Biol 208: Lecture 22 - Avoiding predation + Herbivory
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Herbivory + predation are _____ forces in evolution
SELECTIVE forcers
What are the 2 general methods to avoid going extinct due to predation?
Defense
Take shelter
Generally describe defense, what is its main purpose
What are the 3 methods of Defense?
Fight back
Learning experience for the predator not necessarily death
3 methods:
Aposematic strategy
Mullerian mimicry (type of Aposematic strategy)
Batesian mimicry (type of Aposematic strategy)
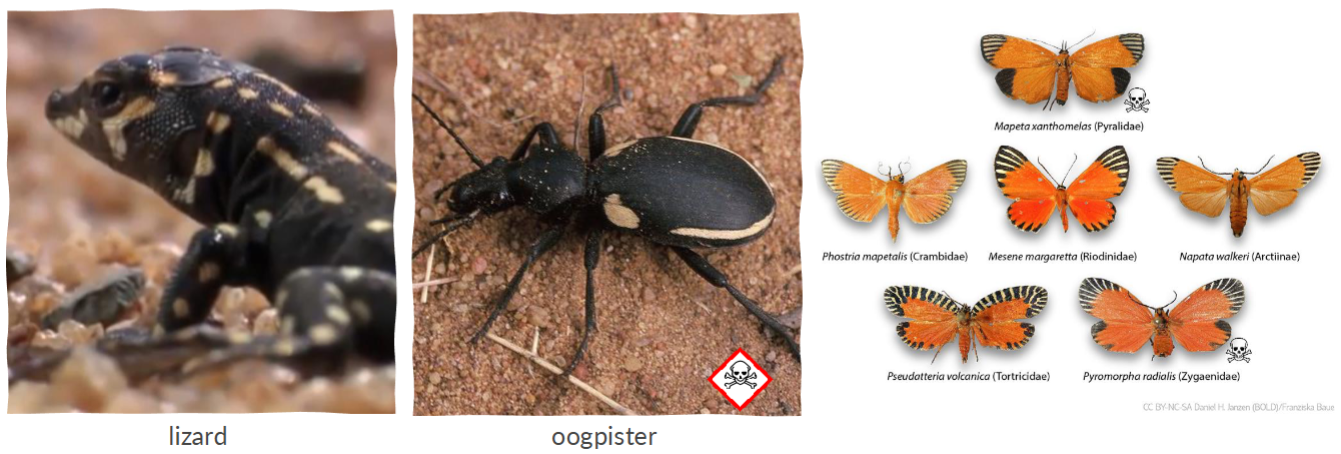
Aposematic strategy
Defensive coloration and behavior
“Don’t eat me i am not tasty”
Bright coloration or distinct patterning or appearance displayed by many toxic or distasteful potential prey species
eg. poison dart frog or skunk
Mullerian mimicry
Give an example
Two or more harmful or toxic species mimicking warning symbols to resemble each other. This mutual resemblance benefits all the species involved, as predators learn to avoid them due to their shared warning signals.
Stinging Hymenoptera (Wasps, hornets + some bee) mimic each other in their coloration traits (black + yellow)
Once stung by a member in this group a predator will most likely not feed on species with theses traits (learning effect increased)
Batesian mimicry
what is a condition for this type of mimicry to work?
NON-toxic species resemble toxic thereby gaining protection from predators. In this case, the mimic benefits from the mistaken identity, while the model is negatively affected
Works as long as density of model is GREATER than density of mimmicks

Spatial Refugia what is it?
What is an example given in class?
Seek refuge + hide where predators cannot find you
Reaching refuge costs Energy and decreases foraging BUT fitness benefits outweigh cost (better not dead than dead)
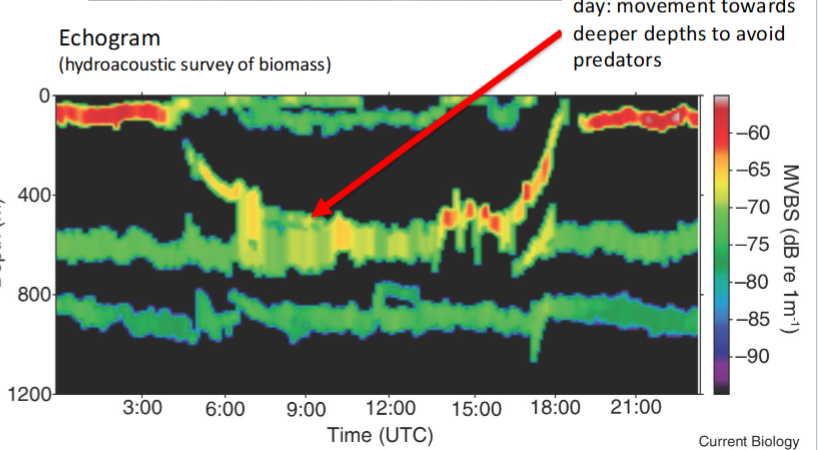
eg. Diel vertical migration
Diel Vertical Migration
Spatial refugia
= the Synchronized movement of organisms int he water column over a daily cycle
displayed by various organisms to avoid predators
During the day = move deeper in water to avoid predators
Protection in Numbers
Refuge
Have populations so large that the risk of any one individual being eaten is low
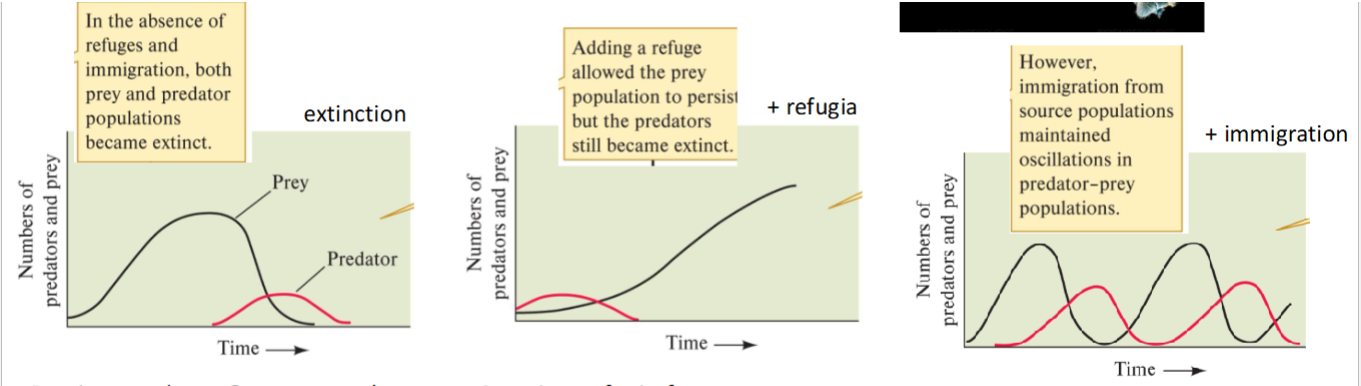
Info dump: Immigration to the rescue - Gause’s predation experiments
Putting predator + Prey together DID NOT result in Oscillations predicted by L-V predator prey model → BOTH predator + prey went extinct
Creating refugia for prey: Prey was able to hide so effectively that predators Died
Created IMMIGRATION by restocking prey population: OSCILLATIONS OCCURED as predicted by L-V models.
critique = immigration created artificially restocking population (masking what can happen in nature)
Info dump: Gause revisited - Hufftaker’s experiment
