B1 - Cell Biologyv
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
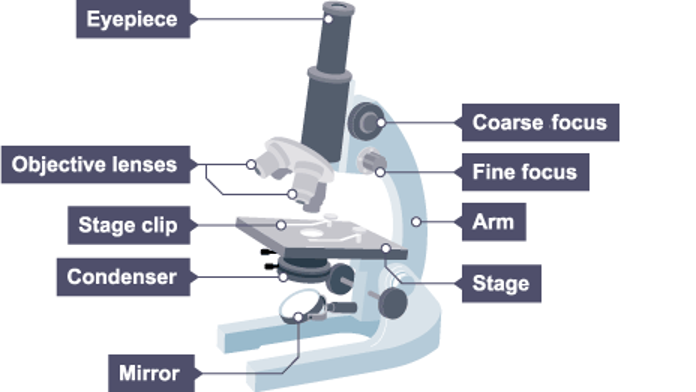
Parts of a Microscope:
Objective
Lens closest to the specimen
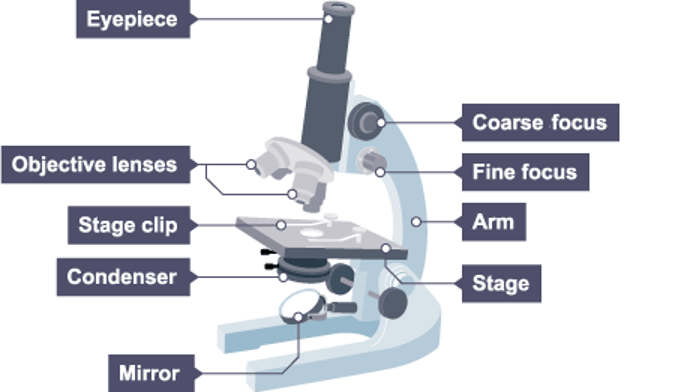
Parts of a Microscope:
Eyepiece
Lens at the top, magnifies image
Magnification =
Image Size / Real Image Size
Resolution
Ability to see 2 points as separate as opposed to being one (blur)

Limitation of Light Microscope
0.2 micrometre resolution
Electron Microscopes
use electron beams instead of light

Types of Electron Microscopes
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) - used at lower magnification
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) - for thin slices, high magnification
Eukaryotic cells
animals and plants
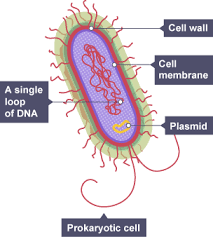
Prokaryotic cells
bacterial and archaea
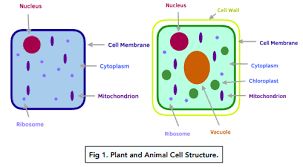
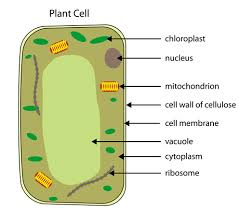
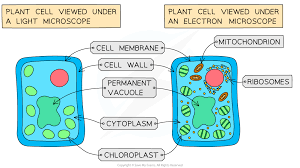
Plant cells
vacuole
chloroplast
cell wall
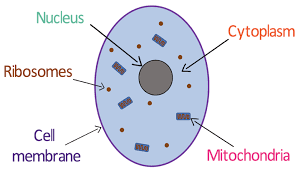
Cell Structures:
Cytoplasm
Contains dissolved nutrients, salts and other organelles – where most chemical reactions occur

