Biology Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Last updated 2:36 AM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
What is an organism chemical process that is very sensitive to temperature changes?
Metabolism
2
New cards
T/F: All Organisms have a temperature range in which they can function.
True.
\
There is a certain temps.
\
There is a certain temps.
3
New cards
What is the definition of thermoregulation?
Maintenance of range (Controlling/adjusting heat exchange between animals and environment)
4
New cards
What are the two groups that are based of how they get their heat source?
Ectotherms, Endotherms
5
New cards
What is the definition of ectotherms and examples?
(Cold Blooded); Warms body by absorbing heat from the environment.
Examples: Inverts. Fish, Amphibians, and reptiles.
Examples: Inverts. Fish, Amphibians, and reptiles.
6
New cards
What is the definition of the endotherms and examples?
(Warm Blooded); heat from metabolism.
Examples: Birds and mammals
Examples: Birds and mammals
7
New cards
Which group (ectotherms or endotherms) tend to have a fairly constant body temperature regardless of the temperature of the environment?
Endotherms.
8
New cards
Which group (ectotherm or endotherm) solves some problems of living on land, movement is more difficult, allows more constant activity, costs more energy, but, allows more cellular resp. to occur also complex circulatory and respiratory systems.
THEY HAVE HIGH ENERGY REQUIREMENTS
THEY HAVE HIGH ENERGY REQUIREMENTS
Endotherms.
9
New cards
What are the requirements of having a endotherm system in birds and mammals?
Complex respiratory, complex circulatory four chambered heart, high energy, and high activity levels.
10
New cards
What is insulation
Fur, Feathers, fat, Bubbler, (Think of a cat hair puffing up or a birds feathers), When fur/feathers is puffed up it creates a air pocket of heat that is better insulation.
11
New cards
What is Vasodilation?
When the nervous system tells muscles of blood vessels near the skin to relax- increase blood flow- allows more heat loss/ cool body
12
New cards
What is vasoconstriction?
When the nervous system tells the muscles of the blood vessels to tighten together, keeps body warm (thinking of a goose leg when swiming)
13
New cards
What is counter current heat exchanger?
In birds and marine mammals, arteries and veins in extremities run close together--warm blood in arteries warms colder blood returning to main body. (Toe to Heart)
14
New cards
What is another purpose of counter current heat exchanger?
Reduces energetic cost of warming returning, also cooling
15
New cards
What are some methods counter current heat exchanger cools off the body?
Panting (evaporation), sweating, bathing
16
New cards
Is basking behavioural?
Yes
17
New cards
Thermoregulation is controlled largely by what in terrestrial mammals
Feedback Mechanisms
18
New cards
What is the control center of the brain?
Hypothalamus
19
New cards
What are feedback mechanisms?
\-When the body temperature is monitored by nerve cells in skin, hypothalamus, and other parts.
\-There are cooling receptors or warming receptors
\-When the temperature is above normal, the cooling mechanisms are turn on (vasodilation) When the body is below average, the warming mechanisms are turned on (vasoconstriction)
\-There are cooling receptors or warming receptors
\-When the temperature is above normal, the cooling mechanisms are turn on (vasodilation) When the body is below average, the warming mechanisms are turned on (vasoconstriction)
20
New cards
When Vasodilation (cooling mechanisms) are turned on, what is activated?
Sweat gland activated (Evaporative cooling)
21
New cards
What is the cause of vasoconstriction during feedback?
To have less heat loss to radiation and more warm blood kept in deep tissue.
22
New cards
What are two factors that produce heat?
Shivering by skeletal muscles, hormonally produced warmth
23
New cards
What is an uncommon way an animal can keep their temperature?
Acclimatization.
24
New cards
What is acclimatization?
A process that some animals use to keep their body temperature normal.
\-Usually over serval days to weeks.
\-Requires changes in thermoregulation mechanisms
\-Also change in cells- ex. different enzymes are produced with different temperature ranges.
\-Usually over serval days to weeks.
