Ch 3 Laboratory Animal Research Facilities Vet Tech
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
basic research
Advances fundamental knowledge life processes and diseases without a specific practical application in mind

applied research
Uses existing knowledge to solve a specific biomedical problem, such as the development of new vaccines or surgical procedures. There is a specific practical application needing improvement.
Animal Models in Research
Live animals are selected as subjects for applied research.
clinical research
Builds on knowledge from basic and applied research and is always conducted on live animals, including humans. Studies health and disease of humans.
experimental group
Receives the treatment (independent variable)

control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment, but receives the placebo

Placebo
a fake drug used in the testing of medication

Observation
First step of scientific method. Formulate an initial question

Hypothesis
A very specific statement based on observations that can be tested through experimentation.

Principal investigator
The PI formulates the hypothesis and writes the experimental design, often holding a PhD or being a veterinary specialist.
American Association for Laboratory Animal Science (AALAS)
Certification exams for laboratory animal technicians, assistants, and technologists.

LAT and LATG
Persons that do lab animal procedures such as blood collection, radiographs, surgical assisting, and other advanced animal nursing procedures.

Assistant laboratory animal technicians (ALATs)?
They help care for research facility animals, including cleaning cages, observing animals, and checking temperature and humidity.
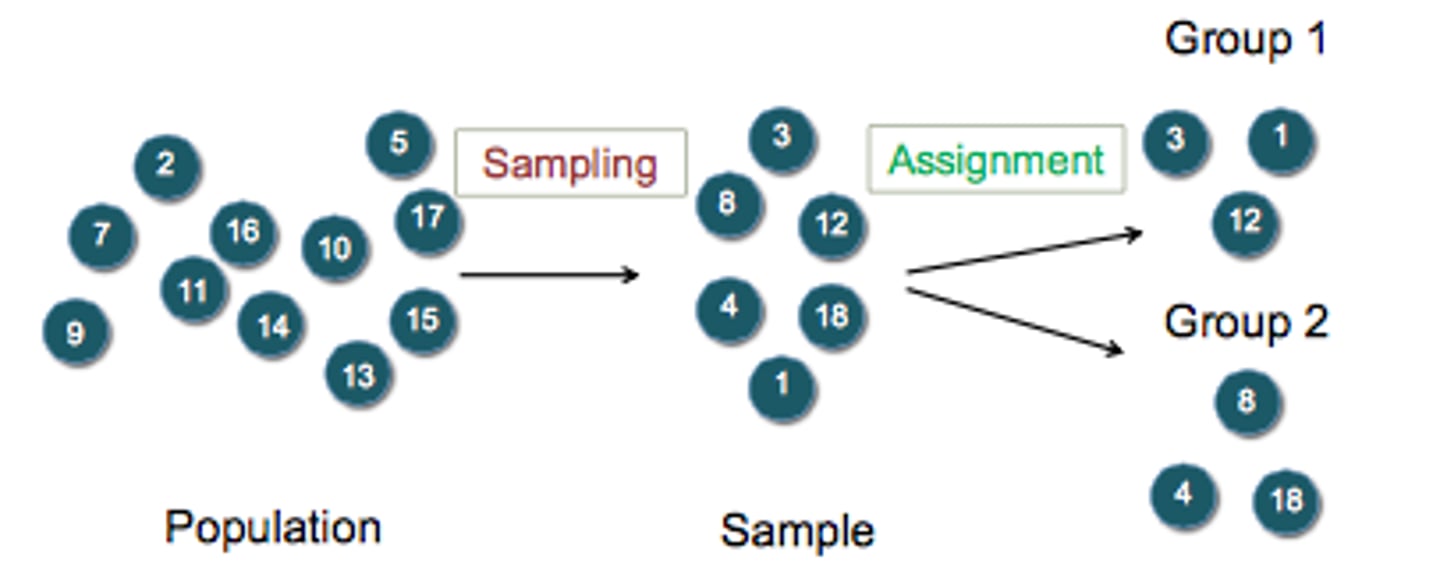
random assignment
It helps ensure that the experimental and control groups are comparable, reducing bias.
FDA Clinical research
All clinical research complies with regulations regarding animal and human subject care.

Applied research models
Computer models, mathematical models, cell or tissue cultures, or live animals.
Construction materials
Materials should be waterproof, seamless, and resistant to damage from regular use.

Conventional facility
Animal and support rooms have single doors opening into a central corridor.
Double corridor facility
Two doors for each room, one leading to a clean corridor and one to a dirty corridor.
Barrier facility
Personnel must shower and wear disposable clothing before entering animal rooms, with airlocks and UV light.
Containment facility
To house animals with infectious or zoonotic diseases, ensuring biosecurity.

