Biomass transfers
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Sun
All organisms found within an ecosystem require a source of energy to perform the functions needed to survive
The Sun is the source of energy for almost all ecosystems
Through photosynthesis, the Sun's light is converted into chemical energy in plants and other photosynthetic organisms
This energy is then transferred to other non-photosynthetic organisms as food
Trophic Levels
Places in the food chain
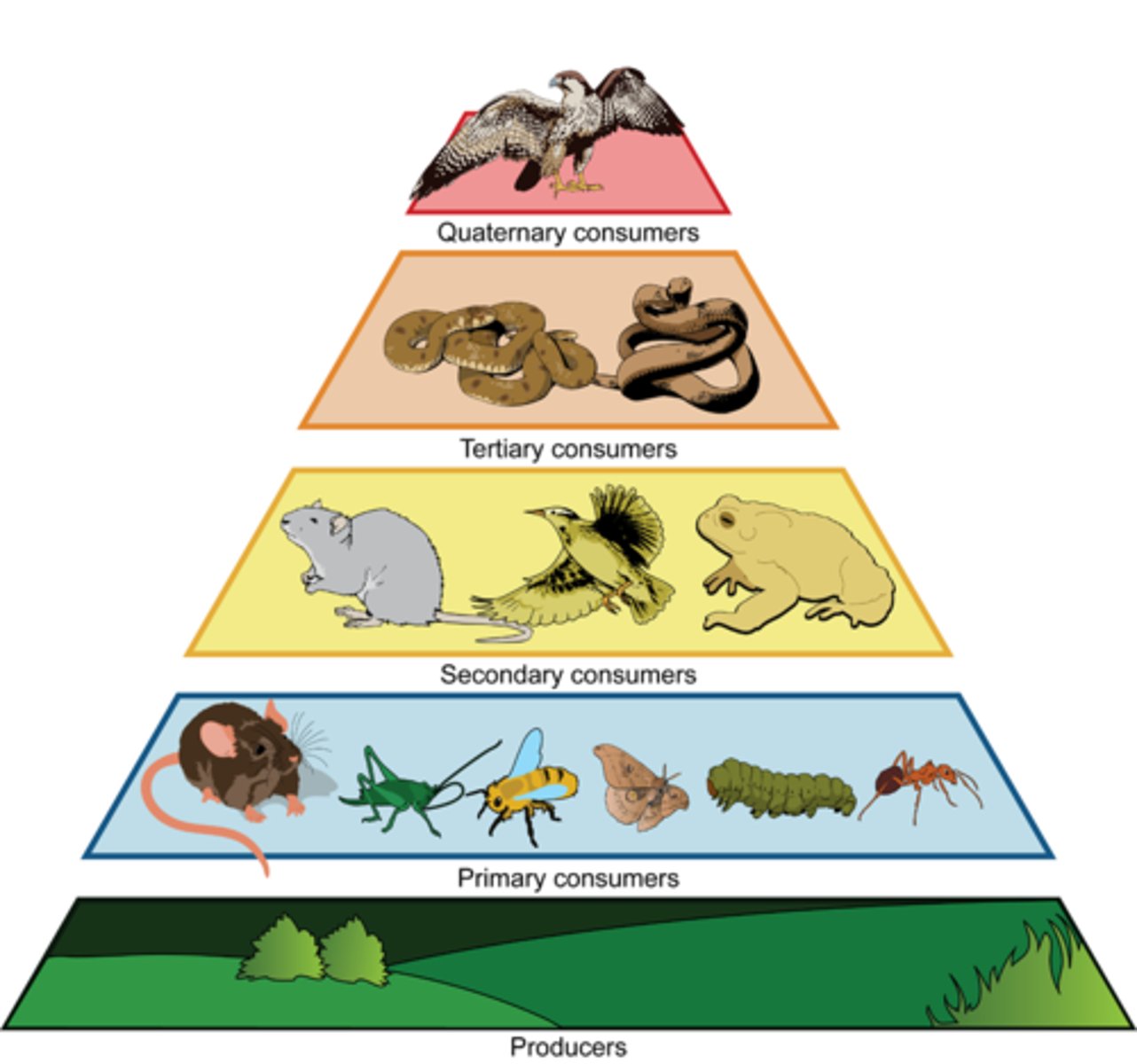
Producer
Fixes carbon using sunlight (photosynthesis)
Primary consumer
Feeds on the producer
Secondary Consumer
Feeds on primary consumer
How to calculate the efficiency of biomass transfers between trophic levels?
