Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ears, taste, sight, smell, sexual reproduction,
Last updated 5:49 AM on 1/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
1
New cards
Smell, taste, sight, hearing, equilibrium
Special senses include
2
New cards
Chemoreceptors, respond to chemicals in an aqueous solution
The sense of smell and taste utilize recepetors called….. which means they
3
New cards
lens
Flexible biconvex crystal-like structure
4
New cards
lacrimal gland
Gland that releases tears
5
New cards
Sclera
White of the eye
6
New cards
Cones
Type of photoreceptor cell that detects colors
7
New cards
Cornea
Transparent portion of the fibrous layer
8
New cards
fovea centralis
Area of greatest visual acuity
9
New cards
Vitreous humor
Type of gel-like substance located in the posterior segment
10
New cards
Retina
Layer that contains millions of photoreceptors
11
New cards
Optic disc
Portion of the optic nerve that lacks photoreceptor cells
12
New cards
middle ear
Tympanic membrane separates the outer ear from this region
13
New cards
Inner ear
Location of equillibrium receptors
14
New cards
inner eat
fluid filled part of the ear
15
New cards
inner ear
location of otoliths
16
New cards
inner ear
location of vestibular apparatus
17
New cards
outer ear
location of ceruminous glands
18
New cards
outer ear
Location of the auricle (pinna) and external acoustic meatus
19
New cards
sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami
the five taste sensations are ….