Biosecurity Levels (BSL)
Levels 1 to 4 that determine the safety measures for handling infectious organisms.
Environmental factors
Temperature, humidity, lighting, ventilation, air pressure, noise, and social enrichment.
Feed and bedding storage at least 20 cm off the floor
To prevent moisture accumulation and vermin infestation.
Autoclaved materials
Requirement for materials entering a barrier facility because animals may be germ-free
Primary enclosures
To define the outer limit within which the animal can move without human assistance.
Stainless steel
Material is known for being strong, rust-free, and resistant to most cleaning chemicals in animal enclosures
aluminum
Lightweight, inexpensive, but less durable than stainless steel
Shoebox cage
Small cage typically used for rodents and may incorporate a feeding station
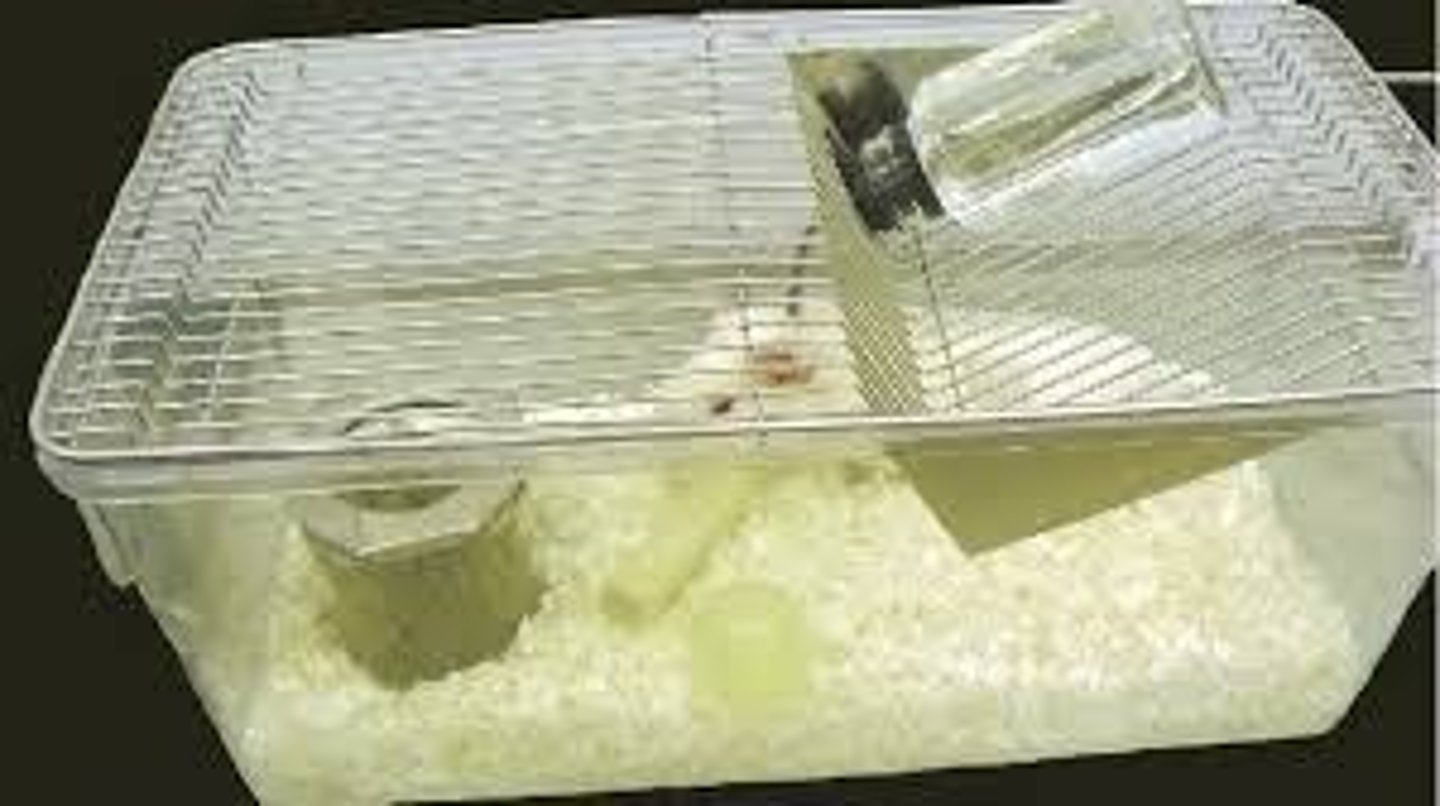

suspended cages
They have a mesh bottom that provides excellent ventilation but creates a poor microenvironment.
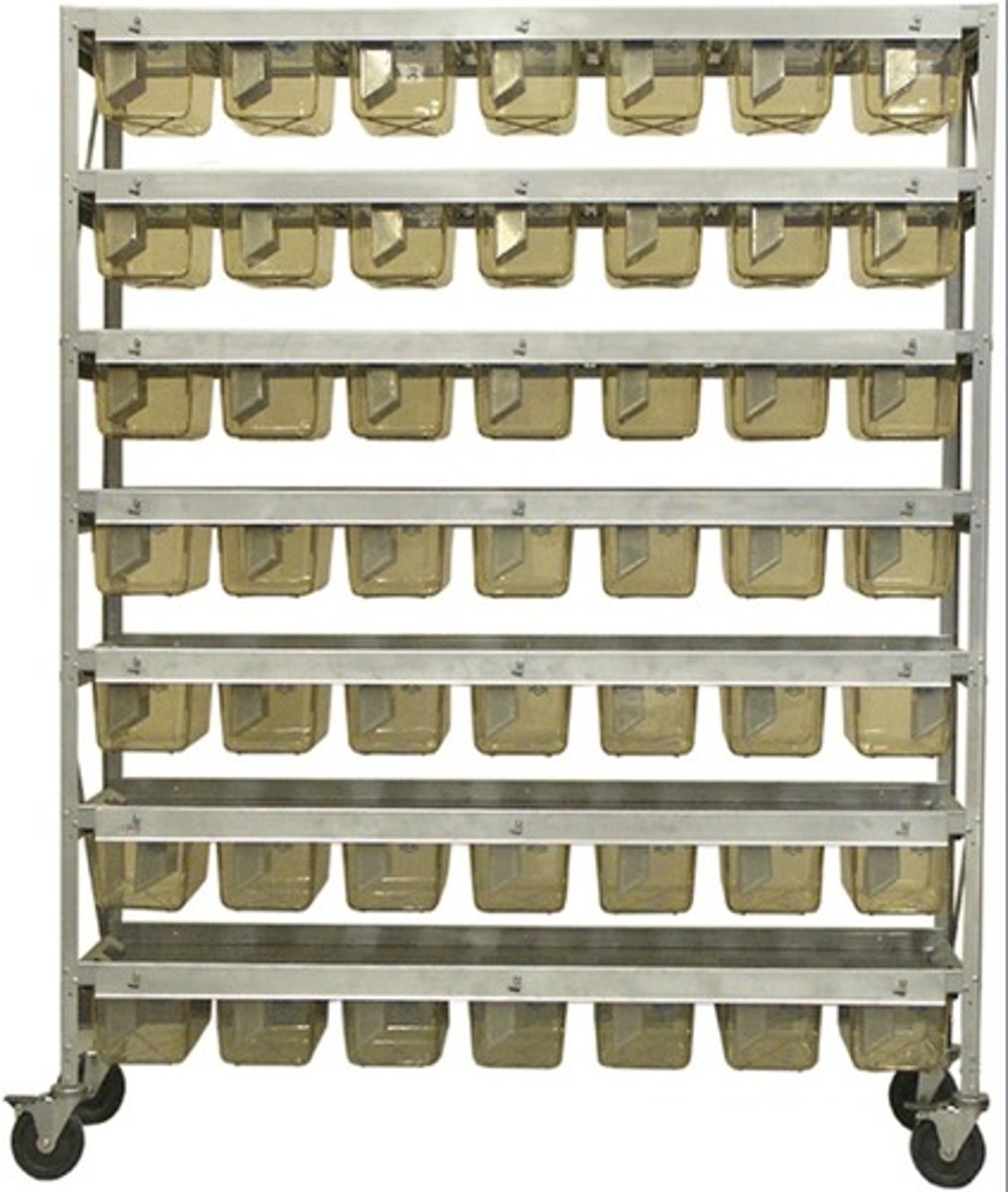