Methods
Results
Predator + prey mites
Method:
Provided food + created Movement barriers for predators + dispersal aids for prey
Results:
OSCILLATIONS reproduced WIHTOUT artificial restocking of populations
Spatial complexity + dispersal allow “Hide + Seek” = coexistence
Metapopulation rescue define
Refuge
Rescue effect - individuals from larger populations may immigrate + “rescue” smaller populations
migration of individuals can increase the persistence of small isolated populations by helping to stabilize a metapopulation, thus reducing the chances of extinction.
Metapopulation definition = in lecture 14
Refuge: size
Too big to eat = pros
Con = takes a lot of E to maintain large body size
Plant defense strategies in response to herbivory:
What are they 2 categories of defense traits
Resistance = makes them less likely to be eaten
Tolerance = reduced harm while being eaten
What are the 2 types of Plant RESISTANCE STRATEGIES?
give examples for each
Constitutive chemical defenses
Toxins (tobacco) + Digestion reducing compounds (tannins tea)
Induced chemical defenses
Volatile compound production is increased after infestation in Tomatoes (PHENOTYPIC PLASTICITY
Latitude differences in Plant chemical defenses:
Tropical rain forest vs. boreal forest - in which do plants have more diversity of chemical defenses and WHY?
How does herbivory change with latitude
Tropical rain forest
Has greater biodiversity of herbivores = need more diverse types of chemical defenses
Herbivory Decreases with an Increase in latitude
True or False: PLANTS do NOT have warning colorations?
Why or Why not
TRUE
Why?
Herbivory normally doesn’t kill plants
= weaker selection pressure to evolve conspicuous visual warnings
Warning signals only work when the effects are quick + herbivores learn quick
Toxins do not act as quickly in plants so the association does not form
Many herbivores rely on chemical cues rather than vision
Toxic fruits?
Usually toxic because:
Not ripe yet (prevent eating B4 seeds are ready)
Reduce risk of seeds being digested
laxative properties
Digestion reducing compounds
Facilitate seed dispersal by frugivores
What is the One Plant TOLERANCE strategy?
How does it work?
What are the causes (5)
Overcompensation
Increased plant growth following herbivory, compared to plants that did not experience herbivory
Taxon specific
most common in grasses + some herbaceous plants
Causes:
High resource availability
Partial defoliation can stimulate growth (light grazing: removal of dead plant material = increase in photosynthesis)
Growing points - Meristems (plants with dormant buds or basal meristems are more likely to overcompensate)
History of grazing (grazed grass = respond more strongly than ungrazed)
Timing of herbivory (grazing early in summer (plants are still growing + can overcompensate)