20
New cards
facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
What are the three cranial nerves that carry taste sensations to the brain
21
New cards
lacrimal
what gland releases tears onto the anterior surface of the eyeball
22
New cards
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
Which cranial nerve transmits both hearing and equilibrium information to the brain
23
New cards
False
True or False: the olfactory receptors are responsible for detecting taste sensations
24
New cards
olfactory receptors, in the roof of the nasal cavity
The “organ” of smell is called ___and is located _____
25
New cards
olfactory receptors
The nose contains specialized chemoreceptors called olfactory
26
New cards
Mucus
What must occur for the receptors to be activated (why does sniffing “increase” sense of smell)?
27
New cards
loss of sense of smell
Can be causes by infection and head injuries
Can be causes by infection and head injuries
Define Anosmias and how it can be caused
28
New cards
taste buds
papillae contains ____
29
New cards
vallate papillae, fungiform papillae, filiform papillae
The three types of papillae
30
New cards
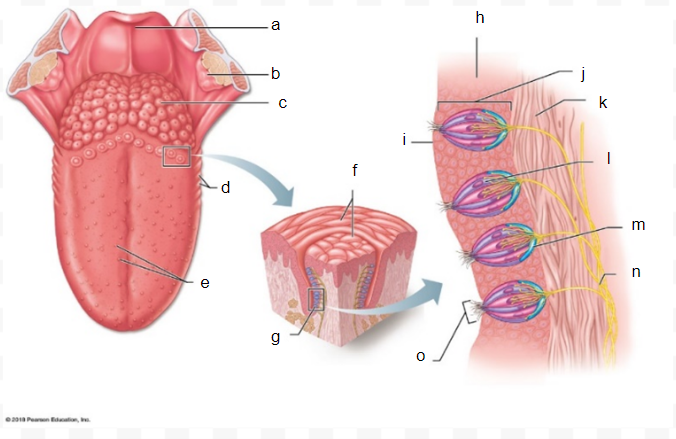
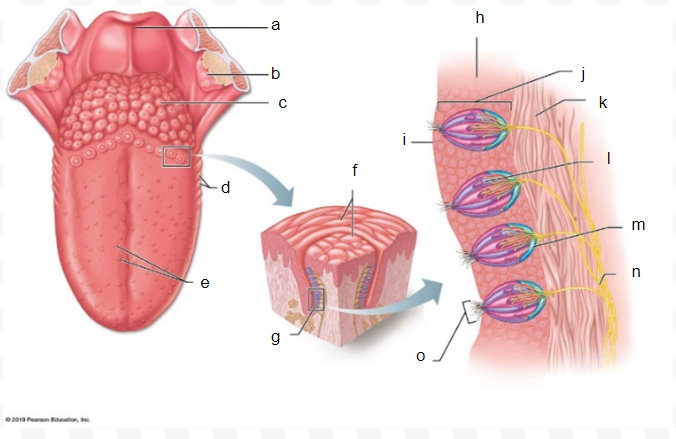
epiglottis
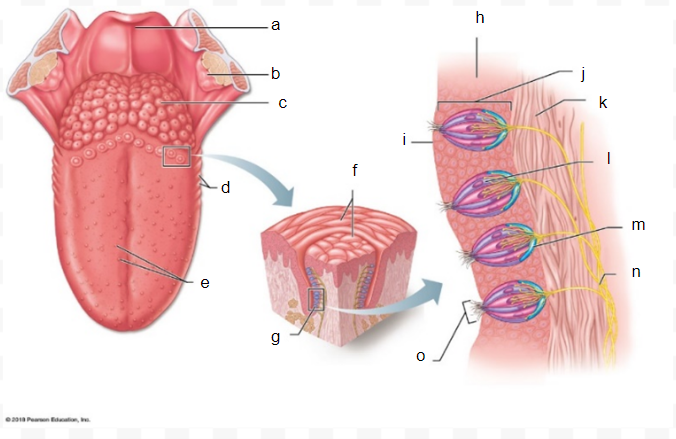
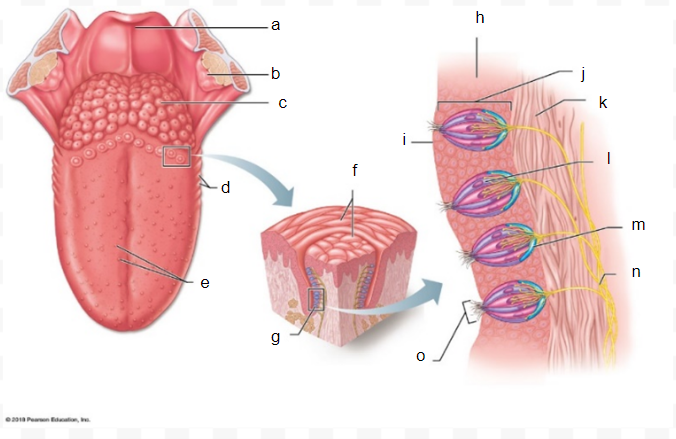
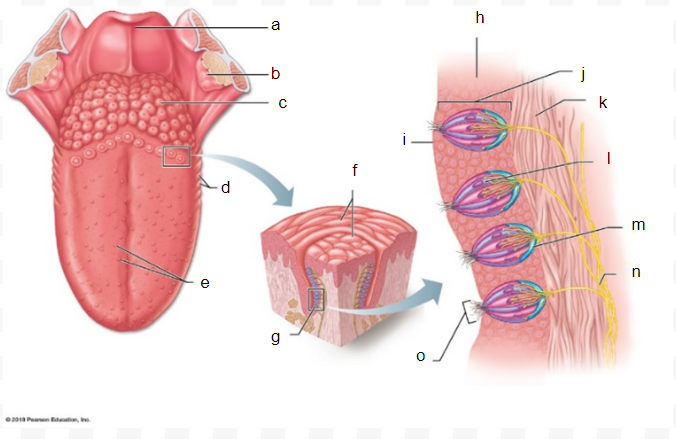
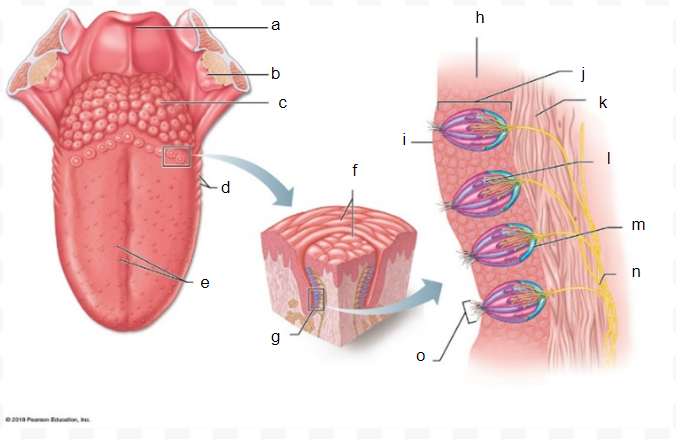
a
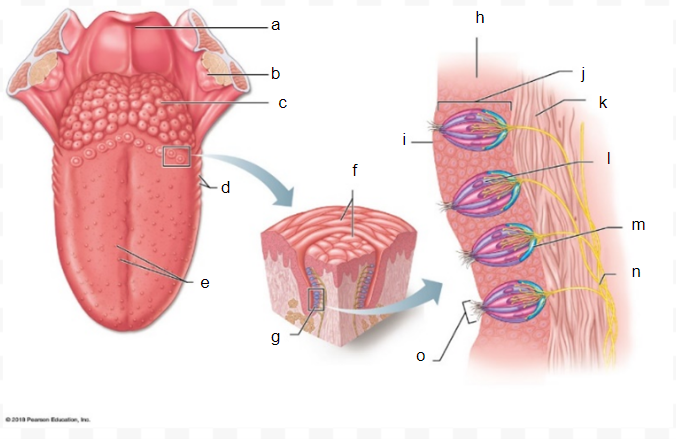
31
New cards
palatine tonsil
b
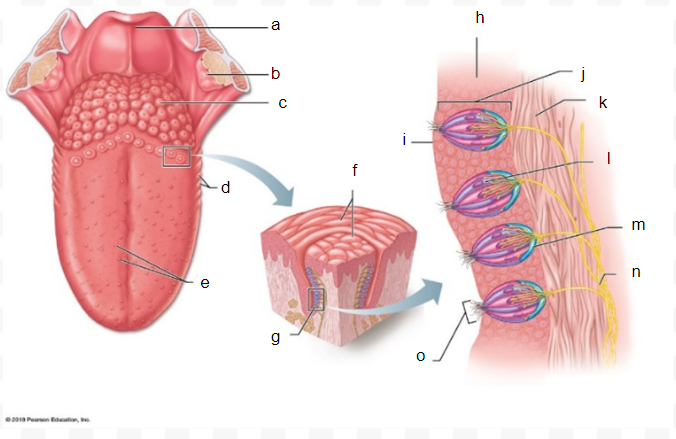
