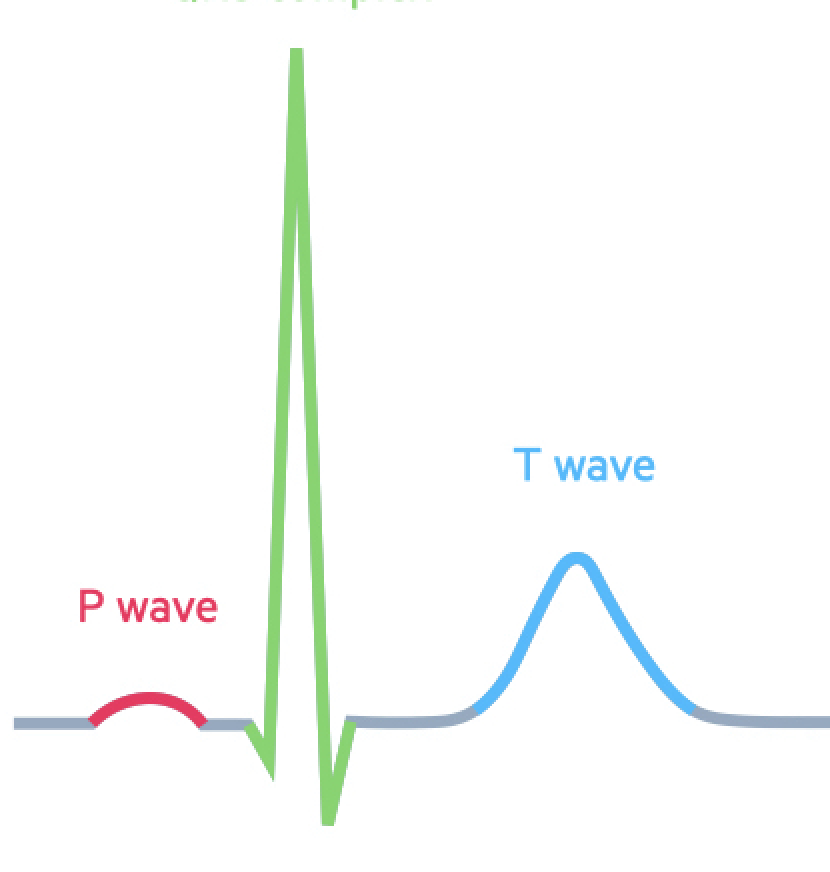
What is the green segment
QRS complex
What does an elevated j point indicate
Early depolarization or MI
What does a depressed j point indicate
ischemia
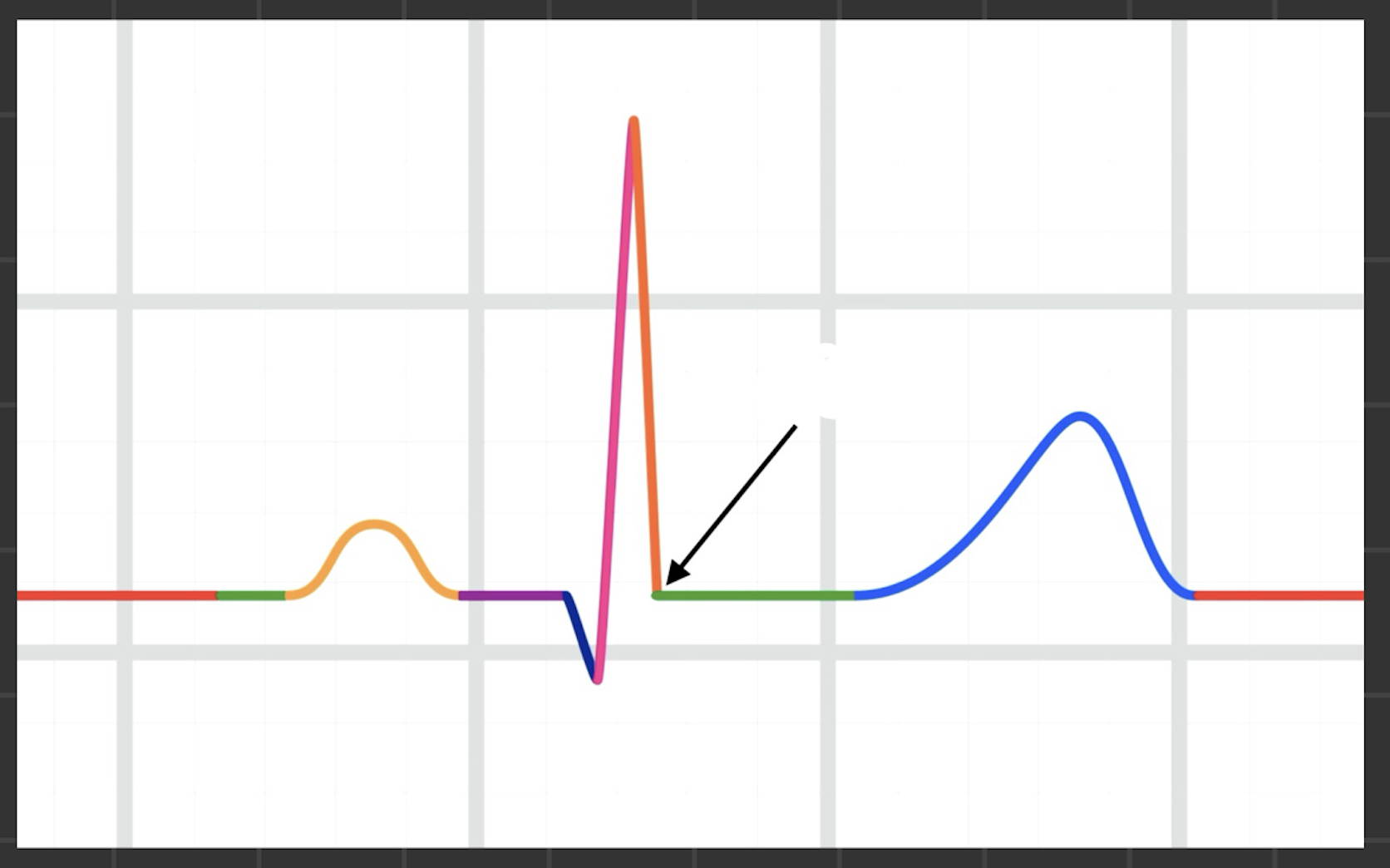
What is the black arrow pointing at
J point
ST segment elevation indicates
AMI
ST segment depression indicates
myocardial ischemia
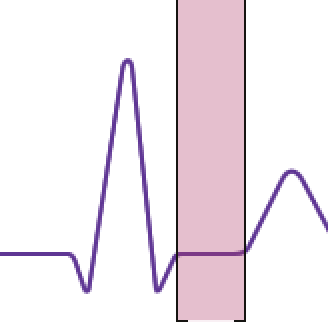
What is the highlighted section
ST segment
Inverted T wave indicates
myocardial ischemia
