PHAR 232: Hematology-RBC
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What are the 16 lab test for hematology?
Hematocrit
hemoglobin
rbc count
mcv
ferritin
iron
iron saturation
MCH
MCHC
reticulocyte count
TIBC
Transferrin Saturation
Transferrin
Folic acid
vitamin B12
blood smear
The assessment of anemia:
The amount of ___ and the amount ____.
The overall dimensions and health of the____.
The amount of iron in the blood and the amount stored in the tissues
The overall dimensions and health of the Red Blood Cells
What is the iron cycle?
Iron is:
absorbed
recycled
excreted (or lost)
Stored
Iron is absorbed by the …
GI tract
What effects iron absorption?
poor diet and malabsorption
Iron is recycled from…
dead blood cells
What are two ways iron is lost?
bleeding due to wounds
ulcer
What can happen if any step of the iron cycle goes wrong?
anemia can develop
excessive iron accumulation can occur
iron by itself is __ in the body
toxic = number one cause of poisoning in children
iron is in the ___ and it is stored in the ___
blood, body
How much of iron are distributed in the body?
approx 50% in the body is in hemoglobin
other 50 is found in tissues and stored as iron
Can you evaluate iron only in the blood or body?
both can be evaluated
How many atoms can ferritin-storage iron store?
can store up to 4500 atoms of iron per molecule
ferritin = ___ + ____
iron, apoferritin
what is serum ferritin?
a small amount of ferritin is found in the blood
What is the best indicator of iron deficiency anemia (IDA)?
serum ferritin
ferritin lab result = ___
serum ferritin
Does normal and high iron levels needs careful evaluation?
yes
What is ferritin?
an acute phase reactant
what is ferritin associated with?
inflammation
Iron levels can be falsely high in…
RA, infection, etc
What is transferrin (TRF)?
a protein that carries serum iron in the serum
What is TIBC and what does it measure?
Total Iron Binding Capacity
→measures the binding ability of transferrin
what is the normal range for TIBC?
250-460 mcg/dL
Will TIBC be high or low in iron deficiency?
high
What is transferrin saturation %?
serum / TIBC
Will transferrin saturation % high or low in iron deficiency?
low
What is the normal range for transferrin saturation %?
30-50%
describe behavior of serum iron and transferrin in normal iron levels.
iron is bound to transferrin-high saturation and low binding capacity
describe behavior of serum iron and transferrin in abnormal or deficient iron levels.
More transferrin is produced when Iron is low.
Low transferrin saturation
what are the 4 main indices for RBC?
Hgb
Hct
RBC count
MCV
What are the secondary indices for RBC?
MCH, MCHC, RDW, reticulocyte count
Helper labs: B12, Folate (folic acid)
Peripheral Blood Smear (PBS)
what is Hgb?
Hgb-Hemoglobin concentration is the
concentration of hemoglobin in g/dL
What is Hct?
Hct-Hematocrit, also called packed cell
volume, is the packed spun volume of blood
that consists of intact RBCs, expressed as a
percentage
equation for Hct
(Hct= MCV x RBC)
what is RBC?
RBC-RBC count is the number of RBCs
contained in a specified volume of whole
blood (# x 106/μl)
What is MCV?
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) =
The average volume (size) of the
patient's RBCs.
→It can be measured or calculated
(MCV in femtoliters [fL] = 10 x HCT [in
percent] ÷ RBC [in millions/microL]).
High MCV
macrocytic
High MCV (macrocytic) usually caused by
Folate or B12 deficiency: Most common macrocytic anemia
Drug toxicity: Zidovudine, hydroxyurea
Abnormal RBC maturation: seen in some leukemias
Alcohol abuse, hypothyroidism, liver disease
low MCV
microcytic
low MCV (microcytic) usually caused by
Iron deficiency
Disorders of heme synthesis
Chronic inflammatory states
What is RDW?
Red cell distribution width
→Coefficient of variation of the MCV
→RDW = Standard deviation of RBC size ÷ MCV x 100
what is Anisocytosis?
An increased RDW indicates the presence of increased variability in red cell size
is RDW useful by iteslf?
no
what is used with RDW for interpretation?
Use with peripheral blood smear for interpretation
What is MCH?
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
→Amount of Hgb per RBC cell count
→(Hgb/RBC count) x10 = MCH
Low MCH is seen in
IDA and thalassemia
High MCH is seen in
macrocytosis
What is MCHC?
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
→Concentration of Hgb per dL of RBC
→Hgb/(MCV x RBC) = MCHC
Low MCHC is seen in
IDA and thalassemia
High MCHC is seen in
rarer diseases, unusual
About how much of RBCs are destroyed daily and replaced with new RBCs?
1%
life span of a RBC
120 days
Normal ranges for RBC
0.5 - 1.5% of total RBC count
What does reticulocyte count indicate?
indicates the ability of bone marrow to produce new RBC
→can show loss of mature RBC
large increase of RBC are seen in
hemolytic anemia or acute blood loss
→if bone marrow is functioning
decrease in reticulocytes indicates
ineffective hematopoiesis despite the anemia
→bone marrow is not functioning
when does reticulocytosis not happen?
will not happen if there is not adequate iron to support erythropoiesis
What are the four anemia focuses?
Macrocytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
Anemia of chronic disease (or inflammation)
What is anemia?
When RBC creation is less than RBC destruction
What are 5 causes of anemia?
Lack of nutrients (Iron, B12, Folate, etc)
Bone marrow disorders (Cancers, radiation exposure, etc.)
Low levels of trophic hormones (EPO)
Chronic inflammation (Chronic disease)
Blood loss (Acute and chronic)
All anemias have what in common?
HCT/Hgb/RBC are low
how are anemias differentiated?
The type of anemia is then differentiated by the RBC indices
Physical presentation of anemia includes:
Pallor
Fatigue
Tachycardia
Orthostatic hypotension
Koilonychia- spoon nail
Stomach pain
Black, tarry stools
→(+)melena
physical presentation of anemia is linked to what?
Physical presentation linked to decreased oxygen delivery to tissues and with acute bleeding, hypovolemia.
hemoglobin, hct, and rbc count are all
concentrations
hemoglobin, hct, and rbc count are all dependent on the
red blood cell mass (RCM) as well as plasma volume
Values for all three parameters (hemoglobin, hct, and rbc count) will be ______ if the RCM is _____ and/or if the plasma volume is _____.
Values for all three parameters will be reduced if the
RCM is decreased and/or if the plasma volume is
increased
Values for all three (hemoglobin, hct, and rbc count) will be ____ if the plasma volume is _______ (ie concentration).
values for all three will be increased if the plasma volume is decreased (ie, hemoconcentration).
what is the first and second step in assessing anemia?
low H&H (hemoglobin and hematocrit) or RBC count, the next step is to evaluate MCV
next step after determining low MCV in anemia
1.evaluate iron stores
2.evaluate possible blood loss
what type of anemia occurs if MCV is low or normal
IDA and Anemia of chronic disease (inflammation)
next step after determining normal MCV in anemia and what type of anemia is this
evaluate reticulocyte count
hemolytic anemia
next step after determining high MCV in anemia
evaluate folate and B12
what type of anemia occurs if MCV is high
macrocytic anemia
Deficiency in what is a common cause of Macrocytic anemia?
B12 and folate
Is macrocytic anemia drug induced and what are some examples?
yes
Bactrim (SMX-TMP)
Methotrexate
Triamterene
Phenytoin
Zidovudine (AZT)
Metformin. (B12 absorption inhibition)
Which type of anemia is the most common?
IDA
is IDA microcytic or macrocytic?
MICROCYTIC----But can be normocytic!
Depends on the extent of the deficiency
what is a common cause of IDA?
chronic GI bleed
How to evaluate chronic GI bleed in IDA in patients?
Evaluate patient for meds that can cause GI
bleed.
Stool Guaiac test (AKA occult blood)
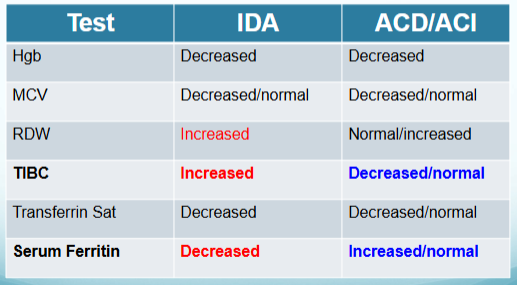
What chronic diseases are ACD or ACI associated with?
COPD
Diabetes
Renal failure
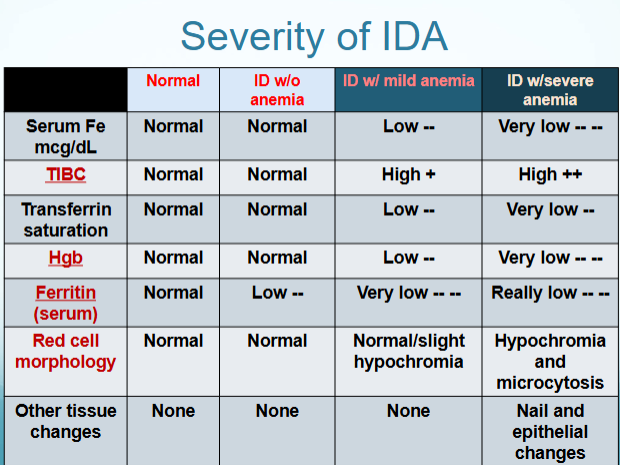
difference between IDA and ACD/ACI
What is the MCV value in hemolytic anemia?
Usually has a MCV that is normal-Normocytic
life span of RBC in hemolytic anemia
Usually an increased destruction of RBCs leading to an
average life span of less than 100 days per RBC
what are some examples of hemolytic anemia?
Examples are: Sickle cell disease, autoimmune
hemolytic anemias, hypersplenism
are reticulocyte levels higher or lower in hemolytic anemia?
Higher levels of reticulocytes can be seen with
hemolytic anemia
what helpful in diagnosing hemolytic anemia?
Blood smear is very helpful in the diagnosis due to sub-
populations of broken or misshapen cells
What else is indirectly elevated in hemolytic anemia?
Indirect bilirubin and Lactose Dehydrogenase can be
elevated