Mcgraw Hill Accounting Chapter 1 & 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Assets vs Liabilities
https://gyazo.com/8095d76f90415857aeaf5368e07a4688
Source Document
Identifies and describes transactions and is the basis for entering an event into the accounting system.
Account
Record within an accounting system in which increases and decreases are entered and stored in a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense.
General ledge/Ledger
Collection of all accounts with their activity and balances that exist in a business
Asset Accounts
Accounts relating to Assets, examples; Buildings, Equipment, Cash,
Cash Account
All increases and decreases in cash are recorded in the Account. Includes funds that a bank accepts for deposits. Ex; coins, checks, money orders, and checking account balances
Accounts Receivable
(IS AN ASSET) held by a seller and are promises of payment from customers to sellers.
Note Receivable / Promissory Note
Promise of another entity to pay a specific sum of money on a specified future date. Considered an asset.
Notes Payable
long-term liabilities that indicate the money a company owes its financiers
Prepaid Accounts
Assets that represent prepayments of future expenses and are increased with a debit (ex prepaid insurance, prepaid rent, and prepaid services) Unexpired portions are treated as assets, expired portions are transferred to expenses category
Supplies Account
Supplies are assets until they are used. When they are used up their costs are reported as expenses
Supplies Asset Account
Unused supplies
Equipment Accounts
Equipment is an asset. Its cost is allocated time to expense, called depreciation.
Buildings Accounts
Buildings such as stores, offices, warehouses, and factories are assets
Land
The cost of land (buildings located on the land is separately recorded in building accounts)
Liability Accounts
Obligations to transfer assets or provide products or services to others
Accounts Payable
Refer to obligations owed by the business and are classified as a liability
Debtors
Individuals or organizations that owe money
Creditors
Individuals or organizations entitled to receive payments
Liabilities
Claims against the assets of a business, claims are made by creditors
Assets
Things of value owned by a business (land, unused equipment, buildings)
Expenses
Cost of doing business (labor, used equipment, wages)
Equity
Owner's claim on a company's assets.
Equity = (Common Stock - Divdens) + (Revenues - Expenses)
Chart of Accounts
List of all ledger accounts which exist in a business and includes an identification number assigned to each account
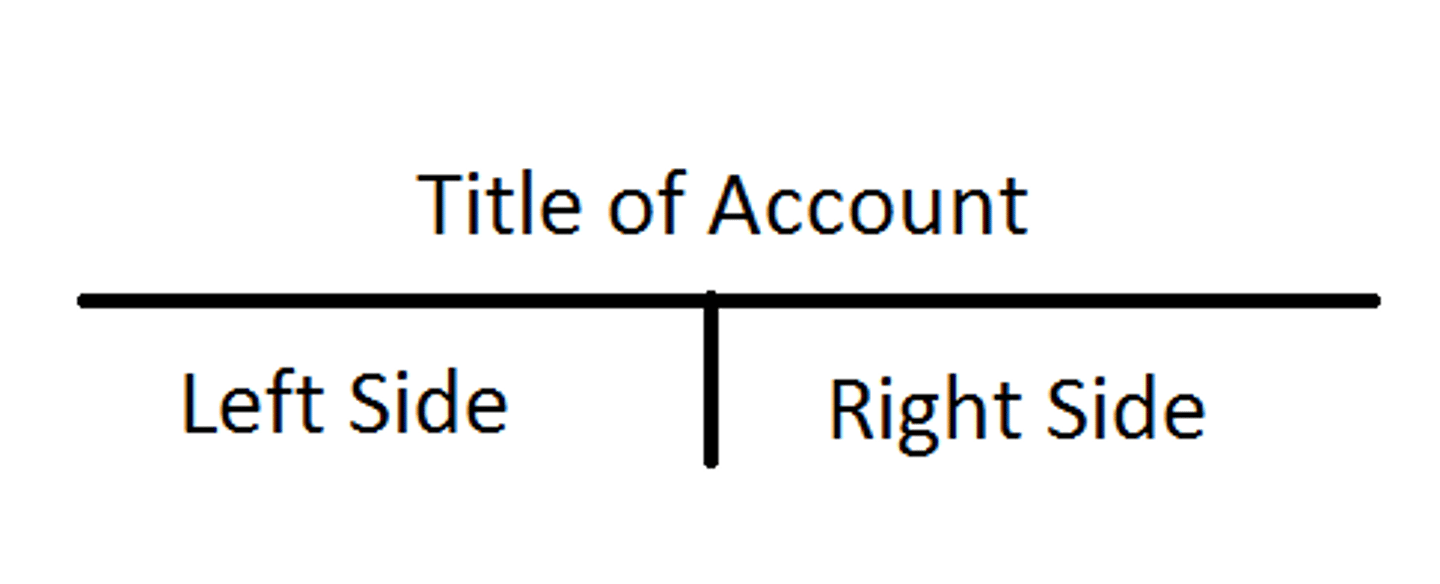
T- Account
Represents a ledger account and is a tool used to understand the effects of one or more transactions.
Journal
Book of original entry that includes a chronological record of all transactions that have occurred within a business during a period that occurred
Trial balance
List of each account and its balance at any given time is used to verify that debits = credits
Journalizing
Process of recording transactions in a journal
Posting
Process of transferring journal entry information to the ledger