metabolism cages
To collect feces and urine, with food and water provided outside the cage.
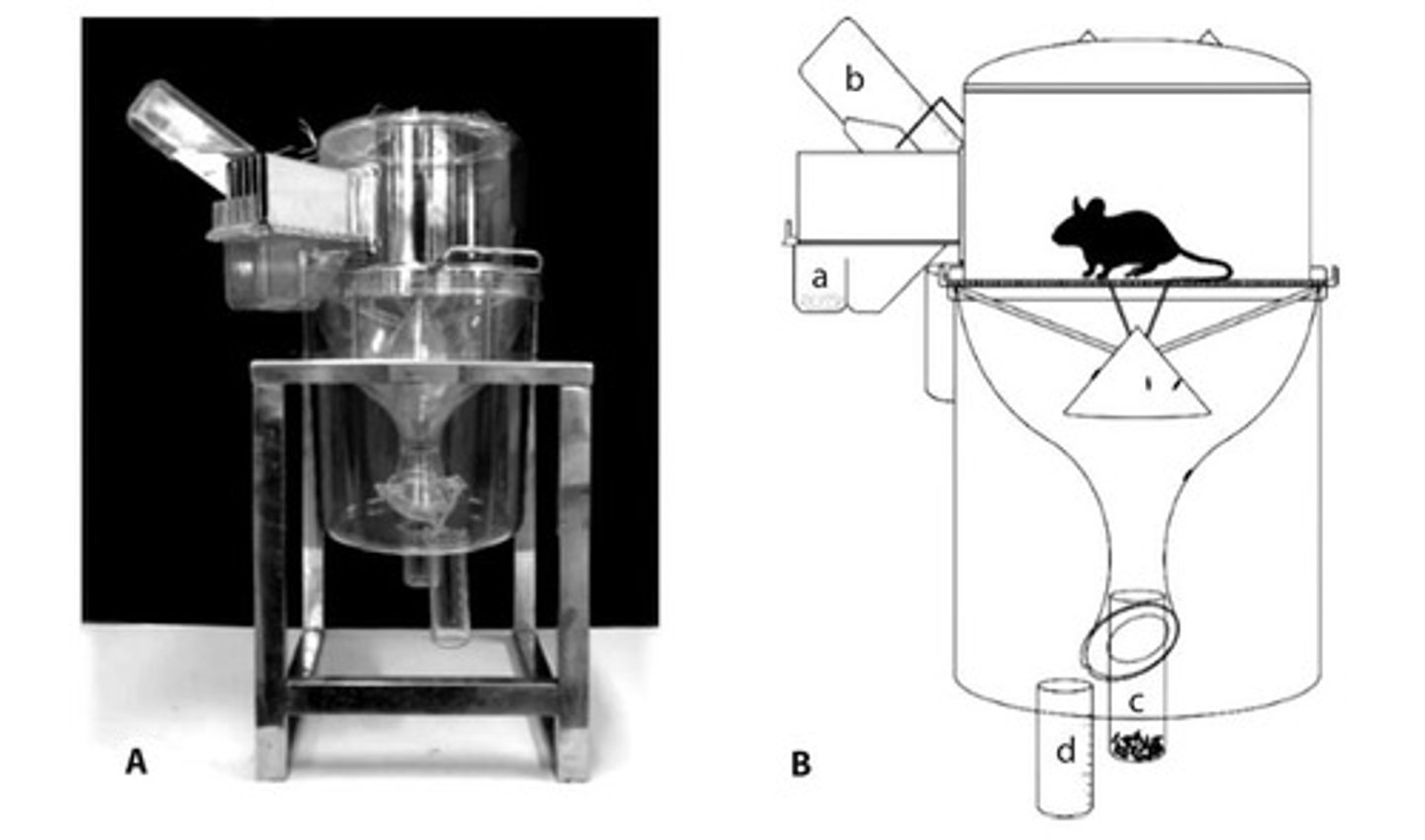
Gang cage
Type of cage allows for group housing and has multiple food and water sites