\-Requires changes in thermoregulation mechanisms
\-Also change in cells- ex. different enzymes are produced with different temperature ranges.
25
New cards
What are two examples of torpor?
Hibernation, Estivation
26
New cards
torpor is used to survive periods of ___ __and__ _____
Extreme temperature; lack of food
27
New cards
What is hibernation?
Allows animals to survive cold temps and lack of food in winter
28
New cards
What is estivation?
Allows animals to survive high temperature and lack of water in summer.
29
New cards
Why do small endotherms animals enter torpor daily?
Metabolic rates are so high that they can not survive periods of inactivity when not feeding.
30
New cards
What are some animals that enter torpor daily?
Bats, Humming Birds, and Chickadees
31
New cards
When does a bat enter torpor?
During the day when they do not eat.
32
New cards
When does a humming bird enter torpor?
During the night when they do not eat
33
New cards
When do chickadees enter torpor?
At night, body temperature may drop very low during winter nights.
34
New cards
What does BOTH water balance and waste disposal depend on?
Transport Epithelial tissue.
35
New cards
What are the characteristics of the transport epithelial tissue that water balance and waste disposal depend on?
Usually single layer of cells
May be part of system with channels leading to exterior
Function of tissue depends on composition of cell memebrane
May be part of system with channels leading to exterior
Function of tissue depends on composition of cell memebrane
36
New cards
Animals produce ___ __from metabolism of__ _______
Ammonia (NH3); Proteins and Nucleic acids
37
New cards
Is ammonia NOT a toxic waste product
NO
38
New cards
Ammonia can be excreted or converted to other compounds for storage excretion
True (Yes)
39
New cards
Which of the following is the correct sequence of blood flow in birds and mammals?
vena cava- right atrium - right ventricle - pulmonary artery
40
New cards
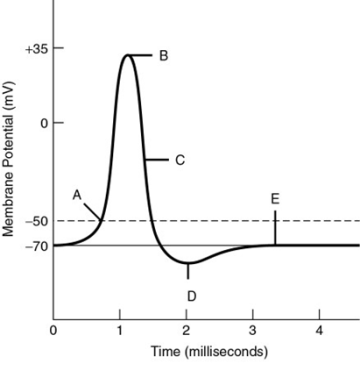
Which of the following is a true statement of point B on the curve?
The neuronal membrane is depolarized and An action potential is being generated
41
New cards
The physical property that predicts the direction of water flow is referred as ________.
water potential
42
New cards
Lysine is an essential amino acid for animals. If an animal did not consume enough lysine in its diet, you might expect that animal to ______?
could not effectively make many necessary proteins
43
New cards
In which of the following pairs are the two terms equivalent?
embryo sac female gametophyte
44
New cards
Which stage in development occurs first?
Zygote
45
New cards
Which of the following is NOT one of the 3 primary germ layers present in the triploblastic embryo?
\
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Pachyderm
\
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Pachyderm
Pachyderm
46
New cards
The protoplast consists of ________.
the living part of the cell, including the cell membrane
47
New cards
The loop of ______ connects the two convoluted tubules of the nephron
Henle
48
New cards
Nephron that extends into the medulla of the kidney
Juxtamedullary
49
New cards
__________ heat exchangers are used by some marine mammals and birds to reduce the cost of warming blood returning to the body from the extremities.
Counter Current
50
New cards
Nitrogenous waste product that is excreted by most aquatic animals but too toxic for storage by terrestrial animals
Ammonia
51
New cards
Very concentrated type of nitrogenous waste excreted by many reptiles and birds
Uric Acid
52
New cards
All of an animal's chemical reactions.
Metabolism
(All of this)
(All of this)
53
New cards
Relatively nontoxic type of nitrogenous waste excreted in urine of mammals.
Urea
54
New cards
Animals whose tissues are nearly isotonic with their environment.
Osmoconformers
55
New cards
Material in nephron after entering the Bowman's capsule
Filtrate
56
New cards
Much secretion and reabsorption occurs in the proximal and distal __________ tubules of the nephron.
