arc 2/3 summative study guide (terms)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
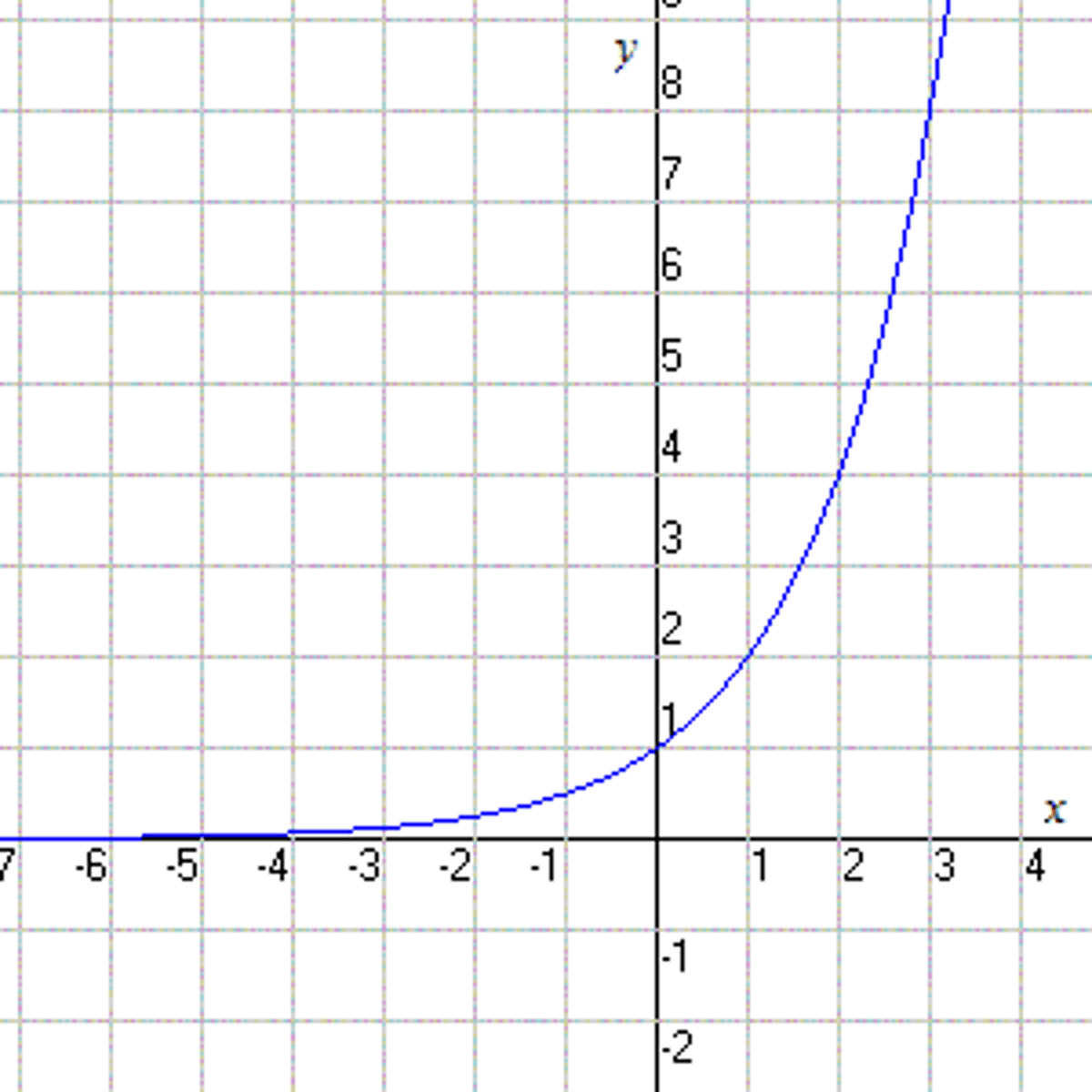
exponential growth
under ideal conditions, a population can increase rapidly over a relatively short amount of time
(J SHAPED)
ex. birth and immigration
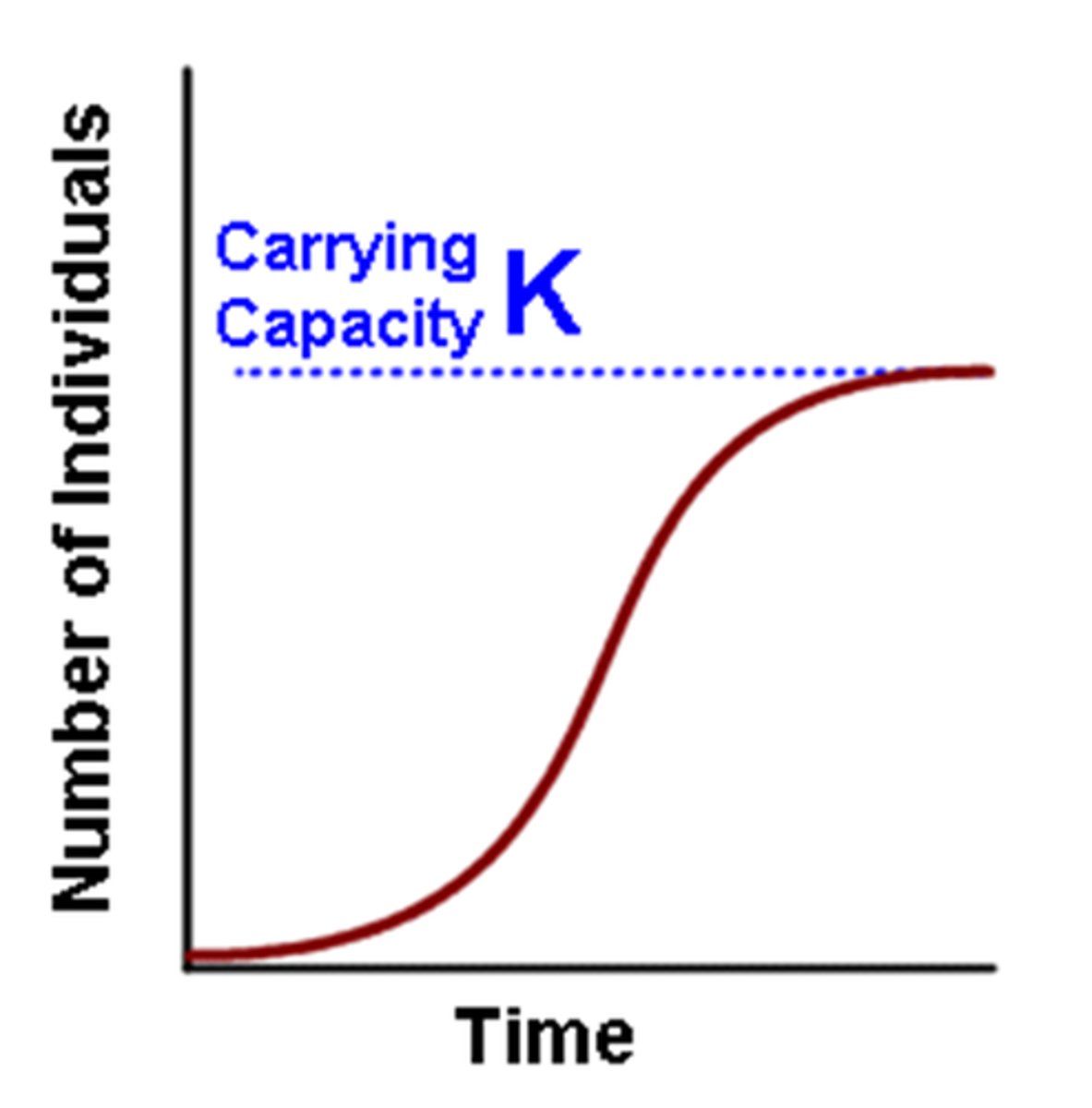
logistic growth
period of slow growth following a period of exponential growth before leveling off to a stable size (reaches carrying capacity)
(S SHAPED)
1. resources are abundant at first, and the population grows quickly
2. resources and growth reduce
3. population levels off to a size the environment can support
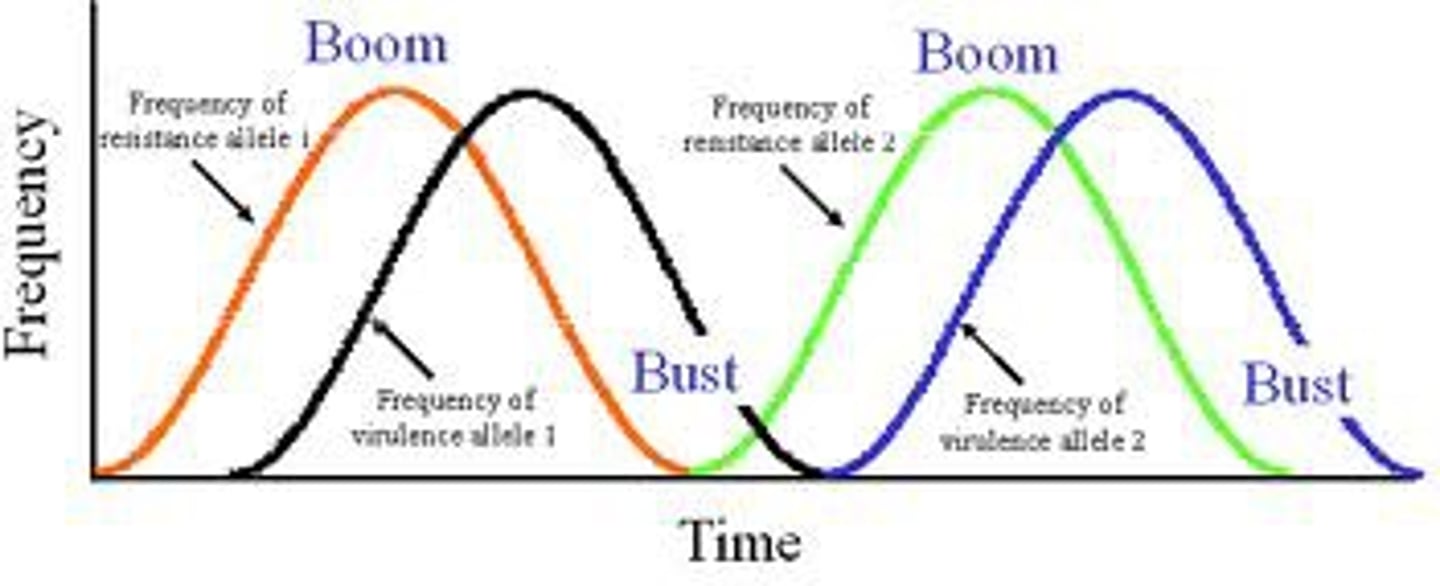
boom and bust