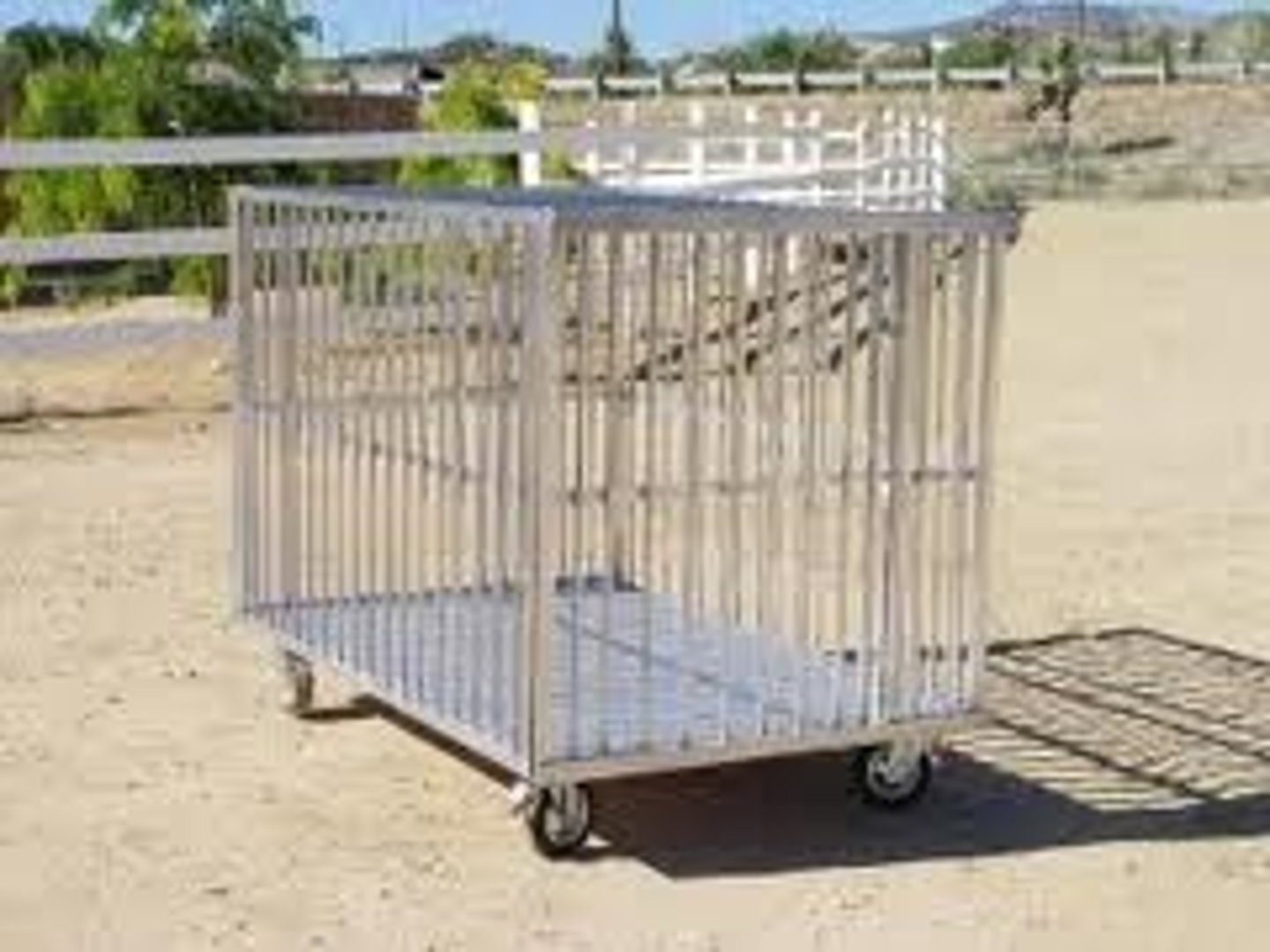
Transport Cages
To move animals from one location to another, often equipped with wheels.

