Male Pelvis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:20 AM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
The organs of the male reproductive system include:
Testes
System of ducts, Accessory sex glands, Several supporting structures, including the scrotum and the penis
System of ducts, Accessory sex glands, Several supporting structures, including the scrotum and the penis
2
New cards
System of ducts includes
epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra
3
New cards
Acessory sex glands
seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands
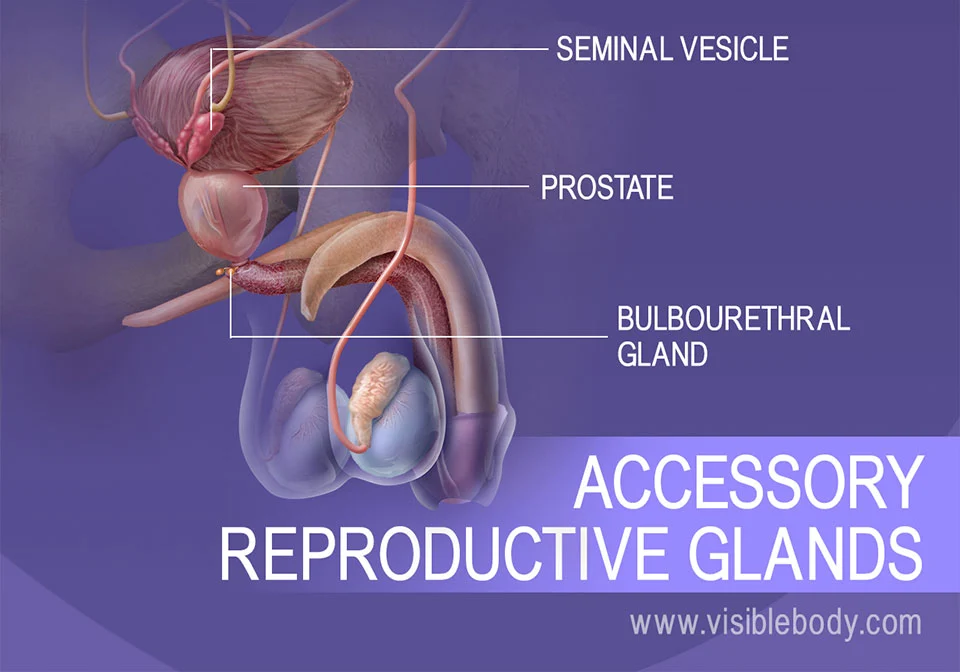
4
New cards
prostate
Largest accessory gland of the male reproductive system
5
New cards
The prostate is ___________ shaped gland that surrounds the _____________
chestnut; prostatic urethra
6
New cards
The secretion of the prostate gland aids in
motility & fertility of the sperm
7
New cards
What does the prostate have a close relationship with?
urethra
8
New cards
What does hypertrophy of the prostate interfere with?
passage of urine
9
New cards
Where is the prostate located in?
retroperitoneum
10
New cards
The prostate is bordered anteriorly by what?
pubic bone
11
New cards
The prostate is bordered posteriorly by what?
rectum
12
New cards
The Prostate is bordered superiorly by the what?
urinary bladder
13
New cards
The Prostate is bordered inferiorly by the what?
urogenital diaphragm
14
New cards
inferior vesical artery
arterial supply to the prostate with branches from the internal iliac artery
15
New cards
What does the inferior vesicle artery branch into?
capsular arteries & urethral arteries
16
New cards
capsular arteries supply
2/3 of the glandular tissue
17
New cards
urethral arteries supply
1/3 of the glandular tissue
18
New cards
The venous drainage occurs
laterally to the capsular vessels
19
New cards
What does the venous drainage consists of?
irregular venous chanels
20
New cards
Irregular venous channels leads to
veins of the vasa deferentia and ultimately to the vesicle and internal iliac veins.
21
New cards
Base of prostate
continues with the neck of the urinary bladder (wider)
22
New cards
Apex of prostate
narrow end rests below of the pelvic floor (more inferior)
23
New cards
How does the prostate normally measure?