population grows exponentially, can exceed the resources available (boom)
=
rapid decline in population, higher death rates (bust)
density-dependent factors
environmental conditions or events whose impact on a population is affected by the population's density
simple terms: things in the environment that affect a group of living things depending on how populated they are
-exert a stronger influence on larger, more densely populated groups of organisms
-help define the carrying capacity
-can alter birth and death rates
ex. competition, predation, disease, parasitism, etc

density-independent factors
environmental influences, often abiotic, that impact a population's size, regardless of density
simple terms: non-living things that affect a population, no matter how crowded they are
ex. natural disasters like floods, wildfires, droughts, hurricanes, etc
ex. some human factors like pollution and habitat destruction

limiting factors
an element in the environment that restricts the growth, distribution, or abundance of a population or organism, determining the ecosystem's carrying capacity
carrying capacity
the maximum population of a species that an environment can hold indefinitely without being damaged or degraded, determined by factors like food, water, shelter, and predation
simple terms: the max population an ecosystem can hold before things get bad

disturbances
events that change communities, remove or destroy organisms from communities, or alter resource availability

ecosystem resilience
an ecosystem's ability to recover from disturbance

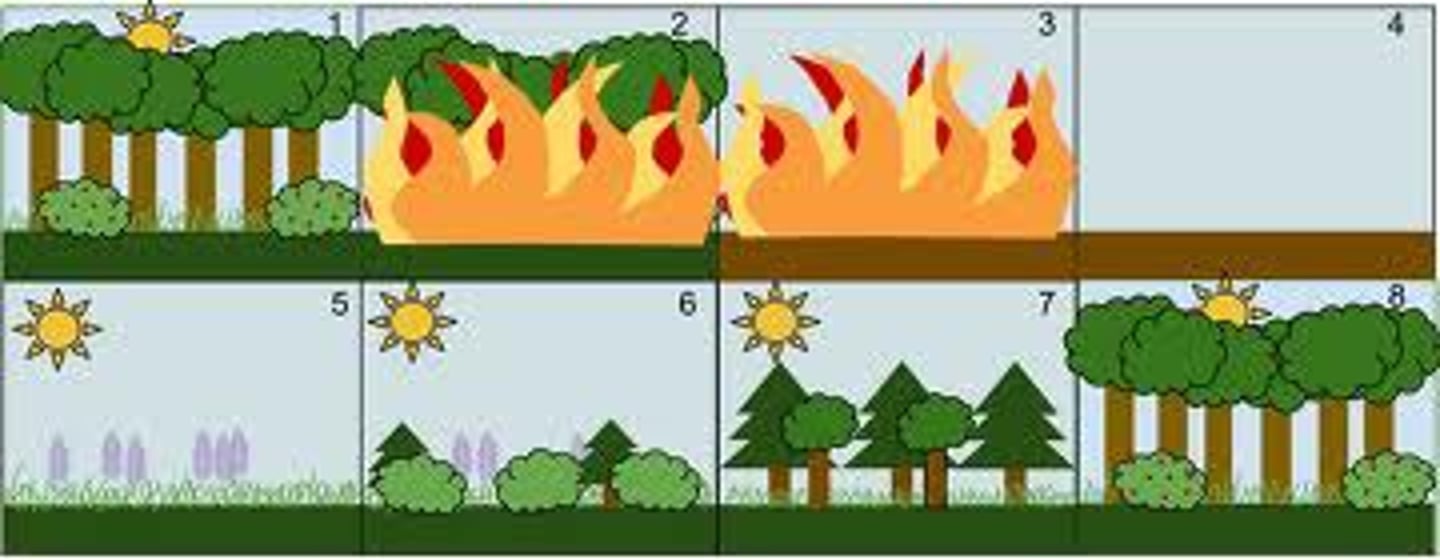
succession
a sequence of biotic changes that restore a damaged community or create a community in a previously uninhabitable area
simple terms: changes to make an unlivable community into a livable community
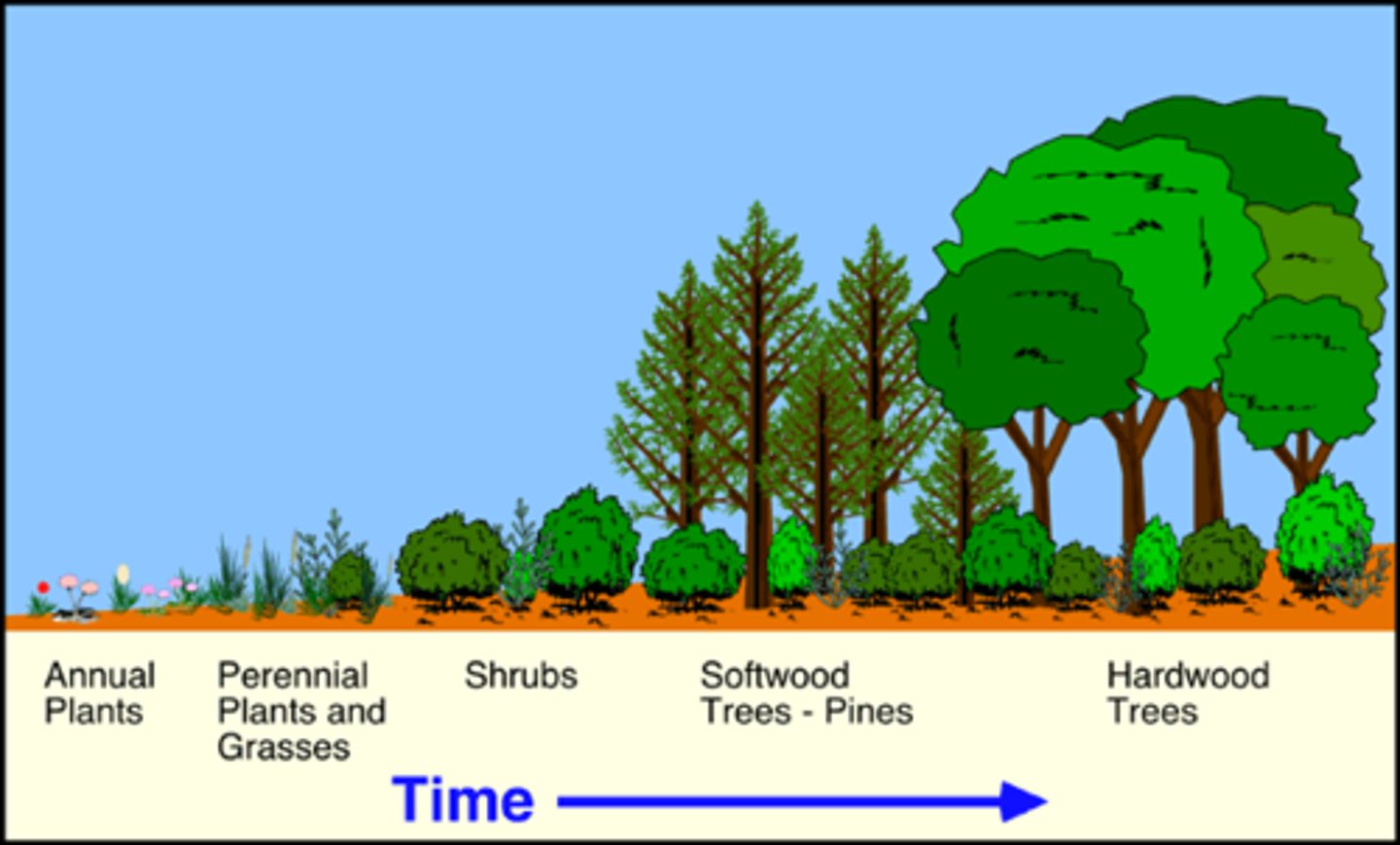
primary succession
the establishment and development of an ecosystem in a previously unhabited area
ex. rocks
secondary succession
restoration of an ecosystem in an area where soil was left intact (soil still on the ground)
-responds faster than primary
-sometimes new plants come and increase biodiversity
what makes a graph scientific?