inhalation cage
To create an enclosed chamber with strict environmental parameters for specific studies. May provide supplemental oxygen after surgey.
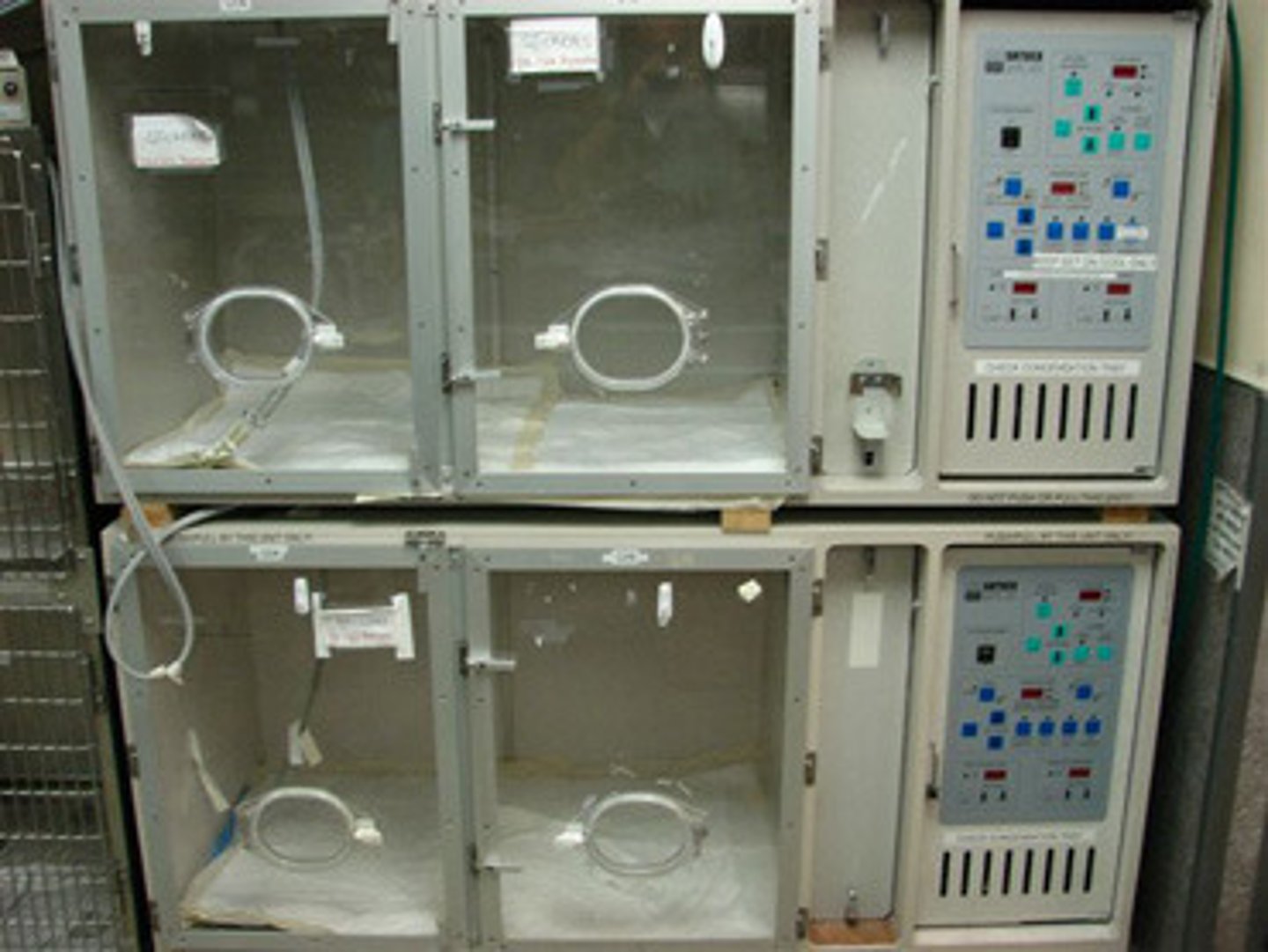

Body weight and surface area
Factors used when calculating cage space requirements for animals

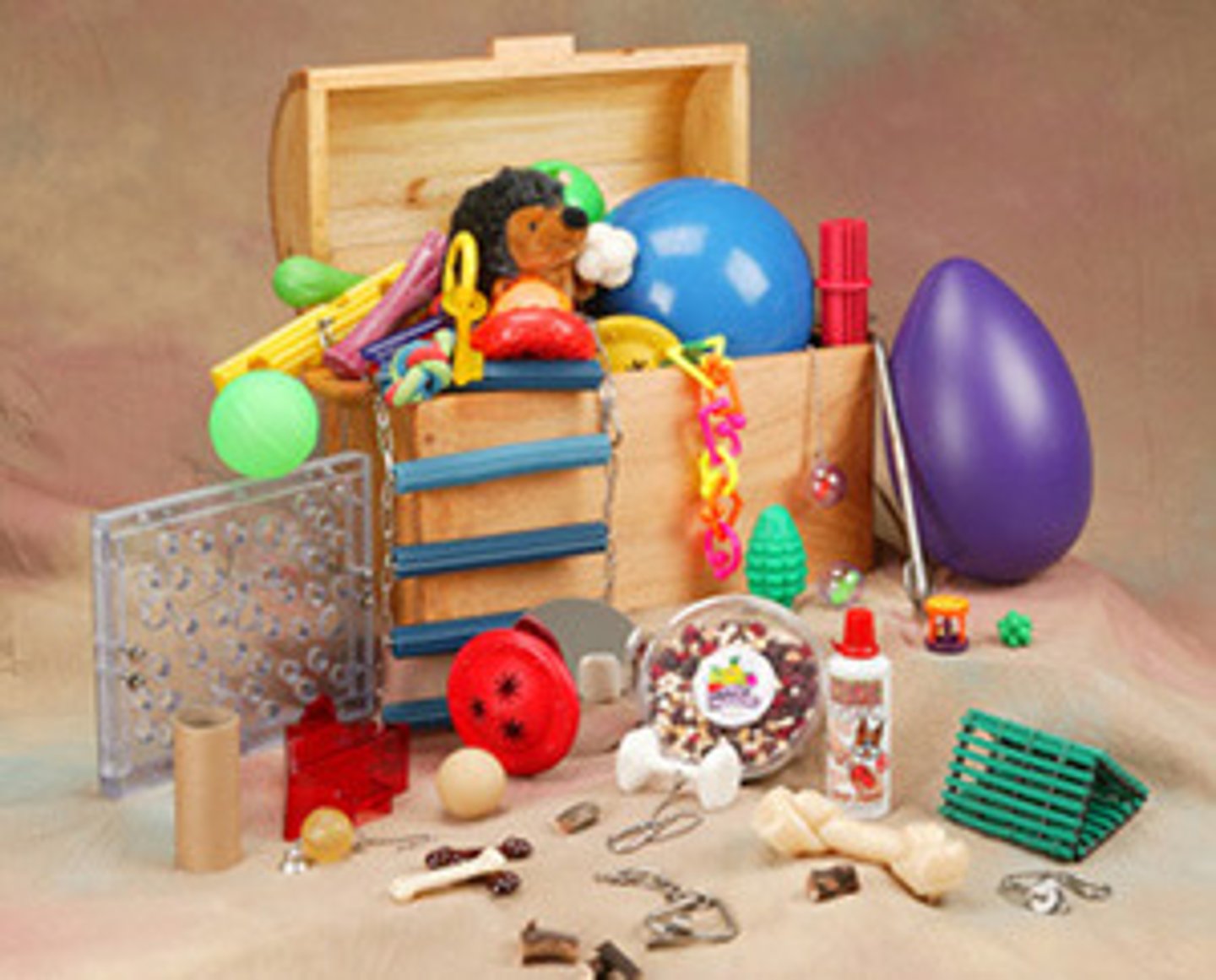
Environmental enrichment
Vertical space, resting ledges, boxes for burrowing, chew toys, climbing ropes, hidden treats, and running wheels.

