Bio Topic 3 - Genetics
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
sexual reproduction
The process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote (fertilised egg cell) and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other.
gamete
sex cell
How are gametes different from normal cells?
They have a haploid nucleus and contain one copy of each chromosomes compared to two copies of each chromosome in normal cells(23 chromosomes compared to 46)
Zygote
a fertilised egg cell that is diploid
disadvantage of sexual reproduction
time/effort to find a mate
difficult for isolated members to reproduce
takes longer than asexual reproduction
advantage of sexual reproduction
genetic variation
the species can adapt to new environments due to variation, giving them a survival advantage
Disease is less likely to affect population due to variation.
What is asexual reproduction?
The process resulting in genetically identical offspring being produced from one parent
Why are the offspring from asexual reproduction genetically identical?
Only 1 parent is needed, so there is no fusion of gametes and therefore no mixing of genetic information
How do bacteria reproduce?
binary fission (asexual)
What is a quick is a cycle of asexual reproduction?
Rapid reproductive cycle
Advantages of asexual reproduction
1. no need for a mate; can live isolated
2. numerous offspring quickly(much faster than sexual)
3. no energy needed for maintenance of reproductive structures
4. Energy and time efficient
4. good with stable environment as genetic variation isn't necessary if the parent cell is thriving in a certain environment.
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
- very little genetic variation among offspring.
- Can result in extinction of species if the environment changes(massive vulnerability to change)
- Disease likely to affect the whole population due to lack of variation
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells/gametes in reproductive organs of sexually reproducing organisms
meiosis vs mitosis differences
- meiosis has 2 cell divisions, mitosis only one
- in meiosis homologous chromosomes pair up on cell's equator, in mitosis homologous chromosomes never pair up
- after pairing in meiosits sections of dna are swapped between pairs which doesn't happen in mitosis
- After anaphase 1 of meiosis sister chromatids are still paired, in anaphase in mitosis, sister chromatids are separated
- meiosis results in 4 haploid cell, mitosis results in 2 diploid cells
- meiosis cells are genetically different but mitosis is genetically identical
In the first cell division (meiosis I),
Homologous chromosomes separate into 2 cells.The chromatids are not separated
second round of meiosis
chromatids separated , one copy of each chromosome is found in 1 in 4 genetically daughter cells
similarities of mitosis and meiosis
genetic material is duplicated
chromatid is condensed to form chromosomes , prophase
microtubules emanating from centrioles are involved in dividing the genetic material, anaphase and metaphase
What is the monomer that makes up proteins?
amino acids
Why are all siblings not identical?
Gametes of both parents have a mixture of chromosomes which combine to produce a unique combination
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
Anti-codon
group of three bases on opposite end of a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
Polypeptide
chain of amino acids
Translation
decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain
What type of cell division occurs in the zygote as it grows?
mitosis
How is a polypeptide formed?
mRNA moves through the ribosome 3 bases at a time. Each codon codes for one amino acid.The tRNA with the anti-codon sequence matching the codon comes to the ribosome with the specific amino acid.The amino acids are added to the growing chain one by one.
Which cells undergo meiosis?