3 cm from top to bottom and front to back
24
New cards
The prostate gland consists of a
small anterior *fibromuscular* region and a much larger posterior *glandular* region
25
New cards
The anterior fibromuscular stroma is located
anterior to the prostatic urethra
26
New cards
Where does most pathology occur?
Glandular areas
27
New cards
The posterior glandular portion/tissue are divided into
4 anatomically distinct zones
28
New cards
Anatomically distinct zones
Peripheral- PZ
Central- CZ
Transitional- TZ
Periurethral glandular zone-PG
Central- CZ
Transitional- TZ
Periurethral glandular zone-PG
29
New cards
The peripheral zone occupies the area ____________ to the ______________
lateral & posterior; distal prostatic urethra.
30
New cards
What zone is the largest portion of the prostate?
peripheral zone
31
New cards
The peripheral zone makes up
70% of the glandular prostate
32
New cards
_______% of malignancies are found in the peripheral zone
70
33
New cards
The central zone is _____________ to the urethra
posterior
34
New cards
The peripheral zone is _______ to the distal prostatic urethra
lateral
35
New cards
The central zone is a ________ spade structure
pyramidal
36
New cards
The central zone extends from the
base of the prostate
37
New cards
The central zone narrows at the level where
ejaculatory ducts join the urethra
38
New cards
The central zone makes up _____% of the gland
25%
39
New cards
_______% of the malignancies are found in the central zone
5-10%
40
New cards
The transitional zone is situated on
lateral aspects of the proximal prostatic urethra superior to the verumontanum
41
New cards
____________ is the smallest zone account for only about ____%
Transitional zone; 5%
42
New cards
In what zone does BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) occur?
transitional zone
43
New cards
______% of malignancies are in the transitional zone
10-20%
44
New cards
Periurethral glandular zone
the tissue that surround the proximal prostatic urethra
45
New cards
Seminal Vesicles
paired accessory glands that consist of coiled tubes
that appear to be twisted to form small pouches
that appear to be twisted to form small pouches
46
New cards
Where are the seminal vesicles located between?
posterior surface of the bladder & anterior to the rectum
47
New cards
The seminal vesicles join with ______________ to form the _______________
associated duct (vas) deferens; ejaculatory ducts
48
New cards
Two ejaculatory ducts pierce the
upper part of the posterior surface of the prostate
49
New cards
Ejaculatory ducts open into the
prostatic urethra at Vernumontanum
50
New cards
Verumontanum
A longitudinal ridge within the urethra in which the orifices of the ejaculatory ducts are located on either side.
51
New cards
Scrotum
Saclike structure that contains the testes, their coverings, and the epididymis
52
New cards
The scrotum consist of
a layer of skin, which covers a thin layer of connective tissue
53
New cards
The scrotum is divided by a
median raphe, or septum into two compartments each containing a testicle
54
New cards
Muscles of the testes
dartos & cremaster
55
New cards
Cremaster muscle
extends through the spermatic cord of the testes
56
New cards
Cremaster muscle functions with the Dartos muscle to
alter the position of the testes to maintain optimum temperature for the production and maturation of spermatozoa
57
New cards
Dartos muscle
A layer of skin, which covers a thin layer of connective tissue
58
New cards
Contraction of the dartos muscle
gives a ____________ appearance to the _________
gives a ____________ appearance to the _________
wrinkled; scrotum
59
New cards
Epididymis
6-7cm flattened and tightly coiled, tubular structures on posterior surface of each testis
60
New cards
The epididymis begins superiorly and then coursing __________ to the testis.
posterolateral
61
New cards
The epididymis becomes the _____________ and continues in the _________
vas deferens; spermatic cord
62
New cards
The epididymis is divided into what 3 parts?
head, body, tail
63
New cards
The tail of the epididymis changes direction and ascends and becomes the ___________ and leaves the ________
vas deferens; scrotal sac
64
New cards
Is the vas deferens a separate structure?