32
New cards
lingual tonsil
c
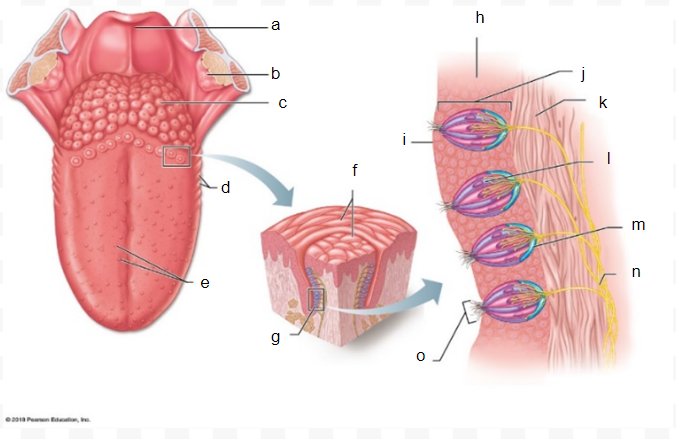
33
New cards
folliae papillae
d
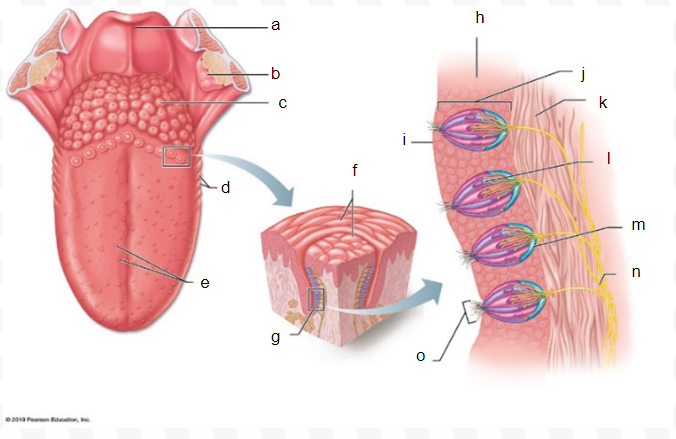
34
New cards
fungiform papillae
e
35
New cards
vallate papilla
f
36
New cards
taste buds
g
37
New cards
epithelium of tongue
h
38
New cards
surface of the tongue
i
39
New cards
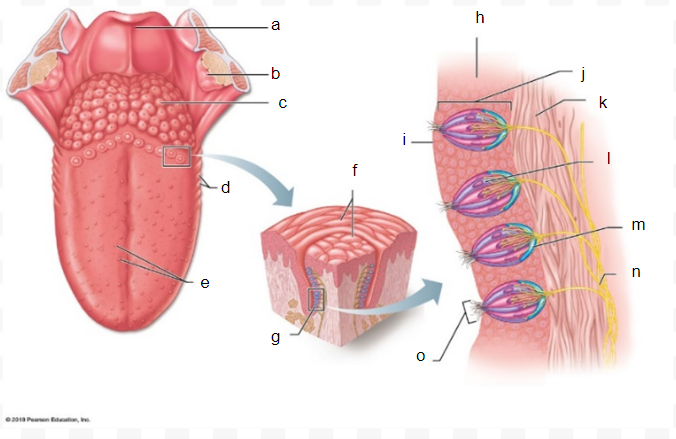
taste bud
J
40
New cards
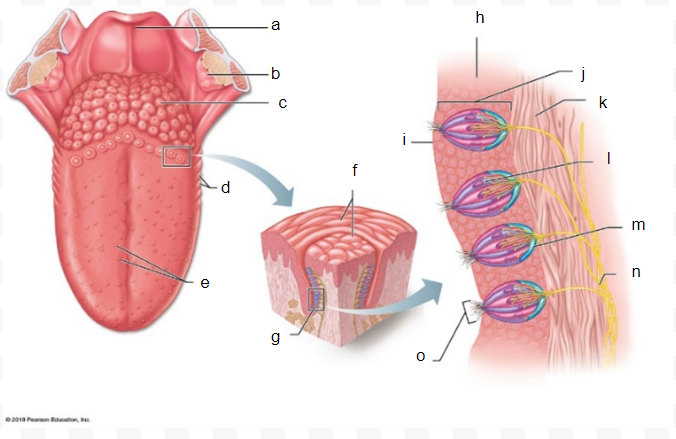
connective tissue
k
41
New cards
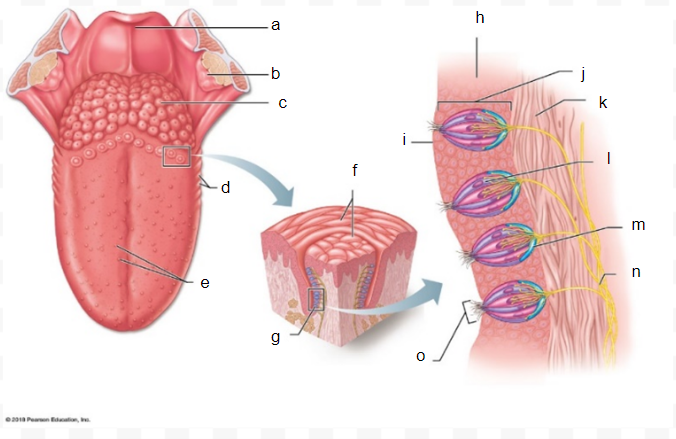
gustatory taste cell
l
42
New cards
taste cell
m
43
New cards
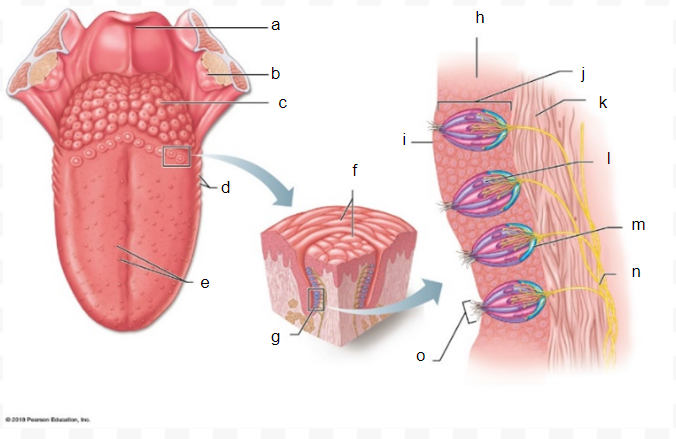
basal cell sensory
n
44
New cards
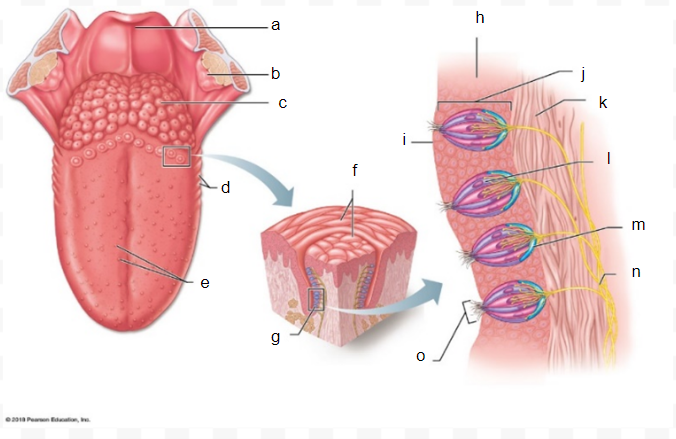
sensory nerve fiber
o
45
New cards
the receptor organs
taste buds house the ___
46
New cards
most are on the tongue, soft palate, superior oart of the pharynx, cheeks
taste buds are located where
47
New cards
receptor cells for taste
gustatory cells are ____
48
New cards
project form the tips of all gustatory epithelial cells and extend through a taste pore to the surface of the epithelium, where they are bathed by saliva
what is the role of gustatory hairs
49
New cards
1\. Sweet receptors respond to sugars, saccharine, some amino acids
2\. sour receptors respond to H+ ions or acids
3\. Bitter receptors respond to alkaloids
4\. Salty receptors respond to metal ions
5\. Umami receptors respond to the amino acid glutamate or the beefy taste of meat
2\. sour receptors respond to H+ ions or acids