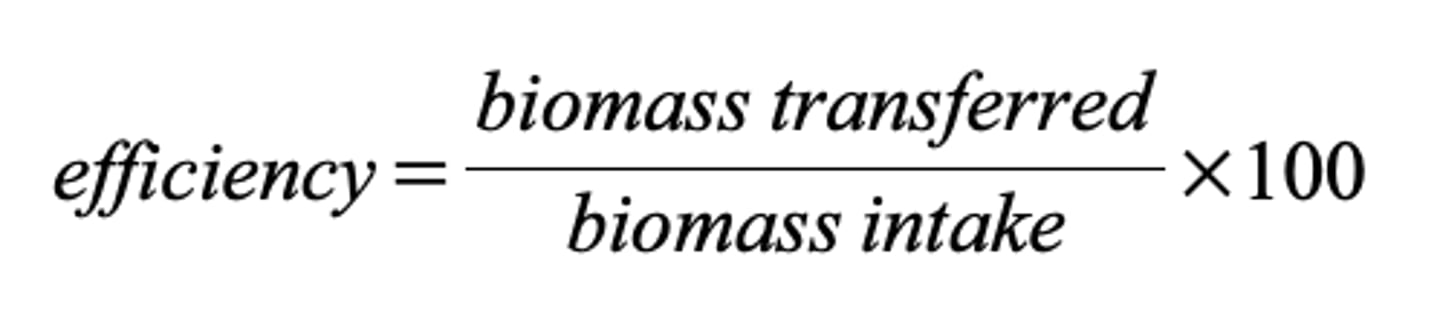
What units are used in biomass transfers?
kg
Does biomass increase or decrease with each trophic level?
decrease
Does energy increase or decrease as it moves up trophic levels?
increase
Why does the energy increase up the trophic levels?
Energy is lost as metabolic heat, when the organisms from one trophic level are consumed by organisms from the next level
Advantage of using dry mass in a pyramid of mass
Removing the water content (to make dry mass) allows for comparisons to be made between different organisms, since different organisms have different water content
Disadvantage of using dry mass in a pyramid of mass
Removing the water, the organism won't survive this process, killing them and bringing to light ethical issues
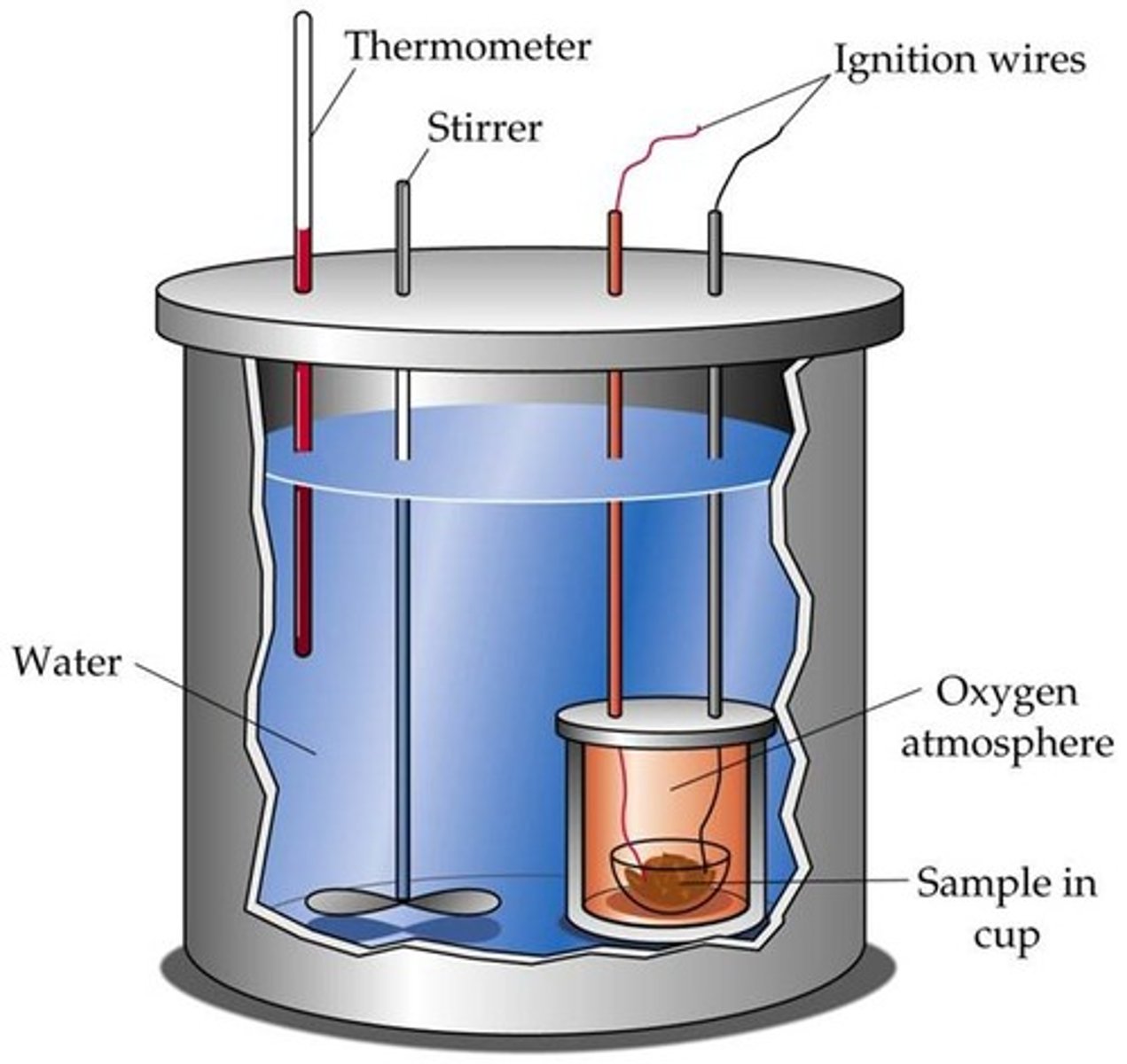
How is the energy content of dry mass obtained?
- Using a bomb calorimeter
- Burn the sample in a high pressure of oxygen
- The rise in the temperature of the water is measured
Why does the biomass decrease in the next trophic level?
- Not all biomass is eaten (bones & roots)
- Some is transferred to the environment as heat
- Some is excreted e.g. urine or faeces
- Some biomass is indigestible (cellulose)
Net primary production
The energy available at each trophic level
Net primary production units
Kj m⁻² yr⁻¹
Ecological efficiency
The efficiency with which biomass or energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. This can be represented by a pyramid of energy
What factors could increase the net primary production?
- High temp
- Increase in sunlight
- More photosynthesis occurs
- More storage of biomass