No, it's a continuation of the tail
65
New cards
_________ is the largest part of the epididymis
head
66
New cards
Epididymal Head measures
6-15 mm
67
New cards
Epididymal Head is located
superior to the upper pole of the testis
68
New cards
The epididymal body and tail is much __________ than the head
smaller
69
New cards
The tail of the epididymis is slightly ________ to the epididymal body
larger
70
New cards
How is the tail of the epididymis positioned??
posterior to the lower pole of
the testis
the testis
71
New cards
The epididymal body and tail follows the
posterolateral aspect of the
testis from the upper pole to the lower pole
testis from the upper pole to the lower pole
72
New cards
Ductus Deferens
A thick-walled muscular tube that is a continuation of the epididymis.
73
New cards
Where do the ductus deferens begin?
In the tail of the epididymis at the inferior pole of the testis
74
New cards
The ductus deferens ascends in the _____________ and passes through the ____________
spermatic cord; inguinal canal
75
New cards
As the ductus deferens enters the pelvis, it crosses over the
external iliac vessels
76
New cards
From the inguinal canal, the ductus deferens descends ________________, along the ___________ wall of the pelvis and then crosses the ____________
retroperitoneally; lateral; ureter & bladder
77
New cards
The ductus deferens descends _________ to the bladder and ________ to the ureter and seminal vesicles
posterior; medial
78
New cards
The terminal portion of the ductus deferences is joined by the duct from the ______________ to form the __________
seminal vesicles; ejaculatory duct
79
New cards
tunica albuginea
though fibrous connective tissue that covers testis
80
New cards
Extensions of the tunica albuginea project ___________, dividing ea testis into ________ lobules
inward; 300
81
New cards
Tunica vaginalis layers
parietal and visceral
82
New cards
parietal layer of tunica vaginalis
lines the scrotum
83
New cards
visceral layer of the tunica vaginalis
coves the testis & epididymis
84
New cards
The spermatic cord extends from
each testis to the inguinal canal on the same side
85
New cards
What contents makes up the spermatic cord?
structures passing to & from the testis
86
New cards
Contents of spermatic cord
Ductus deferns
Testicular artery
Pampiniform plexis
Lymph
Vessels
Nerves
Connective tissue
Testicular artery
Pampiniform plexis
Lymph
Vessels
Nerves
Connective tissue
87
New cards
Spermatic cord is a tubular structure that connects the
scrotum to pelvis
88
New cards
The vascular supply branches from the
internal iliac artery
89
New cards
The cremasteric and deferential arteries accompany the ____________ to supply ___________
testicular artery within the spermatic cord to supply the extratesticular structures
90
New cards
The cremasteric and deferential arteries anastomoses (connect) with the
testicular artery (gonadal artery) and may provide some flow to the testis
91
New cards
Arteries involved in vascular supply to the scrotum
testicular, deferential, cremasteric
92
New cards
Testicular artery arises from _______ to support the ________
aorta; testes
93
New cards
Deferential artery arises from _________ to supply the ________
vesicular artery; vas deferens & epididymis
94
New cards
Cremasteric Artery arises from ___________ to supply the _________
inferior hypogastric; dartos
95
New cards
Venous drainage
Intratesticular veins come together in rete testis
Drains to pampiniform plexus in spermatic cord
Pampiniform plexus converges to testicular vein
Right testicular vein drains to IVC
Left testicular vein drains to Left renal vein
Drains to pampiniform plexus in spermatic cord
Pampiniform plexus converges to testicular vein
Right testicular vein drains to IVC
Left testicular vein drains to Left renal vein
96
New cards
Pampiniform plexus courses in the
spermatic cord
97
New cards
Pampiniform plexus coverages into
3 sets of anastomotic veins (testicular, deferential, cremasteric)
98
New cards
The right testicular vein drains into the ______________ and joins the _________
IVC & left testicular vein; left renal vein
99
New cards
The deferential vein drains into the
pelvic veins
100
New cards
The cremasteric vein drains into the
tributaries of the epigastric and deep pudenal veins