3\. Bitter receptors respond to alkaloids
4\. Salty receptors respond to metal ions
5\. Umami receptors respond to the amino acid glutamate or the beefy taste of meat
Taste sensations include
50
New cards
*Taste tends to decline. The number of receptors decrease over time and are replaced by basal cells, and the sensitivity of receptors decline. We usually see this around the age of 40.*
Taste tends to ____ with age and why
51
New cards
lacrimal canaliculus, lacrimal sac, lacrimal duct, nasal cavity
tears drain across the eye into the ______ then the _______ nasal ______ which empties into the _____
52
New cards
Dilute salt, mucus, antibodies, lysosomes
what substances do tears contain (4)
53
New cards
clean and protect, moist and lubricate the eye
Function of tears
54
New cards
enable the eyes to move in all directions of sight
Function of the extrinsic eye muscle
55
New cards
the white of your eye and connective tissue
what is sclera and what is it made of
56
New cards
Transparent, is in front of lens, allows light to pass through to lens, if damage it can repair itself easily
What is the cornea and can it repair itself if damaged
57
New cards
blood rich and nutritious layer and contains pigment which helps prevent light from scattering
What is the choroid
58
New cards
is the color of the eye and regulates the amount of light
what’s the iris and function
59
New cards
whatever color your eyes are
What is the pigmented layer of your eyes
60
New cards
opening layer in your iris, made up of smooth muscle tissue
what is your pupil and what is it made of
61
New cards
absorbs a light that prevents it from scattering and absorbs vitamin a
what is the outer pigmented layer
62
New cards
rods and cons
inner neural layer contains
63
New cards
photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells
inner neural layer contains what three types of neurons
64
New cards
rods, cones
the millions of photoreceptors contained in the retina are called (two types) __ and ___
65
New cards
blind spot
The spot where there are no photoreceptors in called
66
New cards
in the retina
night vision allows vision in dim light are located in ____ and therefore, are responsible for peripheral vision
67
New cards
*an interference with rod functions, potential causes is vitamin a levels therefore lack of retinol production, and aging*
what is night blindness and some potential causes
68
New cards
Cones, rods
*____* allows for detailed color vision and are denset in the *____*
69
New cards
Wave length
There are three types of cones, depending upon which wave length of visible light each is sensitive to; this allows us to see different color
70
New cards
*interference with cone function or lack of cones, more common in males,*
what is color blindness
71
New cards
Lateral to the blind spot, contains only cones, responsible for visual acuity, cause light can past almost directly to photoreceptors, lacks the vitreous humor
What is the fovea centralis, and what purpose does it serve?