Grass meadow in UK, and Amazon rainforest. Which habitat would have a higher rate of NPP and why?
- Rainforest
- High temp
- Increase in sunlight
- More photosynthesis occurs
- More storage of biomass
- Higher NPP
Producers only convert 1-3% of the sunlight received into chemical energy. Why?
Not all light hits the chlorophyll
Not all light hitting leaves is absorbed. It can be reflected, transmitted through the lead, or off the wrong wavelength
Other factors may limit photosynthesis
Productivity
Rate at which the plant converts light energy into chemical potential energy
Gross Primary productivity
Total quantity of energy converted by plants in this way
Net Primary Productivity
Energy which remains as chemical energy after plants have supplied their own needs in respiration
Ecological Efficiency =
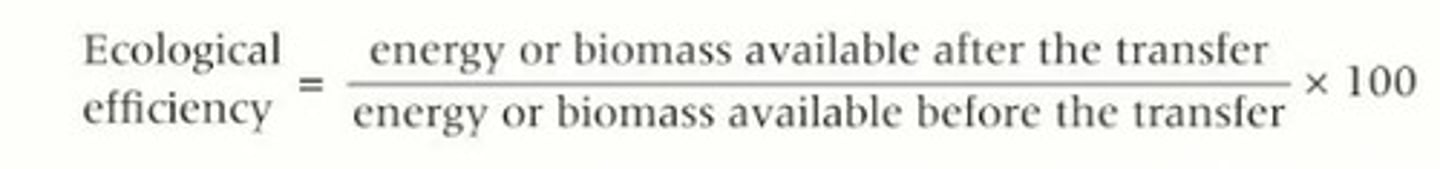
How can humans manipulate the transfer of energy in animals?
Animals being kept indoors in ideal conditions. Keeping them warm and reducing movement to prevent energy being used in respiration
High protein diet will transfer the protein eaten into muscle mass
Vaccinate the animals against diseases so less energy is used in the immune response
Slaughtering animals before they mature
Graph showing the changes in three quantities in a typical ecosystem as it goes through a succession to its climax.
- Biomass leaving as a respiratory loss will always be lower than the gross primary production of biomass
- This is because Gross primary productivity = Net primary productivity + Respiration
What does a food web include?
Primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers
How to calculate ecological efficiency?