Quarantine
To allow recovery from transportation stress and to prevent disease.

Axenic
Germ-free animals maintained in strict barrier facilities.

specific pathogen free
Animals are demonstrated to be free of certain pathogens but not all.
OSHA
To enforce laws that protect workers from hazardous materials.

BSL 1
Agents that do not harm humans
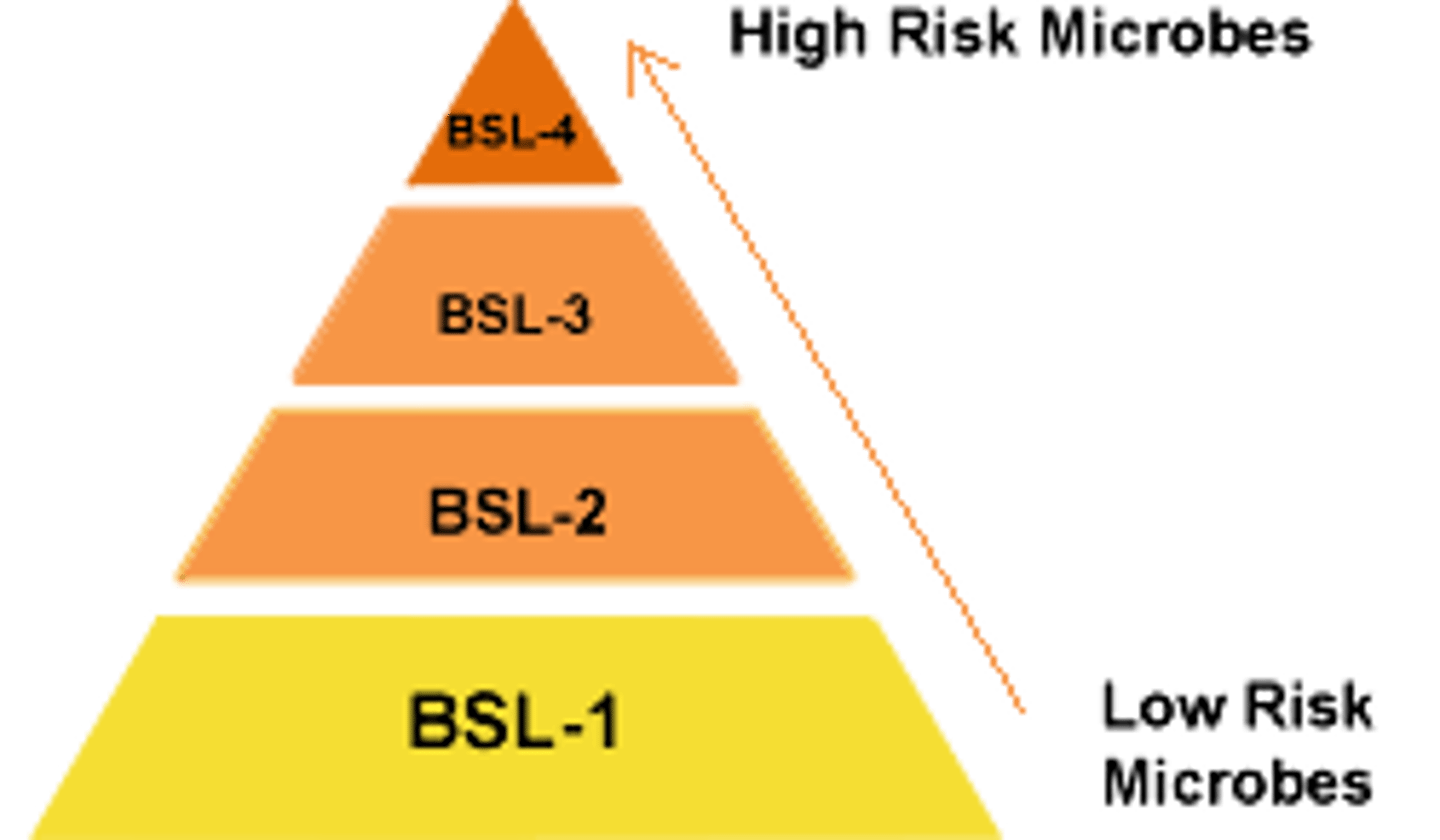
BSL 2
Potential human disease with treatments available
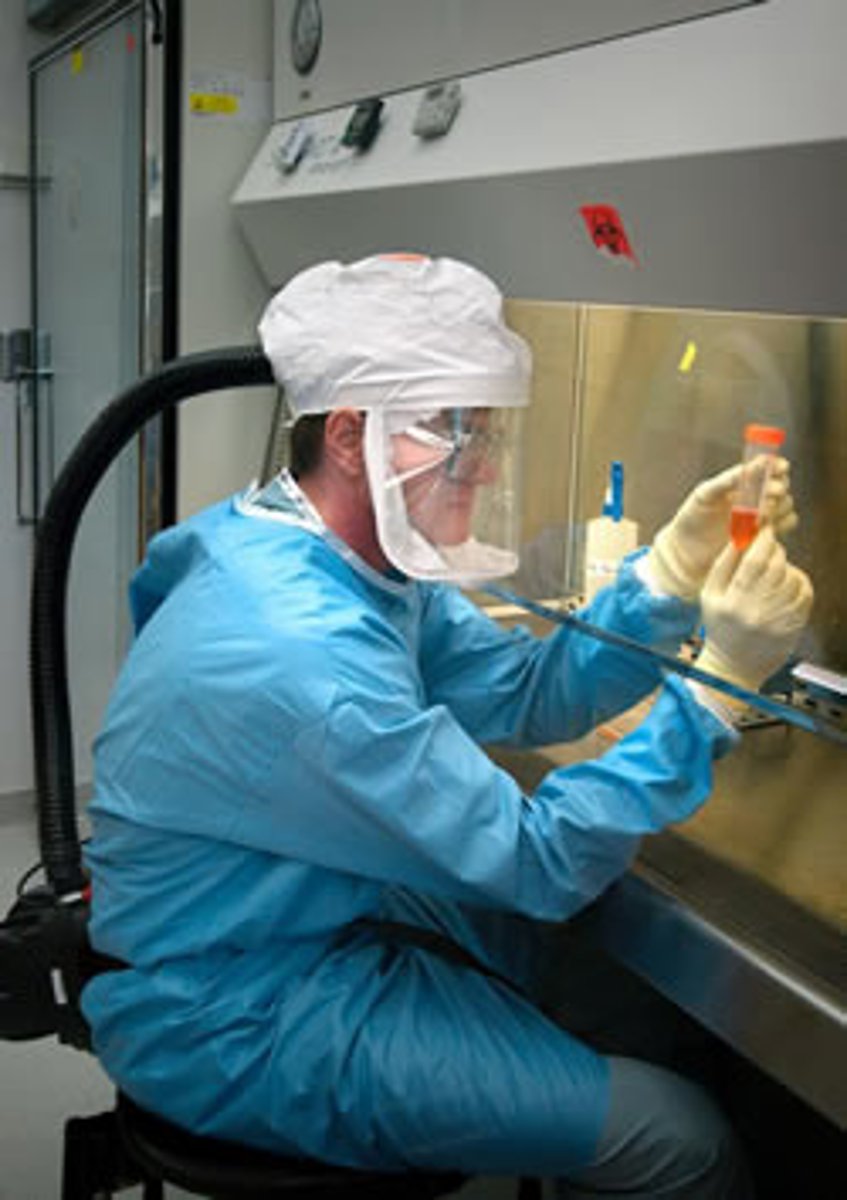