clearly and accurately communicates scientific data
niches
the role of an organism in its habitat, or how it makes its living
multiple niches = competition = bad
species harmony
balance between an ecosystem, all interacting

stable ecosystems
-biodiversity
-niches
-species harmony
-resistance to disturbances
-abundance of resources
-consistent/predictable climate
what causes fluctuations in population size?
-births/deaths
-emmigration/immigrations
-carrying capacity
-density-dependent and independent limiting factors
-disturbances
trophic cascade
an ecological process that happens when the removal or addition of a top predator triggers a chain reaction that impacts other species throughout the ecosystem, cascading down the food web to affect lower trophic levels, from prey populations to the plants they eat
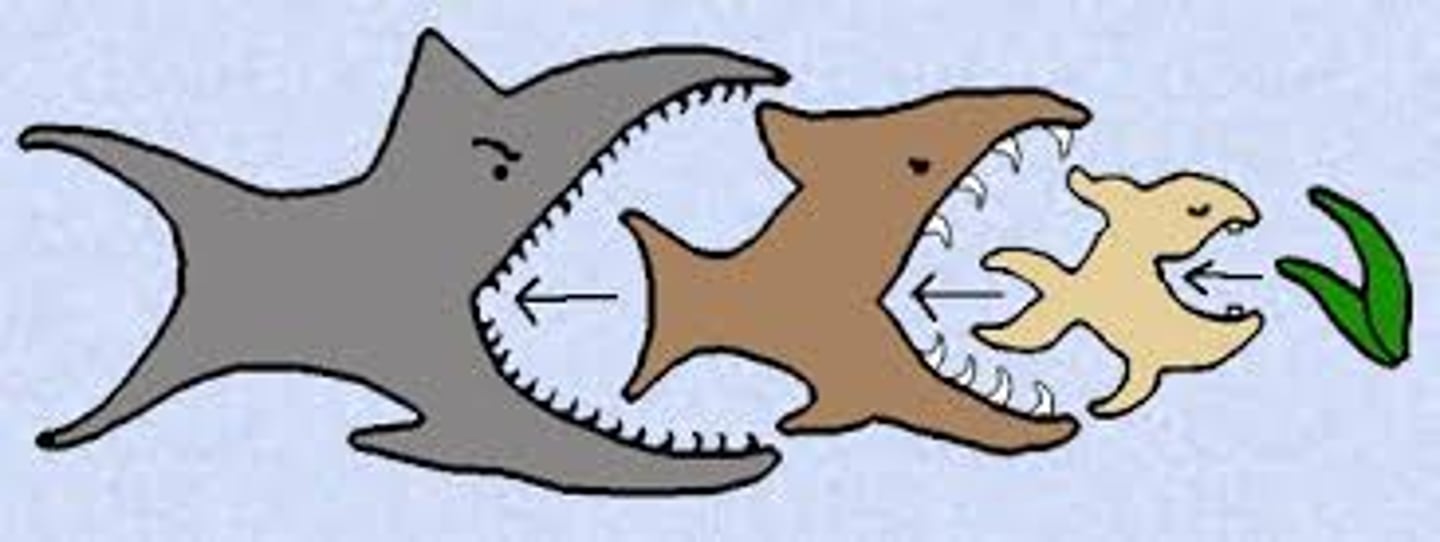
keystone species
organisms that have a disproportionately large effect on their ecosystem relative to their abundance
if they are removed, the ecosystem would collapse