Convoluted
57
New cards
An animal that acquires most of its body heat from the environment.
Ecotoherm
58
New cards
__________ (2wds) factor is a hormone that opposes the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS) system in response to increased blood pressure and volume.
Atrial natriuretic
59
New cards
Enzyme that activates angiotensin II
Renin
60
New cards
Outer part of the kidney.
Cortex
61
New cards
The cup-shaped structure of the nephron where filtration of blood takes place is the __________ capsule
Bowmens
62
New cards
Hormone released in response to angiotensin II that signals reabsorption of water and salt by the distal convoluted tubules
Aldosterone
63
New cards
Marine fish (other than sharks) force excess ____ out of their bodies across their gill epithelium.
Salt
64
New cards
The body “thermostat”
Hypothalamus
65
New cards
Glands that release aldosterone.
Adrenal
66
New cards
____________ hormone is released in response to high blood osmolarity
Antidiuretic
67
New cards
When an animal changes its normal body temperature range, usually in response to changing environmental conditions.
Acclimatization
68
New cards
The ________ apparatus (JGA) monitors blood pressure and volume in the afferent arterioles of the nephron.
Juxtaglomerular
69
New cards
Ball of arterial capillaries where blood is delivered to the nephron for filtration
Glomerulus
70
New cards
Functional unit of the kidney
Nephron
71
New cards
Layer of cells around the human embryo that probably protects it from maternal immune action.
Trophoblast
72
New cards
The tissue lining the uterus is called the _______.
Endometrium
73
New cards
New follicles begin to develop at the beginning of the human _________ cycle.
Ovarian
74
New cards
This hormone is secreted by the posterior pituitary and stimulates uterine contraction during parturition.
Oxytocin
75
New cards
Male gonad.
Testies
76
New cards
Female Gonads
Ovaries
77
New cards
The _______ phase of the ovarian cycle begins right after ovulation.
Luteal
78
New cards
Female external genitalia: lips that surround vestibule.
Labia
79
New cards
Testosterone is an example of (an) __________.
Androgen
80
New cards
Female gamete
Ovum
81
New cards
_________ reproduction requires the fusion of gametes
Sexual
82
New cards
Type of female sexual cycle found in non-primate mammals.
Estrous
83
New cards
Type of asexual reproduction in which an organism splits in two
Fission
84
New cards
This hormone (abr) is released by the anterior pituitary and results in follicle development and, later, ovulation
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
85
New cards
The flow phase marks the beginning of the _______ cycle in human females.
Menstrual
86
New cards
Hormone secreted by the corpus luteum that causes development and maintenance of the endometrium and exercises negative feedback on the hypothalamus
Progesterone
87
New cards
In adult male mammals, the testes reside within the ______ outside of the body cavity.
Scrotum
88
New cards
Each ____ in the ovary consists of a single egg cell surrounded by supporting cells
Follicle
89
New cards
Repository for semen and forms birth canal.
Vagina
90
New cards
The ______ gland empties into the urethra. Its fluids help to neutralize pH and activate sperm.
Prostate
91
New cards
Type of asexual reproduction in which a new individual grows out of the parental body
Budding
92
New cards
Following ovulation, the remaining follicle cells give rise to the _______ _______.
Corpus Luteum
93
New cards
Accessory glands of the male reproductive system that secrete fluid that constitutes 60% of seminal volume.
Seminal Vesicles
94
New cards
In the human female, ________'s glands secrete mucus into the vestibule during arousal for lubrication.
Bartholin
95
New cards
Components of the testes in which sperm are formed
Seminiferous tubules
96
New cards
Describes and animal with both male and female reproductive parts (AKA hermaphroditic)
Monoecious
97
New cards
A sequential hermaphrodite that is female first during its life history
Protogynous
98
New cards
Male gamete
Spermatozoan
99
New cards
Production of ova
Oogenesis
100
New cards
This hormone (abr.) is released by the anterior pituitary and stimulates development of the corpus luteum.
LH (Luienizing Hormone)