BSL 3
Serious human diseases with treatments available
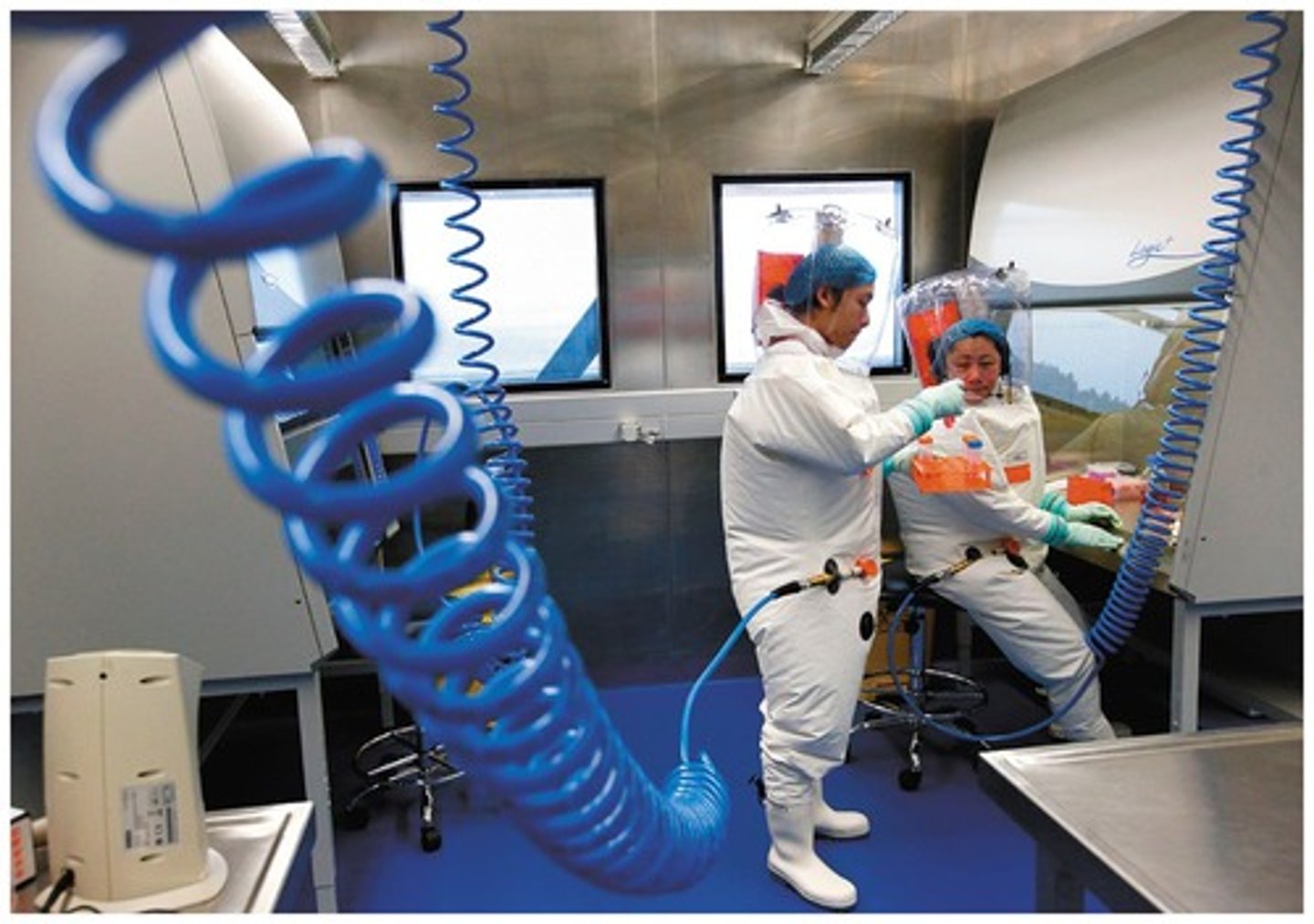