germ cells
Genome
all of an organism's genetic material
DNA double helix structure
complementary base pairs joined by hydrogen bonds
sugar phosphate backbone
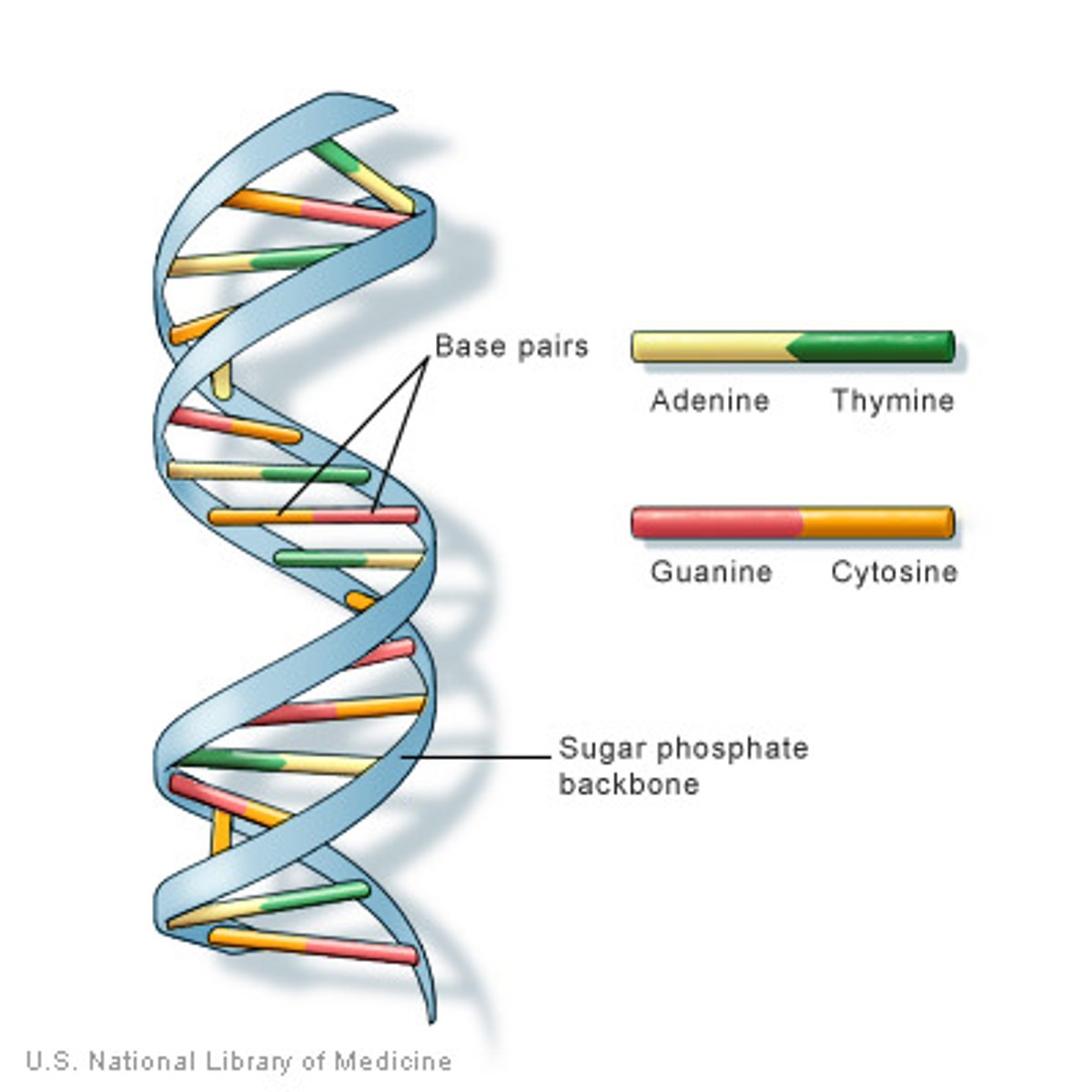
gene
sequence/section of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
What shape is a DNA molecules?
double helix
DNA sequence
order of nucleotides in a strand of DNA
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA
What makes up a nucleotide?
pentose sugar(deoxyribose/ribose), phosphate, nitrogen base
DNA is a _______ made from many ____________
polymer
monomers(nucleotides)
DNA base pairs
Adenine and Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine
Bonds that form between nucleotides/base pairs
(weak)hydrogen bonds
Why does only A bind to T and C to G?
COMPLEMENTARY BASE PAIRING(learn the phrase)
How many strands make up a DNA molecule?