Elevated t wave indicates
hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia
Increased potassium levels
Depressed T wave indicates
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia
Low potassium levels
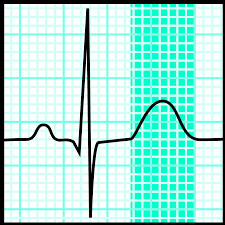
What is the highlighted section
T wave
A prominent U wave indicates…
Hypokalemia
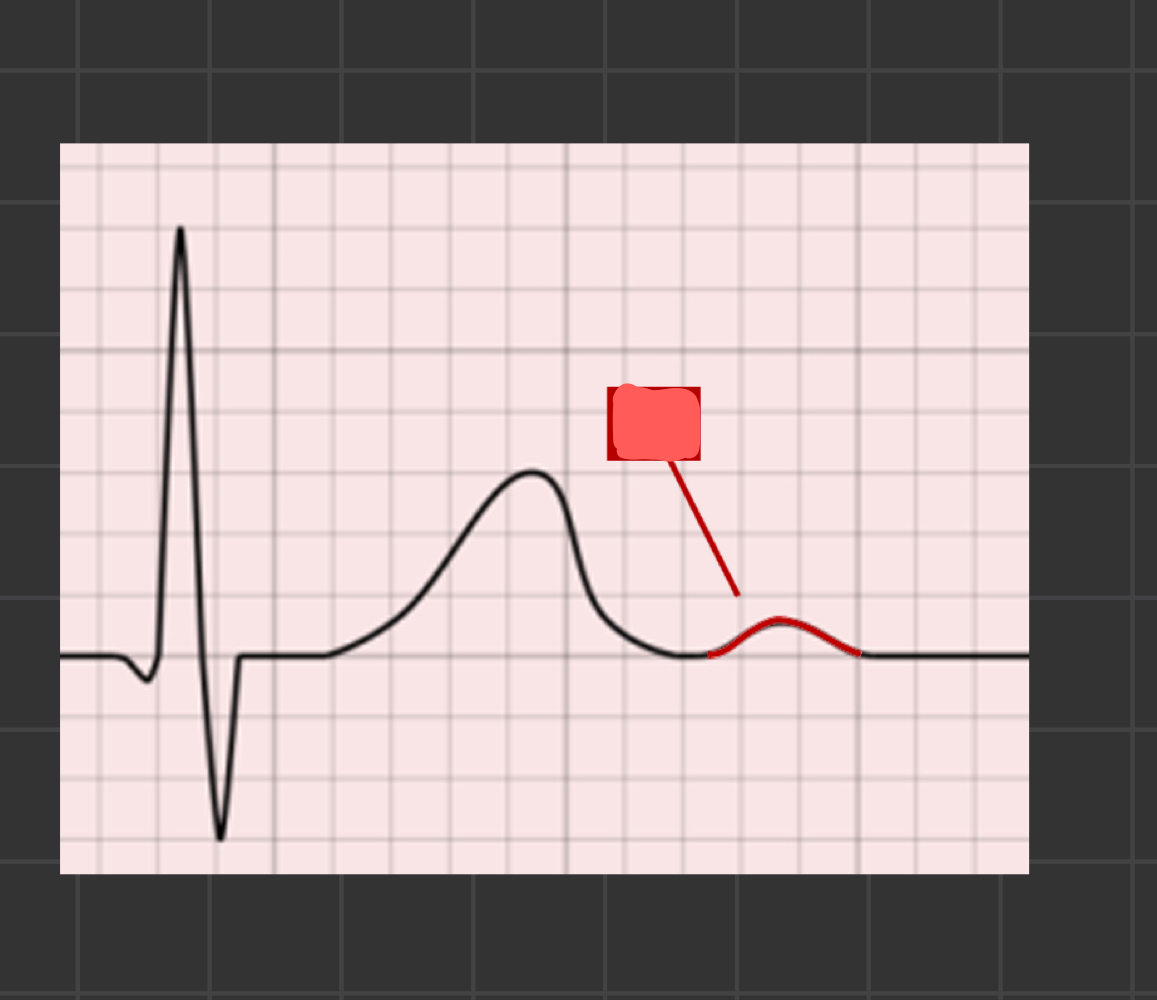
What is the arrow pointing to
U wave
Irregular PP interval indicates
atrial dysrhythmia

what segment is this (bracket)