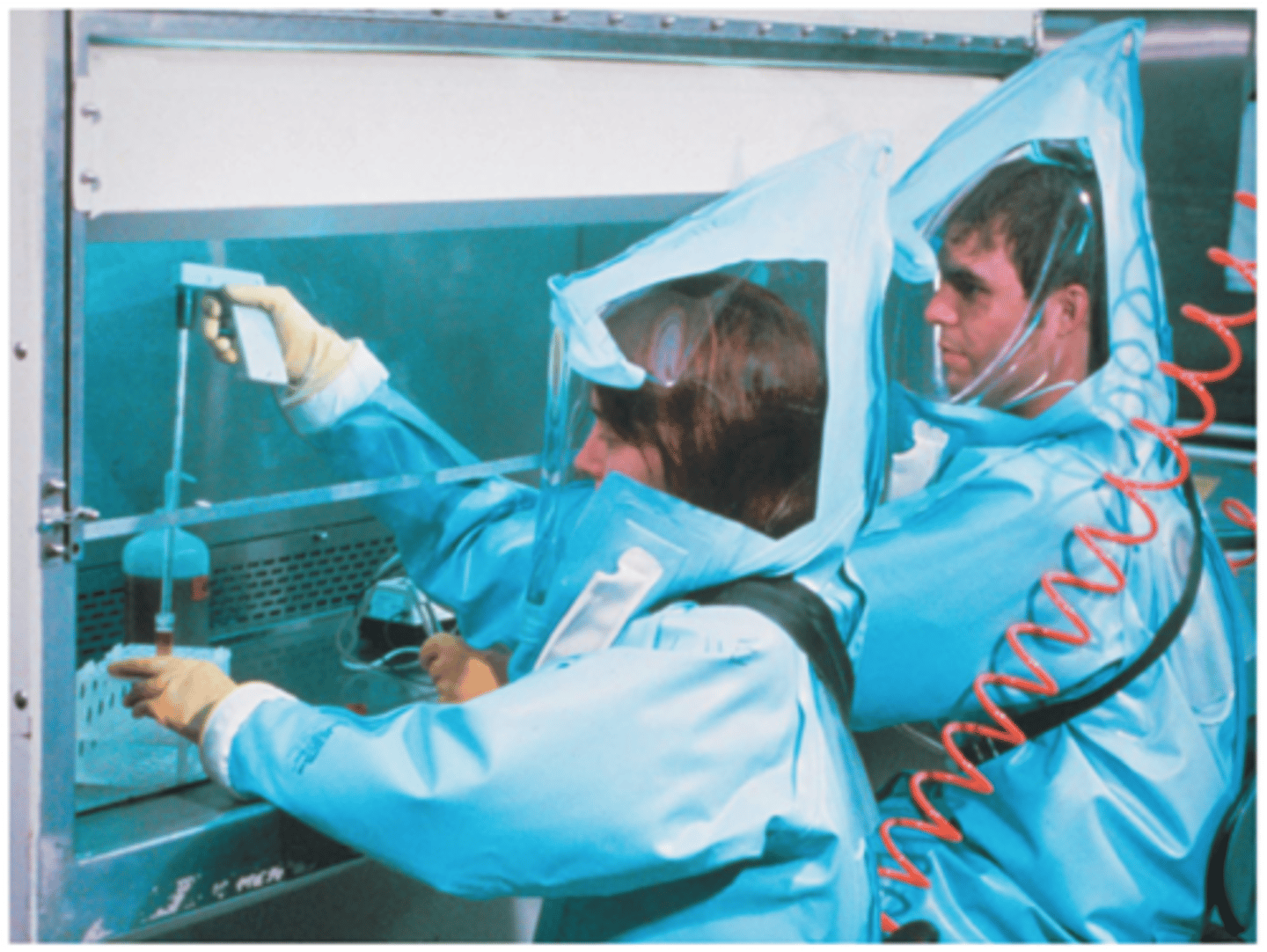
BSL 4
Serious or fatal human diseases without treatments available

Purpose bred
animals bred specifically for research purposes

Random Source Animals
procured from USDA class B dealers who may obtain animals from shelters. Concern is they may be a previous pet