2 strands
Method of DNA extraction from cells
1.Mash fruit or veg in a beaker and add 100 cm3 of water to it
2.Add salt to the 100 cm3 beaker
3.Add detergent to the solution and gently stir until salt dissolves
4.Then, filter into a test tube and then measure 10cm3 of the filtrate into a boiling tube
5. Add two drops of protease solution
6. Add ice cold ethanol by pouring it down the side of the test tube.The amount of ethanol added should not exceed volume of filtrate
7. A white precipitate has formed which can be extracted out using a glass rod
purpose of salt in extracting DNA from cells
helps clump the DNA together so it can be extracted
Why is detergent needed when extracting DNA from cells?
breaks down membrane around the cell and nucleus
Purpose of filtering the mixture (in DNA extraction)
helps isolate DNA by removing any insoluble bits from the mixture
purpose of protease in extracting DNA from cells
breaking down proteins
What is ethanol needed for when extracting DNA from cells?
Precipitating the DNA as it is insoluble in ethanol
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into a strand of mRNA
What enzyme makes mRNA on transcription
RNA polymerase
What might happen to a protein if there is a mutation?
Shape may change and this may affect its function
How does RNA polymerase separate DNA(transcription)?
bonds to non-coding site in front of the DNA and breaks hydrogen bonds of DNA
How is the gene transcribed to mRNA in transcription?
RNA binds to a non-coding region of DNA in front of the gene and separates the two strands of DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds. The RNA polymerase moves along the template strand to make the mRNA strand by adding complementary RNA nucleotides.
Where does the mRNA go after transcription?
leaves the nucleus through nuclear pores, goes to the cytoplasm, binds to a ribosome to be read.
nucleotide in RNA instead of thymine
uracil which pairs with adenine
The sugar in RNA is _____, the sugar in DNA is _______
ribose and deoxyribose
ribose and deoxyribose chemical differences
ribose has one more oxygen, a hydroxide
mRNA sequence of the template strand AATCCAGTGCCA
UUAGGUCACAAU
Why must DNA be transcribed into mRNA before being translated into a protein?
DNA is too big to pass through the nuclear pores
What does mRNA stand for?
messenger ribose nucleic acid
What happens in translation, details?
mRNA enters the ribosome and the ribosome reads the mRNA one codon at a time. A tRNA molecule has an anticodon that matches the codon on mRNA. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid. The amino acids on certain tRNA molecules join together with peptide bonds in between them to make a polypeptide chain, when the tRNA molecules match to their corresponding part of the mRNA. Then, the polypeptide chain folds up to make a specific shape
Where are tRNA molecules found?
cytoplasm
Structure of a tRNA molecule
anticodon on one end which is complementary to the triplet of bases(codon) on the mRNA. On the other end is a specific amino acid
How many codons are needed to make a polypeptide with thirty amino acids?
30
A triplet of mRNA bases that code for a particular tRNA molecule is called a:
codon
Mutation
change in a sequence of bases of DNA of a gene that affects genetic information
Mutation consequences in non coding DNA of gene
RNA polymerase may not bond to dna/find it difficult to bond to translate dna into mRNA, decreasing the amount of mRNA and protein produced, or some mutations may also make binding better and increase the mRNA and protein produced
Mutation consequences in coding DNA of gene
The gene may code for a different sequence of amino acids.This would affect the (highly specific) shape and type of protein produced, which would subsequently impact its function, this could be either increasing decreasing or stopping protein activity. This in turn could also affect the phenotype of the organism
genetic code of proteins
How the order of bases results in amino acids being joined in particular order to make a protein
Genotype
the combination of alleles that control each characteristic
allele
different versions of the same gene
What are alleles caused by?
mutations
Phenotype
An organism's physical characteristics, or visible traits.
Mendel's pea experiment
First experiment:
Tall plus short pea plants made 4 tall pea plants
Second experiment:
Tall plus tall pea plants made 3 tall and 1 short pea plants.
Conclusion: the height of the offspring trees was a result of 'hereditary units' being passed down from parents. The hereditary unit for tall plants (T) was dominant over the hereditary unit for short plants (t) - the latter was recessive.