RR interval
what does an irregular RR interval indicate
atrial fibrillation
Prolonged QT interval indicates
delayed ventricular repolarization (triggers torsades de pointes)
torsades de pointes
type of life threatening ventricular tachycardia
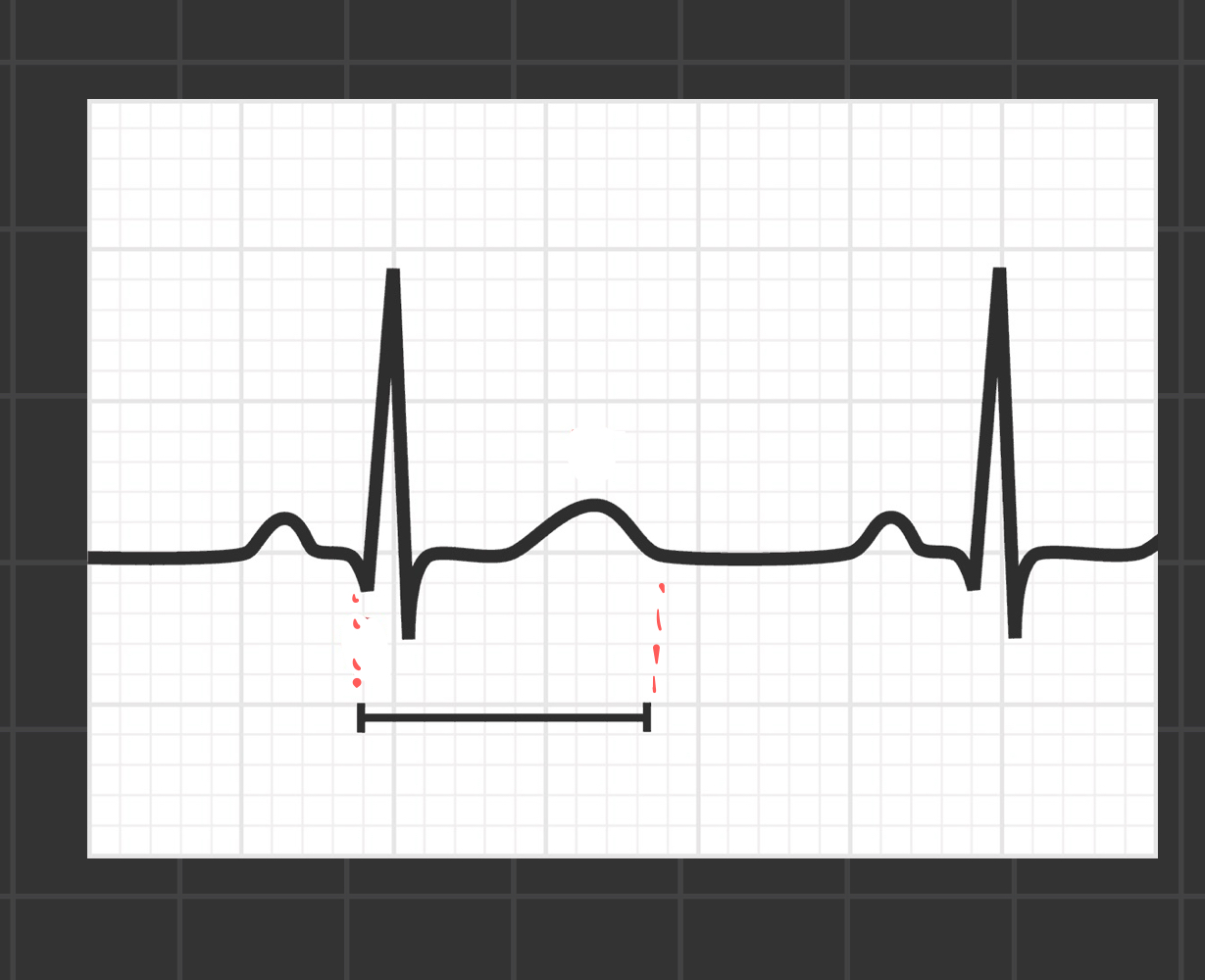
what segment is this
QT interval
epicardium
outermost layer of the heart, made of connective tissue
myocardium
middle layer of involuntary striated muscle tissue
Which layer of the heart is responsible for physical contraction of heart muscle
myocardium
endocardium
innermost layer of the heart, lines chambers of the heart and forms surface of valves
role of endocardium
promotes flow of blood through heart and protects inner surfaces
tricuspid valve
separates right atrium from right ventricle
bicuspid (mitral) valve
Separates left atrium from left ventricle
pulmonary valve
lies between right ventricle and pulmonary arteries
aortic valve
lies between left ventricle and pulmonary aorta