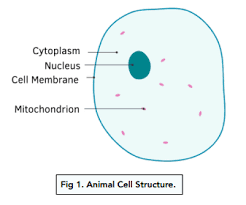
Cell Structures:
Nucleus
Contains genetic material - DNA
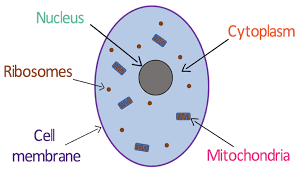
Cell Structures:
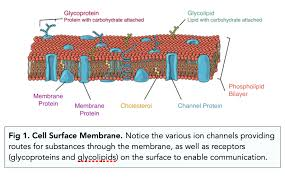
Cell Membrane
Permeable structure
controls movement of substances through cells
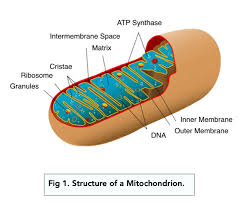
Cell Structures:
Mitochondria
Site of energy release during respiration
Cell Structures:
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
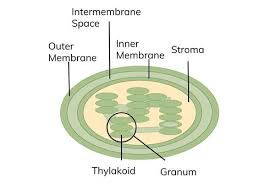
Cell Structures:
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll and enzymes for photosynthesis
Cell Structures:
Cell Wall
Made of cellulose
strengthens and supports cell
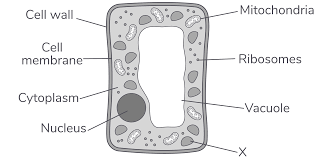
Cell Structures:
Permanent Vacuole
Filled with cell sap
keeps cells turgid
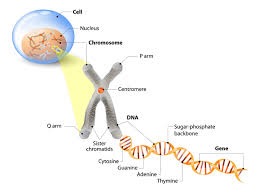
Organisation of Genetic Material
Nucleus > Chromosome > Gene > DNA
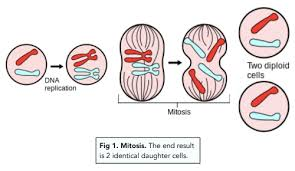
Why do cells divide?
growth
damage
Mitosis
after DNA synthesis
produces 2 identical ‘daughter’ cells
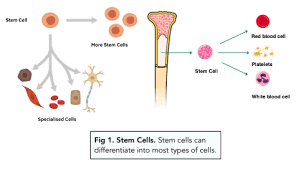
Human Stem Cells
Unspecialised
lost during adulthood
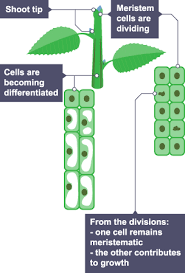
Plant Stem Cells
occurs in meristem region
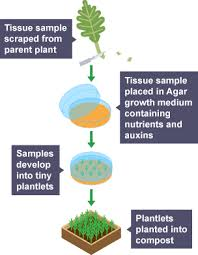
Plant Cloning
from meristem cells
produces plants economically and quickly
genetically identical
Uses of Human Stem Cells
treat diseases by producing new cells
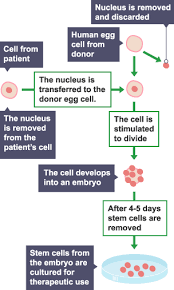
Therapeutic Cloning
cloning and transporting stem cells of a patient back into their body
Stem Cells in Medicine:
Clinical Issues
no guarantee of success
difficulty in finding donors
storing
mutations in stem cells
contamination with viruses
Stem Cells in Medicine:
Ethical Issues
destroying stem cells
embryos as a commodity not as a human
at what point of development are embryos human?
Stem Cells in Medicine:
Social Issues
education is important
do benefits outweigh objections?
is research by commercial clinics patient exploitation?
Diffusion
Movement of particles from high to low concentration
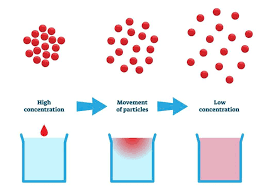
What is Diffusion affected by?
Temperature
Concentration gradient (difference in)
Surface Area
Osmosis
diffusion of water molecules from high to low concentration
across a partially permeable membrane

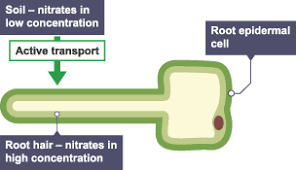
Active Transport
Movement of molecules from low to high concentration
so against a concentration gradient
requires energy