72
New cards
biconvex on both sides (not flat), the lens is flexible and can change shape to make the image clear when light comes into the eye
What is the lens and some characteristics
73
New cards
cloudiness of the lens
What is cataracts
74
New cards
aqueous, or anterior chamber, aqueous humor, water like,
a. Helps maintain Oculate pressure
b. nutrients
c. Reabsorbed into blood
a. Helps maintain Oculate pressure
b. nutrients
c. Reabsorbed into blood
The ______*(*__*or* __ _____)__ segment, which contains _____ ____This is similar in consistency to _____ _____ and functions include: (3)
75
New cards
pressure on the eye
What is glaucoma posteri
76
New cards
Posterior, vitreous chamber, vitreous humer, gel like,
a. Helps main shape
b. Helps maintain intraocular pressure
a. Helps main shape
b. Helps maintain intraocular pressure
The ___ (or ____ ____) segment, which contains ____ It’s has a ____ ____consistency and it’s functions include: (2)
77
New cards
Go through the pupil, lens, refracted, pigmented layer (light is absorbed), neural layer of the retina, then its converted into electrical energy, accommodation, pupils constrict and eyeballs converge, images form on retina
Summarize the pathway of light through the eye to the retina
78
New cards
the lens adjusts and changes shape for things that are near and far away
What is accommodation
79
New cards
reversed, inverted, smaller
* Due to the convex nature of the lens, a “real image” is formed on the retina, which means it is _______________________, _____________________, and __________________ compared to the actual object.
80
New cards
normal vision
Emmetropia
81
New cards
nearsigted
Myopia
82
New cards
Farsighted
Hyperopia
83
New cards
Flattening of the lens
Astigmatism
84
New cards
retinal, opsin
A light absorbing molecule called ___combines with proteins called __to form visual pigments.
85
New cards
rhodopsin
Visual pigments capture light with the help of a special pigment called
86
New cards
phototransduction
When the visual pigments capture the photons of light, light energy is then converted into a graded receptor potential in a process called
87
New cards
retina, action potential
The steps of phototransduction take place in the __ and ultimately cause ___ to be transmitted along the optic nerve.
88
New cards
Optic disc
Bundle of axons that exit the back of the eye carrying impulses from the retina is called the
89
New cards
optic chiassma
The location where the optic nerves cross is called the
90
New cards
optic tract
_____ contain fibers from the lateral side of the eye on the same side and the medial side of the opposite eye
91
New cards
optic radiation
______ are axons from the thalamus that run to the occipital lobe
92
New cards
*Retina receptors, optic nerve, chiasma, optic tract, synapse, thalamus, optic radiation, synapse with occipital lobe (visual cortex),*
Summarize of the pathway of impulses from the retina to the point of visual interpretation
93
New cards
Depth perception is the ability to perceive the world in three dimensions (3D) and to judge the distance of objects. Your brain achieves it by processing different pictures from each eye and combining them to form a single 3D image
Depth Perception *– Briefly explain how we are able to see in 3D.*
94
New cards
Convergence
Reflexive movement of the eyes medially when we focus on a close object
95
New cards
Photo pupillary reflex
Bright lights causes pupils to constrict
96
New cards
Accommodation pupillary reflex
Close objects causes pupils to contrict
97
New cards
prebyopia, close vision
old vision” results from decreasing lens elasticity that accompanies aging is called _____ results in difficulty to focus for close _ ______
98
New cards
mechanoreceptors
The receptor in the ear respond to physical forces (e.g. vibration) and are called
99
New cards
collects sound waves and channels them into the ear canal, where the sound is amplified
function of Auricle (pinna)
100
New cards
collecting sound waves and conveying them to the eardrum
function of External acoustic meatus (auditory canal)