Mendel came to the conclusion that all characteristics were determined by hereditary units that were either dominant or recessive and were passed down from parent to offspring
Given that we have two copies of each chromosome, what can be said about the number of copies of genes and alleles that we have?
As we have two copies of each chromosome, we have two copies of each gene and therefore two alleles for each gene
One of the alleles is inherited from the mother and the other from the father, and these alleles do not have to correspond to the same characteristic
Alleles can either be:
dominant or recessive
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present/only needs to be inherited from one parent in order for the characteristic to show up in the phenotype
recessive allele
An allele that is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present. A recessive allele needs to be inherited from both parents in order for the characteristic to show up in the phenotype.
How to distinguish between dominant and recessive allele on a punnett square
capital letter - dominant allele
lowercase letter - recessive allele
homozygous dominant
2 copies of the dominant allele
homozygous recessive
2 copies of the recessive allele
heterozygous
two alleles of a gene are different i.e. 1 dominant and 1 recessive
Why can't we always determine the genotype based on the phenotype
genotype could either be dominant homozygous or dominant heterozygous
How to draw punnett squares
1.Determine the parental genotypes
2.Select a letter that has a clearly different lower case, for example, Aa, Bb, Dd
3.Split the alleles for each parent and add them to the Punnett square around the outside
4.Fill in the middle four squares of the Punnett square to work out the possible genetic combinations in the offspring
female gamete chromosomes
XX
Male gamete chromosomes
XY - the Y is responsible for the sex of kid
List the possible genotypes and therefore the sex when female and male chromosomes
XX,XY,XY,XX - therefore the chances of offspring being male or female is 50 50
carrier
refers to a person that carries a recessive allele that would express a recessive trait. The person doesn't have the trait themselves(thus their genotype is heterozygous) but there is a possibility of them passing it on to offspring
What kind of inheritance do Punnett squares show?
Monohybrid inheritance
Why is monohybrid inheritance not practical?
Most characteristics are defined by the interaction of multiple genes, not just 1, for example eye colour (polygenic inheritance)
continuous variation
when there are very many small degrees of difference for a particular characteristic between individuals and they are arranged in order and can usually be measured on a scale
discontinuous variation
inheritance pattern in which traits are distinct and are transmitted independently of one another
2 ways in which phenotypic variation can be caused
Genetic
Environmental
What kind of phenotypic variation is continuous data caused by? GIve an example
a mixture of genetics and environment, i.e whilst height is genetic, poor diet can limit growth.
What kind of phenotypic variation is discontinuous data caused by? GIve an example
genetics, for example no environment will have any effect on blood type which is purely genetics
Molecule of DNA is a...
chromosome
How is the shape of a protein determined?
By the chain of specific amino acids
3 different ways a mutation can affect base sequence and its knock on effects
1. Deletion - a random base is removed from the sequence - this affects the base triplets that come after the mutation affecting the whole amino acid chain as now multiple amino acids will be altered
2. Insertion - a new base is randomly inserted into the base sequence - this impacts the base triplets later on in the sequence - having knock on effects as it affects the whole amino acid chain as now multiple amino acids will be altered
3. Substitution - a base in the sequence is randomly swapped for a different base - this only alters 1 amino acid triplet of base so it doesn't have any knock on effects
How can the frequency of mutations increase?
Although it is mostly random,it can be increased by:
1. Exposure to UV/X ray/Gamma rays
2. chemicals i.e tar in tobacco
results of mutations on enzyme activity and structural proteins
potentially decreased as shape affected thus active site shape changes thus substrate cannot fit into active site
structural proteins such as collagen can lose strength if shape changes
How can mutations be beneficial?
A mutation can lead to a new allele and thus a new phenotype.
This can provide survival advantages
How can mutations be dangerous
Can lead to harmful changes which have devastating effects on human i.e. sickle cell anaemia